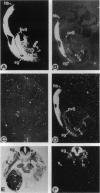
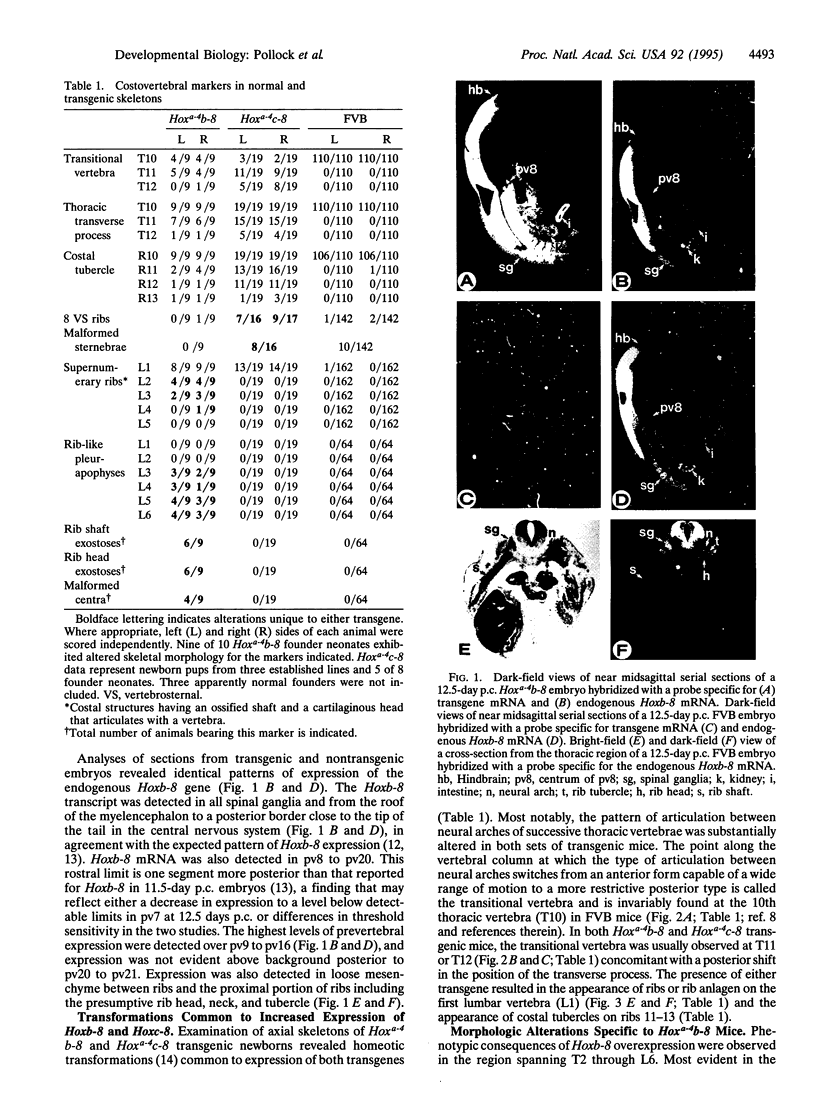
Abstract
To investigate the functions of paralogous Hox genes, we compared the phenotypic consequences of altering the embryonic patterns of expression of Hoxb-8 and Hoxc-8 in transgenic mice. A comparison of the phenotypic consequences of altered expression of the two paralogs in the axial skeletons of newborns revealed an array of common transformations as well as morphological changes unique to each gene. Divergence of function of the two paralogs was clearly evident in costal derivatives, where increased expression of the two genes affected opposite ends of the ribs. Many of the morphological consequences of expanding the mesodermal domain and magnitude of expression of either gene were atavistic, inducing the transformation of axial skeletal structures from a modern to an earlier evolutionary form. We propose that regional specialization of the vertebral column has been driven by regionalization of Hox gene function and that a major aspect of this evolutionary progression may have been restriction of Hox gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behringer R. R., Crotty D. A., Tennyson V. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D., Wolgemuth D. J. Sequences 5' of the homeobox of the Hox-1.4 gene direct tissue-specific expression of lacZ during mouse development. Development. 1993 Mar;117(3):823–833. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.3.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN J. M. Studies on the morphogenesis of the mouse sternum. III. Experiments on the closure and segmentation of the sternal bands. J Anat. 1953 Apr;87(2):130–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charité J., de Graaff W., Shen S., Deschamps J. Ectopic expression of Hoxb-8 causes duplication of the ZPA in the forelimb and homeotic transformation of axial structures. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):589–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisaka O., Capecchi M. R. Regionally restricted developmental defects resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene hox-1.5. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):473–479. doi: 10.1038/350473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie B. G., Capecchi M. R. Mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of Hoxd-3 (Hox-4.1) exhibit anterior transformations of the first and second cervical vertebrae, the atlas and the axis. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):579–595. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condie B. G., Capecchi M. R. Mice with targeted disruptions in the paralogous genes hoxa-3 and hoxd-3 reveal synergistic interactions. Nature. 1994 Jul 28;370(6487):304–307. doi: 10.1038/370304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Dierich A., LeMeur M., Schimmang T., Schuhbaur B., Chambon P., Duboule D. Disruption of the Hoxd-13 gene induces localized heterochrony leading to mice with neotenic limbs. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horan G. S., Wu K., Wolgemuth D. J., Behringer R. R. Homeotic transformation of cervical vertebrae in Hoxa-4 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12644–12648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P., Krumlauf R. Hox codes and positional specification in vertebrate embryonic axes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:227–256. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P., Whiting J., Muchamore I., Marshall H., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and models for patterning the hindbrain and branchial arches. Dev Suppl. 1991;1:187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeannotte L., Lemieux M., Charron J., Poirier F., Robertson E. J. Specification of axial identity in the mouse: role of the Hoxa-5 (Hox1.3) gene. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2085–2096. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jegalian B. G., De Robertis E. M. Homeotic transformations in the mouse induced by overexpression of a human Hox3.3 transgene. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):901–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90387-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappen C., Schughart K., Ruddle F. H. Two steps in the evolution of Antennapedia-class vertebrate homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Balling R., Gruss P. Variations of cervical vertebrae after expression of a Hox-1.1 transgene in mice. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Homeotic transformations of murine vertebrae and concomitant alteration of Hox codes induced by retinoic acid. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):89–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90574-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M. Respecification of vertebral identities by retinoic acid. Development. 1992 Jun;115(2):487–501. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.2.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Allen J., Adams J. M. Expression of Hox-2.4 homeobox gene directed by proviral insertion in a myeloid leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1881–1892. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostic D., Capecchi M. R. Targeted disruptions of the murine Hoxa-4 and Hoxa-6 genes result in homeotic transformations of components of the vertebral column. Mech Dev. 1994 Jun;46(3):231–247. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Mouellic H., Lallemand Y., Brûlet P. Homeosis in the mouse induced by a null mutation in the Hox-3.1 gene. Cell. 1992 Apr 17;69(2):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Mark M., Hart C. P., Dollé P., LeMeur M., Chambon P. Homeotic transformation of the occipital bones of the skull by ectopic expression of a homeobox gene. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):835–841. doi: 10.1038/359835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Krumlauf R. Homeobox genes and axial patterning. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):283–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90471-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendleton J. W., Nagai B. K., Murtha M. T., Ruddle F. H. Expansion of the Hox gene family and the evolution of chordates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6300–6304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock R. A., Jay G., Bieberich C. J. Altering the boundaries of Hox3.1 expression: evidence for antipodal gene regulation. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):911–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90388-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Solis R., Zheng H., Whiting J., Krumlauf R., Bradley A. Hoxb-4 (Hox-2.6) mutant mice show homeotic transformation of a cervical vertebra and defects in the closure of the sternal rudiments. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):279–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90229-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H., Bartels J. L., Bentley K. L., Kappen C., Murtha M. T., Pendleton J. W. Evolution of Hox genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:423–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.002231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle F. H., Bentley K. L., Murtha M. T., Risch N. Gene loss and gain in the evolution of the vertebrates. Dev Suppl. 1994:155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schughart K., Kappen C., Ruddle F. H. Duplication of large genomic regions during the evolution of vertebrate homeobox genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7067–7071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P. Vertebrate homeobox gene nomenclature. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):551–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small K. M., Potter S. S. Homeotic transformations and limb defects in Hox A11 mutant mice. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2318–2328. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappavigna V., Renucci A., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Urier G., Peschle C., Duboule D. HOX4 genes encode transcription factors with potential auto- and cross-regulatory capacities. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4177–4187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappavigna V., Sartori D., Mavilio F. Specificity of HOX protein function depends on DNA-protein and protein-protein interactions, both mediated by the homeo domain. Genes Dev. 1994 Mar 15;8(6):732–744. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.6.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]