Abstract
Cable pili are peritrichous organelles expressed by certain strains of Burkholderia cenocepacia, believed to facilitate colonization of the lower respiratory tract in cystic fibrosis patients. The B. cenocepacia cblBACDS operon encodes the structural and accessory proteins required for the assembly of cable pili, as well as a gene designated cblS, predicted to encode a hybrid sensor kinase protein of bacterial two-component signal transduction systems. In this study we report the identification of two additional genes, designated cblT and cblR, predicted to encode a second hybrid sensor kinase and a response regulator, respectively. Analyses of the deduced amino acid sequences of the cblS and cblT gene products revealed that both putative sensor kinases have transmitter and receiver domains and that the cblT gene product has an additional C-terminal HPt domain. Mutagenesis of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene led to a block in expression of CblA, the major pilin subunit, and a severe decrease in cblA transcript abundance. Using transcriptional fusion analyses, the decrease in the abundance of the cblA transcript in the cblS, cblT, and cblR mutants was shown to be due to a block in transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter, located upstream of the cblBACDS operon. Furthermore, ectopic expression of either cblS or cblR in wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 led to a significant increase, while ectopic expression of cblT resulted in a dramatic decrease, in abundance of the CblA major pilin and the cblA transcript. Our results demonstrate that the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR genes are essential for cable pilus expression and that their effect is exerted at the level of transcription of the cblBACDS operon. These findings are consistent with the proposed function of the cblSTR gene products as a multicomponent signal transduction pathway controlling the expression of cable pilus biosynthetic genes in B. cenocepacia.
The Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) is a large and diverse group of related gram-negative bacteria, which inhabit a wide range of environmental niches, including freshwater and soil. The Bcc currently comprises at least nine distinct genomovars, most of which have been reclassified as distinct species (5, 6, 43). The Bcc genomovar I type strain was originally identified as the etiologic agent of soft rot on onions (4). More recently, members of the Bcc have been associated with serious and sometimes fatal infections of the lower respiratory tract, primarily in compromised individuals and particularly cystic fibrosis (CF) patients (14, 22). While Bcc strains belonging to all nine genomovars have been isolated from CF patients, genomovar III strains, recently reclassified as B. cenocepacia, are most commonly associated with respiratory infections in CF worldwide (43).
Cable pili are peritrichous surface-associated organelles elaborated by certain strains of B. cenocepacia, as well as other species of the Bcc (26, 27). The shape of cable pili resembles intertwined cables, from which these organelles derive their name. Expression of cable pili by B. cenocepacia has been correlated with increased transmissibility of strains and adverse clinical outcome (28, 36). Cable pili have been proposed to facilitate binding to respiratory epithelia and mucin (29, 31) and may also play a role in mediating B. cenocepacia cell-cell interactions (40).
The cable pilus biosynthetic apparatus is encoded by four structural and accessory genes, designated cblB, cblA, cblC, and cblD (32). The B. cenocepacia cblBACD genes are predicted to encode the periplasmic chaperone, major pilin, outer-membrane usher, and minor pilin, respectively, and were shown to be both necessary and sufficient for heterologous expression of cable pili in Escherichia coli (32). Furthermore, insertional inactivation of the cblA gene in B. cenocepacia has been demonstrated to lead to a block in cable pilus biogenesis (40). We have recently initiated a systematic analysis of the regulation of cable pilus expression and have shown that cblBACD, along with a fifth gene, designated cblS, are cotranscribed as an operon from a principal promoter located upstream of cblB (41). We have also mapped the cblB-proximal promoter and demonstrated that its activity, and hence the expression of the cable pilus biosynthetic operon, is modulated by multiple environmental cues, including pH, osmolarity, and temperature (41).
Although the elements mediating control of cable pilus gene expression have not been defined, the amino acid sequence analysis of the cblS gene product revealed a possible regulatory mechanism. The cblS gene, which is transcribed as a part of the cblBACDS operon, is predicted to encode a new member of the sensor kinase family of bacterial two-component signal transduction systems. These systems allow bacteria to recognize and respond to specific cues received from the environment, and in turn modulate the expression of target genes (16, 35).
Two-component signal transduction systems control a variety of cellular processes, including metabolism, development, and virulence, and typically consist of a membrane-bound sensor kinase and a DNA-binding response regulator (7, 9, 35). Upon receiving environmental signals, the sensor kinase undergoes autophosphorylation at a conserved His residue within a domain termed transmitter or core histidine kinase. Autophosphorylation is followed by the transfer of the phosphoryl group onto a conserved Asp residue in the receiver domain of the cognate response regulator. Phosphorylation of the response regulator activates the protein, leading to positive and/or negative modulation of target gene expression. Transcriptional control of gene expression is generally mediated through direct interactions of the response regulator with target gene promoters.
A more complex variation of the two-step His→Asp signal transduction systems is the four-step His→Asp→His→Asp phosphorelay. Instead of only two, there are four distinct active domains required for signal transduction in this pathway. Autophosphorylation of the sensor kinase within its transmitter domain is followed by transfer of the phosphoryl group onto an Asp residue of a receiver domain, distinct from that in the response regulator (16, 35). The phosphoryl group is subsequently transferred to a His residue in a histidine phosphotransfer domain (HPt), followed by final transfer onto an Asp residue within the receiver domain of the response regulator (16, 35). In some systems, such as the Bacillus subtilis Kin/Spo sporulation pathway, all three modules (transmitter, receiver, and HPt) exist as individual proteins (9), while in others, such as the Bordetella spp. BvgAS regulatory system, the first three modules are contained within the sensor kinase (7). Sensor kinases containing multiple signaling modules are known as hybrid sensor kinases. The B. cenocepacia cblS gene is predicted to encode a multidomain hybrid sensor kinase.
In this report we characterized the role of cblS in expression of B. cenocepacia cable pili. The analysis of the B. cenocepacia cbl locus was extended downstream of the cblBACDS operon, identifying two additional genes, designated cblT and cblR. The cblT and cblR genes are predicted to encode a second hybrid sensor kinase and a DNA-binding response regulator, respectively. Genetic and biochemical analyses demonstrated that the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR genes are essential for cable pilus expression and that their effect is exerted at the level of transcription of the cblBACDS biosynthetic operon. The results presented in this study indicate that the cblS, cblT, and cblR genes encode a unique multicomponent signal transduction pathway that transcriptionally regulates the expression of B. cenocepacia cable pili.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and media.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. B. cenocepacia (formerly B. cepacia complex genomovar III) strain BC7 is a cable-piliated CF clinical isolate of B. cenocepacia (30). E. coli strains were grown with aeration at 37°C in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (33) or on LB agar plates supplemented with ampicillin (100 μg/ml), tetracycline (12 μg/ml), chloramphenicol (30 μg/ml), or trimethoprim (1.5 mg/ml) as necessary. B. cenocepacia strains were grown with aeration at 37°C in LB or in M9 minimal medium (33), supplemented with 0.2% glucose and 0.3% (wt/vol) Casamino Acids. For propagation of B. cenocepacia strains harboring transcriptional fusion constructs, tetracycline was added to liquid medium (25 μg/ml) and LB agar (500 μg/ml).
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids
| Strain or plasmid | Relevant characteristics | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli strains | ||
| DH5α | supE44 lacU169 (φ80 lacZΔM15) hsdR17 recA1 endA1 gyrA96 thi-1 relA1 | Bethesda Research Laboratories |
| XL-1 Blue | recA1 endA1 gyrA96 thi-1 hsdR17 supE44 relA1 lac (F′proAB lacIqZΔM15 Tn10) | Stratagene |
| S17-1 | Integrated RP4-2, Tc::Mu, Km::Tn7 | 34 |
| B. cenocepacia strains | ||
| BC7 | Cystic fibrosis clinical isolate, cable-piliated, formerly designated PC7 | 30 |
| CM434 | cblR::cat derivative of strain BC7 | This study |
| CM506 | cblT::tmp derivative of strain BC7 | This study |
| CM543 | ΔcblS derivative of strain BC7 | This study |
| Vectors and plasmid sources of antibiotic resistance cassettes | ||
| pBluescript SK(−) | Cloning and single-stranded phagemid; Apr | Stratagene |
| pGEM-T Easy | TA cloning vector; Apr | Promega |
| p34S-Tp | Source of trimethoprim resistance tmp cassette; Tpr | 8 |
| pCAT1 | Source of cat cassette; Cmr | 39 |
| pCM42 | Chloramphenicol-resistant derivative of pNPTS138; Cmr | This study |
| pMR4 | Broad-host-range vector; Tcr | 39 |
| pNPTS138 | Derivative of pLITMUS38 cloning vector with nptI, RK2 oriT, and B. subtilis sacB; Kmr | M. R. K. Alley |
| pRKlac290 | lacZ transcriptional fusion vector, IncP1 replicon, mob+; Tcr | 13 |
| Plasmid constructs | ||
| p3A4 | Cosmid with a portion of the cbl locus, including the 3′ end of cblD and the entire cblS, cblT, and cblR genes; Tcr | 41 |
| pBJ4 | 3.3-kb fragment harboring the cblT gene, cut with PstI and ligated with the tmp cassette from p34S-Tp; Apr | This study |
| pCM46 | 1.4-kb EcoRI fragment with ΔcblS, cloned into pCM42; Cmr | This study |
| pMT17 | 0.8-kb PCR product with cblA, cloned into pGEM-T Easy; Apr | This study |
| pMT58 | cblB-lacZ transcriptional fusion construct generated in pRKlac290; Tcr | 41 |
| pMT63 | cat cassette cloned into the NruI site internal to cblR; Apr Cmr | This study |
| pMT66 | 1.3-kb EcoRI fragment with cblR coding and promoter regions, cloned into pMR4 in the opposite orientation from the Plac promoter; Tcr | This study |
| pMT100 | 3.9-kb BglII/EcoRI fragment from p3A4 with cblT promoter and coding regions, cloned into BamHI/EcoRI sites of pMR4 in the orientation of the Plac promoter; Tcr | This study |
| pVN3 | 2.2-kb-EcoRI fragment with the cblS coding region, cloned into pMR4 in the orientation of the Plac promoter; Tcr | This study |
DNA manipulations.
DNA-modifying enzymes, including restriction endonucleases, T4 polynucleotide kinase, T4 DNA ligase, T4 polymerase, and Taq polymerase, were obtained from Roche, New England Biolabs, Promega, and Invitrogen. Plasmid DNA was isolated by the boiling lysis method (33) or using the QIAprep Spin Miniprep kit (QIAGEN, Inc.). Recombinant plasmids were introduced into E. coli and/or B. cenocepacia by either electroporation or conjugation, as previously described (39). Genomic DNA from B. cenocepacia was extracted using the PureGene kit (Gentra). Southern blot hybridizations were generally performed as described by Sambrook et al. (33) using Hybond N nitrocellulose membranes and probes labeled with [α-32P]dCTP (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) by the random primer method.
Cloning and sequencing of the B. cenocepacia cblT and cblR genes.
We have previously described the cloning and sequencing of the B. cenocepacia strain BC7 cblBACDS genes (41). Cosmid clone p3A4, identified in these studies, was found to harbor a portion of the cbl locus, including the cblS gene and the DNA region further downstream. A 7.2-kb EcoRI fragment carrying this region was cloned from p3A4 into the corresponding site of pBluescript SK(−), generating pMT76. For sequencing, multiple subclones of pMT76 were generated in pBluescript SK(−), and their sequences were determined on both DNA strands. Nucleotide sequencing was performed by the Advanced Genetic Analysis Center at the University of Minnesota using the dideoxy chain termination method and an ABI 1371A DNA sequencer (Applied Biosystems). Oligonucleotide primers used for sequencing were standard forward and reverse (T3 and T7) pBluescript primers or custom oligonucleotides synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies. Double-stranded sequences were aligned and assembled using the EditSeq and SeqMan components of a demonstration version of the Lasergene sequence analysis software package (DNASTAR Inc.). Nucleotide and amino acid sequence searches and analysis utilized the BLASTX and BLASTP programs at the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
Construction of B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR isogenic mutants.
The cblS gene was inactivated by generating an in-frame deletion in the chromosomal copy of the gene. Initially, the cblS gene was PCR amplified, using primers cbl39 (5′-TTCTATCCCAAGCGAATCG-3′) and cbl42 (5′-ATAGACGGCCCACGTTGC-3′), and cloned into the TA cloning vector pGEM T-Easy (Promega) to generate pVN1. A 741-nucleotide in-frame deletion in cblS was generated by partially digesting pVN1 with PstI, followed by a religation, generating pVN4. The resulting 1.4-kb ΔcblS fragment was cloned as an EcoRI fragment into the suicide vector pCM42, generating pCM46. This construct was subsequently introduced into B. cenocepacia strain BC7 by conjugation, using E. coli S17-1 as the donor strain (39). Single-crossover recombinants were selected on LB agar plates supplemented with chloramphenicol (300 μg/ml). After a single-crossover insertion was confirmed by Southern hybridization, the mutant strain was repeatedly subcultured in 5 ml of LB in the absence of chloramphenicol for five consecutive days to allow a second crossover to occur. The strain was subcultured in fresh LB once mid- to late exponential phase was reached. After 5 days, dilutions of the culture were plated on LB agar plates, and approximately 1,600 of the resulting colonies were restreaked in duplicate onto LB agar plates with or without chloramphenicol (300 μg/ml). Colonies that were Cms were further analyzed and confirmed as cblS in-frame deletion mutants by Southern hybridization, PCR, and sequencing. The BC7 ΔcblS strain was designated CM543.
For insertional inactivation of the cblT gene in B. cenocepacia, a 3.3-kb PCR product encompassing the cblR-cblT intergenic region and the entire cblT coding sequence was amplified from strain BC7 chromosomal DNA, using oligonucleotide primers cbl46 (5′-TCAATGCGATGCGCTCGG-3′) and cbl48 (5′-AGGATCACGACACGGATC-3′), and cloned into pGEM-T Easy, generating pMT74. The 3.3-kb cblT PCR product was excised as a SpeI/EcoRI fragment and cloned into the corresponding sites of pBluescript SK(−), generating pCM48. Plasmid pCM48 was digested with PstI, which removed a 1.7-kb region internal to the cblT gene, and ligated with the trimethoprim resistance cassette (tmp), which was obtained as a PstI fragment from p34S-Tp, generating pBJ4. Plasmid pBJ4 was electroporated into B. cenocepacia strain BC7 as previously described (39), and recombinants were selected on LB agar supplemented with trimethoprim (1.5 mg/ml). A Tpr double-crossover mutant was confirmed by Southern hybridization and designated CM506.
To insertionally inactivate cblR in B. cenocepacia, the gene was PCR amplified from strain BC7 chromosomal DNA, using oligonucleotide primers cbl43 (5′-CGGGCGCCATTTCGAATC-3′) and cbl44 (5′-TGGTGGAGAAAGACACCC-3′). The cblR PCR product was cloned into pGEM T-Easy to generate pMT61 and insertionally inactivated with the cat cassette, cloned as a HincII fragment into the NruI site of cblR (pMT63). This construct was electroporated into B. cenocepacia strain BC7, and recombinants were selected on LB agar supplemented with chloramphenicol (350 μg/ml). The Cmr colonies were further analyzed by Southern hybridization, and a double-crossover mutant was designated CM434.
Generation of constructs for ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, or cblR and complementation analysis.
The cblS gene was cloned as a 2.2-kb EcoRI fragment from pVN1 into the multiple cloning site of the broad-host-range vector pMR4, generating construct pVN3. Since the cblS gene does not have a promoter immediately upstream, the gene was cloned in the same orientation as PlacZ in pMR4. The cblT and cblR genes were cloned into pMR4 with their respective upstream regions, which are likely to harbor the promoters for these two genes, given their divergent orientation (Fig. 1). The cblT gene was cloned into BamHI/EcoRI sites of pMR4 as a 3.9-kb BglII/EcoRI fragment from cosmid p3A4, generating pMT100. The cblR gene was cloned as a 1.3-kb EcoRI fragment from pMT61 into the corresponding site of pMR4, generating pMT66. Each construct was introduced either into B. cenocepacia strain BC7 or into the corresponding isogenic mutant by conjugation.
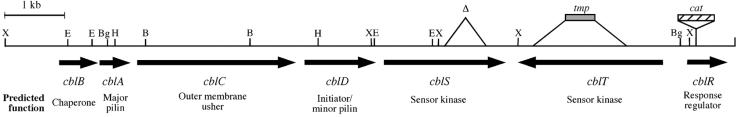
FIG. 1.
Physical map of the B. cenocepacia cblBACDSTR locus. The arrows denote the direction of transcription. The deletion in the cblS gene in strain CM543 is indicated with the Δ symbol. The solid gray box denotes the site of the tmp cassette insertion in the cblT gene in strain CM506, and the hatched box denotes the site of insertion of the cat cassette in the cblR gene in strain CM434. The predicted functions of the deduced gene products are indicated below. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; Bg, BglII; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; X, XhoI.
Immunoblot analysis.
For immunoblot analysis, B. cenocepacia strains were grown in 3 ml of M9 medium for 17 h. Aliquots of the cultures were centrifuged to harvest bacterial cells, and the pellets were resuspended in Laemmli buffer (21). Equal amounts of protein from each strain were boiled, separated by 12.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and analyzed by immunoblotting with CblA-specific antiserum as previously described (40).
RNA dot blot analysis.
For RNA isolation, B. cenocepacia strains were grown in M9 medium, supplemented with 25 μg of tetracycline/ml as necessary, to an A600 of ∼0.45. Total RNA was extracted using the Trizol reagent (Invitrogen). Equivalent amounts of RNA (1.25 μg) were applied on Hybond N nitrocellulose membranes (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) and UV-cross-linked to the membrane using a HybriLinker HL-2000 (Ultra-Violet Products). Membranes were hybridized with a 0.8-kb DNA probe corresponding to the cblA gene, obtained from EcoRI-digested plasmid pMT17, and labeled with [α-32P]dCTP (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) by the random primer method (33). Quantitative RNA dot blot analysis was performed in triplicate, with RNA extracted from three parallel cultures for each strain analyzed. The autoradiograms were scanned, and quantification of cblA transcript levels was performed using NIH Image software, version 1.62.
Electron microscopy.
For transmission electron microscopy (TEM), B. cenocepacia strains were grown in M9 medium to an A600 of ∼1.0, upon which 5-μl aliquots of each culture were applied on formvar-coated electron microscopy grids. After a 10-min incubation, the grids were washed and the attached bacteria were stained with 0.5% uranyl acetate, washed a second time, and dried. TEM was performed at the University of Minnesota Characterization Facility on a JEOL 1200 microscope at 120 kV.
Measurement of β-galactosidase activity.
The cblB transcriptional fusion construct pMT58 was generated as previously described (41). B. cenocepacia strains harboring pMT58 were grown in the presence of tetracycline (25 μg/ml) in order to ensure maintenance of the plasmid. For measurement of β-galactosidase activity, cultures of B. cenocepacia strains harboring pMT58 were grown as previously described (41), and β-galactosidase activities were measured as described by Miller (23). Assays were performed in triplicate with a minimum of three independent experiments.
Nucleotide sequence accession number.
The DNA sequence of the cblT and cblR genes has been deposited in GenBank under accession number AY500852.
RESULTS
Identification of the B. cenocepacia cblT and cblR genes.
We have previously described the cloning and sequencing of the B. cenocepacia cblBACDS operon (41). The fifth gene in this operon, cblS, is predicted to encode a member of the hybrid sensor kinase family of two-component signal transduction systems. Genes encoding response regulator proteins of two-component systems are typically linked to, and often cotranscribed with, the genes encoding their cognate sensor kinases. To examine the possibility that a cognate response regulator is encoded in the proximity of cblS, we extended our analysis downstream of the cblBACDS operon.
Sequence analysis of the region downstream of the cblBACDS operon identified two additional open reading frames (ORFs), designated cblT and cblR (Fig. 1). Both ORFs are predicted to encode proteins with significant homology to known members of bacterial two-component signal transduction systems. Like cblS, the cblT gene is also predicted to encode a hybrid sensor kinase. The cblS and cblT gene products are 43% identical on the amino acid sequence level. Both cblS and cblT are predicted to encode proteins with cleavable signal sequences and membrane-spanning domains, which likely direct their translocation into the cytoplasmic membrane by a Sec-dependent mechanism. The estimated molecular mass of the mature cblS gene product is 74.1 kDa, while that of the mature cblT gene product is 87.2 kDa. The second gene identified downstream of the cblBACDS locus, designated cblR, is predicted to encode a 25.8-kDa protein with high homology to the DNA-binding response regulators of two-component signal transduction pathways (Fig. 1). Analysis of the DNA sequence upstream of the cblBACDS operon, or downstream of cblR, did not identify any other candidate ORFs encoding additional signal transduction components. The putative gene products of cblS, cblT, and cblR all exhibit significant amino acid sequence identity (ranging between 24 and 31%) to components of the Bordetella spp. BvgAS and E. coli RcsBC and ArcAB two-component signal transduction systems.
Domain architecture of the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR gene products.
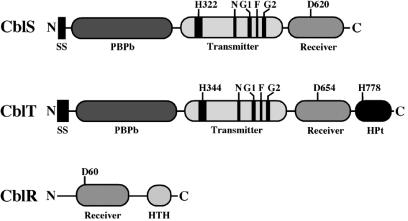
In order to examine whether cblS, cblT, and cblR may encode proteins with the necessary domains and conserved amino acid residues known to be required for signal transduction in other bacterial signal transduction systems, the deduced amino acid sequences of the three gene products were examined. Both cblS and cblT are predicted to encode hybrid sensor kinases with periplasmic substrate-binding domains (PBPb), which are required by other sensor kinases for recognition of specific environmental cue(s) (Fig. 2). Both the cblS and cblT gene products are predicted to have a transmitter domain, which contains the ATP-binding N, G1, F, and G2 boxes, as well as the conserved His residue, which serves as the substrate for autophosphorylation (Fig. 2). Additionally, both the cblS and cblT gene products are predicted to have a receiver domain, which contains a conserved Asp residue. Interestingly, only CblT contains an HPt domain (Fig. 2), including the highly conserved amino acid residues of the HPt module consensus sequence (11). The transmitter and receiver domains of the cblS and cblT gene products, as well as the HPt domain of the cblT gene product, all have the highly conserved His or Asp residues, predicted to undergo phosphorylation and facilitate signal transduction (Fig. 2).
FIG. 2.
Domain architecture of the predicted cblS, cblT, and cblR gene products. The amino (N) and carboxyl (C) termini are denoted. The conserved His (H) and Asp (D) residues in the transmitter, receiver, and HPt domains are indicated. The locations of the ATP-binding H, N, G1, F, and G2 boxes in the transmitter domains of CblS and CblT are shown in black. Abbreviations: HPt, histidine phosphotransfer domain; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain; PBPb, bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding protein domain; SS, signal sequence.
The cblR gene product, predicted to function as a response regulator, has two domains characteristic of this family of proteins. Proximal to the N terminus, a receiver domain was identified that contains the conserved Asp residue (D60) (Fig. 2), which is the substrate for phosphorylation in other bacterial signal transduction systems. The second conserved domain in the cblR gene product is a C-terminal DNA-binding helix-turn-helix (HTH) domain, which is known to interact with target gene promoters in other phosphorelay systems (Fig. 2) (16, 35). Together, the cblS, cblT, and cblR gene products appear to contain all of the necessary and highly conserved domains, as well as the His and Asp residues, required for signal transduction in other bacterial four-step phosphorelay systems.
B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR mutants are blocked in cable pilus expression.
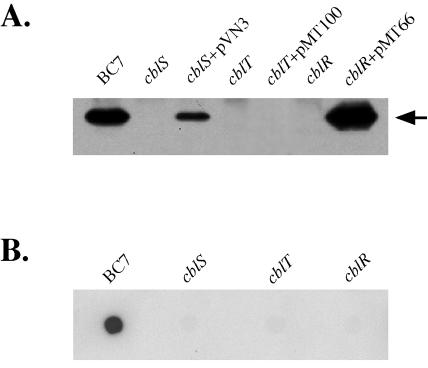
To begin to characterize the role of the cblS, cblT, and cblR genes in cable pilus expression, mutations in each of the three genes were generated, as described in Materials and Methods. Inactivation of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene yielded strains CM543, CM506, and CM434, respectively. In order to examine the effects of the individual mutations on expression of the CblA major pilin, whole-cell extracts of the wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 and the isogenic cblS, cblT, and cblR null strains were subjected to immunoblot analysis with CblA-specific antiserum. An abundant 15-kDa protein, corresponding in size to the CblA major pilin, was detected in the wild-type strain BC7 whole-cell preparation (Fig. 3A). In contrast, there was no detectable CblA protein in the whole-cell extracts of the cblS, cblT, and cblR null strains (Fig. 3A). The absence of the CblA protein is not due to growth defects associated with inactivation of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene, since the corresponding mutant strains exhibited growth kinetics similar to that of wild-type strain BC7 (data not shown).
FIG. 3.
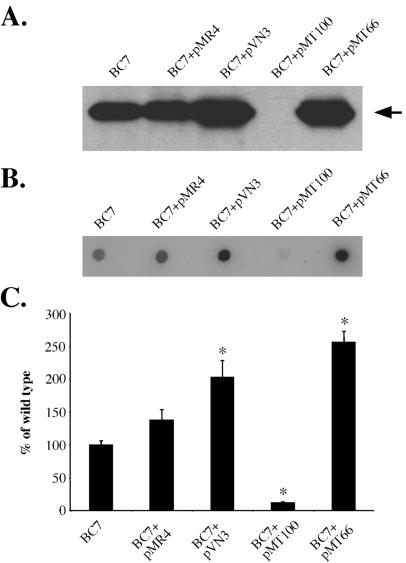
Effects of inactivation of B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, or cblR on CblA major pilin and cblA transcript abundance. (A) Immunoblot of whole-cell extracts from strain BC7 and the isogenic cblS (CM543), cblT (CM506), and cblR (CM434) mutants and the mutant strains with either pVN3 (carrying cblS), pMT100 (carrying cblT), or pMT66 (carrying cblR), probed with CblA-specific antiserum. An equal amount of protein was loaded in each lane. The arrow indicates the position of the CblA protein band. (B) RNA dot blot of total RNA extracted from strain BC7 and the isogenic cblS (CM543), cblT (CM506), and cblR (CM434) mutants, hybridized with a probe specific for cblA.
For complementation analysis, each of the three genes was cloned into the broad-host-range vector pMR4, which we have previously utilized for targeted gene expression in B. cenocepacia (39). The constructs carrying cblS, cblT, or cblR, designated pVN3, pMT100, and pMT66, respectively, were introduced into the corresponding null strains. Expression of the CblA major pilin was restored in the cblS and cblR mutant strains by transcomplementation with plasmids pVN3 and pMT66, respectively (Fig. 3A). However, we were unable to restore CblA expression in the cblT mutant by providing the wild-type cblT gene in trans on plasmid pMT100 (Fig. 3A). It is unlikely that the cblT mutation in strain CM506 is polar, since cblT does not appear to be a part of an operon and is transcribed divergently from cblR and convergently with respect to the cblBACDS operon (Fig. 1). As will be further discussed below, the inability to complement the cblT mutant is likely due to a block in cable pilus expression caused by increased cblT gene dosage and expression levels.
RNA dot blots were performed to examine if the block in CblA expression in the cblS, cblT, and cblR null strains is accompanied by an effect on cblA transcript abundance. Total RNA was extracted from the B. cenocepacia wild-type strain BC7 and the isogenic cblS, cblT, and cblR null mutants and hybridized to a cblA-specific probe. The RNA dot blot analysis revealed that inactivation of cblS, cblT, or cblR resulted in a dramatic decrease in cblA transcript levels (Fig. 3B), suggesting that the corresponding null strains were defective in transcription of cblA and/or cblA transcript stability.
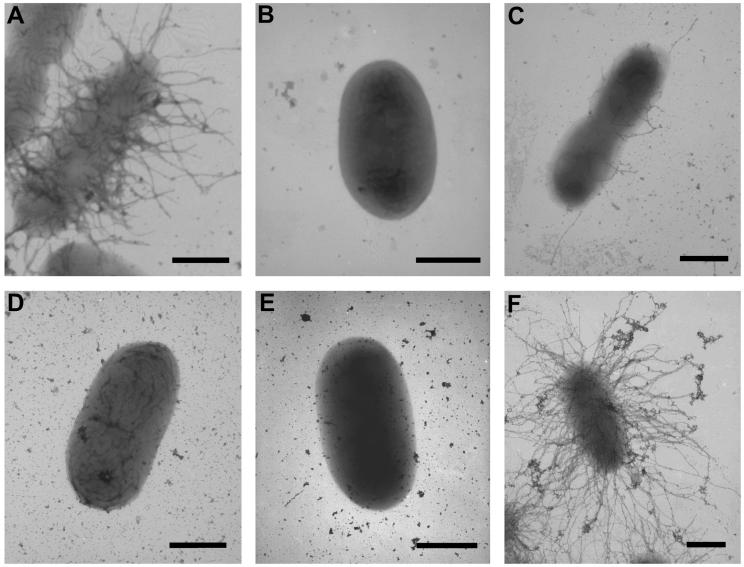
To further confirm that cblS, cblT, and cblR are required for cable pilus expression, the wild-type and mutant strains were examined by TEM. Examination of the wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 revealed numerous peritrichously expressed cable pili on the bacterial cell surface (Fig. 4A). As previously reported, the level of cable pilus expression by wild-type strain BC7 cells was highly variable, with some cells exhibiting numerous cable pili on their surface while other cells had only a few pili or lacked pili altogether (40). Consistent with the lack of expression of the CblA major pilin, cells of the mutant strains CM543 (cblS), CM506 (cblT), and CM434 (cblR) were all devoid of cable pili (Fig. 4B, D, and E). Cable pilus expression was restored in strains CM543 and CM434 by transcomplementation with plasmid pVN3, harboring cblS, or pMT66, harboring cblR, respectively (Fig. 4C and F). Together, our results indicate that cblS, cblT, and cblR are essential for the expression of cable pili and that the block in cable pilus expression in the corresponding null strains is accompanied by a dramatic decrease in CblA pilin and cblA transcript abundance.
FIG. 4.
Effects of the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR mutations on cable pilus expression. Transmission electron micrographs of wild-type strain BC7 (A), the cblS null strain CM543 (B), the cblS null strain transcomplemented with pVN3 (C), the cblT null strain CM506 (D), the cblR null strain CM434 (E), and the cblR null strain transcomplemented with pMT66 (F) are shown. Bars = 0.5 μm.
The cblS, cblT, and cblR genes are required for transcription of the B. cenocepacia cable pilus biosynthetic operon.
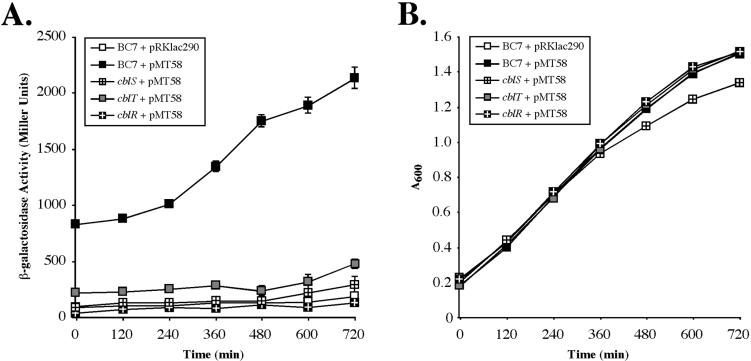
RNA dot blot analysis demonstrated that inactivation of the cblS, cblT, or cblR genes results in a dramatic reduction in the abundance of the cblA transcript. As previously demonstrated, the cblA gene is cotranscribed with the other genes in the cblBACDS operon from a principal promoter located upstream of cblB (41). Two-component signal transduction systems are known to control the expression of target genes at the level of transcription. To determine whether the drastic reduction in cblA transcript abundance in the cblS, cblT, and cblR null strains is due to a block in transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter, the activity of the cblB-lacZ transcriptional fusion construct pMT58 was measured in each of the three mutant backgrounds. Construct pMT58 harbors the cis-acting sequences required for maximal expression from the cblB-proximal promoter (41). Measurements of β-galactosidase activity were taken throughout growth in minimal M9 media—a condition found to result in strong transcriptional activation of the cblB promoter (41). As previously shown, the activity of the cblB transcriptional fusion in wild-type strain BC7 increased approximately twofold during mid- to late exponential phase, with peak activity observed in late exponential and stationary phases (Fig. 5A) (41). In contrast, the activity of the transcriptional fusion construct pMT58 in the cblS, cblT or cblR null strains was drastically reduced, with levels similar to those measured for the vector control pRKlac290 (Fig. 5A). These results demonstrate that inactivation of either cblS, cblT, or cblR leads to a block in transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter.
FIG. 5.
Effects of the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR mutations on activity of the cblB promoter. The β-galactosidase activities of the pRKlac290 vector control in wild-type strain BC7 or the cblB transcriptional fusion construct pMT58 in the wild-type strain BC7 and the cblS, cblT, or cblR mutants, grown in minimal M9 medium, were measured throughout the growth phase at 2-h intervals. (A) β-Galactosidase activity measurements in Miller units on the y axis and time on the x axis. The corresponding growth curves are shown in panel B.
Ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, or cblR modulates cable pilus expression.
To further characterize the role of the B. cenocepacia cblS, cblT, and cblR genes in cable pilus expression, each of the three genes was ectopically expressed in the wild-type strain (BC7) background. Whole-cell extracts from the wild-type strain, BC7, with or without pVN3 (cblS), pMT100 (cblT), or pMT66 (cblR) were prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting with CblA-specific antiserum. Introduction of the plasmid vector pMR4 into B. cenocepacia strain BC7 had no effect on CblA expression (Fig. 6A). Ectopic expression of either cblS, encoding a hybrid sensor kinase, or cblR, encoding the response regulator, resulted in an approximately twofold increase in the abundance of the CblA major pilin (Fig. 6A). Surprisingly, ectopic expression of cblT, predicted to encode a second hybrid sensor kinase, led to a block in CblA expression. These findings demonstrate that ectopic expression of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene product can significantly modulate cable pilus expression. Furthermore, the block in cable pilus biogenesis resulting from increased cblT expression in the wild-type strain suggests that the lack of complementation in the cblT null strain harboring pMT100 (cblT) is also likely to be a consequence of overexpression of the plasmid-borne cblT.
FIG. 6.
Effects of ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, or cblR on CblA major pilin and cblA transcript abundance in wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7. (A) Immunoblot of whole-cell extracts from strain BC7 with or without pMR4 (vector control), pVN3 (carrying cblS), pMT100 (carrying cblT), or pMT66 (carrying cblR), probed with the CblA-specific antiserum. Equal amounts of protein were loaded in each lane. The arrow indicates the position of the CblA protein band. (B) RNA dot blot of total RNA extracted from strain BC7 with or without pMR4 (vector control), pVN3 (carrying cblS), pMT100 (carrying cblT), or pMT66 (carrying cblR), hybridized with the cblA-specific probe. (C) Quantification of cblA transcript levels. The levels of the cblA transcript in each strain were normalized to the level of the cblA transcript in wild-type strain BC7, which was arbitrarily set to 100%. The asterisks denote P values of <0.04.
RNA dot blots were performed in order to examine whether the effects of ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, or cblR on CblA pilin abundance in B. cenocepacia are also manifested at the level of cblA transcript abundance. The levels of cblA transcript in the wild-type strain BC7 with or without the pMR4 vector were similar (Fig. 6B and C). However, when either plasmid pVN3, carrying the cblS gene, or pMT66, carrying the cblR gene, was introduced into B. cenocepacia strain BC7, the level of cblA mRNA increased by approximately twofold. In contrast, when plasmid pMT100, harboring the cblT gene, was introduced into the wild-type strain BC7, the abundance of cblA mRNA was dramatically reduced (Fig. 6B and C). The RNA dot blot analysis of strains ectopically expressing cblS, cblT, or cblR correlates with the immunoblot analysis, together demonstrating that overexpression of either cblS or cblR in B. cenocepacia strain BC7 leads to an increase in CblA expression, whereas overexpression of cblT leads to a dramatic decrease in the expression of CblA (Fig. 6A to C).
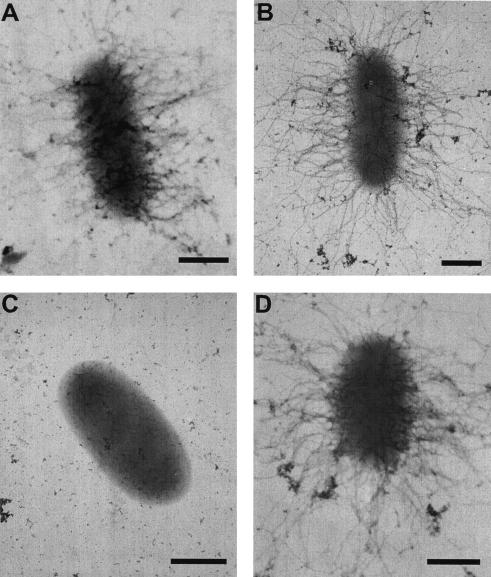
To further confirm the effects of ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, or cblR on cable pilus biogenesis, the wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 with or without plasmid-borne copies of each of the three genes was examined by TEM. Ectopic expression of the cblS or cblR gene appeared to result in a significant increase in the number of heavily piliated cells, with virtually every cell expressing numerous cable pili (Fig. 7B and D). In addition to being more numerous, the cable pili expressed by these strains also appeared increased in length (Fig. 7A, B, and D). Both of these observations are consistent with increased amounts of the CblA major pilin expressed by these strains, compared to wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7. In contrast, cable pili were not observed on cells of the wild-type strain BC7 ectopically expressing cblT (Fig. 7C), confirming that overexpression of cblT in B. cenocepacia strain BC7 leads to a block in cable pilus biogenesis.
FIG. 7.
Effects of ectopic expression of cblS, cblT, and cblR in the wild-type B. cenocepacia strain BC7 on cable pilus expression. Transmission electron micrographs of wild-type strain BC7 (A) or BC7 with pVN3 (carrying cblS) (B), pMT100 (carrying cblT) (C), or pMT66 (carrying cblR) (D). Bars = 0.5 μm.
DISCUSSION
This study describes the identification and characterization of the B. cenocepacia cblT and cblR genes, which, along with the previously identified cblS gene, are predicted to encode a multicomponent signal transduction system controlling the expression of cable pili. Inactivation of the cblS, cblT, or cblR gene led to a block in cable pilus expression and a severe decrease in cblA transcript abundance. The block in cable pilus expression in the cblS, cblT, and cblR null strains was manifested at the level of transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter. The lack of transcription from the cblB-proximal promoter in these mutants lends further support to the hypothesis that cblS, cblT, and cblR encode a signal transduction system controlling transcription of the cable pilus biosynthetic operon. In addition to the requirement of cblS, cblT, and cblR in cable pilus expression, we have also demonstrated that ectopic expression of each of the three genes in the wild-type B. cenocepacia strain has a profound effect on cable pilus expression. Ectopic expression of the cblS and cblR genes led to an increase, while ectopic expression of cblT resulted in a severe reduction in abundance of the CblA major pilin. The levels of the CblA protein were directly proportional to the cblA transcript abundance in the corresponding strains. To our knowledge, this is the first report to identify and characterize members of bacterial two-component signal transduction systems in B. cenocepacia.
The cblS gene, predicted to encode a hybrid sensor kinase, is cotranscribed with the cblBACD biosynthetic genes. The organization of the cbl locus is highly unusual, since bacterial regulatory genes, particularly those encoding members of two-component signal transduction pathways, are typically organized into independent monocystronic or polycistronic genetic units. This study has demonstrated that increased expression of the cblS gene in B. cenocepacia leads to a significant increase in cable pilus expression. It is possible that accumulation of the CblS sensor kinase in B. cenocepacia would result in a positive feedback mechanism, leading to a further increase in cable pilus expression, as well as the expression of the CblS sensor. This positive feedback mechanism may, at least in part, explain the growth-phase-dependent transcriptional activation of the cblB-proximal promoter during mid-exponential growth phase.
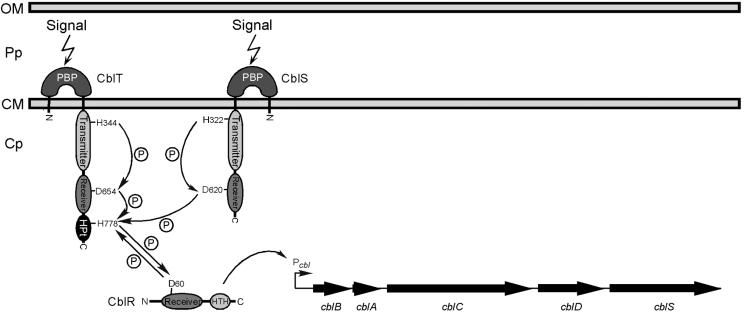
The B. cenocepacia cblS and cblT genes are both predicted to encode hybrid sensor kinases, while the cblR gene is predicted to encode a cognate DNA-binding response regulator. Amino acid sequence analysis of the cblS and cblT gene products revealed a key difference in domain architecture between the two putative sensor kinases. While transmitter and receiver domains were identified in both gene products, only CblT is predicted to have an HPt domain, known to be required for the transfer of phosphoryl groups to the receiver domain of the cognate response regulators in other phosphorelay pathways (Fig. 2) (3, 11, 20, 42). The lack of an HPt domain in CblS suggests that the potential transfer of phosphoryl groups from CblS to CblR must occur through an intermediate protein, which has a functional HPt domain. It is therefore possible that CblS, upon initial phosphorylation, transfers phosphoryl groups onto CblT, which in turn would phosphorylate CblR (Fig. 8). Phosphorylation of the CblR response regulator would lead to its activation and transcription of the cblBACDS cable pilus biosynthetic operon (Fig. 8). Preliminary studies in our laboratory support this model, since we have found that cblT is essential for cable pilus biogenesis (Fig. 3 and 4), while ectopic expression of the CblS putative sensor kinase in the cblT null strain is not sufficient for induction of cable pilus expression (data not shown).
FIG. 8.
A working model for the CblSTR signal transduction pathway. (i) Upon receiving a signal from the environment via their periplasmic domains, the CblS and/or CblT hybrid sensor kinases undergo autophosphorylation at the histidine H322 or H344 residues, respectively, catalyzed by hydrolysis of ATP by the transmitter domain. It is also possible that CblS and CblT form homodimers and/or heterodimers, which may lead to cross-phosphorylation. (ii) Phosphotransfer reactions (indicated by arrows and circled P) are carried out between the transmitter, receiver, and HPt domains of CblS and CblT. The transfers of phosphoryl groups may occur intramolecularly and/or intermolecularly. (iii) The aspartate D60 in the receiver domain of the CblR response regulator is phosphorylated through interactions with the CblT HPt domain, leading to activation of CblR and transcription of the cblBACDS operon, possibly by directly binding the cblB promoter. Abbreviations: HPt, histidine phosphotransfer domain; HTH, helix-turn-helix domain; PBPb, bacterial periplasmic substrate-binding protein domain; Cp, cytoplasm; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; Pp, periplasm; OM, outer membrane.
Hybrid sensor kinases, including Bordetella spp. BvgS and E. coli ArcB, typically function as dimers (7, 15). Homodimerization of sensor kinases results in cross-autophosphorylation of the monomers within their transmitter domains. It is possible that CblS and CblT form homodimers and/or heterodimers, leading to intramolecular and/or intermolecular phosphotransfer reactions, respectively. Such a mechanism would allow CblS to facilitate the flow of phosphoryl groups to the CblR response regulator through the HPt domain of CblT (Fig. 8).
The regulatory pathway controlling the expression of cable pili in B. cenocepacia is unusual for bacteria, since it appears to contain two distinct sensor kinase proteins, encoded by the cblS and cblT genes. Although cross talk between components of certain distinct two-component systems is known to occur (10, 44), most signal transduction systems of this type are comprised of a single sensor kinase and its cognate response regulator. A notable exception to this paradigm is the Kin/Spo signal transduction system controlling sporulation in B. subtilis. In this system, five distinct sensor kinase proteins, designated KinA, KinB, KinC, KinD, and KinE, phosphorylate the receiver domain of Spo0F, which can subsequently phosphorylate the HPt-containing Spo0B protein (18). Phosphorylation of Spo0B leads to the transfer of the phosphoryl group onto the Spo0A response regulator, which activates transcription of the target genes (3). Each of the five B. subtilis sensor kinases is capable of phosphorylating Spo0F, albeit with various efficiencies (18). In contrast, we have shown that both the cblS and cblT genes are essential for transcription of the cblBACDS operon and cable pilus expression, suggesting that the function of the CblS and CblT putative sensor kinases is exhibited at the level of activation of the CblR response regulator.
Another system which may be analogous to the proposed B. cenocepacia CblSTR pathway is the RcsC/YojN/RcsB signal transduction system, which modulates the expression of the capsular polysaccharide (cps) biosynthetic operon in E. coli. The RcsC and YojN proteins are both members of the hybrid sensor kinase family. The phosphorelay is thought to be initiated by autophosphorylation of the transmitter domain of RcsC, followed by transfer of the phosphoryl group onto the conserved Asp residue within the receiver domain of RcsC (38). The phosphoryl group is then transferred onto a conserved His residue in the HPt domain of YojN, which serves as a bridge component for the phosphorylation of the RcsB response regulator, leading to transcriptional activation of cps gene expression. The function of the YojN protein is similar to the proposed function of the B. cenocepacia CblT, whose HPt domain may act as an intermediate in transfer of phosphoryl groups from CblS to CblR. However, in addition to lacking a receiver domain, YojN does not appear to have a functional transmitter domain, suggesting that it may serve solely as a bridge component in the phosphorelay, rather than being able to independently sense and respond to environmental stimuli (38). In contrast, both the CblS and CblT putative sensor kinases of B. cenocepacia appear to have complete transmitter domains, indicating that they are capable of initiating the phosphorelay. Future studies will examine the ability of cblS and cblT gene products to autophosphorylate, as well as precisely mapping the potential flow of phosphoryl groups between components of the B. cenocepacia CblSTR signal transduction pathway.
The putative sensor kinase encoded by the cblT gene appears to be required for the expression of cable pili. However, cblT can also block cable pilus expression when it is expressed at increased levels. These results suggest that the relative levels of CblT sensor kinase need to be within a defined range in order for cable pilus expression to occur. Increased levels of CblT may block expression of cable pili by favoring homodimerization and self-sequestration from CblS. Additionally, it is known that phosphotransfer reactions in bacterial four-step phosphorelays can be reversible. It has been shown that reversal of the flow of phosphoryl groups can lead to dephosphorylation, and thus inactivation, of response regulators by their cognate hybrid sensor kinases (1, 12). The CblT protein, under the conditions examined, may preferentially act as a phosphatase in the absence of a sufficient level of CblS, resulting in dephosphorylation of the CblR response regulator and a block in cable pilus gene expression.
The expression of certain pilus genes in other bacterial species is known to be controlled by two-component signal transduction systems. Expression of E. coli P pili is modulated by the CpxAR two-component system (17), while expression of the type IV pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa is controlled by homologous two-component systems designated PilAB and PilRS, respectively (2, 37). However, the signal transduction system encoded by the cblS, cblT, and cblR genes represents a novel, and thus far unique, mechanism for transcriptional regulation of a pilus gene cluster belonging to the CS1 family. The expression of other CS1 family pilus gene clusters is positively regulated by AraC-like proteins, termed Rns or CfaD, which relieve H-NS-mediated gene repression (19, 24). The cblS, cblT, and cblR genes are a unique feature of the B. cenocepacia locus, which suggests that they have been acquired and/or employed by the pathway after the emergence of the ancestral CS1 pilus biogenesis locus, encompassing orthologs of cblBACD. It is also possible that either the cblS or the cblT gene arose through a duplication event. However, given the significant sequence divergence between cblS and cblT, with the amino acid sequence identity between their respective gene products of 43%, a gene duplication event is unlikely to have occurred in recent evolutionary history.
Cable pilus expression appears to be tightly controlled, since inactivation of either cblS, cblT, or cblR leads to a block in transcription of the cblBACDS biosynthetic operon and cable pilus biogenesis. It is possible that the postulated B. cenocepacia CblSTR signal transduction system responds to changes in osmolarity, pH, and/or temperature, which have been shown to affect transcription of the cblBACDS biosynthetic operon (41). Moreover, certain two-component signal transduction systems, including Bordetella spp. BvgAS and E. coli CpxAR, control the expression of multiple, functionally diverse target genes (7, 25). It will be of interest to examine whether the putative signal transduction system encoded by the B. cenocepacia cblSTR genes also controls the expression of additional B. cenocepacia genes, including both known and unknown virulence factors. Future studies will continue to elucidate the signal transduction pathway of the CblSTR system, its role in cable pilus expression, and its potential control of a larger subset of target genes in B. cenocepacia.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant MOHR02G0 from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. M. T. was the recipient of a Student Traineeship grant (03H0) from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
We thank Victoria Nichols and Bridget Johnson for assistance with generating subclones, Tim Leonard for technical assistance, and Chris Frethem for assistance with TEM, and Gary Dunny for critical reading of the manuscript.
REFERENCES
- 1.Ansaldi, M., C. Jourlin-Castelli, M. Lepelletier, L. Theraulaz, and V. Mejean. 2001. Rapid dephosphorylation of the TorR response regulator by the TorS unorthodox sensor in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 183:2691-2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Boyd, J. M., T. Koga, and S. Lory. 1994. Identification and characterization of PilS, an essential regulator of pilin expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Gen. Genet. 3:565-574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Burbulys, D., K. A. Trach, and J. A. Hoch. 1991. Initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell 64:545-552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burkholder, W. H. 1950. Sour skin: a bacterial rot of onion bulbs. Phytopathology 40:115-117. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Butler, S., C. Doherty, J. Hughes, J. Nelson, and J. Govan. 1995. Burkholderia cepacia and cystic fibrosis: do natural environments present a potential hazard? J. Clin. Microbiol. 33:1001-1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coenye, T., P. Vandamme, J. R. W. Govan, and J. J. LiPuma. 2001. Taxonomy and identification of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39:3427-3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cotter, P. A., and A. M. Jones. 2003. Phosphorelay control of virulence gene expression in Bordetella. Trends Microbiol. 11:367-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DeShazer, D., and D. E. Woods. 1996. Broad-host-range cloning and cassette vectors based on the R388 trimethoprim resistance gene. BioTechniques 20:762-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fabret, C., V. A. Feher, and J. A. Hoch. 1999. Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world. J. Bacteriol. 181:1975-1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fisher, S. L., W. Jiang, B. L. Wanner, and C. T. Walsh. 1995. Cross-talk between the histidine protein kinase VanS and the response regulator PhoB. Characterization and identification of a VanS domain that inhibits activation of PhoB. J. Biol. Chem. 270:23143-23149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Freeman, J. A., and B. L. Bassler. 1999. Sequence and function of LuxU: a two-component phosphorelay protein that regulates quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 181:899-906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Georgellis, D., O. Kwon, P. De Wulf, and E. C. Lin. 1998. Signal decay through a reverse phosphorelay in the Arc two-component signal transduction system. J. Biol. Chem. 273:32864-32869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gober, J. W., and L. Shapiro. 1992. A developmentally regulated Caulobacter flagellar promoter is activated by 3′ enhancer and IHF binding elements. Mol. Biol. Cell 3:913-926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Govan, J. R. W., and V. Deretic. 1996. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol. Rev. 60:539-574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grebe, T. W., and J. B. Stock. 1999. The histidine protein kinase superfamily. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 41:139-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hoch, J. A. 2000. Two-component and phosphorelay signal transduction. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3:165-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hung, D. L., T. L. Raivio, C. H. Jones, T. J. Silhavy, and S. J. Hultgren. 2001. Cpx signaling pathway monitors biogenesis and affects assembly and expression of P pili. EMBO J. 20:1508-1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jiang, M., W. Shao, M. Perego, and J. A. Hoch. 2000. Multiple histidine kinases regulate entry into stationary phase and sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 38:535-542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jordi, B. J. A. M., B. Dagberg, L. A. M. de Haan, A. M. Hamers, B. A. M. van der Zeijst, W. Gaastra, and B. E. Uhlin. 1992. The positive regulator CfaD overcomes the repression mediated by histone-like protein H-NS (H1) in the CFA/I fimbrial operon of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 11:2627-2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kwon, O., D. Georgellis, and E. C. Lin. 2000. Phosphorelay as the sole physiological route of signal transmission by the Arc two-component system of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 182:3858-3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mahenthiralingam, E., A. Baldwin, and P. Vandamme. 2002. Burkholderia cepacia complex infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Med. Microbiol. 51:533-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miller, J. H. 1972. Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 24.Murphree, D., B. Froehlich, and J. R. Scott. 1997. Transcriptional control of genes encoding CS1 pili: negative regulation by a silencer and positive regulation by Rns. J. Bacteriol. 179:5736-5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Raivio, T. L., and T. J. Silhavy. 1999. The sigmaE and Cpx regulatory pathways: overlapping but distinct envelope stress responses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2:159-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Richardson, J., D. E. Stead, and R. H. Coutts. 2001. Incidence of the cblA major subunit pilin gene amongst Burkholderia species. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 196:61-66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sajjan, U., L. Liu, A. Lu, T. Spilker, J. Forstner, and J. J. LiPuma. 2002. Lack of cable pili expression by cblA-containing Burkholderia cepacia complex. Microbiology 148:3477-3484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sajjan, U. S., M. Corey, M. A. Karmali, and J. F. Forstner. 1992. Binding of Pseudomonas cepacia to normal human intestinal mucin and respiratory mucin from patients with cystic fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 89:648-656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sajjan, U. S., and J. F. Forstner. 1992. Identification of the mucin-binding adhesin of Pseudomonas cepacia isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. Infect. Immun. 60:1434-1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sajjan, U. S., L. Sun, R. Goldstein, and J. F. Forstner. 1995. Cable (cbl) type II pili of cystic fibrosis-associated Burkholderia (Pseudomonas) cepacia: nucleotide sequence of the cblA major subunit pilin gene and novel morphology of the assembled appendage fibers. J. Bacteriol. 177:1030-1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sajjan, U. S., F. A. Sylvester, and J. F. Forstner. 2000. Cable-piliated Burkholderia cepacia binds to cytokeratin 13 of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 68:1787-1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sajjan, U. S., H. Xie, M. D. Lefebre, M. A. Valvano, and J. F. Forstner. 2003. Identification and molecular analysis of cable pilus biosynthesis genes in Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiology 149:961-971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sambrook, J., E. F. Fritsch, and T. Maniatis. 1989. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 34.Simon, R., U. Priefer, and A. Puhler. 1983. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Bio/Technology 1:784-790. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stock, A. M., V. L. Robinson, and P. N. Goudreau. 2000. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69:183-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sun, L., R. Jiang, S. Steinbach, A. Holmes, C. Campanelli, J. Forstner, U. Sajjan, Y. Tan, M. Riley, and R. Goldstein. 1995. The emergence of a highly transmissible lineage of cbl+ Pseudomonas (Burkholderia) cepacia causing CF centre epidemics in North America and Britain. Nat. Med. 1:661-666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Taha, M. K., B. Dupuy, W. Saurin, M. So, and C. Marchal. 1991. Control of pilus expression in Neisseria gonorrhoeae as an original system in the family of two-component regulators. Mol. Microbiol. 5:137-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takeda, S.-I., Y. Fujisawa, M. Matsubara, H. Aiba, and T. Mizuno. 2001. A novel feature of the multistep phosphorelay in Escherichia coli: a revised model of the RcsC→YojN→RcsB signalling pathway implicated in capsular synthesis and swarming behaviour. Mol. Microbiol. 40:440-450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tomich, M., C. A. Herfst, J. W. Golden, and C. D. Mohr. 2002. Role of flagella in Burkholderia cepacia host cell invasion. Infect. Immun. 70:1799-1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tomich, M., and C. D. Mohr. 2003. Adherence and autoaggregation phenotypes of a Burkholderia cenocepacia cable pilus mutant. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 228:287-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tomich, M., and C. D. Mohr. 2004. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional control of cable pilus gene expression in Burkholderia cenocepacia. J. Bacteriol. 186:1009-1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Uhl, M. A., and J. F. Miller. 1996. Integration of multiple domains in a two-component sensor protein: the Bordetella pertussis BvgAS phosphorelay. EMBO J. 15:1028-1036. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vandamme, P., B. Holmes, T. Coenye, J. Goris, E. Mahenthiralingam, J. J. LiPuma, and J. R. Govan. 2003. Burkholderia cenocepacia sp. nov.—a new twist to an old story. Res. Microbiol. 154:91-96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Verhamme, D. T., J. C. Arents, P. W. Postma, W. Crielaard, and K. J. Hellingwerf. 2002. Investigation of in vivo cross-talk between key two-component systems of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 148:69-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]