Abstract
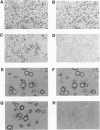
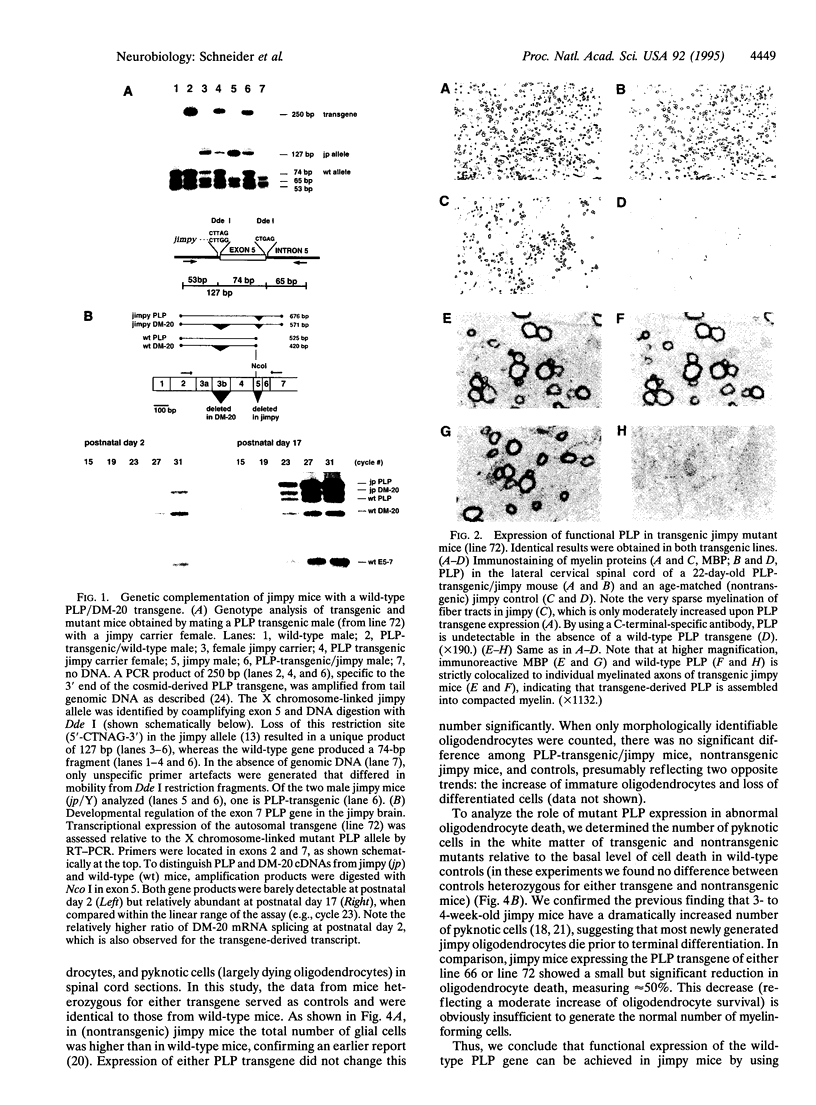
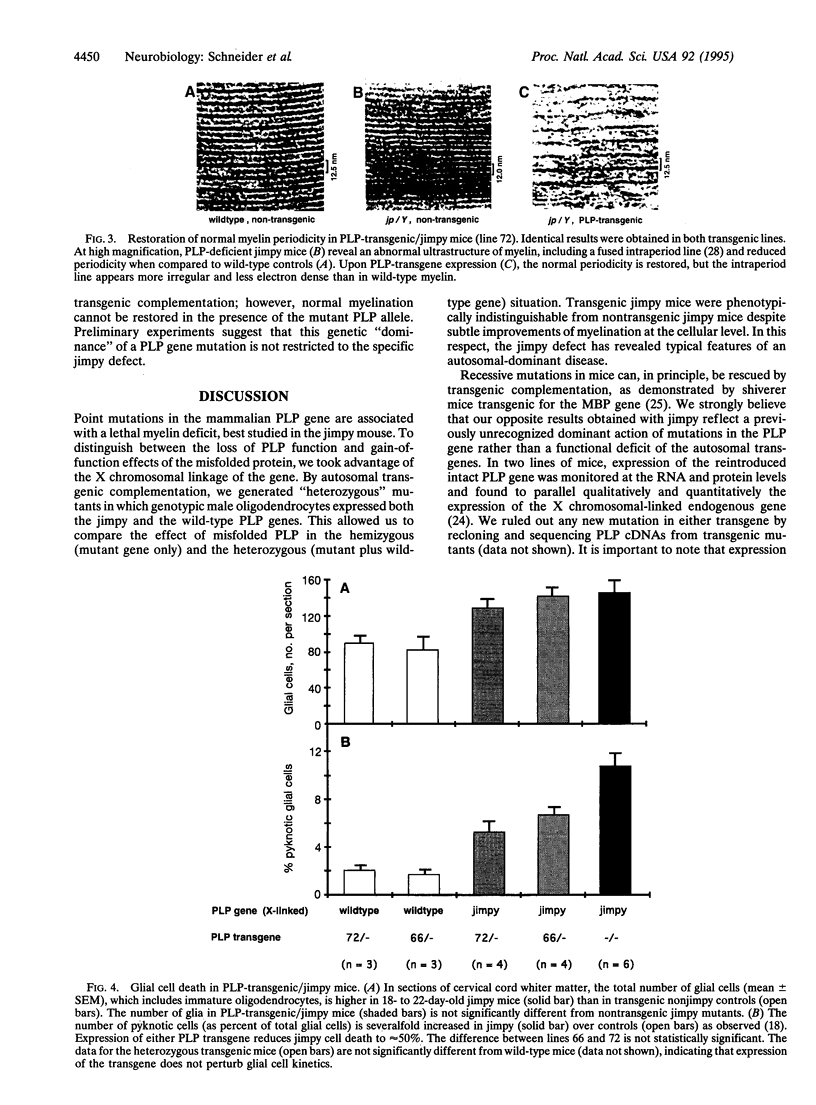
Mutations in genes encoding membrane proteins have been associated with cell death of unknown cause from invertebrate development to human degenerative diseases. A point mutation in the gene for myelin proteolipid protein (PLP) underlies oligodendrocyte death and dysmyelination in jimpy mice, an accurate model for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. To distinguish the loss of PLP function from other effects of the misfolded protein, we took advantage of the X chromosomal linkage of the gene and have complemented jimpy with a wild-type PLP transgene. In this artificial heterozygous situation, the jimpy mutation emerged as genetically dominant. At the cellular level oligodendrocytes showed little increase in survival although endogenous PLP gene and autosomal transgene were truly coexpressed. In surviving oligodendrocytes, wild-type PLP was functional and immunodetectable in myelin. Moreover, compacted myelin sheaths regained their normal periodicity. This strongly suggests that, despite the presence of functional wild-type PLP, misfolded jimpy PLP is by itself the primary cause of abnormal oligodendrocyte death.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautigny A., Mattei M. G., Morello D., Alliel P. M., Pham-Dinh D., Amar L., Arnaud D., Simon D., Mattei J. F., Guenet J. L. The structural gene coding for myelin-associated proteolipid protein is mutated in jimpy mice. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):867–869. doi: 10.1038/321867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. D., Hammang J. P., Goda S., Quarles R. H. Myelination in the jimpy mouse in the absence of proteolipid protein. Glia. 1989;2(3):148–154. doi: 10.1002/glia.440020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow A., Friedrich V. L., Jr, Lazzarini R. A. Many naturally occurring mutations of myelin proteolipid protein impair its intracellular transport. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Apr 1;37(5):574–583. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490370504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T., Ikenaka K., Inoue Y., Kuriyama S., Tsujii T., Nakao J., Nakajima K., Aruga J., Okano H., Mikoshiba K. Glial cell degeneration and hypomyelination caused by overexpression of myelin proteolipid protein gene. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):427–442. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa T., Nakao J., Yamada M., Shimizu K., Hayakawa T., Mikoshiba K., Ikenaka K. Fate of jimpy-type oligodendrocytes in jimpy heterozygote. J Neurochem. 1994 May;62(5):1887–1893. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62051887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp P. E., Dutta S., Skoff R. P. Differences in levels of neuroglial cell death in jimpy male mice and carrier females. Dev Neurosci. 1990;12(3):145–152. doi: 10.1159/000111844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp P. E., Skoff R. P., Redstone D. W. Oligodendroglial cell death in jimpy mice: an explanation for the myelin deficit. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):2813–2822. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-02813.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemke G. Unwrapping the genes of myelin. Neuron. 1988 Sep;1(7):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklin W. B., Gardinier M. V., King K. D., Kampf K. An AG----GG transition at a splice site in the myelin proteolipid protein gene in jimpy mice results in the removal of an exon. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):417–421. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80331-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Okano H., Tamura T., Ikenaka K. Structure and function of myelin protein genes. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:201–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.001221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Lai C., Nave K. A., Lenoir D., Ogata J., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequences of two mRNAs for rat brain myelin proteolipid protein. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadon N. L., Arnheiter H., Hudson L. D. A combination of PLP and DM20 transgenes promotes partial myelination in the jimpy mouse. J Neurochem. 1994 Sep;63(3):822–833. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63030822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. A single nucleotide difference in the gene for myelin proteolipid protein defines the jimpy mutation in mouse. J Neurochem. 1987 Dec;49(6):1873–1877. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Lai C., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. Jimpy mutant mouse: a 74-base deletion in the mRNA for myelin proteolipid protein and evidence for a primary defect in RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9264–9268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Lai C., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. Splice site selection in the proteolipid protein (PLP) gene transcript and primary structure of the DM-20 protein of central nervous system myelin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A. Neurological mouse mutants and the genes of myelin. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Aug 15;38(6):607–612. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490380602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson J. E., Gordon J. W., Pawlyk B. S., Roof D., Hayes A., Molday R. S., Mukai S., Cowley G. S., Berson E. L., Dryja T. P. Transgenic mice with a rhodopsin mutation (Pro23His): a mouse model of autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Neuron. 1992 Nov;9(5):815–830. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90236-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS R. J. Jimpy, a new totally sexlinked gene in the house mouse. Z Indukt Abstamm Vererbungsl. 1954;86(3):322–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00312228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham-Dinh D., Popot J. L., Boespflug-Tanguy O., Landrieu P., Deleuze J. F., Boué J., Jollès P., Dautigny A. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: a valine to phenylalanine point mutation in a putative extracellular loop of myelin proteolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7562–7566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Pham Dinh D., Dautigny A. Major Myelin proteolipid: the 4-alpha-helix topology. J Membr Biol. 1991 Mar;120(3):233–246. doi: 10.1007/BF01868534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskind W. H., Williams C. A., Hudson L. D., Bird T. D. Complete deletion of the proteolipid protein gene (PLP) in a family with X-linked Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1355–1360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C., Popko B., Takahashi N., Shine H. D., Saavedra R. A., Sidman R. L., Hood L. Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C., Schneider A., Griffiths I., Nave K. A. Premature arrest of myelin formation in transgenic mice with increased proteolipid protein gene dosage. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN R. L., DICKIE M. M., APPEL S. H. MUTANT MICE (QUAKING AND JIMPY) WITH DEFICIENT MYELINATION IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. Science. 1964 Apr 17;144(3616):309–311. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3616.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeesch M. K., Knapp P. E., Skoff R. P., Studzinski D. M., Benjamins J. A. Death of individual oligodendrocytes in jimpy brain precedes expression of proteolipid protein. Dev Neurosci. 1990;12(4-5):303–315. doi: 10.1159/000111859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimbs T., Stoffel W. Proteolipid protein (PLP) of CNS myelin: positions of free, disulfide-bonded, and fatty acid thioester-linked cysteine residues and implications for the membrane topology of PLP. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12289–12296. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]