Abstract
INTRODUCTION
The orientation of acetabular component is influenced by pelvic tilt, body position and individual variation in pelvic parameters. Most post-operative adverse events may be attributed to malposition of the component in the functional position. There is evidence that orientation of the pelvis changes from the supine to standing position. Authors report a case of recurrent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty due to excessive pelvic tilting.
PRESENTATION OF CASE A 69-year old female with coxarthrosis had undergone total hip replacement with recurrent dislocation of the hip on bearing weight in spite of using constrained acetabular component.
DISCUSSION
Our case report substantiates the influence of pelvic tilt, incurred by a sagittal deformity of spine, on dynamic orientation of the acetabular cup which was positioned in accordance with the anatomic landmarks alone. If the reference is only bony architecture and dynamic positions of the pelvis are not taken into account, improper functional orientation of the acetabular cup can result in sitting and standing positions. These can induce instability even in anatomically appropriately oriented acetabular component.
CONCLUSION
The sagittal position of pelvis is a key factor in impingement and dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Pelvic tilting affects the position of acetabular component in the sagittal plane of the body as compared with its anatomic position in the pelvis. We suggest a preoperative lateral view of spine-pelvis, in upright and supine position for evaluation of a corrective adaptation of the acetabular cup accordingly with pelvic balance.
Keywords: Dislocation, Impingement, Surgical anteversion, Acetabular component, Spino-pelvis sagittal balance, Total hip arthroplasty
1. Introduction
In total hip arthroplasty, anterior or posterior tilt of the pelvis can affect the position of acetabular component in the sagittal plane of the body as compared with its anatomic position in the pelvis.1–3 The rotation of pelvis leads to anterior tilt (where the upper portion of the pelvis tips forward) and posterior tilt (upper portion of the pelvis tips backward).3 The aging process and spinal deformities may lead to an altered sagittal balance. The sacrum and pelvis therefore forms a rigid structure (sacropelvis), which translates and rotates around the bicoxofemoralaxis for the necessary compensatory balance.4
Of importance is the fact that each individual possesses a pelvic equilibrium which is specific and is different in standing and lying positions; however there are variations in the position of pelvis from the lying to the standing position.2,5,6 Consequently the orientation of the acetabular cup version changes dynamically from supine to standing position. In the presence of a normal range of motion of the spine, the pelvis rotates around the transverse axis giving some room for adjustment during movements of the prosthetic hip. We now report a patient who had recurrent dislocations after total hip arthroplasty because of excessive pelvic tilting.
2. Presentation of case
This was a 69-year old female with painless limp without any significant history of trauma, with associated severe degenerative kypho-scoliosis. She had left hip coxarthrosis [Fig. 1]. Total hip arthroplasty was performed by a posterolateral approach in lateral decubitus position, using a ceramic on metal articulation. A 48 mm acetabular cup (Pinnacle®) 28 mm metal head and a standard offset stem (Summit®) [Depuy, USA] were used.
Fig. 1.
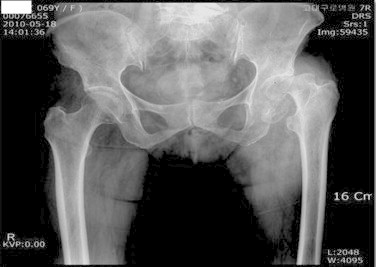
Anteroposterior view of pelvis with both hips showing left hip coxarthrosis.
Postoperative radiographs showed inclination of the cup 45° on anterior posterior view and anteversion 24° on the lateral view [Fig. 2]. Hip was stable preoperatively with adequate soft tissue tension. The hip dislocated anteriorly, postoperative three months during standing position while walking, and was confirmed by radiography [Fig. 3]. Closed reduction was followed by recurrence of anterior dislocation four weeks later. Revision was done with a constrained liner (Duraloc shell, 50 mm constrained liner 28 × 50 mm Depuy USA). Postoperative radiographs showed inclination of the cup 45° and acetabular component anteversion 24° in supine position.
Fig. 2.
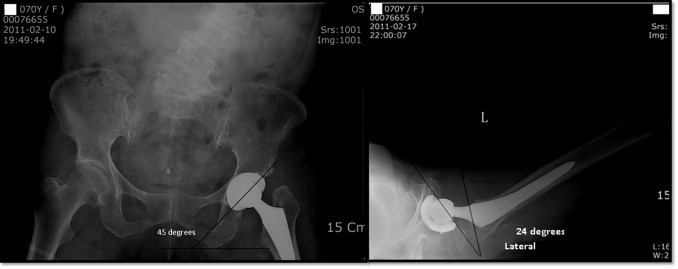
Anteroposterior and lateral view of total hip replacement.
Fig. 3.
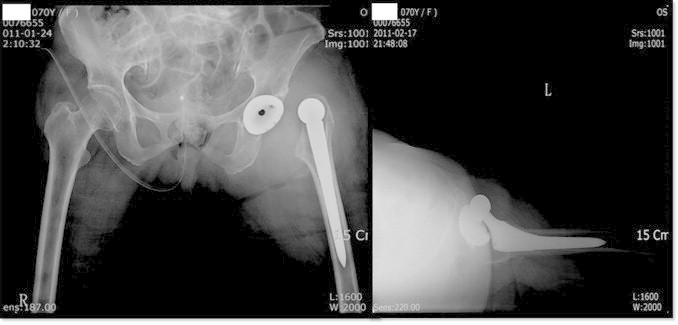
Anteroposterior and lateral view of dislocation of total hip.
After episode of anterior dislocation with constrained liner [Fig. 4], the relevant pelvic parameters were studied but only open reduction with exchange of constrained polyethylene liner was done because patient's guardian refused re-revision of second acetabular cup. During the postoperative period the patient was maintained in the hip brace at 15° abduction and 15° flexion for six months by locking the joint in the brace and allowing only about 75° of flexion of the hip joint and also preventing adduction during walking in standing position. The patient had been amenable to postoperative prophylactic care and the tendency to dislocation eventually had resolved.
Fig. 4.
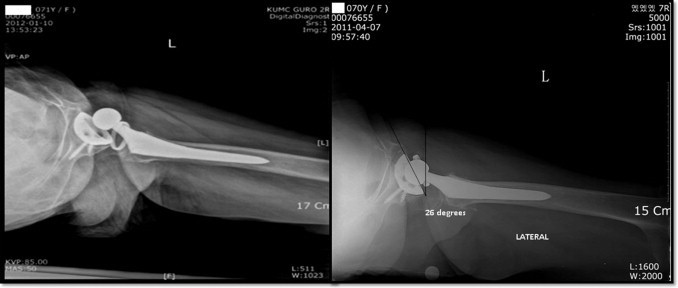
Lateral view of dislocated revised hip and post-relocation of dislocation.
Apart from routine radiographs, sacral tilt (ST) and measured acetabular tilt (MAT) were determined in lateral radiographs for evaluation of any pelvic tilt, as described by Lazennec et al.3 Measurements were made using a digitized computer system PACS (picture archiving and communication system PiView STAR version 5, Infinitt, Seoul Korea). ST measured in supine and standing position was 49° and 16° and MAT in supine and standing position was 25° and 60° respectively [Fig. 5].
Fig. 5.
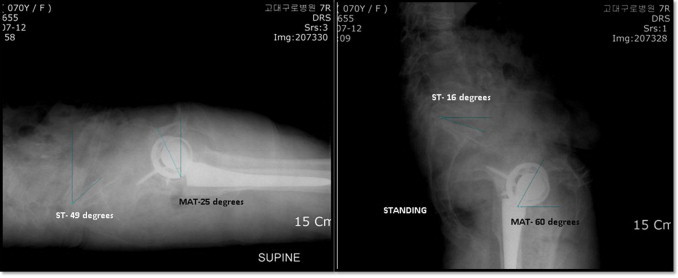
Sacral tilt and measured acetabular tilt in standing and supine positions.
3. Discussion
The sagittal position of pelvis is a key factor in impingement as well as dislocation; it is not vertical nor is it static.7 In supine position, the pelvis tilts anteriorly, which decreases anteversion of the acetabular component, and in the standing and sitting position, the reverse happens and anteversion is increased.3,8
Optimal adjustment of the acetabular cup is of utmost importance for ensuring stability and maximum range of motion of the prosthetic joint, without causing impingement on the femoral neck.10 After total hip arthroplasty increased anterior tilt of acetabular component can cause posterior impingement and anterior dislocation, similarly, posterior tilt or retroversion can cause anterior impingement and posterior dislocation.11
Impingement was prevalent even when components were implanted in the anatomic safe zone in a study of 162 retrieved acetabular components.12 With increased trend of using hard on hard bearing surfaces, minimizing the risk of impingement which leads to catastrophic events like chip fracture, metallosis, and loosening in these bearing surfaces should be considered.
When faced with this disappointing outcome, it is worth reckoning that component orientation is made in static lying position, whereas prosthesis dislocates out of the result of a dynamic phenomenon which occurs during change in position during the movements of daily life.2,3,5,7 This is a reasonable explanation, as to why an anatomically oriented cup, placed in supine position may functionally prove to be wrongly oriented, so favoring subsequent dislocations.
The patient described here had a fixed kyphoscoliotic deformity, which was compensated by pelvis being tilted posteriorly with a more vertical position of the sacrum. This verticalized the cup and placed the hip in hyperextension during change of position from supine to standing position.2,3 A retroverted pelvis led to functional anteversion that was more than the normal range, causing uncovering of the femoral head anteriorly.8 Even though the cup was placed appropriately in accordance with the pelvic bony landmarks it led to posterior impingement and anterior dislocation.
This patient had constant low values of ST in supine and standing position, signifying posterior tilt of the pelvis. ST showed variation of 33° from supine to standing position, which was much more than normal variation.2,6,9 Reported normal range of pelvic extension from supine to standing position is less than 10–15°.2,5 The patient was clearly an outlier among the 5–7% of people who demonstrate excessive hyperextension of hip from supine to standing position.2 There is significant inter-subject and intra-subject variation in ST and MAT values from supine to standing position which is directly influenced by the mechanics of lumbosacral junction and resulted in a dynamic functional anteversion that was high outside the safe zone. These require unique adjustment in acetabular cup alignment to maximize stability and avoid impingement and, or dislocation after total hip arthroplasty.2,3,7
ST and MAT are functional angles and the orientation of acetabulum in supine and standing positions and can be accurately extrapolated from the correlation between pelvic parameters.
4. Conclusion
We would conclude that there are outliers in the pelvis tilt among the patient who undergo total hip arthroplasty. Pelvic tilting is dynamic and not static. A detailed analysis of individual sagittal balance allows a precise evaluation of the amount of sagittal pelvic hyper-rotation which influences acetabular cup orientation and allows preventive or prospective adjustment of the cup. Therefore we intend in future to request a preoperative lateral x-ray view of the spine-pelvis in the upright, supine position and lateral decubitus to evaluate the global sagittal balance, and to plan corrective adaptation of pelvic balance.
Conflict of interest
None.
Funding
None.
Ethical approval
Consent was obtained from patient. The patient's detail has been kept anonymous in the manuscript.
Author's contributions
Prof Won Yong Shon: Performing the surgery, study concept, data interpretation.
Vivek Sharma: Data collection, writing the paper, drafting the article.
Dong Hun Suh: Data analysis,data collection, interpretation.
Jun Gyu Moon: Data analysis,data collection, interpretation.
Jong Keon Oh: Writing the paper, interpretation.
Contributor Information
Won Yong Shon, Email: shonwy@hotmail.com.
Dong Hun Suh, Email: hun.suh@gmail.com.
References
- 1.Haenle M., Heitner A., Mittelmeier W., Barbano R., Scholz R., Steinhauser E. Assessment of cup position from plain radiographs: impact of pelvic tilting. Surg Radiol Anat. 2007;29(1):29–35. doi: 10.1007/s00276-006-0167-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Shon W.Y., Gupta S., Biswal S., Hur C.Y., Jajodia N., Hong S.J. Validation of a simple radiographic method to determine variations in pelvic and acetabular cup sagittal plane alignment after total hip arthroplasty. Skelet Radiol. 2008;37(12):1119–1127. doi: 10.1007/s00256-008-0550-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lazennec J.Y., Charlot N., Gorin M., Roger B., Arafati N., Bissery A. Hip–spine relationship: a radio-anatomical study for optimization in acetabular cup positioning. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004;26(2):136–144. doi: 10.1007/s00276-003-0195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vrtovec T., Janssen M.M.A., Likar B., Castelein R.M., Viergever M.A., Pernus F. A review of methods for evaluating the quantitative parameters of sagittal pelvic alignment. Spine J. 2012;12(5):433–446. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.02.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eddine T.A., Migaud H., Chantelot C., Cotten A., Fontaine C., Duquennoy A. Variations of pelvic anteversion in the lying and standing positions: analysis of 24 control subjects and implications for CT measurement of position of a prosthetic cup. Surg Radiol Anat. 2001;23(2):105–110. doi: 10.1007/s00276-001-0105-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nishihara S., Sugano N., Nishii T., Ohzono K., Yoshikawa H. Measurements of pelvic flexion angle using three-dimensional computed tomography. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(411):140–151. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000069891.31220.fd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ishida T., Inaba Y., Kobayashi N., Iwamoto N., Yukizawa Y., Choe H. Changes in pelvic tilt following total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(6):682–688. doi: 10.1007/s00776-011-0153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Watanabe W, 1, Sato K., Itoi E., Yang K., Watanabe H. Posterior pelvic tilt in patients with decreased lumbar lordosis decreases acetabular femoral head covering. Orthopedics. 2002;25(3):321–324. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-20020301-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lembeck B., Mueller O., Reize P., Wuelker N. Pelvic tilt makes acetabular cup navigation inaccurate. Acta Orthop. 2005;76(4):517–523. doi: 10.1080/17453670510041501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yoshimine F. The safe-zones for combined cup and neck anteversions that fulfill the essential range of motion and their optimum combination in total hip replacements. J Biomech. 2006;39(7):1315–1323. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McCollum D.E., Gray W.J. Dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Causes and prevention. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;261:159–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shon W.Y., Baldini T., Peterson M.G., Wright T.M., Salvati E.A. Impingement in total hip arthroplasty a study of retrieved acetabular components. J Arthroplast. 2005;20(4):427–435. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2004.09.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


