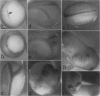
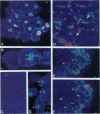
Abstract
Plakoglobin interacts with both classical and desmosomal cadherins. It is closely related to Drosophila aramadillo (arm) gene product; arm acts in the wingless (wg)-signaling pathway to establish segment polarity. In Xenopus, homologs of wg--i.e., wnts, can produce anterior axis duplications by inducing dorsal mesoderm. Studies in Drosophila suggest that wnt acts by increasing the level of cytoplasmic armadillo protein (arm). To test whether simply increasing the level of plakoglobin mimics the effects of exogenous wnts in Xenopus, we injected fertilized eggs with RNA encoding an epitope-tagged form of plakoglobin; this induced both early radial gastrulation and anterior axis duplication. Exogenous plakoglobin accumulates in the nuclei of embryonic cells. Plakoglobin binds to the tail domain of the desmosomal cadherin desmoglein 1. When RNA encoding the tail domain of desmoglein was coinjected with plakoglobin RNA, both the dorsalizing effect and nuclear accumulation of plakoglobin were suppressed. Mutational analysis indicates that the central arm repeat region of plakoglobin is sufficient to induce axis duplication and that this polypeptide accumulates in the nuclei of embryonic cells. These data show that increased plakoglobin levels can, by themselves, generate the intracellular signals involved in the specification of dorsal mesoderm.
Full text
PDF
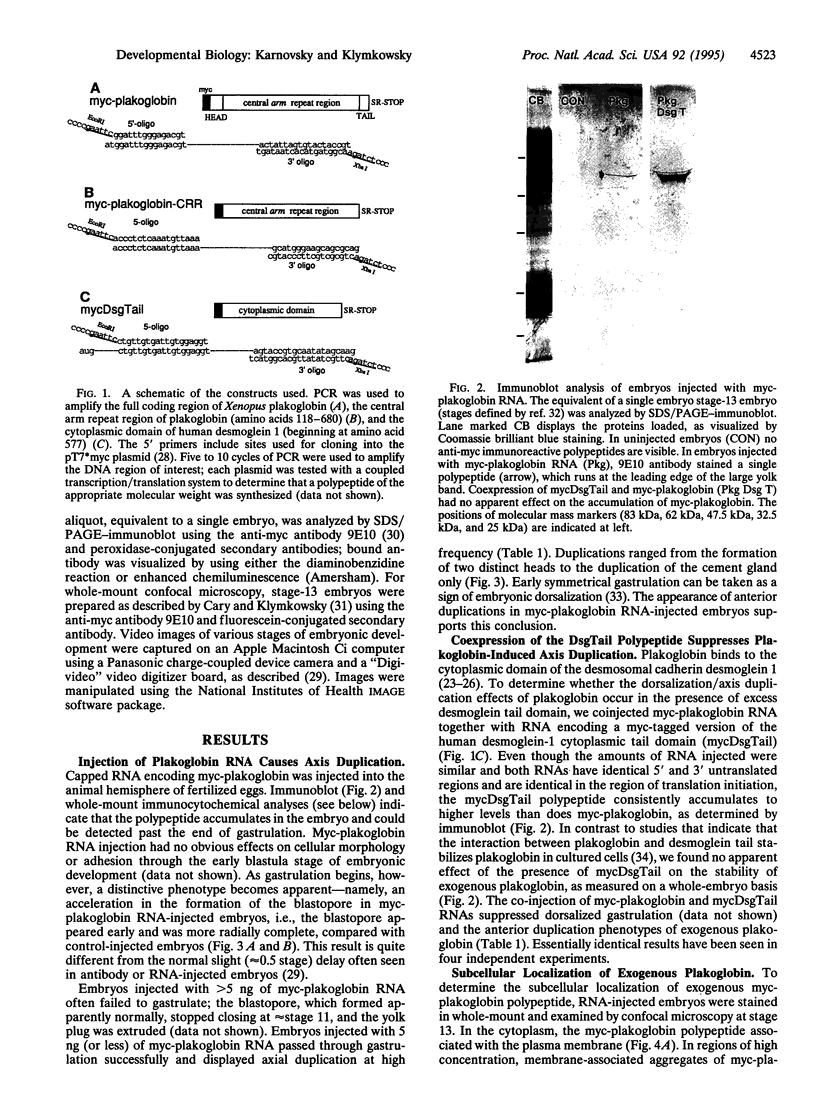
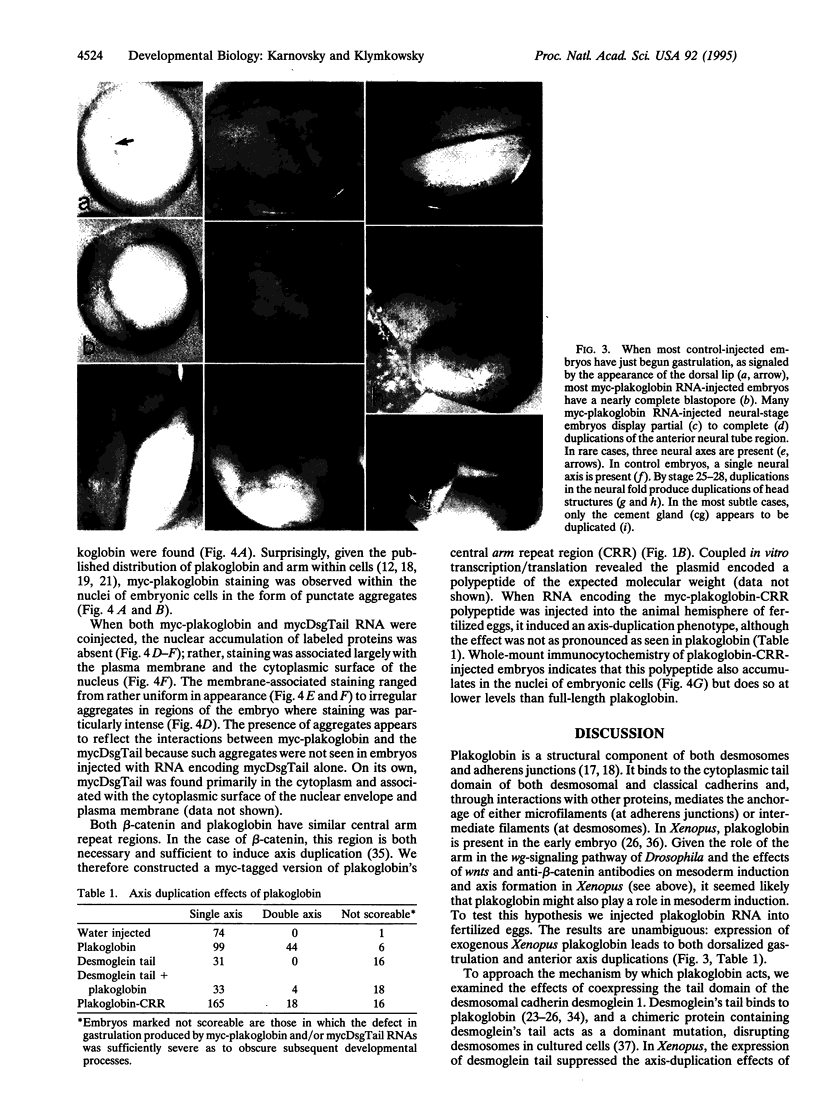
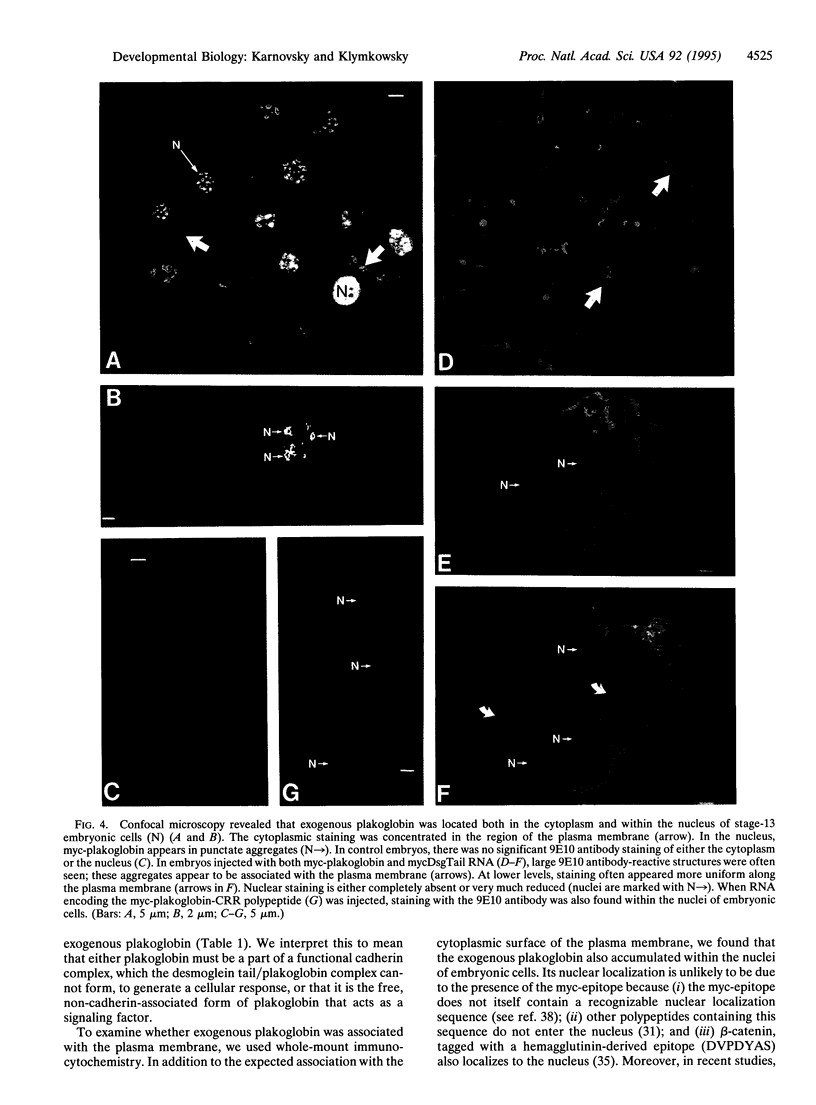

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bejarano E. R., Lichtenstein C. Mutants shed light on plant development. Trends Genet. 1992 Jan;8(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90002-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley R. S., Cowin P., Brown A. M. Expression of Wnt-1 in PC12 cells results in modulation of plakoglobin and E-cadherin and increased cellular adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1857–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrus L. W. Wnt-1 as a short-range signaling molecule. Bioessays. 1994 Mar;16(3):155–157. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary R. B., Klymkowsky M. W. Differential organization of desmin and vimentin in muscle is due to differences in their head domains. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):445–456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary R. B., Klymkowsky M. W., Evans R. M., Domingo A., Dent J. A., Backhus L. E. Vimentin's tail interacts with actin-containing structures in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jun;107(Pt 6):1609–1622. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.6.1609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Kapprell H. P., Franke W. W., Tamkun J., Hynes R. O. Plakoglobin: a protein common to different kinds of intercellular adhering junctions. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90706-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarais A. A., Moon R. T. The armadillo homologs beta-catenin and plakoglobin are differentially expressed during early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1992 Oct;153(2):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90118-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rebay I., Caron L. A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. An activated Notch receptor blocks cell-fate commitment in the developing Drosophila eye. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):555–557. doi: 10.1038/365555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouquet B., Zimbelmann R., Franke W. W. Identification of plakoglobin in oocytes and early embryos of Xenopus laevis: maternal expression of a gene encoding a junctional plaque protein. Differentiation. 1992 Nov;51(3):187–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1992.tb00695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funayama N., Fagotto F., McCrea P., Gumbiner B. M. Embryonic axis induction by the armadillo repeat domain of beta-catenin: evidence for intracellular signaling. J Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;128(5):959–968. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.5.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasman J., Crawford A., Goldstone K., Garner-Hamrick P., Gumbiner B., McCrea P., Kintner C., Noro C. Y., Wylie C. Overexpression of cadherins and underexpression of beta-catenin inhibit dorsal mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinck L., Nelson W. J., Papkoff J. Wnt-1 modulates cell-cell adhesion in mammalian cells by stabilizing beta-catenin binding to the cell adhesion protein cadherin. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(5):729–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.5.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülsken J., Behrens J., Birchmeier W. Tumor-suppressor gene products in cell contacts: the cadherin-APC-armadillo connection. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):711–716. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. R., Elinson R. P. The entire mesodermal mantle behaves as Spemann's organizer in dorsoanterior enhanced Xenopus laevis embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):64–77. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapprell H. P., Cowin P., Franke W. W. Biochemical characterization of the soluble form of the junctional plaque protein, plakoglobin, from different cell types. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):505–517. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klymkowsky M. W., Shook D. R., Maynell L. A. Evidence that the deep keratin filament systems of the Xenopus embryo act to ensure normal gastrulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8736–8740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen K. A., Wheelock M. J. Plakoglobin, or an 83-kD homologue distinct from beta-catenin, interacts with E-cadherin and N-cadherin. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):671–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Nye J. S., Weintraub H. The intracellular domain of mouse Notch: a constitutively activated repressor of myogenesis directed at the basic helix-loop-helix region of MyoD. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2385–2396. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman N. J., Eyre R. W., Klaus-Kovtun V., Stanley J. R. Demonstration of an adhering-junction molecule (plakoglobin) in the autoantigens of pemphigus foliaceus and pemphigus vulgaris. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 7;321(10):631–635. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909073211002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk A. P., Palka H. L., Luu H. H., Nilles L. A., Anderson J. E., Wheelock M. J., Green K. J. Posttranslational regulation of plakoglobin expression. Influence of the desmosomal cadherins on plakoglobin metabolic stability. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):31214–31223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ku M., Melton D. A. Xwnt-11: a maternally expressed Xenopus wnt gene. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1161–1173. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legan P. K., Collins J. E., Garrod D. R. The molecular biology of desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: "what's in a name"? Bioessays. 1992 Jun;14(6):385–393. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Kidd S., Alcamo E., Corbin V., Young M. W. Antineurogenic phenotypes induced by truncated Notch proteins indicate a role in signal transduction and may point to a novel function for Notch in nuclei. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1949–1965. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur M., Goodwin L., Cowin P. Interactions of the cytoplasmic domain of the desmosomal cadherin Dsg1 with plakoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14075–14080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrea P. D., Brieher W. M., Gumbiner B. M. Induction of a secondary body axis in Xenopus by antibodies to beta-catenin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):477–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Moon R. T. Ectopic expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 in Xenopus embryos leads to duplication of the embryonic axis. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1075–1084. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90506-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Christian J. L., Campbell R. M., McGrew L. L., DeMarais A. A., Torres M., Lai C. J., Olson D. J., Kelly G. M. Dissecting Wnt signalling pathways and Wnt-sensitive developmental processes through transient misexpression analyses in embryos of Xenopus laevis. Dev Suppl. 1993:85–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordermeer J., Klingensmith J., Perrimon N., Nusse R. dishevelled and armadillo act in the wingless signalling pathway in Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):80–83. doi: 10.1038/367080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkin N. T., Kitajewski J., Varmus H. E. Activity of Wnt-1 as a transmembrane protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2181–2193. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., McCrea P. D., Green K. J., Wieschaus E., Gumbiner B. M. The vertebrate adhesive junction proteins beta-catenin and plakoglobin and the Drosophila segment polarity gene armadillo form a multigene family with similar properties. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(3):681–691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Sweeton D., Casey M., Wieschaus E. wingless signal and Zeste-white 3 kinase trigger opposing changes in the intracellular distribution of Armadillo. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):369–380. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Sweeton D., Casey M., Wieschaus E. wingless signal and Zeste-white 3 kinase trigger opposing changes in the intracellular distribution of Armadillo. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):369–380. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peifer M., Wieschaus E. The segment polarity gene armadillo encodes a functionally modular protein that is the Drosophila homolog of human plakoglobin. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1167–1176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N. The genetic basis of patterned baldness in Drosophila. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):781–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90351-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Snider L., Weintraub H. Xenopus embryos regulate the nuclear localization of XMyoD. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1311–1323. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried E., Wilder E. L., Perrimon N. Components of wingless signalling in Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):76–80. doi: 10.1038/367076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L. The frog prince-ss: a molecular formula for dorsoventral patterning in Xenopus. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Fitzgerald K., Greenwald I. Intrinsic activity of the Lin-12 and Notch intracellular domains in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troyanovsky S. M., Troyanovsky R. B., Eshkind L. G., Krutovskikh V. A., Leube R. E., Franke W. W. Identification of the plakoglobin-binding domain in desmoglein and its role in plaque assembly and intermediate filament anchorage. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):151–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]