Abstract
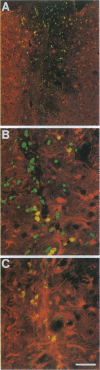
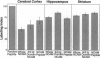
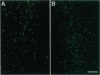
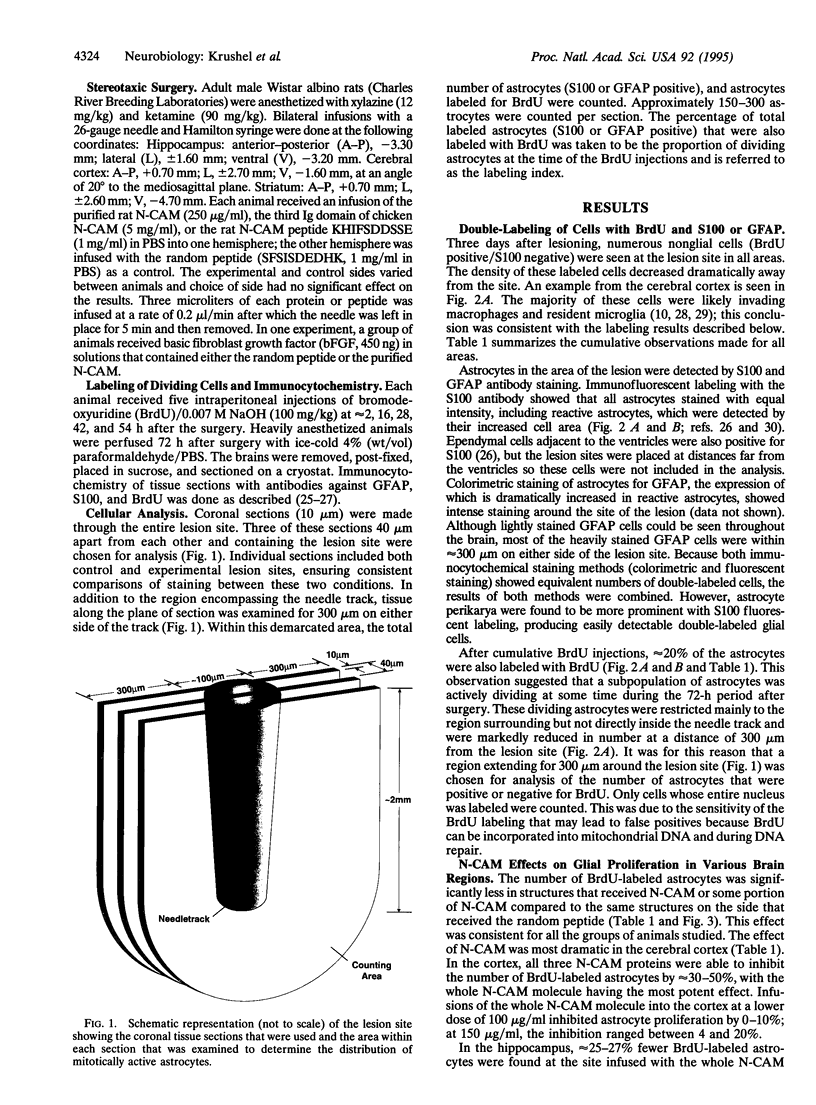
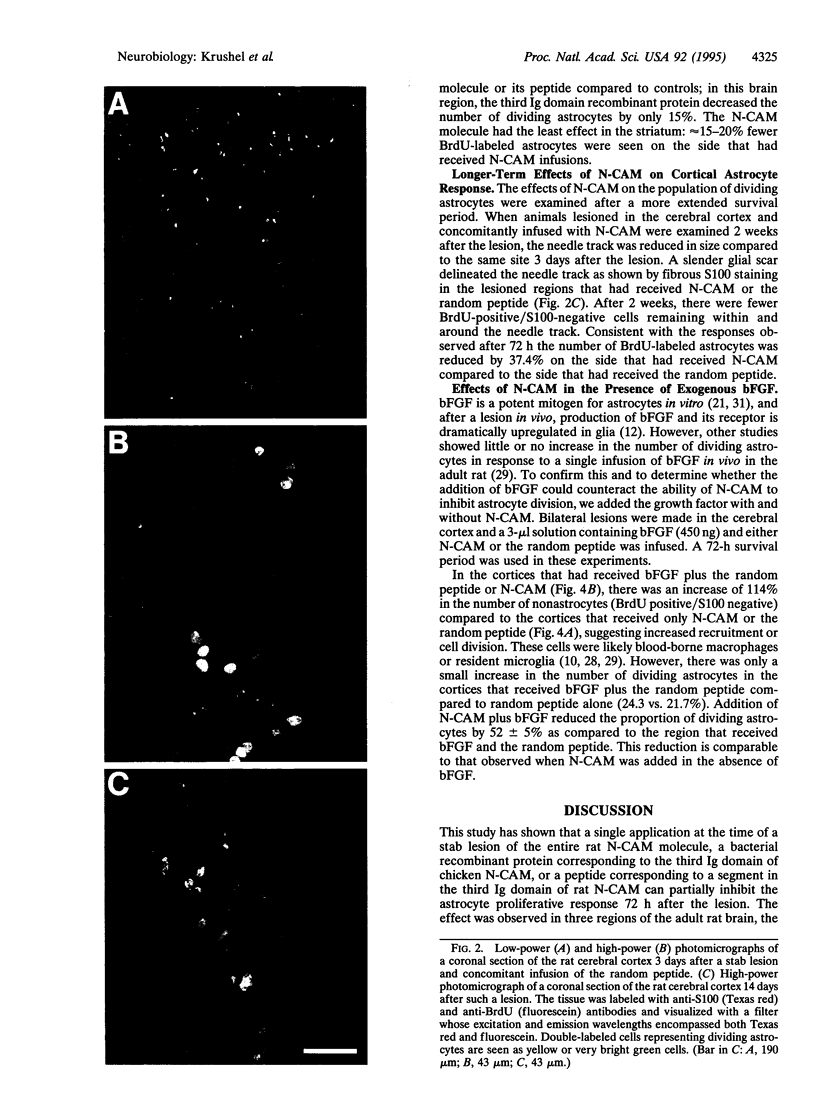
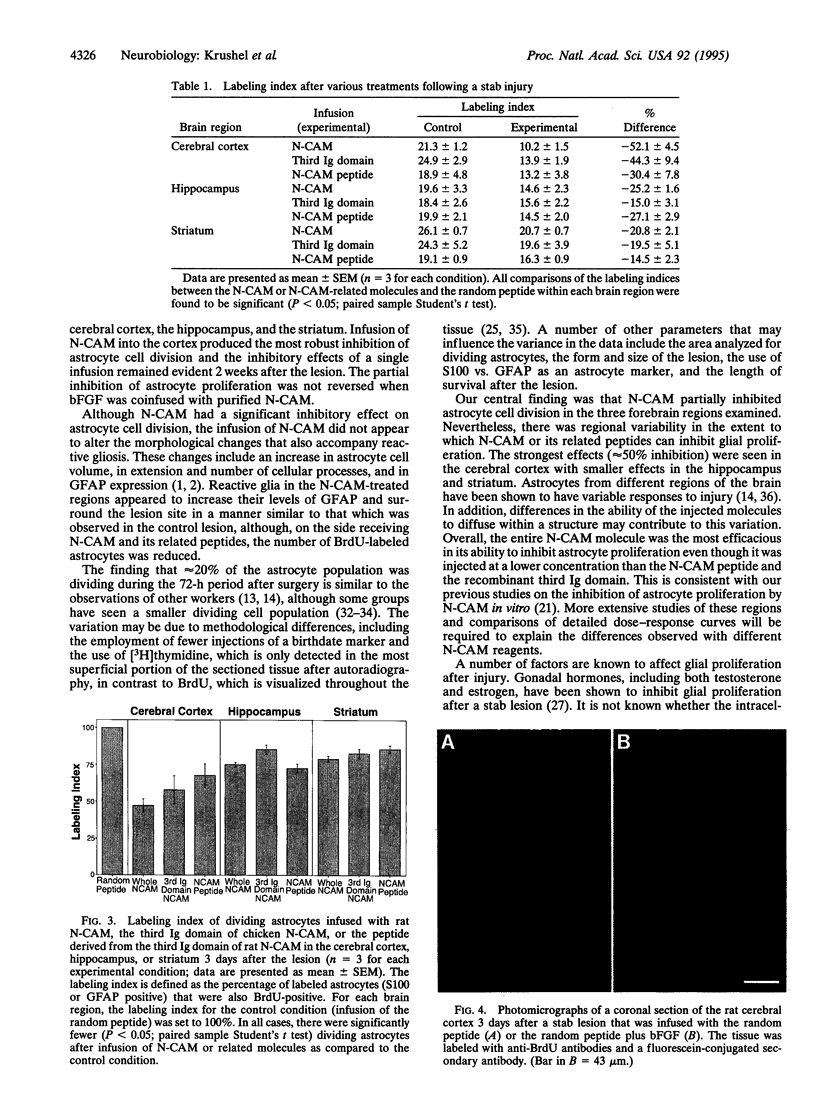
After a penetrating lesion in the central nervous system, astrocytes enlarge, divide, and participate in creating an environment that adversely affects neuronal regeneration. We have recently shown that the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) partially inhibits the division of early postnatal rat astrocytes in vitro. In the present study, we demonstrate that addition of N-CAM, the third immunoglobulin-like domain of N-CAM, or a synthetic decapeptide corresponding to a putative homophilic binding site in N-CAM partially inhibits astrocyte proliferation after a stab lesion in the adult rat brain. Animals were lesioned in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, or striatum with a Hamilton syringe and needle at defined stereotaxic positions. On one side, the lesions were concomitantly infused with N-CAM or with one of the N-CAM-related molecules. As a control, a peptide of the same composition as the N-CAM decapeptide but of random sequence was infused on the contralateral side of the brain. We consistently found that the population of dividing astrocytes was significantly smaller on the side in which N-CAM or one of the N-CAM-related molecules was infused than on the opposite side. The inhibition was greatest in the cortical lesion sites (approximately 50%) and was less pronounced in the hippocampus (approximately 25%) and striatum (approximately 20%). Two weeks after the lesion, the cerebral cortical sites infused with N-CAM continued to exhibit a significantly smaller population of dividing astrocytes than the sites on the opposite side. When N-CAM and basic fibroblast growth factor, which is known to stimulate astrocyte division in vitro, were coinfused into cortical lesion sites, astrocyte proliferation was still inhibited. These results suggest the hypothesis that, by reducing glial proliferation, N-CAM or its peptides may help create an environment that is more suitable for neuronal regeneration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso G., Privat A. Reactive astrocytes involved in the formation of lesional scars differ in the mediobasal hypothalamus and in other forebrain regions. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Apr 1;34(5):523–538. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490340505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. P., Donati E. J., Guth L. Differences between adult and neonatal rats in their astroglial response to spinal injury. Exp Neurol. 1984 May;84(2):374–385. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(84)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodkey J. A., Gates M. A., Laywell E. D., Steindler D. A. The complex nature of interactive neuroregeneration-related molecules. Exp Neurol. 1993 Oct;123(2):251–270. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossin K. L. Cytotactin binding: inhibition of stimulated proliferation and intracellular alkalinization in fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11403–11407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A. Modes of FGF release in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990 Nov;9(3):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00046362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniloff J. K., Levi G., Grumet M., Rieger F., Edelman G. M. Altered expression of neuronal cell adhesion molecules induced by nerve injury and repair. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):929–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. A., Cook G. M., Stern C. D., Keynes R. J. Isolation from chick somites of a glycoprotein fraction that causes collapse of dorsal root ganglion growth cones. Neuron. 1990 Jan;4(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90439-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Estrada J., Del Rio J. A., Luquin S., Soriano E., Garcia-Segura L. M. Gonadal hormones down-regulate reactive gliosis and astrocyte proliferation after a penetrating brain injury. Brain Res. 1993 Nov 19;628(1-2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90964-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Chen J., Ingeman J. E., George J. K., Noponen M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in wound healing after traumatic injury to adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4416–4429. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04416.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the polysialic acid-rich and cytoplasmic domains of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3037–3041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Edelman G. M. The mechanism of binding of neural cell adhesion molecules. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;181:147–160. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4868-9_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman S., Sorkin B. C., White P. C., Brackenbury R., Mailhammer R., Rutishauser U., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Chemical characterization of a neural cell adhesion molecule purified from embryonic brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7720–7729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter K. E., Sporn M. B., Davies A. M. Transforming growth factor-betas inhibit mitogen-stimulated proliferation of astrocytes. Glia. 1993 Mar;7(3):203–211. doi: 10.1002/glia.440070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko K. Spatiotemporal patterns of the astroglial proliferation in rat brain injured at the postmitotic stage of postnatal development: a combined immunocytochemical and autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 24;485(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko K. The proliferative response of S-100 protein-positive glial cells to injury in the neonatal rat brain. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 8;564(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko K. The proliferative response of astrocytes to injury in neonatal rat brain. A combined immunocytochemical and autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1988 Jul 26;456(2):280–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzer R. C., Raff M. C. Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):253–257. doi: 10.1038/325253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Tsuchihashi Y., Fujita S. Initial response of silver-impregnated "resting microglia" to stab wounding in rabbit hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol. 1978 Oct 13;44(1):31–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00691636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniss D. A., Burry R. W. Serum and fibroblast growth factor stimulate quiescent astrocytes to re-enter the cell cycle. Brain Res. 1988 Jan 26;439(1-2):281–288. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latov N., Nilaver G., Zimmerman E. A., Johnson W. G., Silverman A. J., Defendini R., Cote L. Fibrillary astrocytes proliferate in response to brain injury: a study combining immunoperoxidase technique for glial fibrillary acidic protein and radioautography of tritiated thymidine. Dev Biol. 1979 Oct;72(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gal La Salle G., Rougon G., Valin A. The embryonic form of neural cell surface molecule (E-NCAM) in the rat hippocampus and its reexpression on glial cells following kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):872–882. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00872.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan A., Frautschy S. A., Gonzalez A. M., Baird A. A time course for the focal elevation of synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor and one of its high-affinity receptors (flg) following a localized cortical brain injury. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3828–3837. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03828.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKerracher L., David S., Jackson D. L., Kottis V., Dunn R. J., Braun P. E. Identification of myelin-associated glycoprotein as a major myelin-derived inhibitor of neurite growth. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):805–811. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90247-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Thai L., Hong J. S., O'Callaghan J. P., Pennypacker K. R. Brain injury in a dish: a model for reactive gliosis. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Apr;17(4):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon V. K., Landerholm T. E. Intralesion injection of basic fibroblast growth factor alters glial reactivity to neural trauma. Exp Neurol. 1994 Sep;129(1):142–154. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Hattori T., Fukuda M., Kitamura T., Fujita S. Quantitative studies on proliferative changes of reactive astrocytes in mouse cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90757-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake T., Hattori T., Fukuda M., Kitamura T. Reactions of S-100-positive glia after injury of mouse cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 5;489(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay G., Doherty P., Walsh F. S., Crocker P. R., Filbin M. T. A novel role for myelin-associated glycoprotein as an inhibitor of axonal regeneration. Neuron. 1994 Sep;13(3):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Andersson P. B., Gordon S. Macrophages and inflammation in the central nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Jul;16(7):268–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90180-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reier P. J., Houle J. D. The glial scar: its bearing on axonal elongation and transplantation approaches to CNS repair. Adv Neurol. 1988;47:87–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G., Lynch G., Cotman C. W. Hypertrophy and redistribution of astrocytes in the deafferented dentate gyrus. Brain Res Bull. 1976 Jan-Feb;1(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(76)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudge J. S., Silver J. Inhibition of neurite outgrowth on astroglial scars in vitro. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3594–3603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03594.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Kastner R., Szymas J. Immunohistochemistry of glial fibrillary acidic protein, vimentin and S-100 protein for study of astrocytes in hippocampus of rat. J Chem Neuroanat. 1990 May-Jun;3(3):179–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M. E., Kapfhammer J. P., Bandtlow C. E. Inhibitors of neurite growth. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:565–595. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. M., Rutishauser U., Silver J., Miller R. H. Maturation of astrocytes in vitro alters the extent and molecular basis of neurite outgrowth. Dev Biol. 1990 Apr;138(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90204-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporns O., Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. The neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) inhibits proliferation in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):542–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp K. S., Faddis B. T., Vijayan V. K. Trauma-induced proliferation of astrocytes in the brains of young and aged rats. Glia. 1989;2(3):201–211. doi: 10.1002/glia.440020309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rio J. A., Soriano E. Immunocytochemical detection of 5'-bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in the central nervous system of the mouse. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(89)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]