Abstract
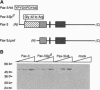
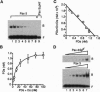
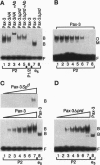
The murine Pax-3 protein contains two DNA-binding domains, a paired domain and a homeodomain, and alterations in the Pax-3 gene are responsible for the neural tube defects observed in the Splotch (Sp) mouse mutant. Of five Sp alleles, Splotch-delayed (Spd) is the only one that encodes a full-length Pax-3 protein, containing a single glycine-to-arginine substitution within the paired domain. To better understand the consequence of this mutation on Pax-3 function, we have analyzed the DNA-binding properties of wild-type and Spd Pax-3, using oligonucleotides that bind primarily to the paired domain (e5) or exclusively to the homeodomain (P2). Wild-type Pax-3 was found to bind e5 in a specific manner. In contrast, the Spd mutation reduced binding of Pax-3 to e5 17-fold, revealing a defect in DNA binding by the paired domain. Surprisingly, the Spd mutation also drastically reduced the homeodomain-specific binding to P2 by 21-fold when compared with the wild-type protein. Interestingly, a deletion which removes the Spd mutation was found to restore P2-binding activity, suggesting that within the full-length Pax-3 protein, the paired domain and homeodomain may interact. We conclude, therefore, that the Spd mutation is phenotyically expressed in vitro by a defect in the DNA-binding properties of Pax-3. Furthermore, it is apparent that the paired domain and homeodomain of Pax-3 do not function as independent domains, since a mutation in the former impairs the DNA-binding activity of the latter.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B., Dörfler P., Aguzzi A., Kozmik Z., Urbánek P., Maurer-Fogy I., Busslinger M. Pax-5 encodes the transcription factor BSAP and is expressed in B lymphocytes, the developing CNS, and adult testis. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1589–1607. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Hoth C. F., Amos J. A., da-Silva E. O., Milunsky A. An exonic mutation in the HuP2 paired domain gene causes Waardenburg's syndrome. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):637–638. doi: 10.1038/355637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Deutsch U., Gruss P. undulated, a mutation affecting the development of the mouse skeleton, has a point mutation in the paired box of Pax 1. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):531–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner S., Bopp D., Burri M., Noll M. Structure of two genes at the gooseberry locus related to the paired gene and their spatial expression during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1247–1267. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Burri M., Baumgartner S., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of a large protein domain in the segmentation gene paired and in functionally related genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90818-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Jamet E., Baumgartner S., Burri M., Noll M. Isolation of two tissue-specific Drosophila paired box genes, Pox meso and Pox neuro. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3447–3457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burri M., Tromvoukis Y., Bopp D., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of the paired domain in metazoans and its structure in three isolated human genes. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Thézé N., Thiebaud P., Hill R. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental appearance of factors that bind specifically to cis-regulatory sequences of a gene expressed in the sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1074–1088. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Fritsch R., Fickenscher H., Deutsch U., Goulding M., Gruss P. The molecular basis of the undulated/Pax-1 mutation. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Goulding M., Read A., Strachan T., Gruss P. Molecular basis of splotch and Waardenburg Pax-3 mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3685–3689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Stoykova A., Wijnholds J., Tremblay P., Gruss P. Pax: gene regulators in the developing nervous system. J Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;24(10):1367–1384. doi: 10.1002/neu.480241009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerny T., Schaffner G., Busslinger M. DNA sequence recognition by Pax proteins: bipartite structure of the paired domain and its binding site. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):2048–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. J., Vekemans M., Gros P. Splotch (Sp2H), a mutation affecting development of the mouse neural tube, shows a deletion within the paired homeodomain of Pax-3. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein D. J., Vogan K. J., Trasler D. G., Gros P. A mutation within intron 3 of the Pax-3 gene produces aberrantly spliced mRNA transcripts in the splotch (Sp) mouse mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):532–536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein J., Cai J., Glaser T., Jepeal L., Maas R. Identification of a Pax paired domain recognition sequence and evidence for DNA-dependent conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 18;269(11):8355–8361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz T., Kothary R., Surani M. A., Halata Z., Grim M. The Splotch mutation interferes with muscle development in the limbs. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1993 Feb;187(2):153–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00171747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio G., Burri M., Bopp D., Baumgartner S., Noll M. Structure of the segmentation gene paired and the Drosophila PRD gene set as part of a gene network. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding M. D., Chalepakis G., Deutsch U., Erselius J. R., Gruss P. Pax-3, a novel murine DNA binding protein expressed during early neurogenesis. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1135–1147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding M., Sterrer S., Fleming J., Balling R., Nadeau J., Moore K. J., Brown S. D., Steel K. P., Gruss P. Analysis of the Pax-3 gene in the mouse mutant splotch. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):355–363. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Walther C. Pax in development. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):719–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90281-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moase C. E., Trasler D. G. Splotch locus mouse mutants: models for neural tube defects and Waardenburg syndrome type I in humans. J Med Genet. 1992 Mar;29(3):145–151. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.3.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Evolution and role of Pax genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E., Edmondson D., Wright W. E., Lin V. K., Guenet J. L., Simon-Chazottes D., Thompson L. H., Stallings R. L., Schroeder W. T., Duvic M. Myogenin is in an evolutionarily conserved linkage group on human chromosome 1q31-q41 and unlinked to other mapped muscle regulatory factor genes. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90028-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. W., Czerny T., Bernasconi M., Genini M., Busslinger M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human PAX-7 cDNA expressed in normal and neoplastic myocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Nov 11;22(22):4574–4582. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Harris R., Balling R., Gruss P., Strachan T. Waardenburg's syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):635–636. doi: 10.1038/355635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Patton M., Gruss P., Harris R., Strachan T. Mutations in the PAX3 gene causing Waardenburg syndrome type 1 and type 2. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):26–30. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman J., Harris E., Desplan C. The paired box encodes a second DNA-binding domain in the paired homeo domain protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):594–604. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogan K. J., Epstein D. J., Trasler D. G., Gros P. The splotch-delayed (Spd) mouse mutant carries a point mutation within the paired box of the Pax-3 gene. Genomics. 1993 Aug;17(2):364–369. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D., Sheng G., Lecuit T., Dostatni N., Desplan C. Cooperative dimerization of paired class homeo domains on DNA. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2120–2134. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannini M., Francis-Lang H., Plachov D., Di Lauro R. Pax-8, a paired domain-containing protein, binds to a sequence overlapping the recognition site of a homeodomain and activates transcription from two thyroid-specific promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4230–4241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]