Abstract
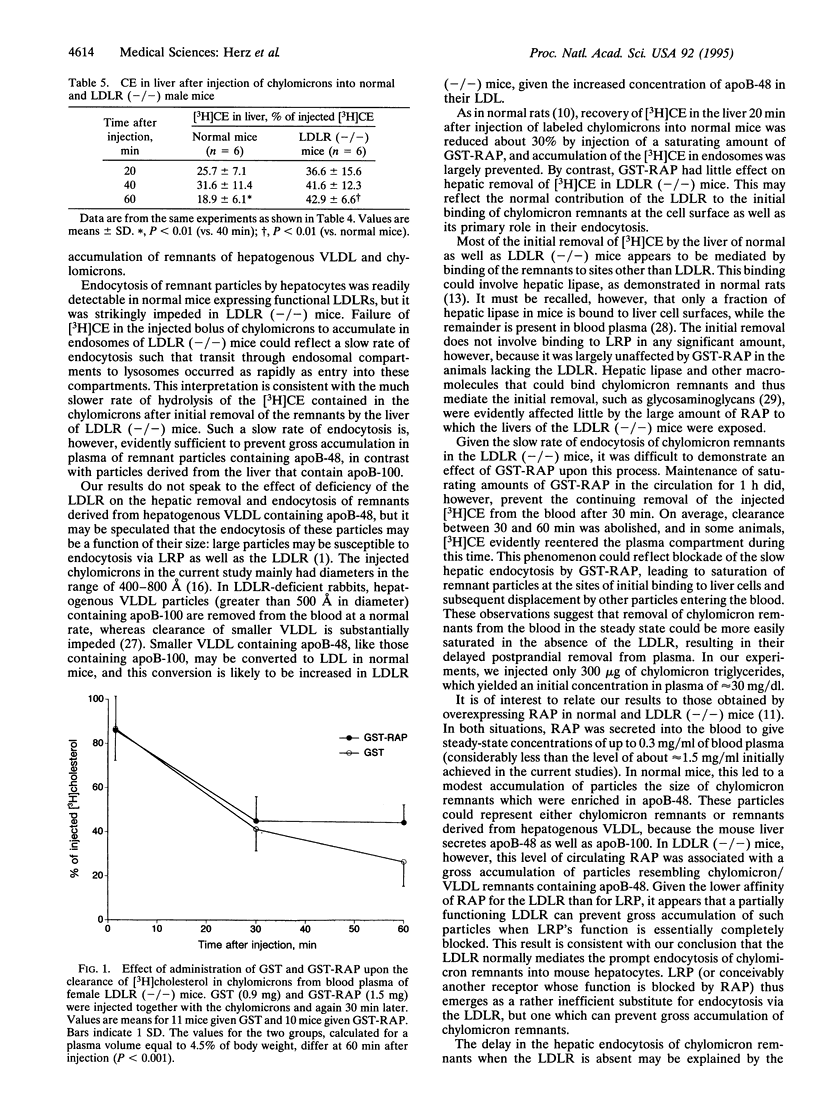
Two endocytic receptors, the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor (LDLR) and the LDLR-related protein (LRP), are thought to act in concert in the hepatic uptake of partially metabolized dietary lipoproteins, the chylomicron remnants. We have evaluated the role of these two receptors in the hepatic metabolism of chylomicron remnants in normal mice and in LDLR-deficient [LDLR (-/-)] mice. The rate of chylomicron remnant removal by the liver was normal up to 30 min after intravenous injection of chylomicrons into LDLR (-/-) mice and was unaffected by receptor-associated protein (RAP), a potent inhibitor of ligand binding to LRP. In contrast, endocytosis of the remnants by the hepatocytes, measured by their accumulation in the endosomal fraction and by the rate of hydrolysis of component cholesteryl esters, was dramatically reduced in the absence of the LDLR. Coadministration of RAP prevented the continuing hepatic removal of chylomicron remnants in LDL (-/-) mice after 30 min, consistent with blockade of the slow endocytosis by a RAP-sensitive process. Taken together with previous studies, our results are consistent with a model in which the initial hepatic removal of chylomicron remnants is primarily mediated by mechanisms that do not include LDLR or LRP, possibly involving glycosaminoglycan-bound hepatic lipase and apolipoprotein E. After the remnants bind to these alternative sites on the hepatocyte surface, endocytosis is predominantly mediated by the LDLR and also by a slower and less efficient backup process that is RAP sensitive and therefore most likely involves LRP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain C. C., Poon L. S., Chan C. S., Richmond W., Fu P. C. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):470–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belcher J. D., Hamilton R. L., Brady S. E., Hornick C. A., Jaeckle S., Schneider W. J., Havel R. J. Isolation and characterization of three endosomal fractions from the liver of estradiol-treated rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasaemle D. L., Cornely-Moss K., Bensadoun A. Hepatic lipase treatment of chylomicron remnants increases exposure of apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res. 1993 Mar;34(3):455–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Validation of a procedure for exogenous isotopic labeling of lipoprotein triglyceride with radioactive triolein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 25;573(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. The metabolism of chylomicron cholesterol ester in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1886–1896. doi: 10.1172/JCI104645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Moorehouse A., Havel R. J. Isolation and properties of nascent lipoproteins from highly purified rat hepatocytic Golgi fractions. J Lipid Res. 1991 Mar;32(3):529–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Role of the liver in hyperlipidemia. Semin Liver Dis. 1992 Nov;12(4):356–363. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Strickland D. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S. 39-kDa protein modulates binding of ligands to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21232–21238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Gerard R. D., Hammer R. E., Herz J. Hypercholesterolemia in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice and its reversal by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):883–893. doi: 10.1172/JCI116663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi S., Herz J., Maeda N., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The two-receptor model of lipoprotein clearance: tests of the hypothesis in "knockout" mice lacking the low density lipoprotein receptor, apolipoprotein E, or both proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4431–4435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Busch S. J., Cardin A. D. Glycosaminoglycans: molecular properties, protein interactions, and role in physiological processes. Physiol Rev. 1991 Apr;71(2):481–539. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.2.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Z. S., Brecht W. J., Miranda R. D., Hussain M. M., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Role of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the binding and uptake of apolipoprotein E-enriched remnant lipoproteins by cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 15;268(14):10160–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Z. S., Lauer S. J., Fazio S., Bensadoun A., Taylor J. M., Mahley R. W. Enhanced binding and uptake of remnant lipoproteins by hepatic lipase-secreting hepatoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13429–13436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Hornick C. A., Havel R. J. Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in WHHL rabbits: a mechanism genetically distinct from the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotite L., Bergeron N., Havel R. J. Quantification of apolipoproteins B-100, B-48, and E in human triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1995 Apr;36(4):890–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Herz J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (LRP). Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:601–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokuno H., Brady S., Kotite L., Herz J., Havel R. J. Effect of the 39-kDa receptor-associated protein on the hepatic uptake and endocytosis of chylomicron remnants and low density lipoproteins in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13238–13243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J., Bengtsson-Olivecrona G., Olivecrona T. Mouse preheparin plasma contains high levels of hepatic lipase with low affinity for heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 14;878(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinsztein D. C., Cohen J. C., Berger G. M., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Coetzee G. A., Gevers W. Chylomicron remnant clearance from the plasma is normal in familial hypercholesterolemic homozygotes with defined receptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1306–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI114839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runquist E. A., Havel R. J. Acid hydrolases in early and late endosome fractions from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22557–22563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafi S., Brady S. E., Bensadoun A., Havel R. J. Role of hepatic lipase in the uptake and processing of chylomicron remnants in rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1994 Apr;35(4):709–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Sheng Z., Ishibashi S., Herz J. Inhibition of hepatic chylomicron remnant uptake by gene transfer of a receptor antagonist. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1471–1474. doi: 10.1126/science.7515194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E., Chao Y., Havel R. J. Determinants of hepatic uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5475–5480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada N., Shames D. M., Takahashi K., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoprotein B-100 in large very low density lipoproteins of blood plasma. Kinetic studies in normal and Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2106–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI113832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



