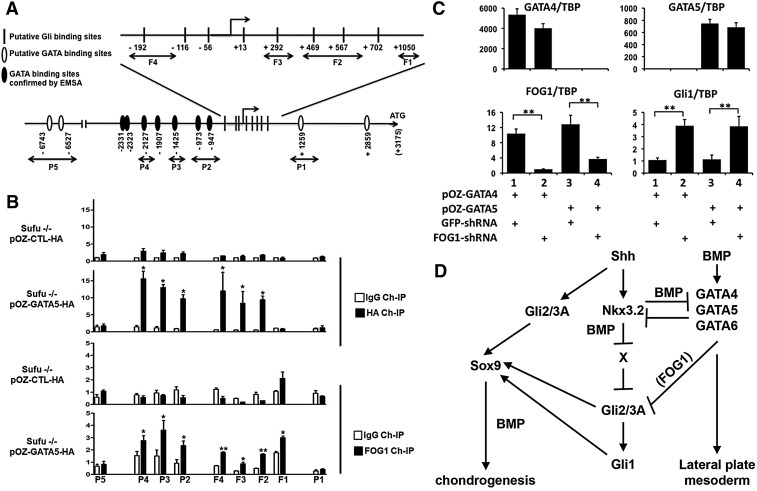
Fig. 7.
GATA factors bind to both GATA and Gli binding sites surrounding the Gli1 promoter. (A) Schematic of the mouse Gli1 gene showing putative Gli binding sites [identified by Dai et al. (1999)] and GATA binding sites (those confirmed by EMSA with in vitro translated GATA6 are depicted as black ovals). (B) ChIP for HA or FOG1-associated sequences in polyclones of Sufu−/− MEFs infected with pOZ-HA (parental retrovirus) or pOZ-GATA5-HA, employing the primers depicted in A. (C) Sufu−/− MEFs programmed to express GATA4 or GATA5 were infected with lentiviruses encoding shRNAs targeting GFP or FOG1, and gene expression was assayed by RT-qPCR. Expression of the various genes was normalized to that of Tbp. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.001, Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.d. n=2 (B, FOG1) or n=3 (B, HA; C). (D) SHH induces the expression of Nkx3.2 in the sclerotome, which both blocks the induction of Gata4/5/6 by subsequent BMP signals and represses the expression of a repressor of hedgehog signaling (termed ‘X’). Conversely, BMP-mediated induction of Gata4/5/6 dampens the response of mesodermal cells to hedgehog signaling (in a FOG-dependent fashion) and consequently blocks SHH-mediated induction of Nkx3.2 and Sox9.