Abstract
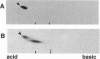
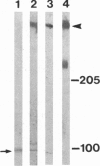
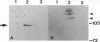
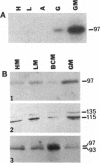
Nerve growth cones isolated from fetal rat brain are highly enriched in a 97-kDa glycoprotein, termed beta gc, that comigrates with the beta subunit of the IGF-I receptor upon two-dimensional PAGE and is disulfide-linked to this receptor's alpha subunit. Antibodies prepared to a conserved domain shared by the insulin and IGF-I receptor beta subunits (AbP2) or to beta gc were used to study receptor distribution further. Subcellular fractionation of the fetal brain segregated most AbP2 immunoreactivity away from growth cones, whereas most beta gc immunoreactivity copurified with growth cones. Experiments involving ligand-activated receptor autophosphorylation confirmed the concentration of IGF-I but not of insulin receptors in growth cone fractions. These results indicate the enrichment of IGF-I receptors in (presumably axonal) growth cones of the differentiating neuron. Furthermore, the segregation of beta gc from AbP2 immunoreactivity suggests that such neurons express an immunochemically distinct variant of the IGF-I receptor beta subunit at the growth cone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess S. K., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Characterization of a neuronal subtype of insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1618–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Grandes P. Nerve sprouting in innervated adult skeletal muscle induced by exposure to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1307–1317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng N., Sahyoun N. Neuronal tyrosine phosphorylation in growth cone glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2417–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Black I. B. Insulin growth factors regulate the mitotic cycle in cultured rat sympathetic neuroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Wallis I., Abreu E., Pfenninger K. H. Nerve growth cones isolated from fetal rat brain. IV. Preparation of a membrane subfraction and identification of a membrane glycoprotein expressed on sprouting neurons. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1977–1989. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Barenton B. Functional and immunological distinction between insulin-like growth factor I receptor subtypes in KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11470–11475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garofalo R. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin and insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptors during central nervous system development: expression of two immunologically distinct IGF-1 receptor beta subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2806–2817. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gültekin H., Heermann K. H. The use of polyvinylidenedifluoride membranes as a general blotting matrix. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 1;172(2):320–329. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90451-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanissian S. H., Chatila T., Sahyoun N. E. Association of neuronal pp60c-src with growth cone glycoproteins of rat brain. J Neurobiol. 1992 Sep;23(7):803–813. doi: 10.1002/neu.480230703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Toledo S. P. Insulin receptors mediate growth effects in cultured fetal neurons. I. Rapid stimulation of protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1989 Sep;125(3):1451–1457. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-3-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Autophosphorylation of the insulin receptor in vitro. Designation of phosphorylation sites and correlation with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11980–11985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Werner H., Faria T. N., Kato H., Adamo M., Roberts C. T., Jr Insulin-like growth factor receptors. Implications for nervous system function. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Aug 27;692:22–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb26202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. N., Quiroga S., Pfenninger K. H. Variable membrane glycoproteins in different growth cone populations. J Neurosci. 1992 Jun;12(6):2393–2402. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-06-02393.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. P., Baker J., Perkins A. S., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Mice carrying null mutations of the genes encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):59–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachemson A. K., Lundborg G., Hansson H. A. Insulin-like growth factor I promotes nerve regeneration: an experimental study on rat sciatic nerve. Growth Factors. 1990;3(4):309–314. doi: 10.3109/08977199009003673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfenninger K. H., Ellis L., Johnson M. P., Friedman L. B., Somlo S. Nerve growth cones isolated from fetal rat brain: subcellular fractionation and characterization. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puro D. G., Agardh E. Insulin-mediated regulation of neuronal maturation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1170–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.6089343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Lang F. F., Ishii D. N. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II permit nerve growth factor binding and the neurite formation response in cultured human neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Rechler M. M., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1211–1219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig S. A., Zetterström C., Benjamin A. Identification of retinal insulin receptors using site-specific antibodies to a carboxyl-terminal peptide of the human insulin receptor alpha-subunit. Up-regulation of neuronal insulin receptors in diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):18030–18034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen S. E., Thompson K., Petersen D. J. Separation of the high affinity insulin-like growth factor I receptor from low affinity binding sites by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16461–16469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toran-Allerand C. D., Ellis L., Pfenninger K. H. Estrogen and insulin synergism in neurite growth enhancement in vitro: mediation of steroid effects by interactions with growth factors? Brain Res. 1988 Jun 1;469(1-2):87–100. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]