Abstract
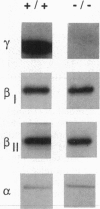
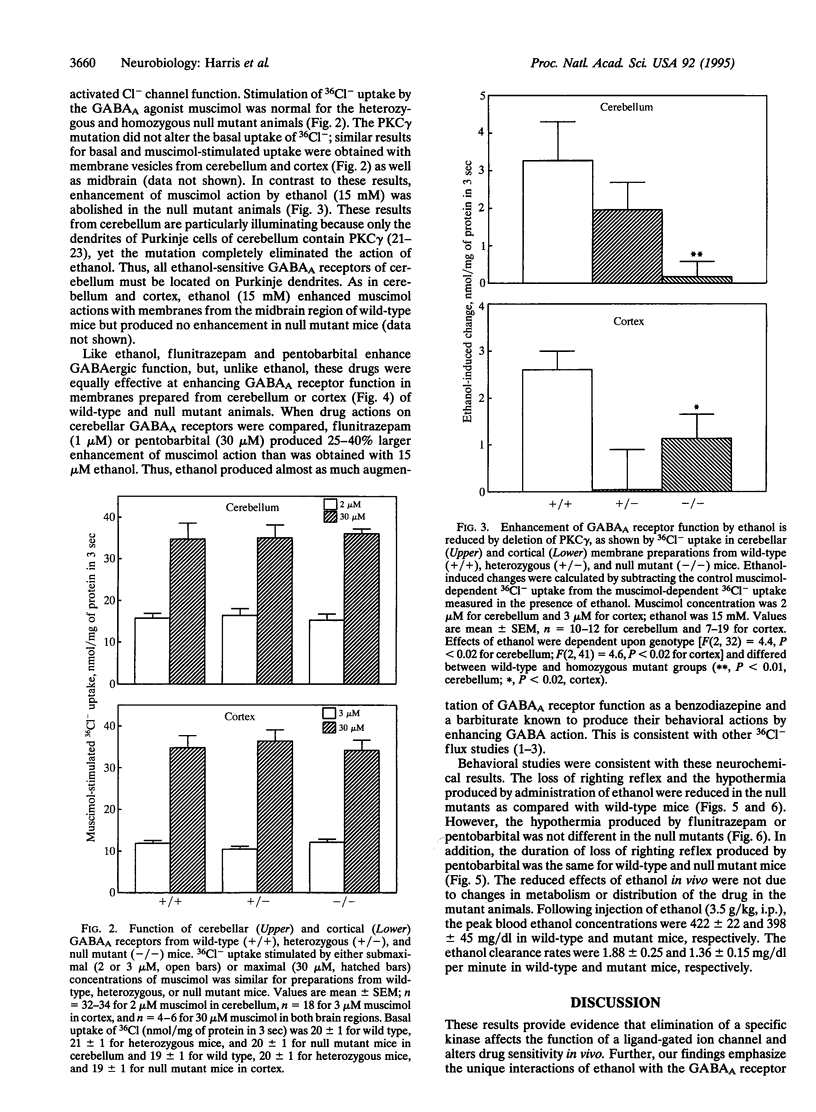
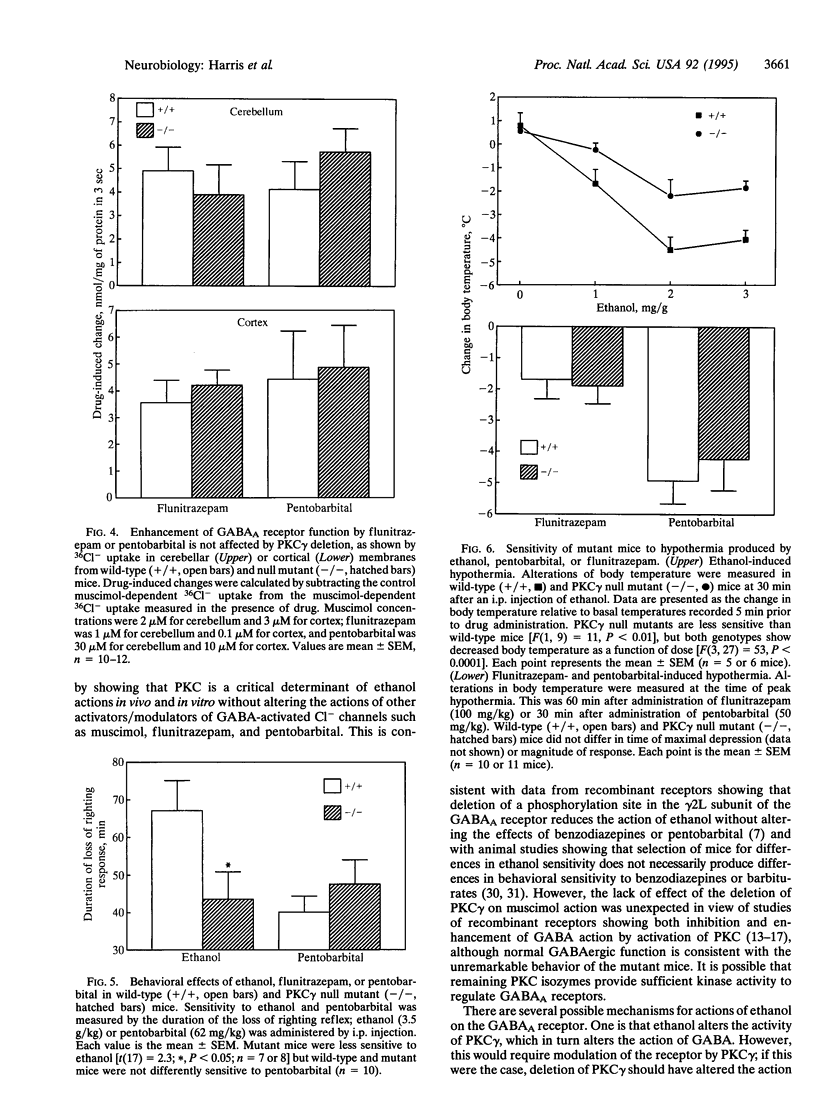
Calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C, PKC) has been suggested to play a role in the sensitivity of gamma-aminobutyrate type A (GABAA) receptors to ethanol. We tested a line of null mutant mice that lacks the gamma isoform of PKC (PKC gamma) to determine the role of this brain-specific isoenzyme in ethanol sensitivity. We found that the mutation reduced the amount of PKC gamma immunoreactivity in cerebellum to undetectable levels without altering the levels of the alpha, beta I, or beta II isoforms of PKC. The mutant mice display reduced sensitivity to the effects of ethanol on loss of righting reflex and hypothermia but show normal responses to flunitrazepam or pentobarbital. Likewise, GABAA receptor function of isolated brain membranes showed that the mutation abolished the action of ethanol but did not alter actions of flunitrazepam or pentobarbital. These studies show the unique interactions of ethanol with GABAA receptors and suggest protein kinase isoenzymes as possible determinants of genetic differences in response to ethanol.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich A., Chen C., Goda Y., Silva A. J., Stevens C. F., Tonegawa S. Modified hippocampal long-term potentiation in PKC gamma-mutant mice. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1253–1262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90613-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abeliovich A., Paylor R., Chen C., Kim J. J., Wehner J. M., Tonegawa S. PKC gamma mutant mice exhibit mild deficits in spatial and contextual learning. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1263–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90614-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan A. M., Harris R. A. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and alcohol actions: neurochemical studies of long sleep and short sleep mice. Life Sci. 1986 Nov 24;39(21):2005–2015. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan A. M., Harris R. A. Sensitivity to ethanol hypnosis and modulation of chloride channels does not cosegregate with pentobarbital sensitivity in HS mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1989 Jun;13(3):428–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1989.tb00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan A. M., Mayes G. G., Draski L. J. gamma-Aminobutyric acid-activated chloride channels in rats selectively bred for differential acute sensitivity to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Mar;15(2):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb01858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M., Young W. S., 3rd Distinct patterns of expression of different protein kinase C mRNAs in rat tissues. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criswell H. E., Simson P. E., Duncan G. E., McCown T. J., Herbert J. S., Morrow A. L., Breese G. R. Molecular basis for regionally specific action of ethanol on gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: generalization to other ligand-gated ion channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Oct;267(1):522–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFries J. C., Wilson J. R., Erwin V. G., Petersen D. R. LS X SS recombinant inbred strains of mice: initial characterization. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1989 Apr;13(2):196–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1989.tb00310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitrich R. A., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Erwin V. G. Mechanism of action of ethanol: initial central nervous system actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Dec;41(4):489–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudek B. C., Abbott M. E. A biometrical genetic analysis of ethanol response in selectively bred long-sleep and short-sleep mice. Behav Genet. 1984 Jan;14(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01066065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin V. G., Jones B. C., Radcliffe R. Further characterization of LSxSS recombinant inbred strains of mice: activating and hypothermic effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990 Apr;14(2):200–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1990.tb00472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund R. K., van Horne C. G., Harlan T., Palmer M. R. Electrophysiological interactions of ethanol with GABAergic mechanisms in the rat cerebellum in vivo. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993 Apr;17(2):321–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1993.tb00770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Hoffman P. L. Receptor-gated ion channels may be selective CNS targets for ethanol. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90478-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T., Ase K., Sawamura S., Kikkawa U., Saito N., Tanaka C., Nishizuka Y. Postnatal development of a brain-specific subspecies of protein kinase C in rat. J Neurosci. 1988 May;8(5):1678–1683. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-05-01678.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. S., Spiegelman B. M., Papaioannou V. Pleiotropic effects of a null mutation in the c-fos proto-oncogene. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90592-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger S., Malherbe P., Sigel E. Function of the alpha 1 beta 2 gamma 2S gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor is modulated by protein kinase C via multiple phosphorylation sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25660–25663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishek B. J., Xie X., Blackstone C., Huganir R. L., Moss S. J., Smart T. G. Regulation of GABAA receptor function by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):1081–1095. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidenheimer N. J., McQuilkin S. J., Hahner L. D., Whiting P., Harris R. A. Activation of protein kinase C selectively inhibits the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor: role of desensitization. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1116–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidenheimer N. J., Whiting P. J., Harris R. A. Activation of calcium-phospholipid-dependent protein kinase enhances benzodiazepine and barbiturate potentiation of the GABAA receptor. J Neurochem. 1993 May;60(5):1972–1975. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lex B. W., Lukas S. E., Greenwald N. E., Mendelson J. H. Alcohol-induced changes in body sway in women at risk for alcoholism: a pilot study. J Stud Alcohol. 1988 Jul;49(4):346–356. doi: 10.15288/jsa.1988.49.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. M., Bickford P. C., Palmer M. R. The effects of ethanol on gamma-aminobutyric acid-induced depressions of cerebellar Purkinje neurons: influence of beta adrenergic receptor action in young and aged Fischer 344 rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Feb;264(2):951–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. M., Freund R. K., Hoffer B. J., Palmer M. R. Ethanol-induced depressions of cerebellar Purkinje neurons are potentiated by beta-adrenergic mechanisms in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Dec;271(3):1175–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. M., Freund R. K., Palmer M. R. Ethanol potentiation of GABA-induced electrophysiological responses in cerebellum: requirement for catecholamine modulation. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Jan 28;122(2):154–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90846-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. M., Freund R. K., Palmer M. R. Sensitization of gamma-aminobutyric acid-induced depressions of cerebellar Purkinje neurons to the potentiative effects of ethanol by beta adrenergic mechanisms in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Apr;265(1):426–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. F., Browning M. D., Dudek E. M., Macdonald R. L. Protein kinase C enhances recombinant bovine alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2L GABAA receptor whole-cell currents expressed in L929 fibroblasts. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1421–1431. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marley R. J., Miner L. L., Wehner J. M., Collins A. C. Differential effects of central nervous system depressants in long-sleep and short-sleep mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta A. K., Ticku M. K. Ethanol potentiation of GABAergic transmission in cultured spinal cord neurons involves gamma-aminobutyric acidA-gated chloride channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Aug;246(2):558–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Shearman M. S., Oda T., Berry N., Shinomura T., Asaoka Y., Ogita K., Koide H., Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A. Protein kinase C family and nervous function. Prog Brain Res. 1991;89:125–141. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61719-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. R., Harlan J. T., Spuhler K. Genetic covariation in low alcohol-sensitive and high alcohol-sensitive selected lines of rats: behavioral and electrophysiological sensitivities to the depressant effects of ethanol and the development of acute neuronal tolerance to ethanol in situ at generation eight. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):879–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. R., Wang Y., Fossom L. H., Spuhler K. P. Genetic correlation of ethanol-induced ataxia and cerebellar Purkinje neuron depression among inbred strains and selected lines of rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1987 Oct;11(5):494–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1987.tb01930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. N., Prasad A., MacDonald J. F. Ethanol modulation of GABA receptor-activated Cl- currents in neurons of the chick, rat and mouse central nervous system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90802-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanna E., Harris R. A. Recent developments in alcoholism:neuronal ion channels. Recent Dev Alcohol. 1993;11:169–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit M. A., Gold E. O. A simultaneous evaluation of multiple markers of ethanol/placebo challenges in sons of alcoholics and controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988 Mar;45(3):211–216. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1988.01800270019002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuckit M. A. Low level of response to alcohol as a predictor of future alcoholism. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Feb;151(2):184–189. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R. Activation of protein kinase C differentially modulates neuronal Na+, Ca2+, and gamma-aminobutyrate type A channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6192–6196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Malherbe P. Recombinant GABAA receptor function and ethanol. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 14;324(2):140–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81380-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen T. N., Smolen A. Blood and brain ethanol concentrations during absorption and distribution in long-sleep and short-sleep mice. Alcohol. 1989 Jan-Feb;6(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0741-8329(89)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Burnett D. M., Leidenheimer N. J., Burt D. R., Wang J. B., Kofuji P., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Sikela J. M. Ethanol sensitivity of the GABAA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes requires 8 amino acids contained in the gamma 2L subunit. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Whiting P. J. Ethanol potentiation of GABAA receptors requires phosphorylation of the alternatively spliced variant of the gamma 2 subunit. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 23;313(2):113–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81424-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]