Abstract
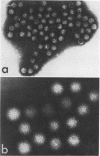
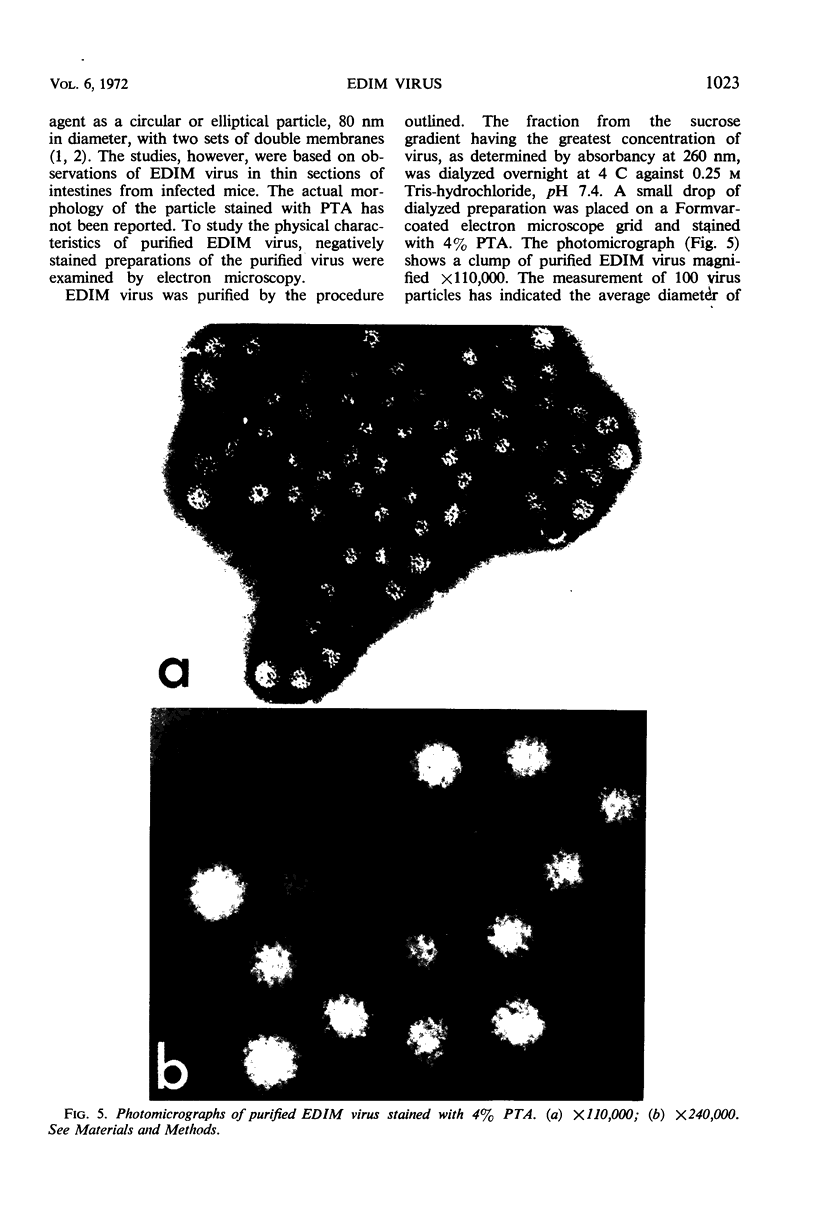
Epizootic diarrhea of infant mice virus has been purified from the intestines of infected mice using enzymatic digestion, precipitation with polyethylene glycol, extraction with Genesolv-D, and sucrose step-gradient centrifugation. The purified virus was found to be stable at −70 C or when treated with ether, chloroform, or sodium deoxycholate. Biochemical analysis of purified virions has suggested that the nucleic acid type of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice virus was of the ribonucleic acid type. Preparations of purified virions stained with phosphotungstic acid showed a particle with icosahedral symmetry, 54 ± 2 nm in diameter and probably composed of 32 hollow capsomeres.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W. R., Kraft L. M. Electron-Microscopic Study of the Intestinal Epithelium of Mice Infected with the Agent of Epizootic Diarrhea of Infant Mice (EDIM Virus). Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):39–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfield W. G., Kasnic G., Blackwell J. H. Further observations on the virus of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice. An electron microscopic study. Virology. 1968 Nov;36(3):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Els H. J., Verwoerd D. W. Morphology of bluetongue virus. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90362-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomatos P. J., Tamm I. THE SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF REOVIRUS RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):707–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAFT L. M. Studies on the etiology and transmission of epidemic diarrhea of infant mice. J Exp Med. 1957 Nov 1;106(5):743–755. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J., Benzinger R. Concentration and purification of vesicular stomatitis virus by polyethylene glycol "precipitation". Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):745–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Coleman P. H., Harrison A. K., Gary G. W., Jr Colorado tick fever virus: an electron microscopic study. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):28–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oellermann R. A., Els H. J., Erasmus B. J. Characterization of African horsesickness virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(2):163–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01249302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H., Doherty R. L. An electron microscopic study of Eubenangee, an Australian arbovirus. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H., Doherty R. L. An electron microscopic study of Eubenangee, an Australian arbovirus. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]