Abstract
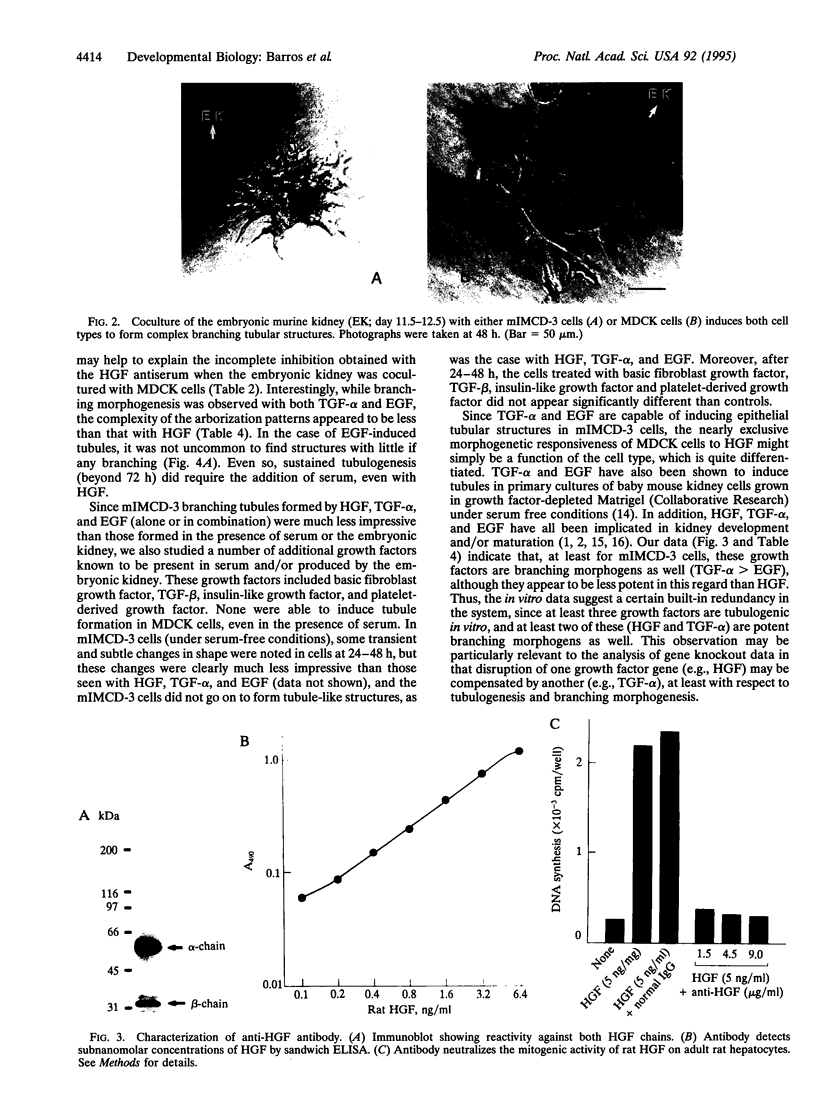
At least two kidney epithelial cell lines, the Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) and the murine inner medullary collecting duct line mIMCD-3, can be induced to form branching tubular structures when cultured with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) plus serum in collagen I gels. In our studies, whereas MDCK cells remained unable to form tubules in the presence of serum alone, mIMCD-3 cells formed impressive branching tubular structures with apparent lumens, suggesting the existence of specific factors in serum that are tubulogenic for mIMCD-3 cells but not for MDCK cells. Since normal serum does not contain enough HGF to induce tubulogenesis, these factors appeared to be substances other than HGF. This was also suggested by another observation: when MDCK cells or mIMCD-3 cells were cocultured under serum-free conditions with the embryonic kidney, both cell types formed branching tubular structures similar to those induced by HGF; however, only in the case of MDCK cells could this be inhibited by neutralizing antibodies against HGF. Thus, the embryonic kidney produces growth factors other than HGF capable of inducing tubule formation in the mIMCD-3 cells. Of a number of growth factors examined, transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha) and epidermal growth factor (EGF) were found to be tubulogenic for mIMCD-3 cells. Whereas only HGF was a potent tubulogenic factor for MDCK cells, HGF, TGF-alpha, and EGF were potent tubulogenic factors for mIMCD-3 cells. Nevertheless, there were marked differences in the capacity of these tubulogenic factors to induce tubulation as well as branching events in those tubules that did form (HGF >> TGF-alpha > EGF). Thus, at least three different growth factors can induce tubulogenesis and branching in a specific epithelial cell in vitro (though to different degrees), and different epithelial cells that are capable of forming branching tubular structures demonstrate vastly different responses to tubulogenic growth factors. The results are discussed in the context of branching morphogenesis during epithelial tissue development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cantley L. G., Barros E. J., Gandhi M., Rauchman M., Nigam S. K. Regulation of mitogenesis, motogenesis, and tubulogenesis by hepatocyte growth factor in renal collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):F271–F280. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.267.2.F271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindroos P. M., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. Hepatocyte growth factor (hepatopoietin A) rapidly increases in plasma before DNA synthesis and liver regeneration stimulated by partial hepatectomy and carbon tetrachloride administration. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):743–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K. Determinants of branching tubulogenesis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 1995 May;4(3):209–214. doi: 10.1097/00041552-199505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSATHANONDH V., POTTER E. L. DEVELOPMENT OF HUMAN KIDNEY AS SHOWN BY MICRODISSECTION. III. FORMATION AND INTERRELATIONSHIP OF COLLECTING TUBULES AND NEPHRONS. Arch Pathol. 1963 Sep;76:290–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada F., Yamaguchi K., Ichihara A., Nakamura T. One of two subunits of masking protein in latent TGF-beta is a part of pro-TGF-beta. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80477-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauchman M. I., Nigam S. K., Delpire E., Gullans S. R. An osmotically tolerant inner medullary collecting duct cell line from an SV40 transgenic mouse. Am J Physiol. 1993 Sep;265(3 Pt 2):F416–F424. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.3.F416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. A., Ryan G., Hammerman M. R. Metanephric transforming growth factor-alpha is required for renal organogenesis in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 2):F533–F539. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.4.F533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen E. M., Nigam S. K., Goldberg I. D. Scatter factor and the c-met receptor: a paradigm for mesenchymal/epithelial interaction. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 2):1783–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salido E. C., Lakshmanan J., Shapiro L. J., Fisher D. A., Barajas L. Expression of epidermal growth factor in the kidney and submandibular gland during mouse postnatal development. An immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Differentiation. 1990 Oct;45(1):38–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos O. F., Barros E. J., Yang X. M., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Park M., Nigam S. K. Involvement of hepatocyte growth factor in kidney development. Dev Biol. 1994 Jun;163(2):525–529. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos O. F., Moura L. A., Rosen E. M., Nigam S. K. Modulation of HGF-induced tubulogenesis and branching by multiple phosphorylation mechanisms. Dev Biol. 1993 Oct;159(2):535–548. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos O. F., Nigam S. K. HGF-induced tubulogenesis and branching of epithelial cells is modulated by extracellular matrix and TGF-beta. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):293–302. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg E., Meyer D., Weidner K. M., Birchmeier C. Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor, the c-met tyrosine kinase, can mediate a signal exchange between mesenchyme and epithelia during mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(1):223–235. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub M., Wang Y., Szczesny T. M., Kleinman H. K. Epidermal growth factor or transforming growth factor alpha is required for kidney tubulogenesis in matrigel cultures in serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H., Iwase T., Matsumoto K., Ito M., Hirono I., Nishida Y., Yamamoto M., Tatematsu M., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T. Immunohistochemical localization of hepatocyte growth factor protein in pancreas islet A-cells of man and rats. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Dec;83(12):1262–1266. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







