Abstract
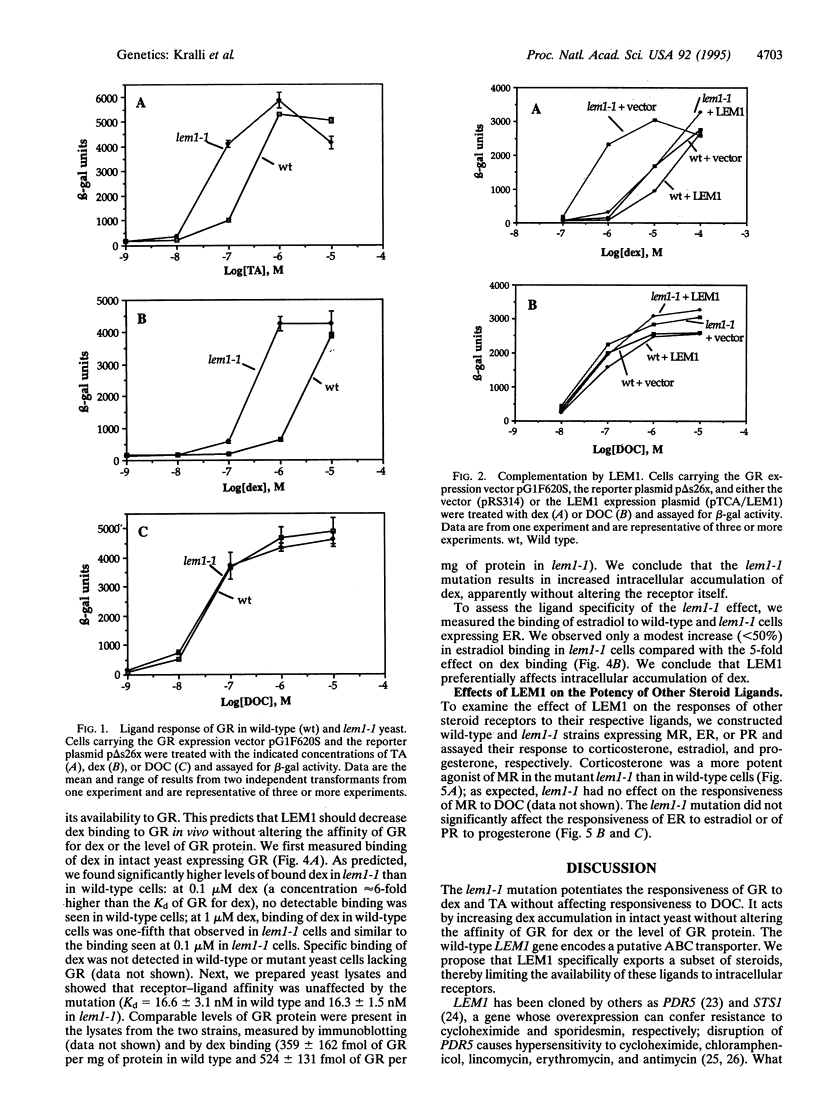
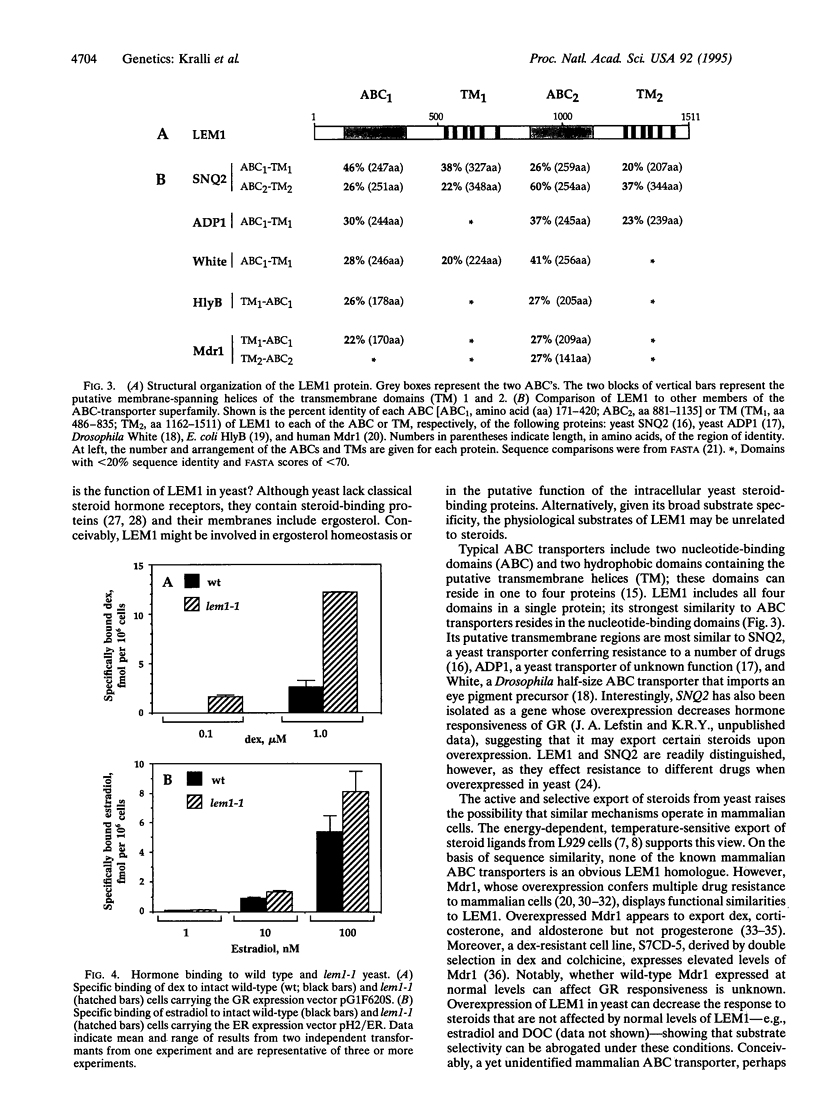
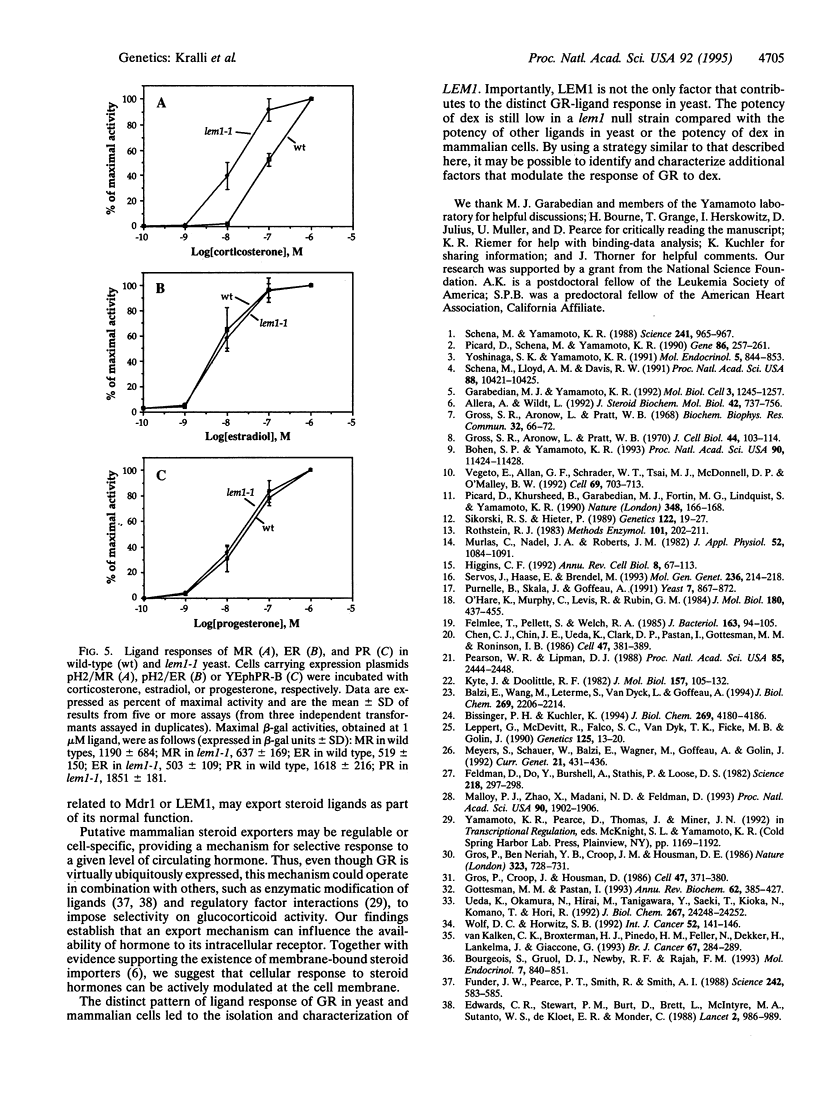
The rat glucocorticoid receptor confers hormone-dependent transcriptional enhancement when expressed in yeast, thereby enabling the genetic identification of nonreceptor proteins that function in the hormone signal-transduction pathway. We isolated a yeast mutant, lem1, with increased sensitivity to dexamethasone and triamcinolone acetonide; responsiveness to a third agonist, deoxycorticosterone, is unaffected. Cloning of wild-type LEM1 revealed a putative transport protein of the ATP-binding cassette family. Dexamethasone accumulation is increased in lem1 cells, suggesting that wild-type LEM1 decreases dexamethasone potency by exporting this ligand. LEM1 appears to affect certain steroids and not others. We propose that transporters like LEM1 can selectively modulate the intracellular levels of steroid hormones. Differential activities of such transporters in mammalian cells might regulate hormone availability and thereby hormone signaling in a cell-type specific manner.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzi E., Wang M., Leterme S., Van Dyck L., Goffeau A. PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulator PDR1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2206–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohen S. P., Yamamoto K. R. Isolation of Hsp90 mutants by screening for decreased steroid receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11424–11428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois S., Gruol D. J., Newby R. F., Rajah F. M. Expression of an mdr gene is associated with a new form of resistance to dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jul;7(7):840–851. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.7.8105374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. J., Chin J. E., Ueda K., Clark D. P., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M., Roninson I. B. Internal duplication and homology with bacterial transport proteins in the mdr1 (P-glycoprotein) gene from multidrug-resistant human cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90595-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. R., Stewart P. M., Burt D., Brett L., McIntyre M. A., Sutanto W. S., de Kloet E. R., Monder C. Localisation of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase--tissue specific protector of the mineralocorticoid receptor. Lancet. 1988 Oct 29;2(8618):986–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90742-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Do Y., Burshell A., Stathis P., Loose D. S. An estrogen-binding protein and endogenous ligand in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: possible hormone receptor system. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):297–298. doi: 10.1126/science.6289434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Pearce P. T., Smith R., Smith A. I. Mineralocorticoid action: target tissue specificity is enzyme, not receptor, mediated. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.2845584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Ben Neriah Y. B., Croop J. M., Housman D. E. Isolation and expression of a complementary DNA that confers multidrug resistance. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):728–731. doi: 10.1038/323728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Croop J., Housman D. Mammalian multidrug resistance gene: complete cDNA sequence indicates strong homology to bacterial transport proteins. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90594-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R., Aronow L., Pratt W. B. The active transport of cortisol by mouse fibroblasts growing in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 11;32(1):66–72. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90427-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R., Aronow L., Pratt W. B. The outward transport of cortisol by mammalian cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1970 Jan;44(1):103–114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert G., McDevitt R., Falco S. C., Van Dyk T. K., Ficke M. B., Golin J. Cloning by gene amplification of two loci conferring multiple drug resistance in Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1990 May;125(1):13–20. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malloy P. J., Zhao X., Madani N. D., Feldman D. Cloning and expression of the gene from Candida albicans that encodes a high-affinity corticosteroid-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1902–1906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Schauer W., Balzi E., Wagner M., Goffeau A., Golin J. Interaction of the yeast pleiotropic drug resistance genes PDR1 and PDR5. Curr Genet. 1992 May;21(6):431–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00351651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murlas C., Nadel J. A., Roberts J. M. The muscarinic receptors of airway smooth muscle: their characterization in vitro. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982 Apr;52(4):1084–1091. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1982.52.4.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Murphy C., Levis R., Rubin G. M. DNA sequence of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):437–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. An inducible expression vector for both fission and budding yeast. Gene. 1990 Feb 14;86(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Lloyd A. M., Davis R. W. A steroid-inducible gene expression system for plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10421–10425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. Mammalian glucocorticoid receptor derivatives enhance transcription in yeast. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3043665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servos J., Haase E., Brendel M. Gene SNQ2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which confers resistance to 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide and other chemicals, encodes a 169 kDa protein homologous to ATP-dependent permeases. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):214–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00277115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Okamura N., Hirai M., Tanigawara Y., Saeki T., Kioka N., Komano T., Hori R. Human P-glycoprotein transports cortisol, aldosterone, and dexamethasone, but not progesterone. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24248–24252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vegeto E., Allan G. F., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., McDonnell D. P., O'Malley B. W. The mechanism of RU486 antagonism is dependent on the conformation of the carboxy-terminal tail of the human progesterone receptor. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):703–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. C., Horwitz S. B. P-glycoprotein transports corticosterone and is photoaffinity-labeled by the steroid. Int J Cancer. 1992 Aug 19;52(1):141–146. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910520125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kalken C. K., Broxterman H. J., Pinedo H. M., Feller N., Dekker H., Lankelma J., Giaccone G. Cortisol is transported by the multidrug resistance gene product P-glycoprotein. Br J Cancer. 1993 Feb;67(2):284–289. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




