Abstract
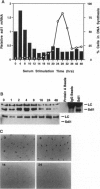
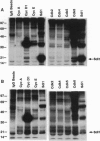
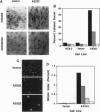
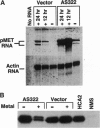
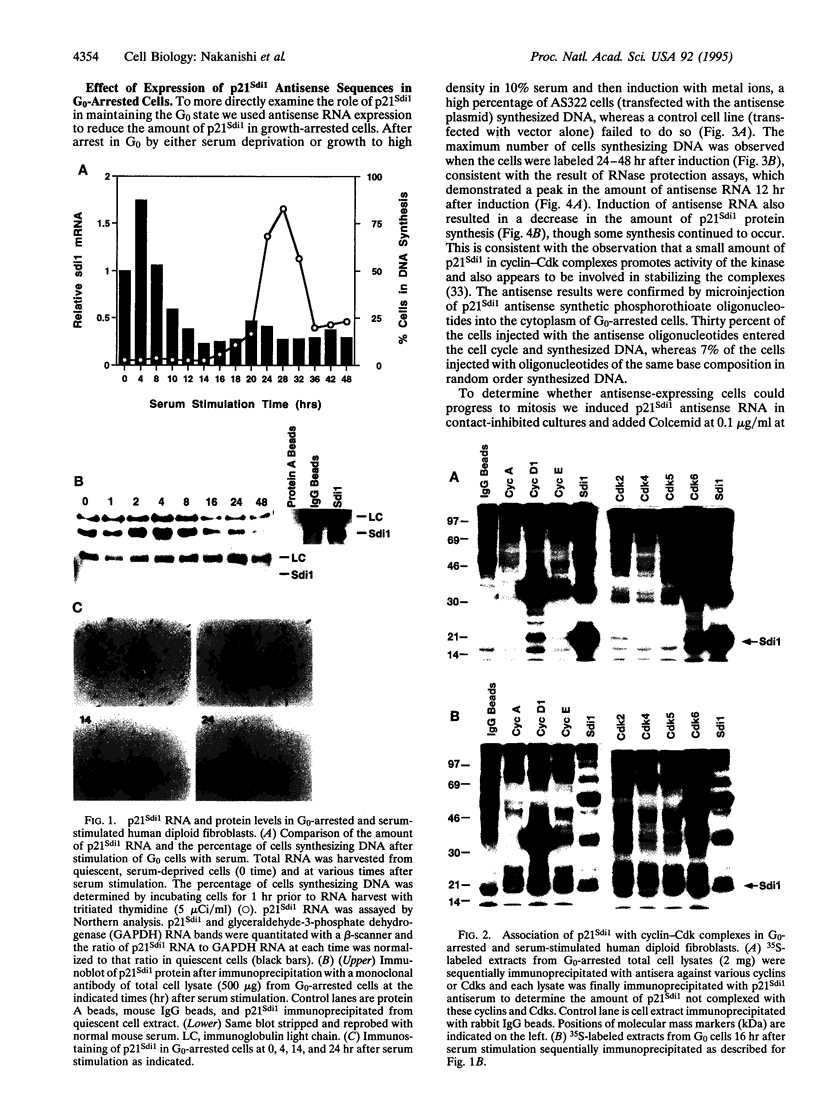
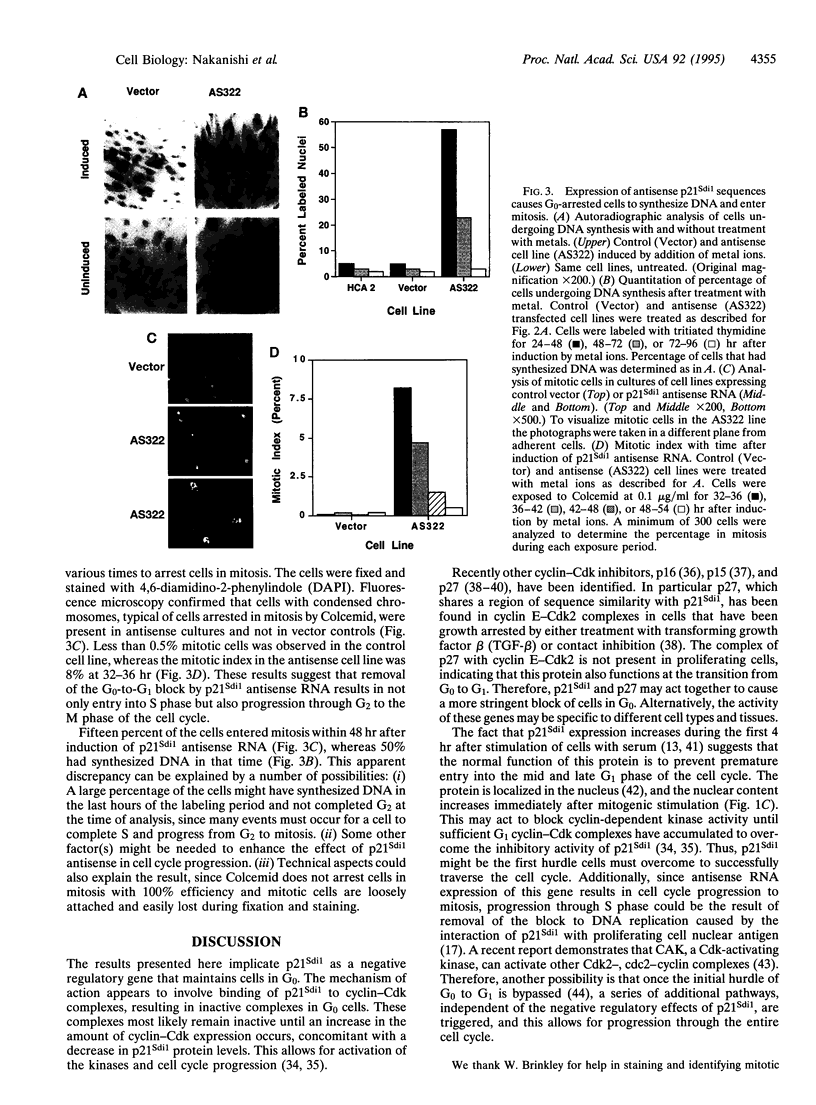
p21Sdi1 (also known as Cip1 and Waf1), an inhibitor of DNA synthesis cloned from senescent human fibroblasts, is an inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) in vitro and is transcriptionally regulated by wild-type p53. In addition, p21Sdi1 has been found to inhibit DNA replication by direct interaction with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. In this study we analyzed normal human fibroblast cells arrested in G0 and determined that an excess of p21Sdi1 was present after immunodepletion of various cyclins and Cdks, in contrast to mitogen-stimulated cells in early S phase. Expression of antisense p21Sdi1 RNA in G0-arrested cells resulted in induction of DNA synthesis as well as entry into mitosis. These results suggest that p21Sdi1 functions in G0 and early G1 and that decreased expression of the gene is necessary for cell cycle progression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G., Babiss L. E. DNA template effect on RNA splicing: two copies of the same gene in the same nucleus are processed differently. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3457–3465. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Nurse P. A cdc2-like protein is involved in the initiation of DNA replication in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):855–862. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90261-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmer G. C., Zeigler C. J., Norwood T. H. Evidence for endogenous polypeptide-mediated inhibition of cell-cycle transit in human diploid cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):187–192. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F., Roberts J., Weintraub H. Simple and complex cell cycles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:341–396. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Drullinger L. F., Lees E., Reed S. I., Stein G. H. Altered regulation of G1 cyclins in senescent human diploid fibroblasts: accumulation of inactive cyclin E-Cdk2 and cyclin D1-Cdk2 complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11034–11038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. Replicative senescence: the human fibroblast comes of age. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1129–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.2204114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Y., Turck C. W., Morgan D. O. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):707–710. doi: 10.1038/366707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. THE LIMITED IN VITRO LIFETIME OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELL STRAINS. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Mar;37:614–636. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Beach D. p15INK4B is a potential effector of TGF-beta-induced cell cycle arrest. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):257–261. doi: 10.1038/371257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensler P. J., Annab L. A., Barrett J. C., Pereira-Smith O. M. A gene involved in control of human cellular senescence on human chromosome 1q. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2291–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M., Dimitrov D., Vojta P. J., Barrett J. C., Noda A., Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Evidence for a p53-independent pathway for upregulation of SDI1/CIP1/WAF1/p21 RNA in human cells. Mol Carcinog. 1994 Oct;11(2):59–64. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Jenkins C. W., Nichols M. A., Xiong Y. Cell cycle expression and p53 regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2261–2268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin C. K., Jr, McClung J. K., Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Existence of high abundance antiproliferative mRNA's in senescent human diploid fibroblasts. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):393–395. doi: 10.1126/science.2421407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Quelle D. E., Shurtleff S. A., Shibuya M., Sherr C. J., Kato J. Y. D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2066–2076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeall J., Sánchez A., Gray P. P., Chesterman C. N., Sleigh M. J. Hyperinducible gene expression from a metallothionein promoter containing additional metal-responsive elements. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Tassan J. P., Nigg E. A., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Weinberg R. A. A cyclin associated with the CDK-activating kinase MO15. Nature. 1994 Sep 15;371(6494):254–257. doi: 10.1038/371254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Hunt T. Cell cycle. Dams and sluices. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):634–635. doi: 10.1038/366634a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ning Y., Weber J. L., Killary A. M., Ledbetter D. H., Smith J. R., Pereira-Smith O. M. Genetic analysis of indefinite division in human cells: evidence for a cell senescence-related gene(s) on human chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5635–5639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda A., Ning Y., Venable S. F., Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Cloning of senescent cell-derived inhibitors of DNA synthesis using an expression screen. Exp Cell Res. 1994 Mar;211(1):90–98. doi: 10.1006/excr.1994.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Lukas J., Baldin V., Ansorge W., Bartek J., Draetta G. Regulation of the cell cycle by the cdk2 protein kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):101–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Smith O. M., Fisher S. F., Smith J. R. Senescent and quiescent cell inhibitors of DNA synthesis. Membrane-associated proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Oct;160(2):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90177-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Genetic analysis of indefinite division in human cells: identification of four complementation groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6042–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Phenotype of low proliferative potential is dominant in hybrids of normal human fibroblasts. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):731–742. doi: 10.1007/BF01543015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Arresting developments in cell-cycle control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Kato J. Y., Solomon M. J., Sherr C. J., Massague J., Roberts J. M., Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):9–22. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The role of p34 kinases in the G1 to S-phase transition. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:529–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Hannon G. J., Beach D. A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):704–707. doi: 10.1038/366704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. R. Inhibitors of DNA synthesis derived from senescent human diploid fibroblasts. Exp Gerontol. 1992 Jul-Aug;27(4):409–412. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(92)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. H., Atkins L. Membrane-associated inhibitor of DNA synthesis in senescent human diploid fibroblasts: characterization and comparison to quiescent cell inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9030–9034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. H., Yanishevsky R. M. Entry into S phase is inhibited in two immortal cell lines fused to senescent human diploid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Apr;120(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90546-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Lees E., Faha B., Harlow E., Riabowol K. The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1593–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Hannon G. J., Beach D., Stillman B. The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):574–578. doi: 10.1038/369574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Hannon G. J., Zhang H., Casso D., Kobayashi R., Beach D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):701–704. doi: 10.1038/366701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Hannon G. J., Beach D. p21-containing cyclin kinases exist in both active and inactive states. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1750–1758. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]