Abstract
Background
The aim of the study presented in this article is to analyse the determinants of telemedicine use. To that end, the study makes two basic contributions. First, it considers six working hypotheses in the context of technology acceptance models (TAMs). Second, it uses data obtained for three samples of physicians from three different countries (Spain, Colombia and Bolivia). Obtaining and comparing evidence on an international scale allows determinants of telemedicine use to be evaluated across different contexts.
Methods
In Bolivia, the survey was conducted in hospitals and health care centres of the urban and rural districts of the municipality of Sucre, in a population comprising a total of 350 physicians. In Spain, the survey population consisted of medical professionals of all profiles affiliated with health care within the Canary Islands Health Service, comprising a total of 356 physicians. Finally, in Colombia, it was conducted in the Society of Surgery Service at San José Hospital of Bogotá, in a population comprising a total of 184 physicians. Using an extended TAM and survey data from 510 physicians (113 in Spain, 118 in Colombia and 279 in Bolivia), binary logistic regression analysis was performed.
Results
In the three samples, it was found that the physician's level of information and communication technology (ICT) use in his/her personal life was the variable that had the highest explanatory power regarding telemedicine use. In the Spanish sample, the physicians' perceived ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice and propensity to innovate were the two other variables that determined telemedicine use, whereas in the Colombian and Bolivian samples, it was the level of optimism about ICTs.
Conclusion
The results facilitated a more complete model that includes personal, usability, and innovatory aspects in the explanation of Telemedicine use in Spain, whereas the results for the Latin American samples indicated a more primary model in the explanation of Telemedicine use, which was completed by an optimism factor that did not emerge in the Spanish sample.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13012-014-0128-6) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Telemedicine, Technology acceptance and adoption, Medical profession, Telemedicine diffusion, Information and communication technology
Introduction
A range of methodological and disciplinary approaches have been employed in order to understand the drivers of telemedicine adoption. Technology-oriented research has noted that Roger's diffusion of innovations (DOI) theory and Davis's technology acceptance model (TAM) have been successfully used to understand some of the factors that explain the use of information and communication technologies (ICTs) by health care professionals [1],[2]. Information systems and social-oriented research have highlighted that clinical practice may be intimately interconnected to a range of digital devices and forms of information [3]-[5] and to the ways that users use them in their private lives. Organisation-oriented research has shown that the structure of health care organisations, tasks, public policies, incentives and decision-making processes play a major role in explaining how medical professionals overcome barriers to ICT use [6]. Ethical and legal-oriented research has suggested that changes in the nature of the doctor-patient relationship, the status of health informatics, and also the hardware/software providers tend to have an effect on ICT use by medical professionals [7]. Finally, usability-oriented research has shown that compatibility between clinical ICT systems and physicians' tasks, ICT support for information exchange, communication and collaboration in clinical practice and interoperability and reliability also explain the success of ICT use in health care [8].
The incorporation of telemedicine into clinical practice has generated huge expectations as a means of health care cost containment, since it offers the potential to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of health care organisations, as well as the quality of the services provided [9]-[12]. However, its use in day-to-day clinical practice is still limited [13],[14]. There is general consensus that its slow, arduous implementation can be attributed to the lack of definitive scientific evidence supporting its positive impact on clinical practice (improved quality and effectiveness) and economic outcomes (improved cost-benefit) [13],[15]-[22].
In order to understand the effects of telemedicine use on health outcomes, it is crucial to analyse the prior step, that is, to determine what factors explain physicians' telemedicine use. Obtaining and comparing evidence on an international scale represents an important contribution to the literature, in the sense that it will allow the determinants of telemedicine use to be evaluated across national contexts.
This study analyses and compares the determinants of telemedicine use by samples of physicians from three countries. By doing so, the intention is to attain a twofold objective: first, to characterise and develop a typology of physicians according to their ICT use and expectations in their clinical practice and their personal lives and, second, to identify the determinants that foster or hinder the physicians' telemedicine use. In order to attain the latter part of the objective, this study involved a comparative analysis of three samples of physicians from three Ibero-American countries (Spain, Colombia and Bolivia).
Hypothesis and model
TAM is the theoretical system most widely applied to research into the acceptance of new information technologies in the professional sphere [23]-[29]. In particular, the model has the capacity to robustly explain the intention to use ICTs, taking into account individuals' perceptions of technology: perceived usefulness and perceived ease-of-use [30],[31]. Thus, the first two hypotheses of the study are as follows:
H1. The perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice explains telemedicine use.
H2. The perceived ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice explains telemedicine use.
Despite its widespread acceptance, this model has a series of limitations that mainly stem from the fact that it does not take the influence of other types of variables into account. Bagozzi [32] and Venkatesh et al. [33] underscored the need to increase the explanatory power of this model by incorporating additional variables. According to Davis, identifying variables like these in TAM can increase the explanatory power of the system users' acceptance [24],[34]. This is particularly important to the development of TAMs in the field of health care. The consideration of variables relating to the individual, to his or her psychological or sociodemographic characteristics, and to his or her exposure to social influence is a standard feature. Consequently, the theoretical model used needs to take into account contributions made by other models such as those:
Tending to stress the importance of technology, such as DOI [35]
Tending to stress the importance of the user profile and of social influence (subjective norm), such as the theory of reasoned action (TRA) [36] and the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) [37]
That have a mixed approach, comprising elements that refer to both the user profile and to technology, such as Parasuraman's theory of technology readiness (TR) [38]
TR considers the need to incorporate user profile elements, in the sense of mental states resulting from facilitators or inhibitors, which together have the potential to determine one's predisposition towards using new technologies. In this respect, the third hypothesis is as follows:
H3. The user's optimism about technology explains telemedicine use.
Similarly, we must consider that while each person's stance on technology is different, in a group of people, each stance can be situated on a continuum ranging from strongly positive to strongly negative. Thus, peoples' stances, as situated on this continuum, are correlated to their propensity to adopt and use new technology. In this respect, the fourth hypothesis is as follows:
H4. The user's propensity to innovate explains telemedicine use.
Finally, it should be noted that physicians use ICTs in their professional and personal lives. As an ICT user, the medical professional may use technology with differing degrees of intensity and frequency. It would seem clear that an individual who uses ICTs intensively is more likely to adopt them in his or her clinical practice, hence, the need to incorporate the intensity of ICT use as an explanatory factor of telemedicine use. In this respect, the fifth hypothesis is as follows:
H5. The ICT user profile of the physician - as an individual, in his or her personal life - explains telemedicine use.
A summary of the proposed model and hypotheses is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
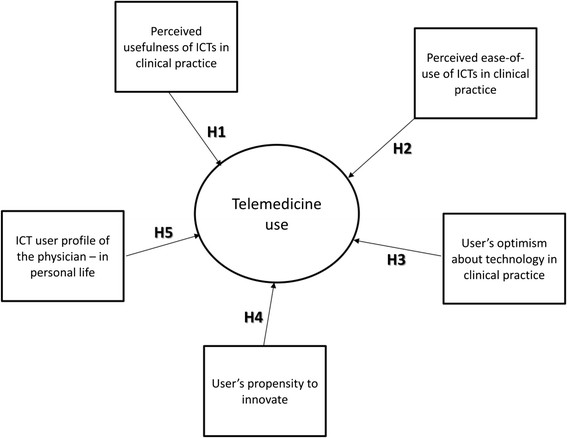
Drivers of telemedicine use model.
In addition to the determinants identified above, we stress the importance of the geographical, legal, social, cultural and economic contexts of the country or territory [39] to the adoption of ICTs in clinical practice. The digital divide refers to the existence of varying degrees of ICT implementation and adoption in different countries. Economic circumstances clearly influence the quantity and quality of technological equipment and infrastructure. In some sectors, social and cultural aspects also play a key role [11], as do other circumstantial variables such as experience and training [40]. Depending on the country being analysed, the above model can be expected to show significant differences, and this is proposed in the sixth hypothesis:
H6. The degree of ICT implementation in the country's health care system explains the importance of each of the determinants of the physician's telemedicine use.
Data collection, empirical methodology and validation
Three samples of physicians from three countries with varying degrees of implementation of ICT use in clinical practice were taken as the reference: Spain, Colombia and Bolivia. The study compares samples of physicians from different territories with varying levels of development according to the economic indicators provided by the IMF for 2012 and 2014 [41]:
Spain, a developed country belonging to the European Union, with a GDP of US$1,340.266 billion and GDP per capita of US$30,740 in 2012 according to IMF estimates. According to the official statistics provided by the Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality [42], spending on public health care, including long-term care, was €58.466 billion. This represents 71.2% of the country's total health care spending, which is €82.064 billion. As a percentage of GDP, total health care spending in Spain is 8.4%. According to the data provided by the World Bank [43], the mean annual percentage of GDP spent on health care in the 2009–2013 period was 9.3%.
Colombia, a developing country with a GDP of US$365.402 billion and a GDP per capita of US$11,284 in 2012. The lack of official statistics for public health care spending in Colombia means that we have taken the figures provided by the World Bank as the reference indicator. That institution states that, for the 2009–2013 period, mean health care spending as a percentage of GDP was 6.8% [43].
Bolivia, a country with low level of development and a GDP of US$26.749 billion and a GDP per capita of US$4,996 in 2012.
Table 1 shows the descriptive information for the data collection in each of the three contexts.
Table 1.
Described information for the data collection conducted in Spain, Colombia and Bolivia
| Spain | Colombia | Bolivia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sampling universe | 356 physicians from hospitals, health care services and research centres of the Canary Islands Health Service | 184 physicians affiliated to the Society of Surgery Service, San José Hospital of Bogotá | 350 physicians from hospitals and health care centres in Sucre |
| Sample | 113 | 118 | 279 |
| Interview | Self-administered questionnaire | Self-administered questionnaire | Self-administered questionnaire |
| Margin of error | 7.6% p = q = 95% confidence level | 5.4% p = q = 95% confidence level | 2.7% p = q = 95% confidence level |
| Fieldwork | January to June 2012 | February to April 2012 | August to September 2011 |
Instrument design: the CICUS project
The use of a methodology and working tools that have already been validated within an international project is a strength of this work. The Ibero-American Cluster for University Collaboration on Health (CICUS, reference C/030942/10) is an international scientific cooperation project led by the Open University of Catalonia (UOC) in accordance with the criteria set out in the Scientific Research and Inter-University Cooperation Programme (PCI) between Spain and Latin America, funded in full by the Spanish Agency for International Development Cooperation (AECID).
The mission of the CICUS project is to promote and develop innovation, research, technological and academic cooperation programmes in the field of Health Sciences through the collaborative networking of the various centres forming part of it. The CICUS vision is to become a space of excellence that facilitates networking for the creation and sharing of state-of-the-art knowledge on new forms of health care based on the integration of ICTs, which respond to the challenges posed by the socioeconomic changes of the 21st century.
The project began in 2010 with the participation of the UOC (Spain), Simón Bolívar Andean University (UASB, Bolivia) and the Central University of Ecuador (UCE, Ecuador). Performing an analysis of the situation regarding the participating countries' ICT use in the field of health care was one of the first goals set. A qualitative methodology was chosen, and a questionnaire was designed as the data collection instrument.
A review of the literature together with the health care professionals' experience served as the basis to create the study variables and the metrics used in the first version of the instrument. The final questionnaire was organised into four blocks of questions: sociodemographic and professional background; opinions about ICT and Internet use in health care; degree of ICT and Internet use in general and degree of IT-system, ICT and Internet use at work. The instrument was validated following a pre-test. This was done through a pilot study that involved having 48 postgraduate students (all health care professionals) in the master's degree programmes in Public Health and in Clinical Pharmacology offered by UASB's Health Area that completes the measure. This took place for 2 months during the academic year (from 10 May 2011 to 15 June 2011). The instrument was tested and modified in accordance with the suggestions made by the respondents (Additional file 1).
Besides the UOC's Faculty of Health Sciences and the UASB's Health Area, two new organisations took part: the Canary Islands Health Service (SCS) and the Society of Surgery Service, San José Hospital of Bogotá, Colombia. The same questionnaire was used for all three samples, thus ensuring that the variables measured and the metrics used were exactly the same. A preliminary questionnaire was sent for revision to the other two organisations participating in our study (the Canary Islands Health Service (SCS) and the Society of Surgery Service, San José Hospital of Bogotá, Colombia). The purpose of this stage was to finalise the drafting, content and general design of the questionnaire and to test both the instrument and its suitability to the contextual characteristics of each country. Between 9 and 27 January 2012, the questionnaire was sent for revision and adaptation to several health care professionals with academic and practical experience with information systems at the SCS. A similar procedure was implemented in Colombia between 23 January and 7 February 2012. After the instrument had been tested and modified in accordance with the respective experts' suggestions, we proceeded with the study in the three samples of physicians from the three countries in question (Additional files 2 and 3).
The survey was anonymous and optional. Throughout the process, all the necessary procedures were implemented to safeguard the confidentiality of the information and the anonymity of the participants in all study materials. The participants were also informed about the potential restrictions in relation to the confidentiality of the information provided.
Data collection and populations
In Bolivia, the study was conducted in hospitals and health care centres of the urban and rural districts of the municipality of Sucre. It had 115 health care establishments (87% primary care, 8% secondary care and 5% tertiary care), where a total of 350 physicians practised. The health care professionals were contacted in person between August and September 2011. After explaining the reasons for and aim of the study, potential participants were asked to collaborate by answering the survey, which was completed by hand. Data collection was concluded in mid September, with a total of 279 completed surveys (79.7% response rate). The survey data were then entered manually into an electronic. This was done through the collaboration of postgraduate students on the master's degree programmes in Public Health and in Clinical Pharmacology offered by UASB's Health Area.
In Spain, the study population consisted of medical professionals of all profiles affiliated with the field of health care within the SCS, comprising a total of 356 physicians across health care centres, secondary care hospitals and research centres/universities, who received an invitation to take part in the SCS online survey by e-mail. The fieldwork was carried out between 31 January and 28 June 2012, with a total of 113 completed surveys (31.7% response rate).
Finally, the Society of Surgery Service at San José Hospital of Bogotá had a staff of 184 physicians, who attended to an average of 161,000 patients per year in outpatient services. On 13 February 2012, the medical director of the Society of Surgery Service, San José Hospital of Bogotá, sent an invitation to take part in the online survey by e-mail to the 184 health care professionals. The fieldwork was carried out between 13 February and 30 April 2012, with a total of 118 (64.1% response rate) completed surveys. No mechanism to incentivise the health care professionals' participation was implemented in any of the three cases.
Study variables
Table 2 shows the variables used in the study.
Table 2.
Study variables
| Variable | Definition | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Telemedicine use | ICT use for diagnosing, monitoring and treating patients in situations where those involved are separated by place and/or time [44] | Dichotomous variable. 0 = no; 1 = yes. The variable is additive and considers ICT use for the purposes of contacting national and international professionals of exchanging valid information for diagnosing, monitoring and treating patients and of disseminating research activities with the aim of improving people's health |
| Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice | Degree to which the physician considers that using ICTs in clinical practice means that less efforts will be required to perform his or her tasks | Categorical variable. 1 = perceived ease-of-use is nil; 2 = very low; 3 = low; 4 = average; 5 = quite high; 6 = high; 7 = very high |
| Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Degree to which the physician believes that using ICTs in clinical practice improves his or her performance in an activity in the short-term | Metric variable obtained from exploratory factor analysis. The original variables included in the analysis are measured on a 5-point Likert scale. The variables making up the factor are those indicating how the physician perceives that using ICTs enables errors to be controlled when performing an activity or a patient's evolution to be monitored |
| Optimism | Degree to which the physician considers that using ICTs in clinical practice will enable him or her to obtain benefits or reduce effort in the future | Metric variable obtained from exploratory factor analysis. The original variables included in the analysis are measured on a 5-point Likert scale. The variables making up the factor are those indicating how the physician perceives that using ICTs enables relationships with patients to be improved and better treatments to be recommended |
| Propensity to innovate | The individual's propensity to innovate in his or her day-to-day work using ICTs | Categorical variable. 5 = the individual totally agrees; 1 = totally disagrees |
| Level of ICT use | Degree to which the physician uses ICTs outside work | Dichotomous variable. 0 = his or her ICT use is low; 1 = high |
The hypothesised multidimensional nature of the variables Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice and Optimism suggested that exploratory factor analysis (EFA) should be performed.
EFA is a data dimensionality reduction technique. Starting with the analysis of a set of original variables, it seeks to determine the smallest number of dimensions capable of explaining the maximum amount of information contained in the data [45]. In order to extract the factor dimensions, seven variables were considered in total. Each variable was designed to assess the physicians' perceived benefits of using ICTs in their clinical practice.
As Patil et al.[46] suggest, EFA typically requires decisions about three key issues: factor extracting strategy, factor retention criteria and factor rotation. For our three samples, the exploratory analysis was performed by applying the principal axis extraction and Promin rotation methods [47]. In this context, polychoric correlation matrices were used. These are particularly suitable for items with a Likert-type response format [48]. Also, in order to obtain the appropriate number of factors, an approach combining multiple criteria were used: the scree testa[49]-[51] and parallel analysisb[46],[52]-[54].
The Factor 9.20 programme [55] was used to perform the EFA. This programme allows polychoric correlation matrices to be analysed and procedures such as parallel analysis to be performed. Parallel analysis was performed using the optimal parallel analysis option in Factor 9.20 in which characteristics of the data were taken into account, and the polychoric correlations and random permutations of the answers were utilised [54].
Table 3 shows the variables included in the factor analyses for the three samples of physicians. It also shows the factor scores obtained, the percentage variance explained by each factor, and the component transformation matrix.
Table 3.
Main factor analysis results
| Spain | Colombia | Bolivia | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Optimism | Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Optimism | Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Optimism | |
| Variables | ||||||
| Looking up medical or health-related information on the Internet improves the doctor-patient relationship | 0.577 | 0.852 | 0.680 | |||
| Looking up medical or health-related information on the Internet leads to doubts about the health care professional's knowledge | 0.747 | 0.809 | 0.705 | |||
| Looking up medical or health-related information on the Internet improves knowledge of the patient and facilitates his or her treatment | 0.765 | 0.809 | 0.735 | |||
| The existence of computerised data allows the evolution of the patient's clinical status to be viewed | 0.946 | 0.772 | 0.788 | |||
| I am in favour of creating a single computerised medical history for each patient, which can be accessed by any health care professional regardless of the centre where the patient is attended | 0.943 | 0.785 | 0.844 | |||
| With excessive ICT use, there is greater control of errors | 0.862 | 0.639 | 0.783 | |||
| In most cases, computerisation and ICT use in the field of health care minimise bureaucracy and have a major impact on improved clinical practice | 0.703 | 0.770 | 0.605 | |||
| % variance explained | 0.57788 | 0.15195 | 0.15521 | 0.47019 | 0.42973 | 0.14720 |
| Eigenvalue | 4.0451 | 1.06362 | 1.08644 | 3.29133 | 3.00810 | 1.03041 |
| Cronbach's alpha | 0.811 | 0.874 | 0.891 | 0.877 | ||
| Correlation matrix | Correlated variables, values higher than 0.5 | Correlated variables, values higher than 0.5 | Correlated variables, values higher than 0.5 | |||
| Determinant of the matrix | 0.001992139587910 | 0.156882043355530 | 0.318942324331276 | |||
| KMO index | 0.90176 | 0.88039 | 0.73541 | |||
| Bartlett's statistic | 645.7*** | 410.8 *** | 514.1*** | |||
| Measurement of sample adequacy | Coefficients between 0.62 and 0.80 | Coefficients between 0.62 and 0.80 | Coefficients between 0.62 and 0.80 | |||
| Component correlation matrix | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 1.000 | 0.646 | 1.000 | 0.525 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| 2 | 0.646 | 1.000 | 0.525 | 1.000 | 0.400 | 1.000 |
***Significant at 99% confidence level.
In order to confirm the technique's goodness of fit for the three samples, various statistical tests were performed in accordance with the proposals by Bilodeu and Brenner [56], Fabrigar et al. [45] and Nunnally and Bernstein [57]. The analysis of the sample correlation matrix for the three analyses performed showed that the variables were highly intercorrelated. In every case, the correlation coefficient values were higher than 0.5. Likewise, the Bartlett's test of sphericity values were high, indicating that the null hypothesis of multivariate normality was rejected in every case, thus confirming that the variables were highly interrelated and appropriate for factor analysis. Also, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) coefficient indices obtained for the three samples were 0.90176 (Spain), 0.88039 (Colombia) and 0.73541 (Bolivia)c. That confirms the adequacy of the matrix for factor analysis.
As shown in Figures 2, 3 and 4, the scree test yielded two-factor solutions in all of the three analyses. Parallel analysis also yielded these two-factor structures.
Figure 2.
Sedimentation graph of the Spanish sample.
Figure 3.
Sedimentation graph of the Colombian sample.
Figure 4.
Sedimentation graph of the Bolivian sample.
After determining the number of factor to be extracted, the Promin correlated factors rotation method was used [47]. This method of oblique rotation tends to yield the most parsimonious solution.
As shown in Table 3, each of the three different analyses performed enabled two factors to be obtained. Taking into account the seven variables considered in the analysis, the factors were identified with the constructs Optimism and Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice. In two of the three analyses identified, the factor called perceived usefulness had a higher eigenvalue and explained a higher percentage of total variance. In particular, for the Spanish sample, the total variance explained by these two factors was 72.9%. The two factors present a high correlation (r = 0.646). Regarding the Colombian sample, the total variance explained by the factors was 62.6%. The two factors show a moderate correlation (r = 0.525). Finally, for the Bolivian sample, the two factors explained 57.69% of the total variance. The two factors also show a moderate correlation (r = 0.400).
Finally, it should be noted that using the above-mentioned factors as explanatory variables of the proposed theoretical model meant that the reliability of the metric scales had to be calculated. As shown in Table 3, the Cronbach's alpha coefficient value obtained for each of the constructs was high. It was higher than 0.70 in every case. According to Nunnally and Bernstein [57], this indicator must have values higher than 0.7 in general and 0.6 in the case of new scales. Thus, it is possible to assume that the scales used were reliable. Additionally, the content and construct scales' discriminant, convergent and nomological validity were also addressed. With regard to the content, the scales were developed following a major review of the literature.
Preliminary evidence obtained
Physician's profile
Regarding the physician's profile, in the three samples analysed, it was found that the majority was male (almost 60%). In the sample of Spanish physicians, almost 40% were over 50 years of age and had been in post for a considerable length of time (44.4% had over 20 years' experience). In comparison to this profile, the physicians in the Colombian sample were younger; 59.9% were between 40 and 50 years of age. Finally, the physicians in the Bolivian sample were younger still; 58% were under 40 years of age (see Table 4).
Table 4.
Descriptive analysis of the physicians' characteristics
| Spain | Colombia | Bolivia | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 67.3 | 60.2 | 40.5 |
| Female | 32.7 | 39.8 | 59.5 | |
| Age | <40 years | 14.2 | 59.0 | 50.6 |
| 40–50 years | 30.1 | 27.3 | 33.3 | |
| 50–60 years | 46.0 | 8.6 | 12.9 | |
| >60 years | 9.7 | 5.1 | 3.2 | |
| Workplace | Health care centre's central services | 8.3 | ||
| Research centre University | 0.9 | 23.7 | ||
| Tertiary care hospital | 46.9 | 37.3 | 13.3 | |
| Secondary care hospital | 8.0 | 13.7 | 56.6 | |
| Health care centre | 35.8 | 31.3 | 30.1 | |
| Occupation | Administrative post | 18.5 | 26.2 | 8.9 |
| Non-administrative post | 81.4 | 73.7 | 91.0 | |
Irrespective of origin, in more than half of the cases analysed, it was found that the medical professional had a permanent contract or was even a career civil servant and worked mainly in secondary and tertiary care hospitals.
Regarding the physician's relationship with technology, and his or her perceptions and personal and professional use of it, significant differences between the three samples were found. These differences appeared to stem from the individual's profile and the country where he or she worked.
Table 5 shows the results of analyses of variance (ANOVAs), where Gender, Age and the Post occupied by the physician in the health care institution were included as independent variables, and the physician's degree of Optimism and Propensity to innovate, Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice and perceived Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice, Level of ICT use and Telemedicine use were dependent variables. In order to facilitate data analysis and sample comparison, the Age and Post variables were dichotomised. Consequently, it was considered that young professionals were under 45 years of age, and the level of responsibility associated with a medical professional's post was higher when he or she performed managerial, directorship or operational group manager functions.
Table 5.
Descriptive statistics (ANOVA analysis)
| Descriptive statistics | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | N | Mean | Standard deviation | F | Age | N | Mean | Standard deviation | F | Post | N | Mean | Standard deviation | F | |
| Spain | |||||||||||||||
| Optimism | Female | 37 | −0.0535 | 1.11965 | - | <45 | 33 | 0.0526 | 1.04442 | - | No responsibility | 92 | 0.0516 | 0.97009 | NS |
| Male | 76 | 0.0279 | 0.94657 | >45 | 80 | −0.0212 | 0.99450 | Responsibility | 21 | −0.2270 | 1.14416 | ||||
| Total | 113 | 0.0000 | 1.00471 | Total | 113 | 0.0000 | 1.00471 | Total | 113 | 0.0000 | 1.00471 | ||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 37 | 0.0306 | 1.02422 | ** | <45 | 33 | 0.1881 | 0.82224 | - | No responsibility | 92 | 0.0786 | 0.95412 | * |
| Male | 76 | −0.0161 | 0.95961 | >45 | 80 | −0.0758 | 1.06505 | Responsibility | 21 | 0.3463 | 1.16729 | ||||
| Total | 113 | −0.0001 | 1.00481 | Total | 113 | −0.0001 | 1.00481 | Total | 113 | −0.0001 | 1.00481 | ||||
| Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 37 | 4.4054 | 0.55073 | - | <45 | 33 | 4.3636 | 0.82228 | - | No responsibility | 92 | 4.4130 | 0.68182 | NS |
| Male | 76 | 4.4605 | 0.70125 | >45 | 80 | 4.4750 | 0.57313 | Responsibility | 21 | 4.5714 | 0.50709 | ||||
| Total | 113 | 4.4425 | 0.65381 | Total | 113 | 4.4425 | 0.65381 | Total | 113 | 4.4425 | 0.65381 | ||||
| Propensity to innovate | Female | 37 | 4.49 | 0.559 | - | <45 | 33 | 4.18 | 0.635 | * | No responsibility | 92 | 4.33 | 0.681 | NS |
| Male | 76 | 4.30 | 0.731 | >45 | 80 | 4.44 | 0.691 | Responsibility | 21 | 4.52 | 0.680 | ||||
| Total | 113 | 4.36 | 0.682 | Total | 113 | 4.36 | 0.682 | Total | 113 | 4.36 | 0.682 | ||||
| Telemedicine use | Female | 37 | 0.4054 | 0.49774 | ** | <45 | 33 | 0.4242 | 0.50189 | - | No responsibility | 92 | 0.5109 | 0.50262 | NS |
| Male | 76 | 0.6053 | 0.49204 | >45 | 80 | 0.5875 | 0.49539 | Responsibility | 21 | 0.6667 | 0.48305 | ||||
| Total | 113 | 0.5398 | 0.50063 | Total | 113 | 0.5398 | 0.50063 | Total | 113 | 0.5398 | 0.50063 | ||||
| Level of ICT use | Female | 37 | 0.7568 | 0.43496 | ** | <45 | 33 | 0.8485 | 0.36411 | - | No responsibility | 92 | 0.8370 | 0.37143 | NS |
| Male | 76 | 0.9079 | 0.29110 | >45 | 80 | 0.8625 | 0.34655 | Responsibility | 21 | 0.9524 | 0.21822 | ||||
| Total | 113 | 0.8584 | 0.35019 | Total | 113 | 0.8584 | 0.35019 | Total | 113 | 0.8584 | 0.35019 | ||||
| Colombia | |||||||||||||||
| Optimism | Female | 47 | −0.0718 | 0.79464 | - | <45 | 88 | −0.0201 | 1.05199 | - | No responsibility | 87 | −0.0168 | 1.04077 | NS |
| Male | 71 | 0.0475 | 1.12464 | >45 | 30 | 0.0592 | 0.86231 | Responsibility | 31 | 0.0473 | 0.90804 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.00420 | Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.000420 | Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.00420 | ||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 47 | −0.0906 | 0.93006 | - | <45 | 88 | 0.0681 | 0.99543 | - | No responsibility | 87 | 0.0102 | 0.98079 | NS |
| Male | 71 | 0.0599 | 1.05260 | >45 | 30 | −0.1997 | 1.02010 | Responsibility | 31 | −0.0287 | 1.08359 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.00421 | Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.00421 | Total | 118 | 0.0000 | 1.00421 | ||||
| Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 47 | 1.13 | 1.583 | - | <45 | 88 | 0.92 | 1.432 | - | No responsibility | 87 | 0.80 | 1.337 | NS |
| Male | 71 | 0.73 | 1.230 | >45 | 30 | 0.80 | 1.270 | Responsibility | 31 | 1.13 | 1.522 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 0.89 | 1.388 | Total | 118 | 0.89 | 1.388 | Total | 118 | 0.89 | 1.388 | ||||
| Propensity to innovate | Female | 47 | 2.98 | 1.011 | - | <45 | 88 | 3.18 | 1.023 | - | No responsibility | 87 | 3.18 | 1.006 | NS |
| Male | 71 | 3.27 | 1.055 | >45 | 30 | 3.07 | 1.112 | Responsibility | 31 | 3.06 | 1.153 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 3.15 | 1.043 | Total | 118 | 3.15 | 1.043 | Total | 118 | 3.15 | 1.043 | ||||
| Telemedicine use | Female | 47 | 0.2128 | 0.41369 | ** | <45 | 88 | 0.3636 | 0.48380 | - | No responsibility | 87 | 0.2874 | 0.45515 | * |
| Male | 71 | 0.4085 | 0.49505 | >45 | 30 | 0.2333 | 0.43018 | Responsibility | 31 | 0.4516 | 0.50588 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 0.3305 | 0.47240 | Total | 118 | 0.3305 | 0.47240 | Total | 118 | 0.3305 | 0.47240 | ||||
| Level of ICT use | Female | 47 | 0.5532 | 0.50254 | ** | <45 | 88 | 0.6932 | 0.46382 | - | No responsibility | 87 | 0.7011 | 0.46041 | NS |
| Male | 71 | 0.7606 | 0.42978 | >45 | 30 | 0.6333 | 0.49013 | Responsibility | 31 | 0.6129 | 0.49514 | ||||
| Total | 118 | 0.6780 | 0.46925 | Total | 118 | 0.6780 | 0.46925 | Total | 118 | 0.6780 | 0.46925 | ||||
| Bolivia | |||||||||||||||
| Optimism | Female | 113 | −0.0412 | 1.16294 | - | <45 | 184 | −0.0411 | 1.06828 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 0.0254 | 0.98879 | NS |
| Male | 166 | 0.0280 | 0.87805 | >45 | 95 | 0.0795 | 0.85832 | Responsibility | 25 | −0.2587 | 1.11443 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00181 | Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00181 | Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00181 | ||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 113 | −0.1198 | 0.94670 | ** | <45 | 184 | −0.0282 | 1.04199 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 0.0230 | 0.99880 | NS |
| Male | 166 | 0.0815 | 1.07059 | >45 | 95 | 0.0544 | 0.92169 | Responsibility | 25 | −0.2344 | 1.02209 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00175 | Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00175 | Total | 279 | 0.0000 | 1.00175 | ||||
| Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice | Female | 113 | 0.44 | 0.499 | - | <45 | 184 | 0.46 | 0.500 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 0.46 | 0.499 | ** |
| Male | 166 | 0.50 | 0.502 | >45 | 95 | 0.51 | 0.503 | Responsibility | 25 | 0.68 | 0.476 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 0.48 | 0.500 | Total | 279 | 0.48 | 0.500 | Total | 279 | 0.48 | 0.500 | ||||
| Propensity to innovate | Female | 113 | 4.21 | 0.700 | - | <45 | 184 | 4.22 | 0.714 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 4.24 | 0.650 | NS |
| Male | 166 | 4.24 | 0.662 | >45 | 95 | 4.25 | 0.601 | Responsibility | 25 | 4.08 | 0.909 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 4.23 | 0.677 | Total | 279 | 4.23 | 0.677 | Total | 279 | 4.23 | 0.677 | ||||
| Telemedicine use | Female | 113 | 0.2566 | 0.43872 | *** | <45 | 184 | 0.3750 | 0.48544 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 0.3543 | 0.47925 | *** |
| Male | 166 | 0.4639 | 0.50020 | >45 | 95 | 0.3895 | 0.49022 | Responsibility | 25 | 0.6400 | 0.48990 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 0.3799 | 0.48624 | Total | 279 | 0.3799 | 0.48624 | Total | 279 | 0.3799 | 0.48624 | ||||
| Level of ICT use | Female | 113 | 0.9558 | 0.20656 | - | <45 | 184 | 0.9457 | 0.22732 | - | No responsibility | 254 | 0.9528 | 0.21258 | NS |
| Male | 166 | 0.9458 | 0.22713 | >45 | 95 | 0.9579 | 0.20189 | Responsibility | 25 | 0.9200 | 0.27689 | ||||
| Total | 279 | 0.9498 | 0.21871 | Total | 279 | 0.9498 | 0.21871 | Total | 279 | 0.9498 | 0.21871 | ||||
NS not significant, ***significant at 99% confidence level, **significant at 95% confidence level, *significant at 90% confidence level.
Regarding the sample of Spanish physicians, Gender was found to have an influence on Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice, Level of ICT use in personal life and Telemedicine use. In particular, men had a higher Level of ICT use in their personal lives and more Telemedicine use in their clinical practice. In contrast, women had a greater Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice. In every case, the mean value for the group and each sub-group was considered moderate. Also in every case, the relationship between the variables was significant at the 95% confidence level.
On the other hand, the medical professionals over 45 years of age had a greater Propensity to innovate, whereas those occupying posts of responsibility had a greater Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice. In both cases, the value of the variables was significant at the 90% confidence level. Regarding the variable Post, it should be noted that the two groups differed considerably in size - one was almost five times bigger than the other - so the mean value of the variable for the total sample had a strong bias towards the group of professionals not occupying posts of responsibility.
In the sample of Colombian physicians, it was found that men also had a higher Level of ICT use in their personal lives and more Telemedicine use in their clinical practice. In both cases, the value of the variables was moderate, being significant at the 95% confidence level. However, medical professionals occupying posts of responsibility had more Telemedicine use in their clinical practice, in a population where the number of medical professionals not occupying posts of responsibility was three times higher than those who did. The value of the variables was marginally significant at the 90% confidence level. Taking into account the ages of the individuals in the sample, no significant differences between the mean values of the variables were found.
Finally, in the sample of Bolivian physicians, once again, it was found that men had more Telemedicine use and a greater Perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice. In both cases, the value of the variables was moderate, being significant at the 99% and 95% confidence levels, respectively. No significant differences were found as regards Age in a population where the number of professionals under 45 years of age was two times higher than those over 45. However, significant differences were found as regards the posts they occupied. In a population where the proportion of medical professionals occupying posts of responsibility - such as chief or general manager of medical staff - was 1 to 10, medical professionals occupying posts of responsibility had more Telemedicine use and a greater perceived Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice. Once again, the value of the variables in both cases was moderate, being significant at the 99% and 95% confidence levels, respectively.
Drivers of telemedicine adoption
In order to test the hypotheses proposed above, a binary logistic regression analysis was performed. Table 6 shows the results for the three samples. The goodness of fit of the three samples was high, as confirmed by the values and levels of significance reached by the Chi-square statistics and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test. Moreover, the values of Nagelkerke's statistic indicated that the three samples had explanatory power. The value of this statistic was 27.5% for the Spanish sample, 16.1% for the Colombian sample and 19.7% for the Bolivian sample.
Table 6.
Relationships between the explanatory variables and telemedicine use for the three samples of physicians
| B | S.E. | Wald | Df | Significant | Exp(B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | ||||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTS in clinical practice | 0.200 | 0.445 | 0.202 | 1 | 0.653 | 1.222 |
| Ease-of-use of ICTS in clinical practice | 0.667 | 0.364 | 3.354 | 1 | 0.067 | 1.948 |
| Optimism | −0.498 | 0.437 | 1.302 | 1 | 0.254 | 0.607 |
| Propensity to innovate | 0.724 | 0.373 | 3.769 | 1 | 0.052 | 2.062 |
| Level of ICT use | 2.661 | 1.077 | 6.103 | 1 | 0.013 | 14.316 |
| Constant | 0.724 | 0.373 | 3.769 | 1 | 0.052 | 2.062 |
| Chi-square, 24.859; significant, 0.000 | ||||||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow test, 19.273; significant, 0.018 | ||||||
| Nagelkerke R Square, 0.275 | ||||||
| Colombia | ||||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTS in clinical practice | −0.192 | 0.253 | 0.575 | 1 | 0.448 | 0.826 |
| Ease-of-use of ICTS in clinical practice | 0.108 | 0.182 | 0.347 | 1 | 0.556 | 1.113 |
| Optimism | 0.485 | 0.269 | 3.254 | 1 | 0.071 | 1.624 |
| Propensity to innovate | 0.361 | 0.232 | 2.423 | 1 | 0.120 | 1.435 |
| Level of ICT use | 1.212 | 0.511 | 5.626 | 1 | 0.018 | 3.360 |
| Constant | −2.878 | 0.951 | 9.163 | 1 | 0.002 | 0.056 |
| Chi-square, 14.489; significant, 0.013 | ||||||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow test, 14.564; significant, 0.045 | ||||||
| Nagelkerke R Square, 0.161 | ||||||
| Bolivia | ||||||
| Perceived usefulness of ICTS in clinical practice | 0.131 | 0.141 | 0.866 | 1 | 0.352 | 1.140 |
| Ease-of-use of ICTS in clinical practice | 0.321 | 0.256 | 1.571 | 1 | 0.210 | 1.379 |
| Optimism | 0.484 | 0.150 | 10.371 | 1 | 0.001 | 1.622 |
| Propensity to innovate | 0.033 | 0.189 | 0.031 | 1 | 0.861 | 1.034 |
| Level of ICT use | 2.040 | 1.049 | 3.780 | 1 | 0.052 | 7.689 |
| Constant | -2.224 | 1.375 | 2.618 | 1 | 0.106 | 0.108 |
| Chi-square, 20.704; significant, 0.000 | ||||||
| Hosmer-Lemeshow test, 14.705; significant, 0.072 | ||||||
| Nagelkerke R Square, 0.197 |
The Spanish sample had a high goodness of fit, explaining more than 27% of the dependent variable's variance. Of the independent variables analysed, only Level of ICT use, Propensity to innovate and Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice had a significant effect. In particular, the health care professional's Level of ICT use outside work was the variable that had a higher explanatory power. In order of importance, it was followed by the variables Propensity to innovate and Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice. In both cases, the value of the variables was moderate, being significant at the 95% and 90% confidence levels, respectively. Taking into account these results, it is possible to conclude that hypotheses H2, H4 and H5 were confirmed for the Spanish sample.
Regarding the Colombian sample, the goodness of fit was high, albeit lower than the previous case. Of the independent variables analysed, only the professional's Level of ICT use and Optimism about the effects of ICTs on clinical practice were significant. In particular, in the same way as in the previous case, Level of ICT use was the variable that had a higher explanatory power. At some distance, it was followed by the variable Optimism with a beta value of 0.485, being significant at the 90% confidence level. Taking into account these results, it is possible to conclude that hypotheses H3 and H5 were confirmed for the sample of Colombian health care professionals.
Finally, the Bolivian sample had a lower goodness of fit and a lower explanatory power of the dependent variable. Of the independent variables analysed, only Level of ICT use and Optimism had a higher explanatory power and level of significance within it. The variable Level of ICT use had the greatest weight, with a very high beta coefficient, being significant at the 95% confidence level. Optimism was second in order of importance, with a relatively low explanatory power, being significant at 99%. Taking into account these results, it is possible to conclude that hypotheses H3 and H5 were confirmed for the Bolivian sample.
A comparative analysis of the three samples showed that there were differences in the importance of the explanatory variables considered, thus confirming hypothesis H6.
In summary, Table 7 shows the accepted and rejected hypotheses for each of the samples.
Table 7.
Accepted and rejected hypotheses for the Spanish, Colombian and Bolivian samples
| Hypotheses | Spain | Colombia | Bolivia |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1. The perceived usefulness of ICTs in clinical practice explains telemedicine use | Rejected | Rejected | Rejected |
| H2. The perceived ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice explains telemedicine use | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| H3. The user's optimism about technology explains telemedicine use | Rejected | Accepted | Accepted |
| H4. The user's propensity to innovate explains telemedicine use | Accepted | Rejected | Rejected |
| H5. The ICT user profile of the physician - as an individual, in his or her personal life - explains telemedicine use | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted |
| H6. The degree of ICT implementation in the country's health care system explains the importance of each of the determinants of the physician's telemedicine use | Accepted | Accepted | Accepted |
Discussion
Research into the uses of technology in health care usually distinguishes between the analysis of the determinants of use (ex-ante research) and the analysis of the outcomes of use (ex-post). While most studies have focused on the outcomes of technology use, it should be noted that ex-ante analysis is important for several reasons. First, it provides evidence of the drivers and barriers explaining technology use (or not). Second, understanding the factors that explain use means that it may be possible to influence the outcomes of such use.
In this sense, the aim of this study was to explain the determinants of telemedicine use by samples of physicians in three countries: Spain, Colombia and Bolivia. Obtaining and comparing evidence on an international scale from an ex-ante analysis determining which factors explain physicians' telemedicine use allow the common and distinct aspects of its use to be identified. To that end, a theoretical model based on a modified TAM was used as the analysis tool. Qualitative methodology was used to design a questionnaire as the data collection instrument. The questionnaire was sent to the professionals working for the health care organisations taking part in the study. In the three samples, the physician's Level of ICT use in his or her personal life had the highest explanatory power for Telemedicine use. This is understandable because telemedicine can be considered an advanced ICT use. Thus, if a physician uses ICTs in his or her personal life, he or she will be more likely to use them in his or her clinical practice too. However, despite the fact that it was the most important variable in all three samples, the value of its coefficient varied considerably. The highest coefficient was found in the Spanish sample, followed by the Bolivian sample and the Colombian sample.
In the case of the Spanish sample, Telemedicine use was also determined by the physicians' perceived Propensity to innovate and Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice. The results showed a clear relationship between Level of ICT use in personal life, perceived Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice and Propensity to innovate in the explanation of Telemedicine use by physicians in Spain. The combination of these three factors indicated a more complete model that contemplated personal, usability and innovatory aspects in the explanation of Telemedicine use in Spain.
Regarding the Colombian and Bolivian samples, the variables explaining Telemedicine use were Level of ICT use in personal life, as mentioned previously, and the level of Optimism about ICTs.
Unlike the behaviour observed in the sample of Spanish physicians, the results for the Latin American samples indicated a more primary model in the explanation of Telemedicine use. Despite the fact that Level of ICT use in personal life was also the main explanatory component, Telemedicine use in Colombia and Bolivia was not explained by either Ease-of-use of ICTs in clinical practice or Propensity to innovate. The explanatory model was completed by an Optimism factor that did not emerge in the Spanish sample.
The most plausible explanation is the well-known problems in health care in Latin America, where a variety of factors limit access to high-quality, timely health care, such as the scarcity of human resources, medication, equipment, infrastructure and cultural and geographical accessibility to health care services [58]. And Colombia and Bolivia are no exception to this. In a context plagued by deficiencies such as these, it would seem logical to think that physicians should be more optimistic about telemedicine's potential to resolve those deficiencies. In Spain, however, where there is a greater implementation of ICTs in health care, optimism about telemedicine's potential was no less important, ceding ground to ease of use of ICTs in clinical practice and the physicians' propensity to innovate.
The study presented in this article has several limitations, particularly the empirical approach taken, the lack of a prospective study design and the variables and restrictions imposed on the analysis. However, the availability of three samples of physicians from three different countries provided an excellent opportunity to analyse the determinants of telemedicine use. In this respect, and bearing in mind the importance of this type of analysis to health care organisations, the availability of more data on other groups of physicians to widen the comparison, a time series, better indicators and new analyses relating the determinants of telemedicine use to its outcomes would suggest that new approaches could be taken. In addition, the study's sample limitations are of particular note. Although the comparison made is relevant, increasing the number of observations to improve the representativeness of the samples, for both the set of physicians and for the health care systems, will be a future line of study in our research programme.
Conclusions
Two substantive conclusions can be drawn from this work. First of all, the considerable value that the variable physician's Level of ICT use - as an individual, in his or her personal life - has in the main explanatory power on Telemedicine use. Second, our findings suggest that Telemedicine use can also be determined by other factors of health care services (such as the lack of human resources, infrastructure, equipment, medication and cultural and geographical accessibility) and the level of ICT implementation in the field of health care, conferring different models in the explanation of its use.
These results support for the need for a dynamic approach to the design of telemedicine use, especially when it targets a variety of end users from different countries and health care systems. Hence, the importance of conducting studies prior to using telemedicine and attempting to identify which of the above-mentioned variables could exert an influence and how. Research is confronted with the challenge of producing such evidence, a prerequisite for the generalised adoption of telemedicine [59]. In this respect, it is reasonable to assume that the variations in barriers to technology adoption have more to do with local factors than technology infrastructure development. This scenario poses a considerable challenge for the formulation of public policies and strategies by countries and states, where decisions regarding can affect ultimate adoption and implementation of technological innovations. The potential to reduce limitations to health care access and improve the health sector's efficiency can therefore be considered a twofold positive aspect of incorporating telemedicine use into health care.
Endnotes
aCattell's scree test is a widely known approach for determining the number of factors. In this procedure, the eigenvalues of the correlation matrix are computed and then plotted in order of descending values. Thus, the method offers a visual exploration of a graphical representation of the eigenvalues.
bParallel analysis is a method based on the generation of random variables to determine the number of factors to retain. Thus, the method compares the observed eigenvalues extracted from the correlation matrix to be analysed with those obtained from uncorrelated normal variables. Zwick and Velicer [53] show that among the different factor retention criteria that can be used, parallel analysis is the most accurate, showing the least variability and sensitive to different factors.
cBartlett's test of sphericity and the KMO test are two measures of Appropriateness of Factor Analysis. Bartlett's test of sphericity is used to test the null hypothesis that the variables in the population correlation matrix are uncorrelated. In other words, this analysis tests if the correlation matrix is an identity matrix, i.e. all diagonal elements are 1 and all off-diagonal elements are 0, implying that all of the variables are uncorrelated. If the significant value for this test is less than our alpha level, we reject the null hypothesis that the population matrix is an identity matrix. The significant value for this analysis leads us to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there are correlations in the data set that are appropriate for factor analysis. On the other hand, the KMO index is used to compare the magnitudes of partial correlation coefficients; the lower its value is, the higher the partial correlation coefficients' values are, and consequently, the less appropriate it is to perform EFA [56]. According to the proposal made by those authors, coefficient values equal to or higher than 0.5 are acceptable.
Additional files
Electronic supplementary material
Additional file 1: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Bolivian physicians.(DOC 354 KB)
Additional file 2: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Spanish physicians.(DOC 198 KB)
Additional file 3: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Colombian physicians.(DOC 204 KB)
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the physicians who agreed to participate in this study, Dorian Gorena Urizar and Carolina Terán Calderón who implemented the survey and collected the data in Bolivia, Antonio M. Ojeda Cruz who implemented the survey and collected the data in Spain, and Nandy Consuelo Rodríguez Velàsquez who implemented the survey and collected the data in Colombia. The English language version of this article was revised by a native English-speaking language practitioner thanks to the support provided by the eLearn Center at the Open University of Catalonia.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
The survey was principally undertaken by FSR, who received support from JTS and AJZ for the statistical modelling and analysis. FSR is the guarantor of the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Francesc Saigí-Rubió, Email: fsaigi@uoc.edu.
Joan Torrent-Sellens, Email: jtorrent@uoc.edu.
Ana Jiménez-Zarco, Email: ajimenezz@uoc.edu.
References
- 1.Masters K. For what purpose and reasons do doctors use the Internet: a systematic review. Int J Med Inform. 2008;77(1):4–16. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2006.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jimoh L, Pate MA, Lin L, Schulman KA. A model for the adoption of ICT by health workers in Africa. Int J Med Inform. 2012;81(3):773–781. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2012.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berg M, Toussaint P. The mantra of modeling and the forgotten powers of paper: a sociotechnical view on the development of process-oriented ICT in health care. Int J Med Inform. 2003;69(2-3):223–234. doi: 10.1016/S1386-5056(02)00178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Al-Gahtani SS, King M. Attitudes, satisfaction and usage: factors contributing to each in the acceptance of information technology. Beha Inform Technol. 1999;18(4):277–297. doi: 10.1080/014492999119020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gagnon MP, Pluye P, Desmaris M, Car J, Pagliari C, Labrecque M, Frémont P, Gagnon J, Njoya M, Légaré F. A systematic review of interventions promoting clinical information retrieval technology (CIRIT) adoption by healthcare professionals. Int J Med Inform. 2010;79:669–680. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lluch M. Healthcare professional's organisational barriers to health information technologies: a review literature. Int J Med Inform. 2011;80(2):849–862. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2011.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kluge EHW. Ethical and legal changes for health telematics in a global world: telehealth and the technological imperative. Int J Med Infor. 2011;80:eI–e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Viitanen J, Hyppönen H, Lääveri T, Vänskä J, Reponen J, Winblad I. National questionnaire on clinical ICT systems proofs: physicians suffer from poor usability. Int J Med Inform. 2011;80:708–725. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2011.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Commission E. eHealth for Safety Report. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chaudhry B, Wang J, Wu S, Maglione M, Mojica W, Roth E, Morton SC, Shekelle PG. Systematic review: impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(10):742–752. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-144-10-200605160-00125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ammenwerth E, Graber S, Herrmann G, Burkle T, Konig J. Evaluation of health information systems—problems and challenges. Int J Med Inform. 2003;71:125–135. doi: 10.1016/S1386-5056(03)00131-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Keane MG. Review of the use of telemedicine in South America. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13(Suppl. 1):34–35. doi: 10.1258/135763307781645202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Broens TH, Veld RM, i't H, Vollenbroek-Hutten MM, Hermens HJ, van Halteren AT, Nieuwenhuis LJ. Determinants of successful telemedicine implementations: a literature study. J Telemed Telecare. 2007;13:303–309. doi: 10.1258/135763307781644951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.De BA, Bal Telemedicine in interdisciplinary work practices: on an IT system that met the criteria for success set out by its sponsors, yet failed to become part of every-day clinical routines. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2008;8:47. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-8-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grigsby J, Brega AG, Devore PA. The evaluation of telemedicine and health services research. Telemed J E Health. 2005;11:317–328. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2005.11.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ekeland AG, Bowes A, Flottorp S. Effectiveness of telemedicine: a systematic review of reviews. Int J Med Inform. 2010;79:736–771. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2010.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Roig F, Saigí F. Difficulties of incorporating telemedicine in health organizations: analytical perspectives. Gac Sanit. 2009;23(147):e1–e4. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2008.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Christensen MC, Remler D. Information and communications technology in U.S. health care: why is adoption so slow and is slower better? J Health Polit Polic. 2009;34(6):1011–1034. doi: 10.1215/03616878-2009-034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jha AK, Doolan D, Grandt D, Scott T, Bates DW. The use of health information technology in seven nations. Int J Med Inform. 2008;77(12):848–854. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2008.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Poon EG, Jha AK, Christino M, Honour MM, Fernandopulle R, Middleton B, Newhouse J, Leape L, Bates DW, Blumenthal D, Kaushal R. Assessing the level of healthcare information technology adoption in the United States: a snapshot. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2006;6:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-6-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Murray E, Burns J, May C, Finch T, O'Donnell C, Wallace P, Mair F. Why is it difficult to implement e-health initiatives? A qualitative study. Implementation Sci. 2011;6:6. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-6-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rigby M. Impact of telemedicine must be defined in developing countries. BMJ. 2002;324(7328):47. doi: 10.1136/bmj.324.7328.47a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Davis FD. Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 1989;13:319–340. doi: 10.2307/249008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: system characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. In J Man Mach Stud. 1993;38:475–487. doi: 10.1006/imms.1993.1022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Davis FD, Bagozzi RP, Warshaw PR. User acceptance of computer technology. Manage Sci. 1989;35:982–1003. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.35.8.982. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Davis FD, Venkatesh V. A critical assessment of potential measurement biases in the technology acceptance model: three experiments. Int J Hum-Comput St. 1996;45:19–45. doi: 10.1006/ijhc.1996.0040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma Q, Liu L. The technology acceptance model: a meta-analysis of empirical findings. J Org End-User Comput. 2004;16(1):59–72. doi: 10.4018/joeuc.2004010104. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee Y, Kozar KA, Larsen KRT. The technology acceptance model: past, present and future. Commun Assoc Inform Syst. 2003;12:752–780. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Venkatesh V, Morris MG. Why don't men ever stop to ask for directions? Gender, social influence, and their role in technology acceptance and usage behavior. MS Quarterly. 2000;24(1):114–139. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Venkatesh V, Davis FD. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manag Sci. 2000;46/2:186–204. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McKechnie S, Winklhofer H, Ennew C. Applying the technology acceptance model to the online retailing of financial services. IJRDM. 2006;34/4:388–410. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bagozzi RP. The legacy of the technology acceptance model and a proposal for a paradigm shift. J Assoc Inf Sys. 2007;8/4:244–254. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD. User acceptance of information technology: towards a unified view. MIS Q. 2003;27(3):425–478. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Venkatesh A, Davis FD. A model of the antecedents of perceived ease of use: development and test. Decisions Sci. 1996;27:451–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.1996.tb01822.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rogers Everett M. Diffusion of innovations. New York: Free Press; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ajzen I, Fishbein M. Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Englewood Cliffs NJ: Prentice Hall; 1980. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Armitage CJ, Conner M. Efficacy of the theory of planned behaviour: a meta-analytic review. Brit J Soc Psycho. 2001;40(4):471–499. doi: 10.1348/014466601164939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Parasuraman A, Grewal D. The impact of technology on the quality-value-loyalty chain: a research agenda. JAMS. 2000;28(1):168–174. doi: 10.1177/0092070300281015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fitgeral G, Piris L, Serrano A. Identification of Benefits and Barriers for the Adoption of E-Health Information Systems Using a Socio-Technical Approach, 30th International Conference on Information Technology Interfaces; 2008 Jun 23-26; Cavtat/Dubrovnik, Croatia. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Agarwal AR, Prasad J. Are individual differences germane to the acceptance of new information technologies? Decis Sci. 1999;30(2):361–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.1999.tb01614.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.IMF: IMF.] [accessed 1 April 2014., [http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/02/weodata/index.aspx]
- 42.Ministerio de sanidad, servicios sociales e igualdad. [accessed 1 April 2014]., [http://www.msssi.gob.es/organizacion/sns/docs/gasto08.pdf]
- 43.World bank. [accessed 30 March 2014., [http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.XPD.TOTL.ZS]
- 44.Norris AC. Essentials of Telemedicine and Telecare. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fabrigar LR, Wegener DT, McCullum RC, Strahan E. Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychol Methods. 1999;4:272–299. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.4.3.272. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Patil VH, Singh SN, Mishra S, Donovan DT. Efficient theory development and factor retention criteria: abandon the "eigenvalue greater than one" criterion". J Bus Res. 2008;61:162–170. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2007.05.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lorenzo-Seva U. Promin: a method for oblique factor rotation. Multivar Behav Res. 1999;34:347–356. doi: 10.1207/S15327906MBR3403_3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lorenzo Muthen B, Kaplan D. A comparison of some methodologies for the factor analysis of non-normal Likert variables: a note on the size of the model. Brit J Math Stat Psy. 1992;45:19–30. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8317.1992.tb00975.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cattell RB. The scree test for the number of factors. Multivar Behav Res. 1966;1:245–276. doi: 10.1207/s15327906mbr0102_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Cattell RB, Asper J. A geral plasmode (No. 30-10-5-2) for factor analysis exercises and research. Multivar Behav Res Monographs. 1967;67:3–15. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ledesma RD, Valero Mora P. Determining the number of factors to retain in EFA: an easy-to-use computer program for carrying out parallel analysis. Practical Assessment Research & Evaluation. 2007;12:2. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Horn JL. A rationale and test for the number of factors in factor analysis. Psychometrika. 1965;30:179–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02289447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zwick WR, Velicer WF. Comparison of five rules for determining the number of components to retain. Psychol Bull. 1986;99:432–442. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.99.3.432. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Timmerman ME, Lorenzo-Seva U. Dimensionality assessment of ordered polytomous items with parallel analysis. Psychol Methods. 2011;16:209–220. doi: 10.1037/a0023353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lorenzo Seva U, Ferrando PJ. FACTOR: a computer program to fit the exploratory factor analysis model. Behav Res Meth Instrum Comput. 2006;38(1):88–91. doi: 10.3758/BF03192753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bilodeau M, Brenner D. Theory of multivariate statistics. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rodrigues RJ, Risk A. eHealth in Latin America and the Caribbean: development and policy issues. J Med Internet Res. 2003;5(1):e4. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5.1.e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Call to action on global eHealth evaluation: consensus statement of the WHO Global eHealth Evaluation Meeting Bellagio. 2011, eHealth evaluation evidence, Bellagio
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Bolivian physicians.(DOC 354 KB)
Additional file 2: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Spanish physicians.(DOC 198 KB)
Additional file 3: Final questionnaire used in the sample of Colombian physicians.(DOC 204 KB)


