Abstract
The premyofibril model proposes a three-stage process for the de novo assembly of myofibrils in cardiac and skeletal muscles: premyofibrils to nascent myofibrils to mature myofibrils. FRAP experiments and jasplakinolide, a drug that stabilizes F-actin, permitted us to determine how decreasing the dynamics of actin filaments affected the dynamics of tropomyosin, troponin-T, troponin-C, and two Z-Band proteins (alpha-actinin, FATZ) in premyofibrils versus mature myofibrils. Jasplakinolide reduced markedly the dynamics of actin in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils in skeletal muscles. Two isoforms of tropomysin-1 (TPM1α, TPM1κ) are more dynamic in premyofibrils than in mature myofibrils in control skeletal muscles. Jasplakinolide reduced the exchange rates of tropomyosins in premyofibrils but not in mature myofibrils. The reduced tropomyosin recoveries did not match the YFP-actin recoveries in premyofibrils in jasplakinolide. There were no significant differences in the effects of jasplakinolide on the dynamics of troponins in the thin filaments or of two Z-band proteins in premyofibrils or skeletal mature myofibrils. Cardiac control mature myofibrils lack nebulin, and small decreases in actin (~5%) and two tropomyosin isoforms (~10–15%) dynamics are detected in premyofibril to mature myofibril transformations compared with skeletal muscle. In contrast to skeletal muscle, jasplakinolide lowered the dynamics of actin and tropomyosin isoforms in the cardiac mature myofibrils. These results suggest that the dynamics of tropomyosins in control muscle cells are related to actin exchange. These results also suggest a stabilizing role for nebulin, an actin and tropomyosin binding protein, present in mature myofibrils but not in premyofibrils of skeletal muscles.
Keywords: actin, tropomyosin, alpha-actinin, FATZ, premyofibril, mature myofibril
INTRODUCTION
How myofibrils are assembled de novo, and maintained in living muscle cells are outstanding problems in the field of muscle research (Piccirillo et al., 2013). The premyofibril model that was first proposed twenty years ago (Rhee et al., 1994) postulated that de novo myofibrillogenesis involved three steps, i.e. premyofibrils to nascent myofibrils to mature myofibrils. Although this model was first developed from observations of antibody localization in cultured avian cardiomyocytes, it was tested subsequently with time-lapse imaging in cultures of live cardiomyocytes expressing GFP-alpha-actinin (Dabiri et al., 1997). Antibody localization results have been confirmed in cardiac explants (Du et al., 2003), in embryonic hearts fixed in situ (Du et al., 2008), and in zebrafish (Sanger et al., 2009). Recent support for the premyofibril model was reported by Liu et al. (2013) using a novel form of microscopy, i.e., two-photon excited fluorescence-second harmonic generation, or TREF-SHG, to follow the incorporation of unlabeled myosin II filaments onto premyofibrils to form nascent myofibrils in living neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.
In addition to the structural differences between premyofibrils, nascent, and mature myofibrils, the dynamic exchange of the proteins between a cytoplasmic pool and myofibrils also differs between premyofibrils, nascent and mature myofibrils. The quantitative optical technique of FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) demonstrated that sarcomeric proteins localized in premyofibrils are more dynamic than when the same proteins are organized in mature myofibrils. In cardiac and skeletal muscle cells all Z-Band proteins tested were more dynamic in the Z-Bodies of premyofibrils than in the Z-Bands of mature myofibrils (Wang et al., 2005a). It was hypothesized that closer interactions between some of the Z-Body proteins occur as Z-bodies in premyofibrils reorganize into Z-Bands during myofibrillogenesis (Wang et al., 2005a). This prediction is supported by FRET, (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) measurements showing that proximities of Z-Band protein pairs decrease during myofibrillogenesis (Stout et al., 2008).
The recovery of fluorescence versus time after bleaching in FRAP experiments can be modeled mathematically to determine mobile fractions and half times of the recovery process after photobleaching (Sprague and McNally, 2005). Many of the experimental curves obtained in the study of Z-Band FRAP experiments fit two exponentials (Wang et al., 2005a) suggesting at least two different processes are involved. What these two processes represent is often very difficult to determine. This is especially true in Z-Bands in muscle cells where there are a large number of interacting proteins with multiple binding partners (Wang et al., 2005a; Sanger and Sanger, 2008). The thin filaments of muscles contain a smaller number of interacting proteins, i.e., F-actin, tropomyosin, three members of the troponin complex (troponin-T, troponin-C, troponin-I), and, in the case of mature myofibrils in skeletal muscle, nebulin, which binds both actin and tropomyosin (Bang et al, 2006; Witt et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2008). We used jasplakinolide, an F-actin stabilizing drug that acts by blocking monomer loss at the ends of the actin filaments, and prevents the F-actin severing action of cofilin (Bubb et al., 1994; 2000; Hagiwara et al., 2011; van Goor et al., 2012) to determine how changing the stability of F-actin affected the dynamics of tropomyosin, a protein that binds and stabilizes actin in the thin filaments of muscle.
We analyzed the dynamic exchange and mobile fractions of tropomyosin (TPM1α and TPM1κ isoforms), troponin-T, troponin-C, and two Z-band proteins (alpha-actinin; FATZ) in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. We speculate that differences observed between skeletal and cardiac myofibrils can be attributed to the actin and tropomyosin binding protein, nebulin, which extends along the thin filaments in mature skeletal myofibrils, but is present only in minor amounts in cardiac myofibrils. Our results also suggest that there may be two processes of tropomyosin exchange from the thin filaments of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells: release from the sides of a stable F-actin core of the thin filament, and a release caused when cofilin severs within a group of actin monomers that binds each tropomyosin dimer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Constructs, cell culture and transfections
The preparation of the probes for YFP-actin, YFP-alpha-actinin, YFP-FATZ, YFP-myotilin, YFP-telethonin, YFP-TPM1α and YFP-TPM1k were described previously (Wang et al., 2005, 2007, 2008, 2011). The cDNAs of actin, FATZ, myotilin and telethonin were derived from RT-PCR reactions using the human skeletal muscle library (Stratagene La Jolla, CA). The cDNAs of alpha-actinin, TPM1α and TPM1k were made from chicken skeletal muscle library and all cloned into the pEYFP-N1 vector (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). The c-DNAs for troponin-C (accession number: M22307) and troponin-T (accession number: M21984) were isolated from a human skeletal muscle library and the sequences confirmed, and cloned into the pEYFP-C3 vector (Clontech, Mountain View, CA). Muscle cells were isolated from breast muscles of nine-day quail embryos (Wang et al., 2005) and embryonic mouse hearts (Lin et al., 2005, 2008; Wang et al., 2012). These cells were plated on 35 mm MatTek (Ashland, MA) dishes at 105 cells per dish using procedures described in Dabiri et al. (1999). The culture medium for skeletal muscle cells were 10% horse serum (Gibco, Grand Island, NY; catalogue # 16050), 10% chicken embryo extract, 1% glutamine (Gibco, catalogue # 7231) and 1% Antibiotics Antimyotics (ABM; Gibco, catalogue # 3857) in Minimum Essential Medium (MEM; Gibco, catalogue # 10370) for skeletal muscle cells. The neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes were cultured in MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, catalogue # 10082) and 1% ABM. The MatTek dishes have part of the plastic bottoms of the dishes cut out that is replaced by a glass coverslip. We coated the glass bottoms of the MatTek dishes used for the culturing of skeletal myoblasts with rat-tail collagen (BD Biosciences, Belford, MA; catalogue # 354236). The MatTek dishes used for the culturing of the neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes were coated with laminin (Lin et al., 2005, 2008; Wang et al., 2012).
Both types of muscle cells were transfected after two days in culture with FuGene HD (Promega, Madison, WI) with plasmids encoding different YFP-sarcomeric proteins (Dabiri et al., 1999; Ayoob et al., 2000, 2001; Wang et al., 2007). Jasplakinolide was added on the fourth day of tissue culture for both cell types.
Microscopy of living cells
The technique of fluorescence recovery after photobleaching or FRAP was performed on a Leica SP5 confocal microscope to measure the dynamics of YFP-actin and six YFP-sarcomeric proteins that bind actin and localize in the premyofibrils and mature myofibrils of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. The details of this quantitative biophysical procedure and analysis are described in Wang et al. (2005a; 2007a; 2008). FRAP experiments were conducted using time points separated by 30 seconds intervals over 20 minutes collection period. The first post-bleach images were obtained immediately after photobleaching (scanning time: 3 seconds). Jasplakinolide (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) was dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 1mM and added to the muscle cells at a final concentration of 1μM. FRAP experiments were performed after 30 minutes of jasplakinolide treatment in 37°C. At a concentration of 0.1uM, jasplakinolide (Tsuji et al., 2009; Minamide et al., 2010) had no effect on the myotubes, whereas 5uM resulted in the contractile myotubes detaching from the substrate.
RESULTS
Jasplakinolide affects premyofibril arrangements but not that of mature myofibrils
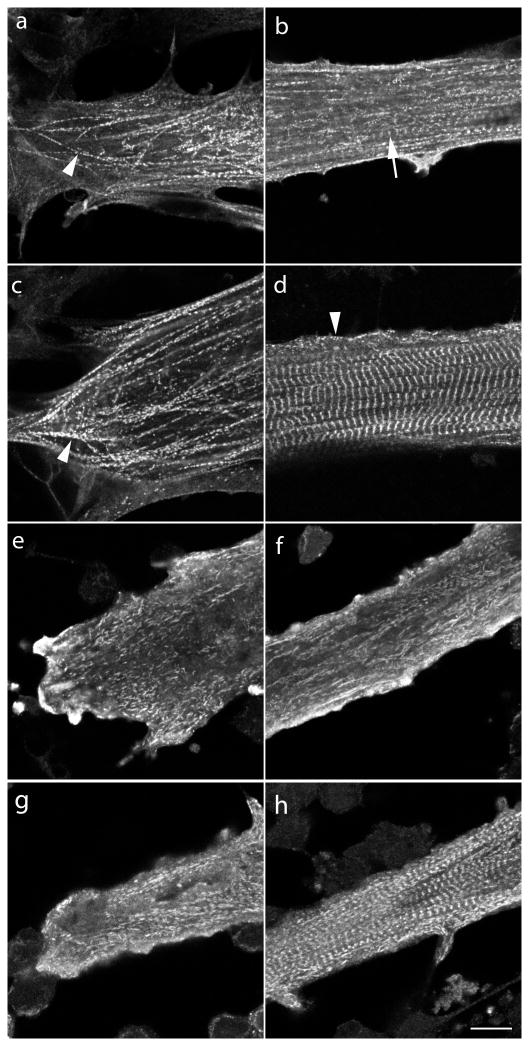
Quail embryonic myoblasts multiply over the first several days in culture, and then fuse with one another to form elongated multinucleated myotubes. By day four in culture, premyofibrils bounded by Z-bodies spaced one micron or less apart are evident at the spreading ends and sides of the myotubes, as well as in the central regions of the myotube where a few mature myofibrils can be detected (Figure 1a, b). (Rhee et al., 1994; Sanger et al., 2006; White et al., 2014). One day later in culture premyofibrils continue to form in the elongating ends and along edges of the myotubes (Figure 1c and arrowhead 1d), and mature myofibrils with aligned Z-Bands occupy the central region of the myotubes (Figure 1d; see also Wang et al., 2000). When four-day-old control myotubes were exposed to jasplakinolide for one day, premyofibrils were depleted from the ends (Figure 1e), and sides (Figure 1f), of the five-day-old myotubes (Figure 1f). In addition, jasplakinolide also prevented mature myofibrils formation in the central regions of the myotubes. Compare the mature myofibrils in the five-day control myotube in Figure 1d with the same age myotube exposed at day four to jasplakinolide for one day in Figure 1f. When five-day-old control myotubes were exposed to jasplakinolide for one day, the premyofibrils in the ends and sides of the six-day-old myotubes were disrupted (Figure 1g), but the mature myofibrils that had formed in the first five days in culture were still present (Figure 1h).
Figure 1. Effect of jasplakinolide (1μM) on the formation of premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in cultured quail myotubes.
Control and jasplakinolide-treated myotubes were fixed, permeabilized and stained with sarcomeric alpha-actinin antibodies to localize premyofibrils at the spreading ends of myotubes (a, c, e, g) and mature myofibrils in the central regions of myotubes (b, d, f, h). Myotubes were grown in control muscle medium (a–d) or in muscle medium with 0.1uM jasplakinolide (e–h).
(a and b) Myotubes fixed on the morning of the fourth day in control culture. (a) Z-Bodies of the premyofibrils (arrowhead) were in linear arrays of minisarcomeres about one micron or less. (b) A few mature myofibrils (arrow) were present among many more premyofibrils in the central region of a myotube. (c and d) Myotubes were fixed on the fifth day in control culture (c) Premyofibrils (arrowhead) were aligned in the end of a myotube. (d) A few premyofibrils (arrowhead) were localized along the membrane in the central region of a myotube that was filled with aligned Z-bands of mature myofibrils. (e and f) Jasplakinolide was added to myotubes on the fourth day of culture for 24 hours and fixed on the fifth culture day. (e) Most premyofibrils were absent from the spreading edge and (f) mature myofibrils were absent in the middle region of a myotube. (g and h) Jasplakinolide was added to five-day-old control myotubes that were incubated for another day in the presence of the drug. (g) aligned premyofibrils were absent from the end of this myotube. (h) In a central region mature myofibrils were still present in this thinner myotube, presumably ones formed previously in control medium on day five before jasplakinolide addition. These results suggest that jasplakinolide prevents the transition of premyofibrils to mature myofibrils during myofibrillogenesis. Bar = 10 microns.
Dynamics of YFP-sarcomeric probes in six-day old cultured skeletal muscle cells
Actin
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) of YFP-actin expressed in premyofibrils (Figure 2a, b) and mature skeletal myofibrils (Figure 2c, d) illustrates the marked difference in actin dynamics in control medium (Figure 2a, c) compared to medium containing one micromolar jasplakinolide (Figure 2b, d). Premyofibrils, marked by their unbanded actin patterns near the ends of the myotubes, recovered very quickly from the photobleaching process (Figure 2a), whereas in the presence of jasplakinloide, recovery was markedly slower (Figure 2b). A similar relationship was seen in mature myofibrils where the recovery of actin-YFP was dramatically reduced in the presence of jasplakinolide in comparison to mature myofibrils in control medium (Compare 5 min. and 20 min. time points in 2d and 2c).
Figure 2.
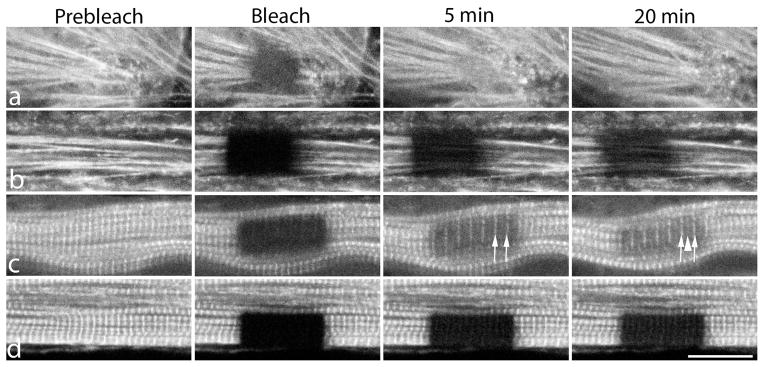
Examples of FRAP experiments in premyofibrils (a, b) and mature myofibrils (c, d) in quail myotubes expressing YFP-actin. Actin fluorescence was bleached selectively in a group of premyofibrils in control medium (a) or in medium with jasplakinolide (b) and in a group of mature myofibrils in control medium (c), or in jasplakinolide-containing medium (d). Note that fluorescence recovery after photobleaching occurred faster in premyofibrils in control medium than in jasplakinolide (a vs. b) and in mature myofibrils recovery was also faster in control medium than in jasplakinolide (c vs. d). Incorporation of YFP-actin first occurs at the Z-Band insertions of actin filaments (arrows in 5 minute time point in c), and then at the overlap regions of the actin filaments in the middle of the sarcomeres (arrowhead) in the 20 minute time point in c. Scale = 10 microns.
Actin-YFP localizes in mature myofibrils in a banded pattern that is brightest at the Z-Bands where the plus ends of actin filaments in adjacent sarcomeres overlap (Huxley, 1963; Littlefield et al., 2001). In sarcomeres shorter than two microns, a third band is present where the minus ends of the actin filaments overlap in the middle of the sarcomere. Five minutes after bleaching, recovery of fluorescence was detected first at the Z-Bands (Figure 2c, arrows). After 20 minutes of recovery in control cells, YFP-actin fluorescence increased at the Z-Bands, and in bands in the middle of the sarcomere (Figure 2c, arrowhead). Similar results have been reported in cardiomyocytes in sarcomeres shorter than two microns (Littlefield et al., (2001). Overnight, fluorescence recovered between the Z-Bands and the overlap in the middle of the sarcomere occurred We did not detect any sign of flow of YFP-actin from the Z-Bands towards the middle of the sarcomeres during the 20-minute recovery (Figure 2c).
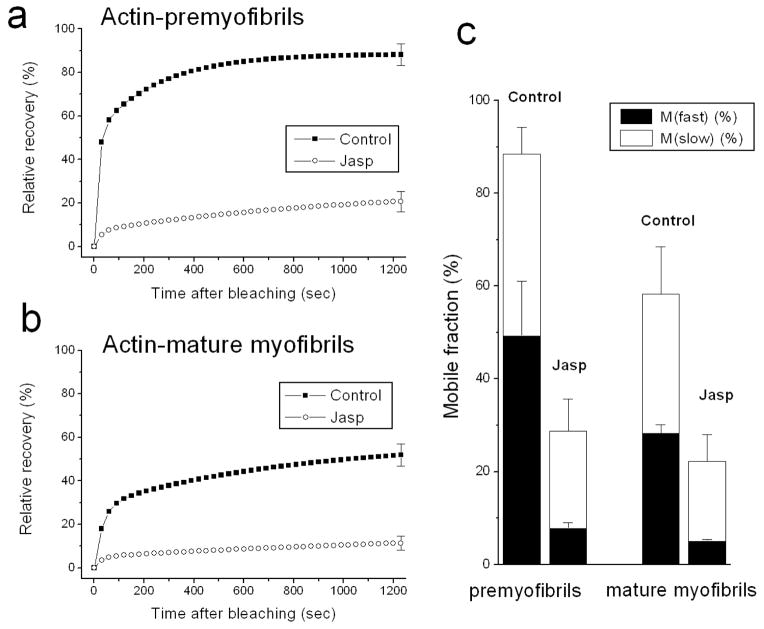
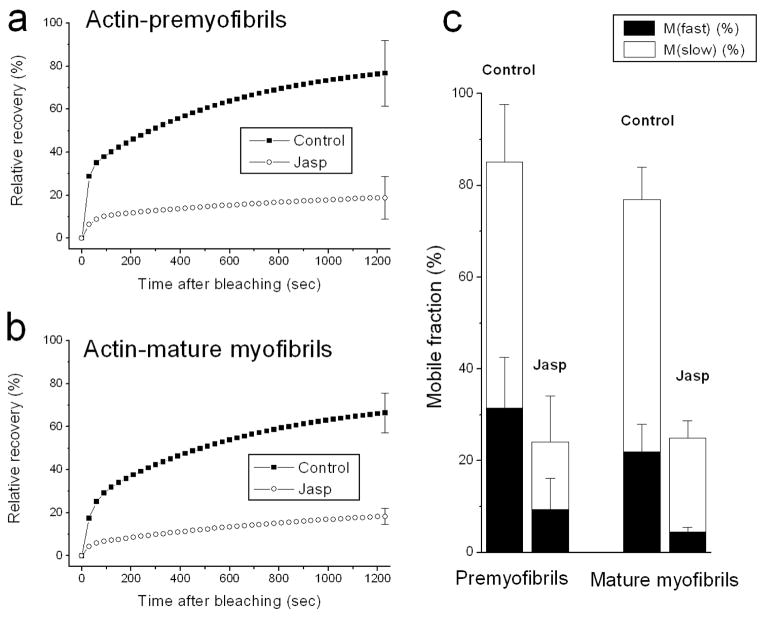
A comparison of fluorescence intensity, normalized and plotted as a function of time after bleaching, is shown for control and jasplakinolide-treated premyofibrils and mature myofibrils (Figure 3). In premyofibrils the recovery of YFP-actin fluorescence decreased from ~90% at 20 minutes in control cells to ~20% in jasplakinolide-treated cells Figure 3a). In mature myofibrils the recovery decreased from ~50% at 20 minutes in control medium to ~10% recovery in jasplakinolide (Figure 3b). Curve fitting of the fluorescence recovery can be modeled as consisting of two processes that describe fast and slow mobile fractions (Wang et al., 2005a). In jasplakinolide, both fast and slow mobile fractions of actin were suppressed compared with control values in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils (Figure 3c).
Figure 3.
Fluorescence recovery rates of YFP-actin in premyofibrils (a) and mature myofibrils (b) of cultured skeletal myotubes in control medium and in the presence of jasplakinolide. Note the dramatic decreases in the rates of YFP-actin recovery after the photobleaching in the presence of jasplakinolide (lower curves a, b). (c) Calculations of mobile fractions of YFP-actin reveal dramatic decreases of both fast and slow mobile fractions in the presence of jasplakinolide in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils.
Tropomyosin
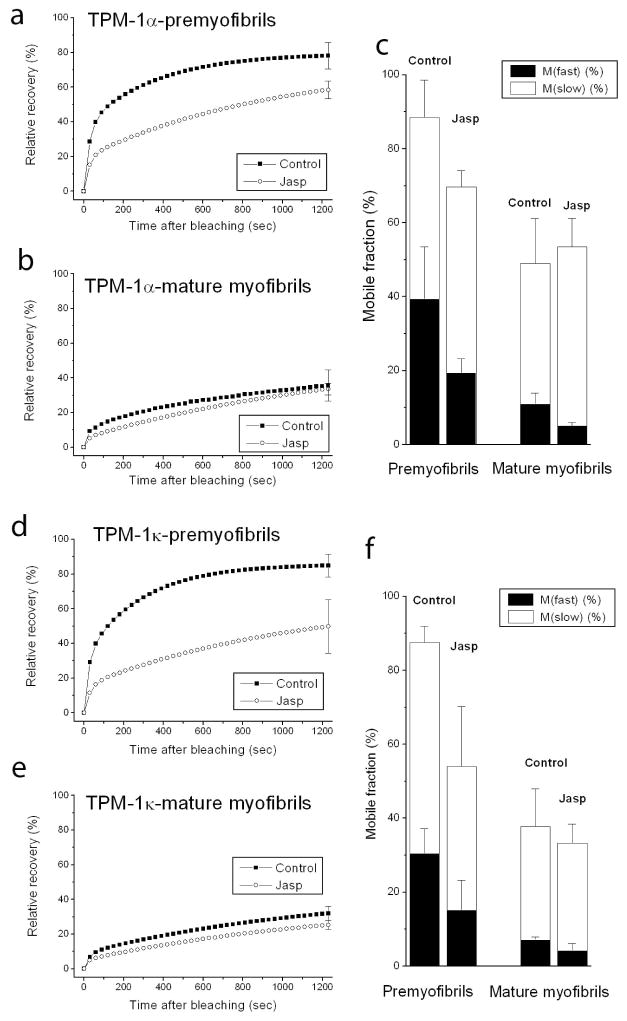
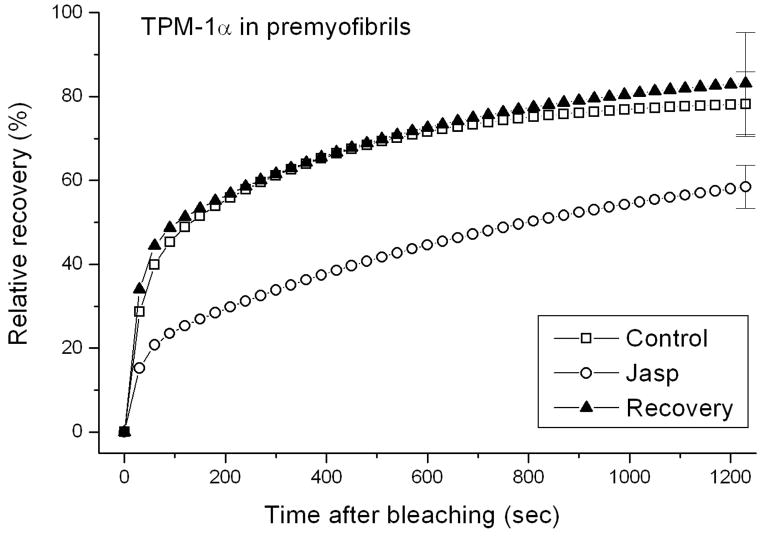
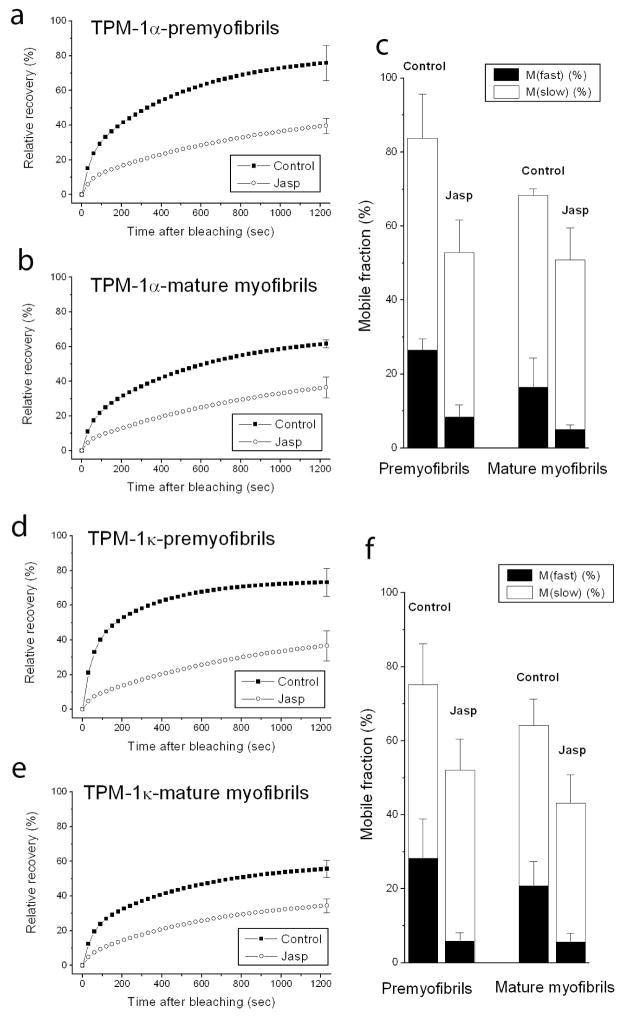
The major actin-associated protein in muscle, tropomyosin, binds as dimers along the length of actin filaments in myofibrils. Jasplakinolide allowed us to examine whether suppressing actin dynamics in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils also affected the dynamics of tropomyosin in thin filaments of myofibrils. In premyofibrils, YFP-TPM1α fluorescence recovered rapidly after it was photobleached in control myotubes compared to the slower recovery in jasplakinolide-treated premyofibrils (Figure 4a vs. b). The exchange of YFP-TPM1α fluorescence in mature myofibrils, however, was similar in control and jasplakinolide-treated cells (Figure 4c vs. d). Analysis of FRAP recovery data for two isoforms of YFP-TPM, expressed in jasplakinolide-treated premyofibrils and mature myofibrils, is shown in Figure 5. Note that there was a marked decrease in the dynamics of both tropomyosin isoforms in control medium between premyofibrils and mature myofibrils (Figure 5 upper curves: a vs. b and d vs. e). Jasplakinolide, however, had minimal effect on FRAP recovery values of TPM in mature myofibrils (Figs 5b and 5e). Replacement of jasplakinolide with control medium led to the return of control values for recovery of YFP-TPM1α fluorescence of premyofibrils forty minutes after photobleaching (Figure 6). Exposing actin in premyofibrils to jasplakinolide significantly reduced the dynamics of both TPM isoforms in premyofibrils: YFP-TPM1α (~80% control to ~60% in jasplakinolide (Figure 5a)), YFP-TPM1κ (~80% control to ~50% in jasplakinolide (Figure 5d)). The change, however, was much smaller than that seen for YFP-actin in premyofibrils treated with jasplakinolide (Figure 3a). In mature myofibrils exposed to jasplakinolide, however, there was negligible change in YFP-TPM dynamics compared to controls (Figs 5b and 5e). Replacement of jasplakinolide with control medium led to the return of control values for recovery of YFP-TPM1α fluorescence of premyofibrils forty minutes after photobleaching (Figure 6).
Figure 4.
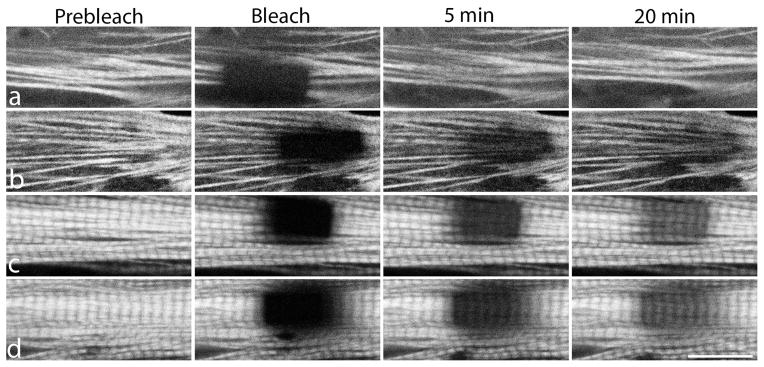
Examples of FRAP experiments in premyofibrils (a, b) and mature myofibrils (c, d) in quail myotubes expressing YFP-TPM1α. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching was measured to determine if stabilization of actin by jasplakinolide affected dynamic exchange of YFP-TPM1α in sarcomeres. Note the recoveries from photobleaching of YFP-TPM1α in premyofibrils (b) are delayed when treated with jasplakinolide (compare a versus b). In contrast to premyofibrils, the recoveries of bleached regions of YFP-TPM1α is comparable in mature sarcomeres in the control myotube (c), and in jasplakinolide-treated mature myofibrils (d). Scale = 10 microns.
Figure 5.
Fluorescence recovery rate in premyofibrils of both YFP-TPM1α (a) and YFP-TPM1κ (d) decreased in jasplakinolide medium as compared with control medium. In mature myofibrils, however, the recovery of both YFP-TPM1α (b) and YFP-TPM1κ (e) did not significantly differ in control and treated medium (b). In control medium, the recovery rates in premyofibrils of both YFP-TPM1α (a, upper curve) and YFP-TPM1κ (d, upper curve) were faster than in mature myotubes (upper curves, b and e) Graphs in (c) and (f) quantitate the slow and fast mobile fractions of YFP-TPM1α (c) and YFP-TPM1κ (f) in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in medium with or without jasplakinolide.
Figure 6.
Reversal of jasplakinolide effect on premyofibrils in skeletal muscle cells. Fluorescence recovery after bleaching of YFP-TPM1α was measured over 20 minutes in premyofibrils that were bleached in the presence of jasplakinolide. The drug-treated myotubes were then rinsed several times to wash out jasplakinolide. Forty minutes later, YFP-TPM1α in premyofibrils in myotubes reversed from jasplakinolide exposure were photobleached and fluorescence recovery was recorded. Measurements indicated that fluorescence recovered to the prebleached levels of control cells that had not been exposed to jasplakinolide.
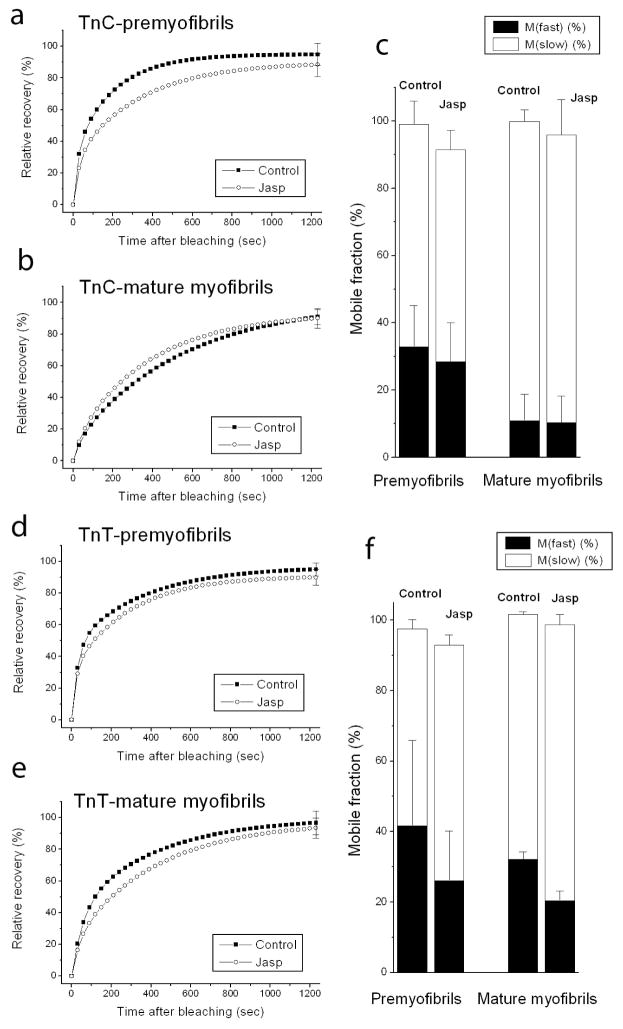
Troponins
In addition to interacting with actin in thin filaments of muscle, tropomyosin links the troponin regulatory complex to actin through binding to troponin-T (Gomes et al., 2002; Willott et al., 2010). Both troponin-T and a second troponin subunit that it binds, troponin-C, recovered fluorescence rapidly when expressed as YFP fusions and photobleached in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils (Figure 7 and Figure 8 control curves, a, b, d, e). In the presence of jasplakinolide there was very little difference in the fluorescence recoveries (Figures 8, jasplakinolide curves, a, b, d, e).
Figure 7.
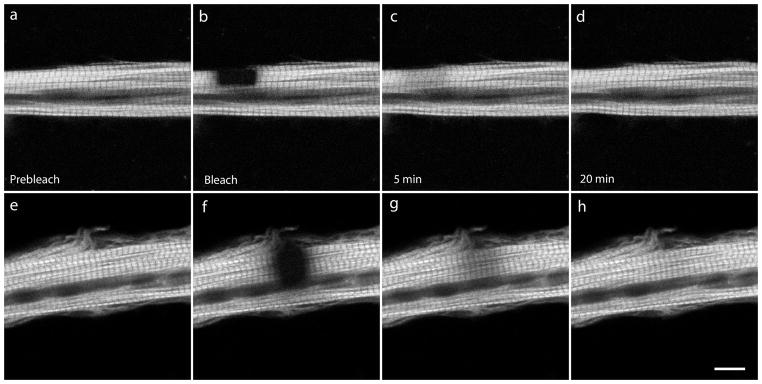
Examples of FRAP experiments in control (a–d) and jasplakinolide-treated (e–h) mature myofibrils expressing YFP-troponin-C (YFP-TnC). The rate of the fluorescence exchange of YFP-TnC was rapid and comparable in control (a–d) and in jasplakinolide-treated (e–h) conditions. Scale = 10 microns.
Figure 8.
Graphs of fluorescence recovery rates in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils of two troponins, YFP-troponin C (TnC) (a, b) and YFP-troponin T (TnT) (d, e), in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in myotubes in control medium or in the presence of jasplakinolide. Note that there were no marked effects of jasplakinolide on the dynamics of YFP-TnC and YFP-TnT in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils. (c) Analyses of the mobile fractions of YFP-TnC(c) and YFP-TnT (c and f) showed similar recoveries in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils and revealed no significant changes in the presence of jasplakinolide.
Two Z-Band Proteins: alpha-actinin and FATZ
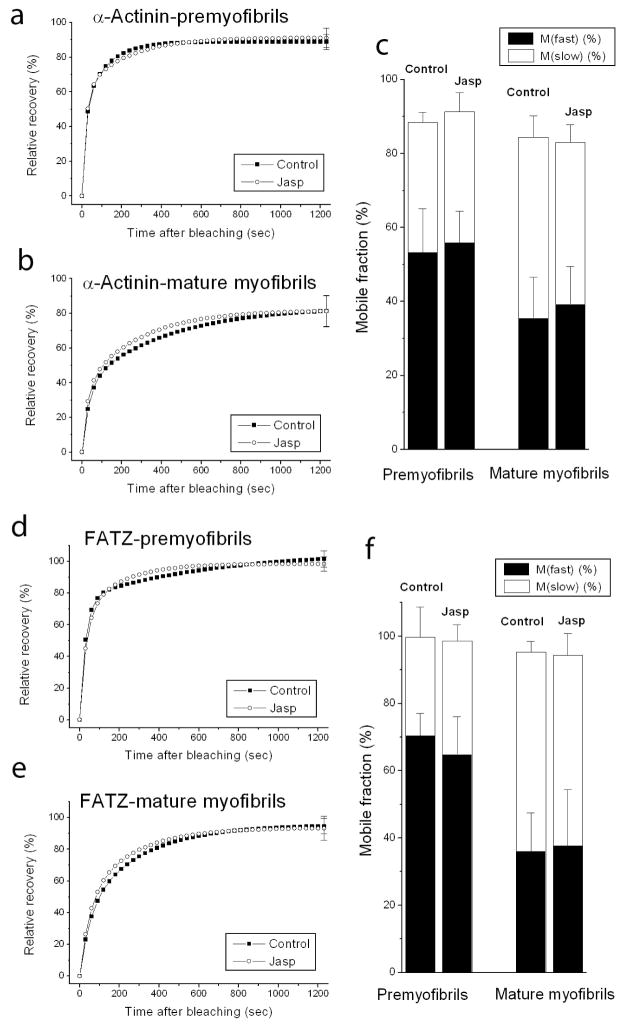
Two actin-binding proteins, alpha-actinin and FATZ, expressed as YFP fusions, localize in Z-bodies of premyofibrils and Z-bands of mature myofibrils (Rhee et al., 1994) and exchange rapidly in response to photobleaching of premyofibrils and mature myofibrils (Wang et al., 2005a). Fluorescence recovery in both premyofibrils (Figures 9a, d) and in mature myofibrils (Figure 9b, e) was unaffected in the presence of jasplakinolide. Analyses of the slow and fast mobile fractions of YFP-alpha-actinin (Figure 9c) and YFP-FATZ (Figure 9e) in the dense bodies of premyofibrils, and the Z-bands of mature myofibrils revealed no effects of jasplakinolide.
Figure 9.
Graphs of fluorescence recovery rates of two proteins that bind actin in the Z-band, YFP-alpha-actinin (a, b) and YFP-FATZ (d, e). Exchange was measured in premyofibrils (a and d) and mature myofibrils (b and e) of myotubes in control medium or in the presence of jasplakinolide (a, b and d, e). Recoveries of both proteins showed no significant change between premyofibrils (a and d) and mature myofibrils (b and e). Jasplakinolide had no effect on the exchange of the proteins in both types of myofibril. This is shown in the analyses of the mobile fractions of YFP-alpha-actinin (c) and YFP-FATZ (f) in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils, in control medium or in the presence of jasplakinolide.
Dynamics of the YFP-sarcomeric probes in cultured cardiac muscle cells
To compare the effect of jasplakinolide on actin and tropomyosin dynamics in cardiomyocytes with that in skeletal myotubes, we first measured the dynamics of five Z-band proteins previously analyzed in quail myotubes (Wang et al., 2005a) and in zebrafish somites (Sanger et al., 2009) and compared the dynamics of the same five proteins in cultured neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes (Figure 10). In both the skeletal and the cardiac muscle cells the most dynamic Z-band protein was YFP-myotilin, followed by YFP-FATZ. The least dynamic protein was YFP-telethonin. Four proteins, YFP-FATZ, YFP-alpha-actinin, YFP-actin, and YFP-telethonin, were notably more dynamic in Z-Bands of cardiac muscle than in Z-Bands of skeletal muscle cells (Figure 10).
Figure 10.
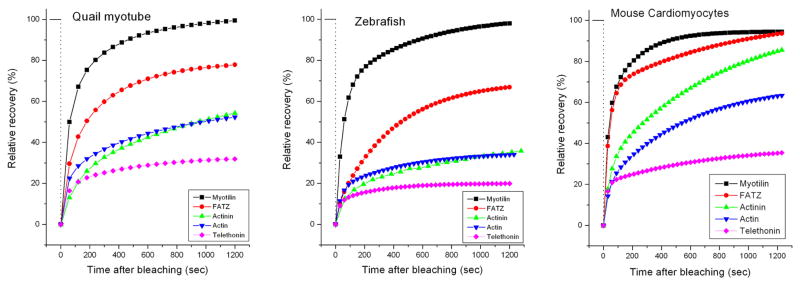
Comparison of the dynamics of five Z-band proteins in the Z-Bands of mature myofibrils in quail myotubes and zebrafish myotomes with the results in mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes. In all three muscles the fastest exchanging protein is YFP-myotilin and slowest exchanging protein is YFP-telethonin. Note that relative recovery of fluorescence of YFP-FATZ, -alpha-actinin, -actin and -telethonin is higher in cardiomyocytes than the exchange rates of their counter parts in the two different types of skeletal muscle cells shown. The curves for the quail and zebrafish were previously published by Sanger et al, (2009), and are reproduced here with the permission of the publisher to enable comparison with the new results in the neonatal cardiomyocytes.
In the transition from premyofibrils to mature myofibrils in mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes, there were no significant decreases in actin and tropomyosin dynamics (Figure 11a, b; Figure 12a, b; c, d top curves) unlike the decreases seen in skeletal myofibrils (Wang et al., 2008 and Figures 3 and 5 controls). Jasplakinolide had a marked effect on actin dynamics in both the premyofibrils and mature myofibrils of cardiomyocytes (Figure 11). YFP-TPM1α (Figure 12a, b) and YFP-TPM1κ (Figure 12d, e) also were both inhibited, although the inhibition was more pronounced for actin (Figures 11 and 13) than for TPM (Figures 12 and 14). Whereas jasplakinolide had a negligible effect on TPM dynamics in mature skeletal myofibrils (Figure 5b, e), in mature cardiomyocyte myofibrils, TPM dynamics were inhibited by jasplakinolide (Figure 12, 14).
Figure 11.
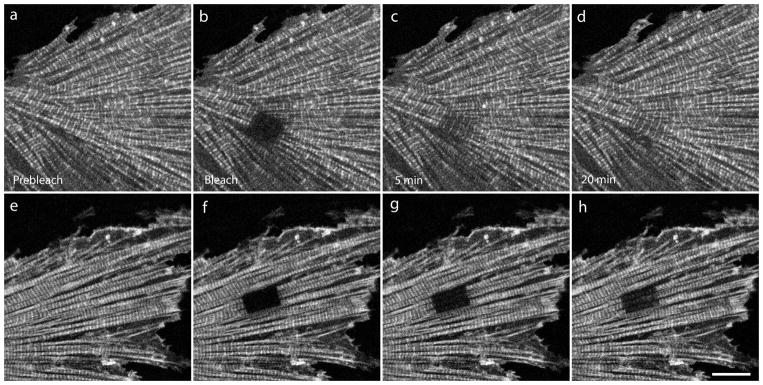
Images of FRAP experiments showing recovery of YFP-actin in mature myofibrils in mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes in control (a–d) or jasplakinolide-treated medium (e–h). Note that the recovery occurs much more quickly in sarcomeres bleached in control medium (a–d), than in jasplakinolide (e–h). Compare (c, d) with (g, h). Scale = 10 microns.
Figure 12.
Fluorescence recovery rates of YFP-actin in a) premyofibrils and in (b) mature myofibrils in cultured mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes in control medium and in jasplakinolide-treated medium. There was negligible change in recovery rates between premyofibrils and mature myofibrils. In both types of myofibrils, jasplakinolide caused a pronounced decrease in the rate of YFP-actin recovery (c) Note the large decreases in the mobile fractions in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils in jasplakinolide-treated cardiomyocytes.
Figure 13.
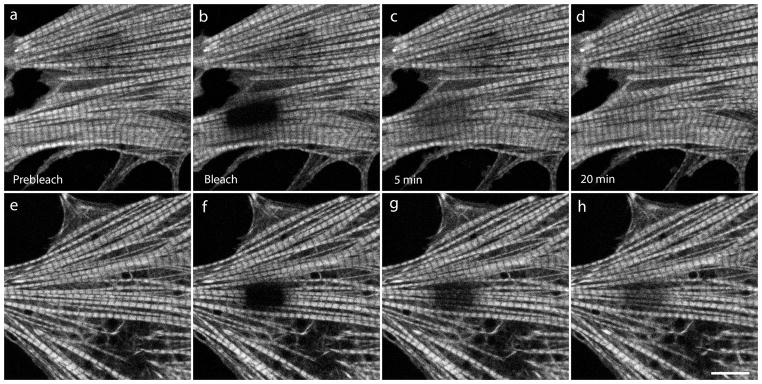
Images FRAP experiments showing recovery of YFP-TPM1α in mature myofibrils of mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes in control medium (a–d) or in jasplakinolide-treated medium (e–h). FRAP experiments illustrate a much slower exchange of YFP-TPM1α in the presence of jasplakinolide (e–h) than in control medium (a–d) Compare (c, d) with (g, h). Scale = 10 microns.
Figure 14.
Fluorescence recovery rates of YFP-TPM1α and YFP-TPM1κ in (a and d) premyofibrils and (b and e) mature myofibrils of mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes in control medium and in the presence of jasplakinolide. Jasplakinolide caused marked decreases in the recovery of YFP-TPM1α and -TPM1κ in both premyofibrils and mature myofibrils, in sharp contrast to the absence of an effect in the mature myofibrils in skeletal muscle cells (See Figure 5b). (f) Note that there are large decreases in the mobile fractions of YFP-TPM1α in premyofibrils and in mature myofibrils in jasplakinolide-treated cardiomyocytes.
DISCUSSION
Premyofibril model of myofibrillogenesis and dynamic realignment of proteins in living muscle cells
The premyofibril model of de novo assembly of myofibrils postulates that the organization of muscle proteins in contractile myofibrils begins with a premyofibril stage followed by a nascent myofibril stage and ends with mature myofibrils (Sanger et al., 2010 b). The steps from premyofibril to nascent and mature myofibrils occur with addition of proteins and changes in fibril organization that result in more ordered arrangements of proteins in myofibril subunits: Z-bands, I-bands and A-bands. In skeletal and cardiac muscle cells microinjected with fluorescently labeled alpha-actinin (Sanger et al., 1986a, b), or expressing YFP-alpha-actinin, Z-bodies have been recorded forming and fusing into Z-bands (Dabiri et al., 1997; Golson et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2005a, 2005b; Manisastry et al., 2009). The banded distribution of muscle myosin II in periodic A-bands together with myosin-binding proteins, myomesin and C-protein, are preceded by localization of muscle myosin in unbanded fibrils in nascent myofibrils (Rhee et al., 1994; Sanger et al., 2004, 2004, 2005, 2008, 2010).
In addition to their ordered arrangement in myofibrils, muscle proteins also are present in a cytoplasmic pool in muscle cells. The technique of FRAP provides a method for analyzing protein exchange between a cytoplasmic pool and a complex of interacting proteins in live cells. We have found that the exchange of most sarcomeric proteins that we have measured occurred at a faster rate i.e. were more dynamic, for proteins in premyofibril structures than when the same protein were component of mature myofibrils. (Sanger et al., 2010b; Wang et al., 2005a, 2007a, 2008a, 2011). In this study we used the F-actin stabilizing drug, jasplakinolide (Bubb et al., 1994; Bubb et al., 2000), to determine how altering actin filament stability affected mature myofibrils and premyofibrils and several proteins that bind to actin filaments in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils. Stabilizing F-actin dynamics inhibited the transformation of premyofibrils (Figure 1e, f). These experiments support the importance of actin dynamics in myofibrillogenesis.
Table 1 summarizes the major effects of jasplakinolide on fluorescence recovery in premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Jasplakinolide at 1μM suppressed YFP-actin dynamics by about the same amount in premyofibrils of skeletal (~81%) and cardiac (~75%) muscle cells, as well as in mature myofibrils of skeletal (~70%) and cardiac (~75%) muscles. Jasplakinolide exposure also inhibited the dynamics of tropomyosin in premyofibrils of both cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. However, in mature myofibrils there was a major difference between cardiac and skeletal muscle in the effect of jasplakinolide exposure on tropomyosin dynamics. Tropomyosin dynamics decreased markedly in cardiomyocyte mature myofibrils (TPM1α, 50%; TPM1κ, 47%), but there was no change in tropomyosin dynamics in mature skeletal myofibrils. This may be due to the presence of nebulin, a protein that binds actin and tropomyosin in mature skeletal myofibrils, but is present at very low levels in mature ventricular cardiomyocytes (Bang et al., 2006; Witt et al., 2006). There are two nebulin molecules per thin filament in skeletal mature myofibrils versus at most one nebulin molecule per 50 thin filaments in ventricular heart mature myofibrils (Witt et al., 2006). No jasplakinolide effect was detected, in either premyofibrils or mature myofibrils, in the dynamics of two troponin proteins (TnT, TnC) or two Z-band proteins, alpha-actinin and FATZ.
Table 1.
Summary of effect of Jasplakinolide on fluorescence recovery of different myofibril proteins in skeletal myotubes and cardiomyocytes
| Average of FRAP inhibition by Jasplakinolide | ||
|---|---|---|
| Myotubes | Premyofibrils | Mature myofibrils |
| Actin | 81 ± 5% | 80 ± 2% |
| TPM1α | 41 ± 9% | NS |
| TPM1κ | 52 ± 16% | NS |
| TnT | NS | NS |
| TnC | NS | NS |
| Actinin | NS | NS |
| FATZ | NS | NS |
| Cardiomyocytes | ||
| Actin | 75 ± 12% | 75 ± 6% |
| TPM1α | 54 ± 7% | 50 ± 10% |
| TPM1κ | 57 ± 13% | 47 ± 9% |
The FRAP inhibition was calculated by 1- RJasp/RControl at each time point during FRAP experiment. RControl is the relative fluorescence recovery in control myotubes, RJasp is the relative fluorescence recovery in the jasplakinolide treated myotubes. The averages of FRAP inhibition by Jasplakinolide are presented as the means ± standard deviation (SD). NS, no significant difference for α = 0.05 significance level.
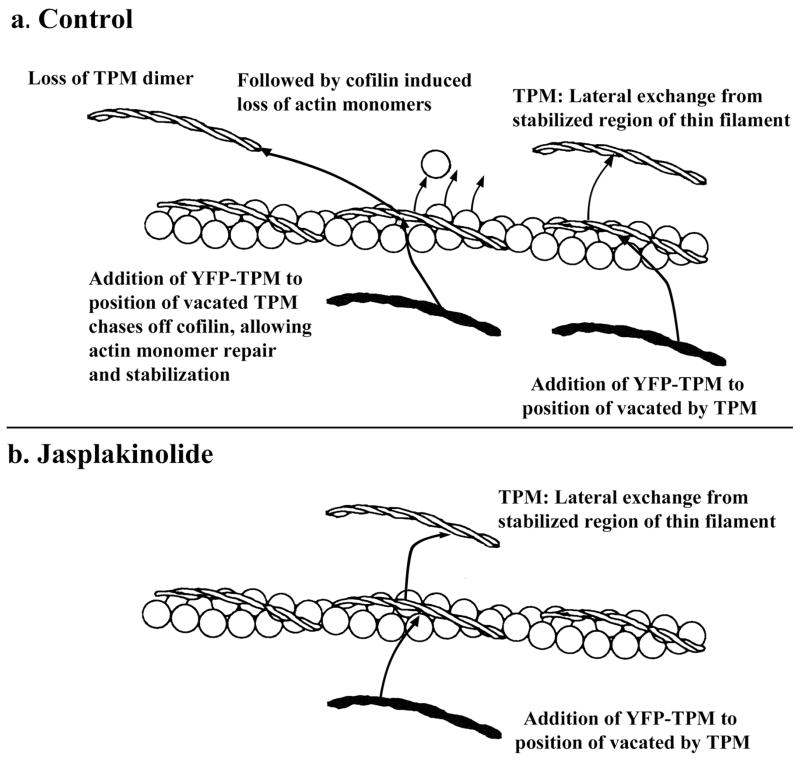
In both skeletal and cardiac premyofibrils, and in cardiac mature myofibrils, jasplakinolide exposure led to greater inhibition of actin dynamics (skeletal: Figures 3 vs. 5a, d) than tropomyosin dynamics (cardiac: Figures 11 vs. 12). We speculate that the differences between actin and tropomyosin exchanges in the presence of jasplakinolide may reflect the two types of tropomyosin release from the thin filaments, only one of which is affected by jasplakinolide (Figure 15). The thin filaments consist of two helical strands of actin subunits. Each tropomyosin dimer has seven actin-binding repeats with the dimers binding head to tail along the length of the actin fibers in the thin filament. The loss of one actin-binding repeat leads to a striking decrease in the binding of tropomyosin to F-actin. (Hitchcock-DeGregori and An, 1996). Jasplakinolide prevents cofilin severing of actin polymers in the middle of thin filaments and suppresses addition of actin monomers to the ends of the actin filaments (Tsuji et al., 2009; Minamide et al., 2010). Figure 15 illustrates a model for two processes for tropomyosin dimer exchange that depend on the state of the seven actin subunits binding tropomyosin. The first process, in control conditions (Figure 15a) is depicted lateral exchange of tropomyosin from a stabilized, seven-subunit region of the thin filament The second process available in control medium, posits that loss of a tropomyosin dimer allows cofilin to bind to the thin filament leading to excisions of actin monomers and repolymerization with stronger binding of tropomyosin dimers to the repaired regions (Bernstein and Bamburg, 1982; Ono and Ono, 2002). Tropomyosin subsequently could exchange laterally from these restabilized regions of actin filaments. In jasplakinolide-treated cells (Figure 15b), the second process for tropomyosin exchange would be inhibited by jasplakinolide, which prevents cofilin binding to actin filaments.
Figure 15. Diagram illustrating two possible types of tropomyosin exchange form the thin filament.
(a). In control muscle cells, tropomyosin dimers could exchange laterally from thin filaments and also could be released if cofilin activity induced loss of actin monomers affecting tropomyosin binding. Subsequent addition of TPM to the site would chase off cofilin allowing actin monomer polymerization and stabilization of the site (cofilin not shown in diagram). (b) Stabilization of thin filaments by jasplakinolide should not inhibit TPM lateral exchange, but the inhibition of cofilin activity by jasplakinolide would prevent TPM exchange that occurs when actin filament integrity is breached by cofilin.
The difference between the curves for tropomyosin exchange in control medium and the curves in jasplakinolide would represent the exchange of tropomyosin due to excision of actin subunits by cofilin in control cells. We further suggest that the absence of a jasplakinolide effect on the dynamics of tropomyosin in skeletal mature myofibrils (Figure 5b, e) is due to the presence in skeletal muscle of nebulin molecules that bind both tropomyosin and actin. We had previously demonstrated that nebulin was a late assembling protein in mature myofibrils of skeletal muscles, but was not present in premyofibrils (Wang et al., 2008), and proposed that nebulin acted to suppress the dynamics of tropomyosin in skeletal myofibrillogenesis (Wang et al., 2008) The jasplakinolide results for mature myofibrils in cardiac and skeletal muscle support this model, and also suggest that when tropomyosin is bound to nebulin, actin is not the sole determinate of tropomyosin’s exchange properties in sarcomeres as it must be in cardiomyocytes. Novel methods will be needed to detect these two predicted methods of exchange of tropomyosin, and the excision of actin subunits aided by cofilin or other excising molecules in living muscle cells.
Nebulin and nebulette
There are two nebulin molecules, with variable molecular weights of 600–900 kD, binding along the length of each thin filament in skeletal muscle cells (Witt et al., 2006), but in mouse cardiomyocytes, there is at most one nebulin per 50 thin filaments (Witt et al., 2006). We and others were unable to detect any nebulin in embryonic chick cardiomyocytes via immunofluorescence (Wang et al., 2008). It is unlikely that the small amount of nebulin in cardiac muscle cells plays a role in tropomyosin binding to thin filaments or in thin filament stabilization or length determination as it is proposed to do in skeletal myofibrils (ref). Nebulette, a member of the nebulin family is absent in skeletal muscle, but present in cardiac cells where there is evidence that it participates in both structure and function of myofibril assembly in cardiomyocytes (Moncman and Wang, 2002; Witt et al., 2006). It has a molecular weight of 107 kD, and 23 copies of nebulin-like, 35 amino acid repeats that are responsible for the binding to actin monomers in the thin filaments. Electron microscopic data indicated that nebulette molecules extended from cardiac Z-Bands for 0.086 microns at most along the one-micron thin filaments i.e. only 8.6% of the thin filament lengths (Millevoi et al., 1999), making it unlikely that nebulette plays a major role in stabilizing tropomyosin along the length of thin filaments of cardiac muscle. Without the stabilizing effect of nebulin, tropomyosin exchange along thin filaments in cardiomyocytes (Figure 12) differs very little between premyofibrils and mature myofibrils; unlike the case in skeletal myofibrils where tropomyosin exchange decreases significantly in mature myofibrils (Figure 5).
Dynamics of troponins in living muscle cells
The troponin complex is composed of three separate proteins in equal molar amounts i.e., troponin-T, troponin-C and troponin-I (Gomes et al., 2002). The synthetic half-lives of troponin-T and troponin-I are about three days, while troponin-C is about 5.5 days (Everett et al., 1981; Martin, 1981), raising the question of how a tertiary complex of proteins that do not have the same synthetic half-lives exchange their subunits. Our FRAP results indicate that YFP-troponin-T (Figure 8a–c) and YFP-troponin-C (Figure 8d–f) exchange at nearly the same rates (~90 % 20 minutes post-bleach), much faster than their synthetic half-lives. The three different components could exchange singly between the cytoplasm and tropomyosin in the thin filaments, or exchange as a complex preassembled in the cytoplasm that attaches to the thin filaments via tropomyosin. The exchange of the three different troponin subunits may be aided by the sensitivity of the binding of TnC to TnI as a function of the changing calcium ion concentrations in the cell, i.e., relaxation versus contraction states of the muscles (Gomes et al., 2002).
Tropomyosins exchange uniformly along the thin filaments of cardiac and skeletal muscle cells
In contrast to the initial exchange of fluorescent dye labeled actin and YFP-actin at the Z-bands of the mature myofibrils in both cardiac and skeletal muscle cells (LoRusso et al., 1992; Imanaka-Yoshida et al., 1993; Littlefield et al., 2001), YFP-tropomyosins, YFP-TnT and TnC exchanged uniformly all along the thin filaments (Figures 4a–d; 7 a–d; 14 a–d). The rapid exchange of YFP-tropomyosin in the mature myofibrils in cultured embryonic mouse cardiomyocytes is different from the Flag-tagged tropomyosin expressed in serum starved adult rat cardiomyocytes where two days post-infection Flag-tagged tropomyosin was detected at just the minus ends of actin filaments in the middle of sarcomere (Michele et al., 1999). The serum starved cells fixed four days post-infection, showed Flag-tagged tropomyosin patterns that were wider, but did not reach the Z-bands. In contrast, similar experiments using viruses encoding Flag-tagged TnI revealed that the flag-tagged TnI was uniformly incorporated along the thin filaments after two days. These differences with our exchange results from FRAP measurements in living cultured cells may reflect differences in muscle cells assembling myofibrils versus a steady state induced by serum starved conditions over a several day period. It will be important to conduct these experiments in a living animal as was accomplished for YFP-Z-band proteins in living zebrafish (Figure 10 in this report; Sanger et al., 2009).
Dynamics of proteins in cardiac versus skeletal muscle cells
It is of interest that several of YFP-sarcomeric proteins are more dynamic in cardiac muscle cells than in skeletal muscle cells: actin, tropomyosin, alpha-actinin, FATZ and telethonin (Figure 10). It will be important to see if this applies to the proteins in the thick filaments, i.e. e., muscle myosin II and C-Protein. Skeletal muscle diseases usually involve actin and tropomyosin mutations (Laing and Nowak, 2005; Kee and Hardeman, 2008). In contrast, cardiomyopathies involve a number of proteins of both the thin and thick filaments, as well as Z-bands (Morita et al., 2005; Frank et al. 2006). The higher dynamic rates of exchange of several proteins in cardiac cells may make myofibril assembly and maintenance more precarious when the sarcomeric proteins are mutated.
Summary
Jasplakinolide reduces the dynamics of the actin molecules in the thin filaments in the premyofibrils and mature myofibrils in both skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Stabilizing the sarcomeric actin filaments in the premyofibrils leads to a depression of the exchange of two different tropomyosin isoforms in the premyofibrils of both skeletal and cardiac sarcomeres. The effect of stabilizing the actin components of the sarcomeric thin filaments in mature myofibrils leads to different effects on tropomyosin in skeletal versus cardiac sarcomeres. Jasplakinolide does not change the amount of exchange of tropomyosin in the mature myofibrils of skeletal muscle cells, but does do so in the mature myofibrils in cardiac muscle cells. These results are consistent with the hypothesis of Wang et al. (2007, 2008) that the addition of nebulin to mature myofibrils decreases the dynamics of actin and tropomyosin as premyofibrils are transformed into skeletal muscle myofibrils. Pappas et al. (2010) used siRNA reagents directed against nebulin, and found that by decreasing the amount of nebulin in the mature myofibrils, they reported increases in the dynamics of actin and tropomyosin in mature myofibrils. Cardiac muscle cells lack nebulin, and do not show the dramatic decrease in actin and tropomyosin as their premyofibrils are transformed into mature myofibrils (Wang et al., 2005; 2007, 2008). Jasplakinolide reduces the actin and tropomyosin dynamics in the mature myofibrils of cardiac muscle cells. Since, there are no reports that jasplakinolide binds to tropomyosin, the reduced dynamics of tropomyosin must be a reflection of the reduced levels of actin dynamics induced by the drug. We speculate that some of the tropomyosin exchanges in the control myofibrils are due to the release of tropomyosin from the thin filaments exchanging cofilin excised actin molecules intermediate between the barbed and pointed ends of the thin filaments. The jasplakinolide results demonstrate the important roles of the dynamics of actin and tropomyosin in the transformation of premyofibrils into mature myofibrils during myofibrillogenesis. These insights are supported by Miyauchi-Nomura et al. (2012) who reported that decreasing the levels of cofilin in chick myotubes affected the early stages of myofibril assembly but not the existing mature myofibrils. FRAP analysis of sarcomeric proteins show that there is a dynamic exchange of subunits during myofibrillogenesis, that has the potential to be used for the maintenance of mature myofibrils through the incorporation of newly synthesized sarcomeric molecules (Sanger et al., 2010 b).
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health under Award Number AR-57063-01A. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. JWS is also indebted to the Hendricks Fund for support of this work.
References
- Ayoob JC, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Visualization of the expression of Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) linked genes. In: Tuan RS, Lo CW, editors. Methods in Molecular Biology: Developmental Biology Protocols. III. Humana Press; 2000a. pp. 153–157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayoob JC, Shaner NC, Sanger JW, Sanger JM. Expression of green or red fluorescent protein (GFP or DsRed) linked proteins in nonmuscle and muscle cells. Mol Biotechnology. 2001;17:65–71. doi: 10.1385/MB:17:1:65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang ML, Xiaodong L, Littlefield R, Bremner S, Thor A, Kirk U, Knowlton U, Lieber RL, Chen J. Nebulin-deficient mice exhibit shorter thin filament lengths and reduced contractile function in skeletal muscle nebulin-deficient mice exhibit shorter thin filament lengths and reduced contractile function in skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 2006;173:905–916. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200603119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein BW, Bamburg JR. Tropomyosin binding to F-actin protects the F-actin from disassembly by brain actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF) Cell Motil. 1982;2:1–8. doi: 10.1002/cm.970020102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubb MR, Senderowicz AMJ, Sausville EA, Duncan KLK, Korn ED. Jasplakinolide, a cytotoxic natural product, induces actin polymerization and competitively inhibits the binding of phalloidin to F-actin. J Biol. 1994;269:14869–14871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubb MR, Spector I, Beyer BB, Fosen KM. The effects of jasplakinolide in the kinetics of actin polymerization: an explanation for certain in vivo observations. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5163–5170. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.7.5163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri GA, Turnacioglu KK, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Myofibrillogenesis visualized in living embryonic cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:9493–9498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.17.9493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabiri GA, Ayoob JC, Turnacioglu KK, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Use of green fluorescent protein linked to cytoskeletal proteins to analyze myofibrillogenesis in living cells. Methods Enzymol. 1999;302:171–186. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(99)02017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du A, Sanger JM, Linask KK, Sanger JW. Myofibrillogenesis in the first cardiomyocytes formed from isolated quail precardiac mesoderm. Dev Biol. 2003;257:382–394. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du A, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Cardiac myofibrillogenesis inside intact embryonic hearts. Dev Biol. 2008;318:236–246. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett AW, Pryor G, Zak R. Equilibration of leucine between the plasma compartment and leucyl-tRNA in the heart, and turnover of cardiac myosin heavy chain. Biochem J. 1981;194:365–368. doi: 10.1042/bj1940365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D, Kuhn C, Katus HA, Frey N. The sarcomeric Z-disc: a nodal point in signaling and disease. J Mol Med. 2006;84:446–468. doi: 10.1007/s00109-005-0033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golson M, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Inhibitors arrest myofibrillogenesis in skeletal muscle cells at early stages of assembly. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004;59:1–16. doi: 10.1002/cm.20017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes AV, Potter JD, Szczesna-Cordary D. The role of troponins in muscle contraction. IUBMB Life. 2002;54:323–333. doi: 10.1080/15216540216037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara A, Tanaka Y, Hikawa R, Morone N, Kusumi A, Kimura H, Kinoshita M. Submembranous septins as relatively stable components of actin-based membrane skeleton. Cytoskeleton. 2011;68:512–25. doi: 10.1002/cm.20528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock-DeGregori SE, An Y. Integral repeats and a continuous coiled coil are required for binding of striated muscle tropomyosin to the regulated actin filament. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:3600–3603. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.7.3600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley HE. Electron microscope studies on the structure of natural and synthetic protein filaments from striated muscle. J Mol Biol. 1963;7:281–308. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka-Yoshida K, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Contractile protein dynamics of myofibrils in paired adult rat cardiomyocytes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1993;26(4):301–12. doi: 10.1002/cm.970260405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kee A, Hardeman Tropomyosins in skeletal muscle diseases. Advan Exp Med and Biol. 2008;644:143–157. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-85766-4_12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laing NG, Nowak KJ. When contractile proteins go bad: the sarcomere and skeletal muscle disease. BioEssays. 2005;27:809–822. doi: 10.1002/bies.20269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X, Gemel J, Beyer EC, Veenstra RD. Dynamic model for ventricular junctional conductance during the cardiac action potential. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1113–H1123. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00882.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin X, Zemlin C, Hennan JK, Petersen JS, Veenstra RD. Enhancement of ventricular gap-junction coupling by rotigaptide. Cardiovas Res. 2008;79:416–426. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littlefield R, Almenar-Queralt A, Fowler VM. Actin dynamics at pointed ends regulates thin filament length in striated muscle. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:544–51. doi: 10.1038/35078517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H, Shao Y, Qin W, Runyan RB, Xu M, Ma Z, Borg TK, Markwald R, Gao BZ. Myosin filament assembly onto myofibrils in live neonatal cardiomyocytes observed by TPEF-SHG microscopy. Cardiovasc Res. 2013;97:262–270. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoRusso S, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Shuman H, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Incorporation of fluorescently labeled contractile proteins into freshly isolated living adult cardiac myocytes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;21:111–122. doi: 10.1002/cm.970210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manisastry SM, Zaal KJ, Horowits R. Myofibril assembly visualized by imaging N-RAP, alpha-actinin, and actin in living cardiomyocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:2126–2139. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.02.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin AF. Turnover of cardiac troponin subunits. Kinetic evidence for a precursor pool of troponin-I. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:964–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michele DE, Albayya FP, Metzger JM. Thin filament protein dynamics in fully differentiated adult cardiac myocytes: toward a model of sarcomere maintenance. J Cell Biol. 1999;145:1483–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.7.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millevoi S, Trombitas K, Kolmerer B, Kostin S, Schaper J, Pelin K, Granzier H, Labeit S. Characterization of nebulette and nebulin and emerging concepts of their roles for vertebrate Z-Discs. J Mol Biol. 1998;282:111–123. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamide LS, Maiti S, Boyle JA, Davis RC, Coppinger JA, Bao Y, Huang TY, Yates J, Bokoch GM, Bamburg JR. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic cofilin-actin rods. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:5450–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.063768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi-Nomura S, Obinata T, Sato N. Cofilin is required for organization of sarcomeric actin filaments in chicken skeletal muscle cells. Cytoskeleton. 2012;69:290–302. doi: 10.1002/cm.21025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncman CL, Wang K. Targeted disruption of nebulette protein expression alters cardiac myofibril assembly and function. Exp Cell Res. 2002;273:204–218. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita H, Seidman J, Seidman CE. Genetic causes of human heart failure. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:518–526. doi: 10.1172/JCI200524351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S, Ono K. Tropomyosin inhibits ADF/cofilin-dependent actin filament dynamics. J Cell Biol. 2002;156:1065–1076. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200110013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappas CT, Krieg PA, Gregorio CC. Nebulin regulates actin filament lengths by a stabilization mechanism. J Cell Biol. 2010;189:859–870. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201001043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccirillo R, Demontis F, Perrimon N, Goldberg AL. Mechanisms of muscle growth and atrophy in mammals and Drosophila. Dev Dyn. 2013 Aug 29; doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24036. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee D, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. The premyofibrils: evidence for its role in myofibrillogenesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1994;28:1–24. doi: 10.1002/cm.970280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JM, Sanger JW. The Dynamic Z-bands of striated muscle cells. Science Signal. 2008;1:pe37. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.132pe37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JM, Mittal B, Pochapin BM, Sanger JW. Myofibrillogenesis in living cells microinjected with fluorescently labeled alpha-actinin. J Cell Biol. 1986a;102:2053–2066. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JM, Mittal B, Pochapin MB, Sanger JW. Observations of microfilament bundles in living cells microinjected with fluorescently labeled contractile proteins. J Cell Science Suppl. 1986b;5:17–44. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_5.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JM, Wang J, Gleason LM, Chowrashi P, Dube DK, Mittal B, Zhukareva V, Sanger JW. ArgBP2, a Z-body and Z-band protein, binds sarcomeric, costameric and signaling molecules. Cytoskeleton. 2010;67:808–823. doi: 10.1002/cm.20490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JW, Sanger JM, Franzini-Armstrong C. Assembly of the skeletal muscle cell. In: Engel AG, Franzini-Armstrong C, editors. Myology. 3. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2004. pp. 35–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JW, Kang S, Siebrands CC, Freeman N, Du A, Wang J, Stout AL, Sanger JM. How to build a myofibril. J Muscle Res Cell Motility. 2005;26:343–354. doi: 10.1007/s10974-005-9016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JW, Wang J, Holloway B, Du A, Sanger JM. Myofibrillogenesis in skeletal muscle cells in zebrafish. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009;66:556–566. doi: 10.1002/cm.20365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger JW, Wang J, Fan Y, White J, Sanger JM. Assembly and dynamics of myofibrils. J Biomed Biotech. 2010;2010:Article ID 858606, 8. doi: 10.1155/2010/858606. ( www.hindawi.com/journals/jbb/2010/858606.html) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaner NC, Sanger JW, Sanger JM. Actin and alpha-actinin dynamics in the adhesion and motility of EPEC and EHEC on host cells. Cell Motil Cytoskel. 2005;60:104–120. doi: 10.1002/cm.20047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague BL, James G, McNally JG. FRAP analysis of binding: proper and fitting. Trends Cell Bio. 2005;15:84–91. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2004.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout AL, Wang J, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Tracking changes in Z-band organization during myofibrillogenesis with FRET imaging. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008;65:353–367. doi: 10.1002/cm.20265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji T, Miyoshi T, Higashida C, Narumiya S, Watanabe N. An order of magnitude faster AIP1-Associated actin disruption than nucleation by the Arp2/3 complex in lamellipodia. PLoS One. 2009;4:e4921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Goor D, Hyland C, Schaefer AW, Forscher P. The role of actin turnover in retrograde actin network flow in neuronal growth cones. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030959.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Shaner N, Mittal B, Zhou Q, Chen J, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Dynamics of Z-band based proteins in developing skeletal muscle cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005a;61:34–48. doi: 10.1002/cm.20063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Differential effects of Latrunculin-A on stress fibers and myofibrils in living cultures of skeletal muscle cells: Insights into mechanisms of myofibrillogenesis. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2005b;62:35–47. doi: 10.1002/cm.20083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Sanger JM, Kang S, Thurston H, Abbott LZ, Dube DK, Sanger JW. Ectopic expression and dynamics of TPM1a and TPM1k in myofibrils of avian myotubes. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2007;64:767–776. doi: 10.1002/cm.20221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Thurston H, Essandoh E, Otoo M, Han M, Rajan A, Dube S, Zajdel RW, Sanger JM, Linask KK, Dube DK, Sanger JW. Tropomyosin expression and dynamics in developing avian embryonic muscles. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008;65:379–392. doi: 10.1002/cm.20267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Dube DK, Mittal B, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Myotilin dynamics in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. Cytoskeleton. 2011;68:661–670. doi: 10.1002/cm.20542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Dube DK, White J, Fan Y, Sanger JM, Sanger JW. Clock is not a component of Z-bands. Cytoskeleton. 2012;69 (#12):1021–1031. doi: 10.1002/cm.21058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J, Sanger JW, Sanger JM. Localization of sarcomeric proteins during myofibril assembly in cultured mouse primary skeletal myotubes. Anat Record. 2014 doi: 10.1002/ar.22981. (In Press) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willott RH, Gomes AV, Chang AN, Parvativar MS, Pinto JR, Potter JD. Mutations in troponin that cause HCM. DCM, and RCM: what can we learn about thin filament function? J Mol Cell Card. 2010;48:882–892. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2009.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt CC, Burkart C, Labeit D, McNabb M, Wu Y, Granzier H, Labeit S. Nebulin regulates thin filament length, contractility, and Z-disk structure in vivo. EMBO J. 2006;25:3843–3855. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]