Abstract
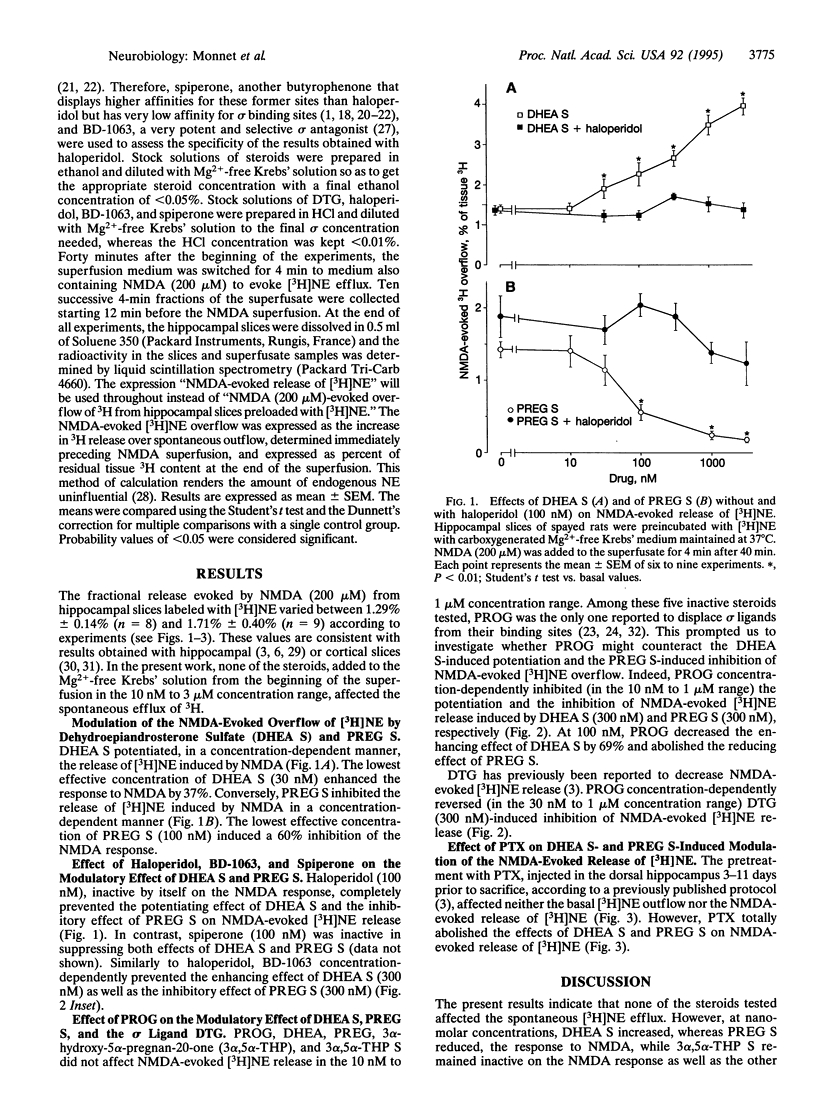
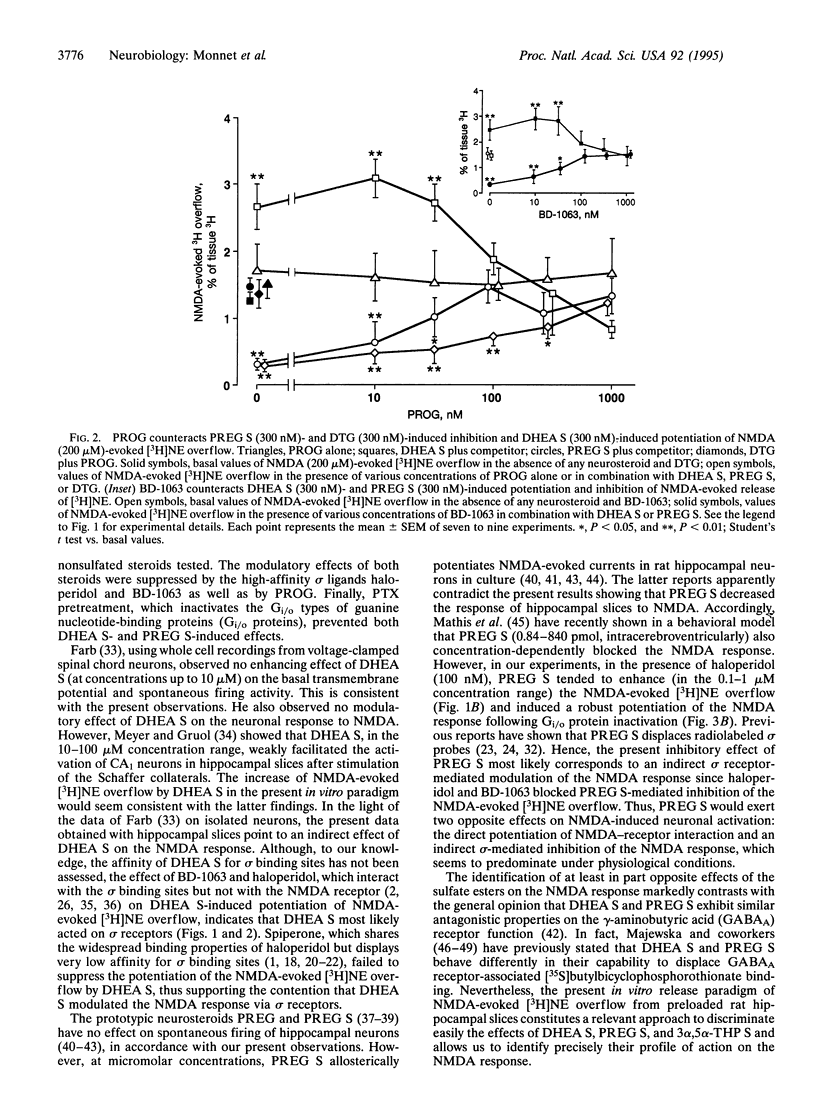
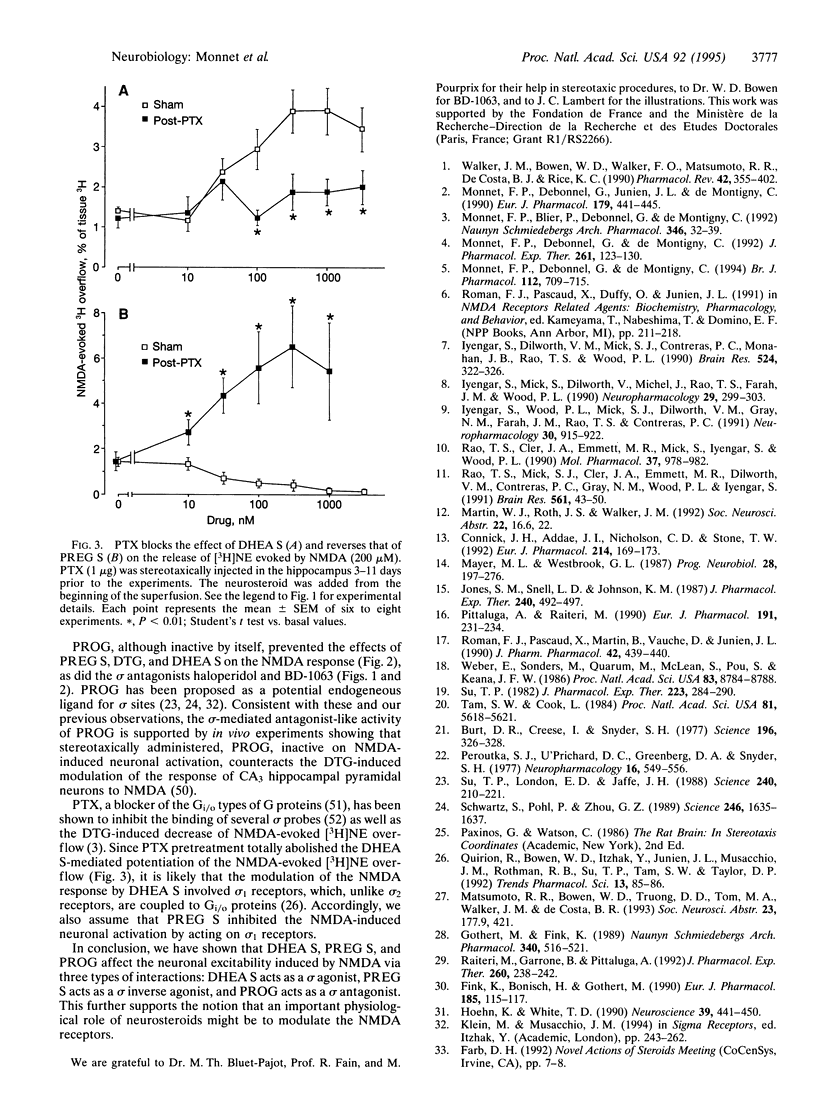
N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA, 200 microM) evokes the release of [3H]norepinephrine ([3H]NE) from preloaded hippocampal slices. This effect is potentiated by dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA S), whereas it is inhibited by pregnenolone sulfate (PREG S) and the high-affinity sigma inverse agonist 1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine, at concentrations of > or = 100 nM. Neither 3 alpha-hydroxy-5 alpha-pregnan-20-one nor its sulfate ester modified NMDA-evoked [3H]NE overflow. The sigma antagonists haloperidol and 1-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-ethyl]-4-methylpiperazine, although inactive by themselves, completely prevented the effects of DHEA S, PREG S, and 1,3-di(2-tolyl)guanidine on NMDA-evoked [3H]NE release. Progesterone (100 nM) mimicked the antagonistic effect of haloperidol and 1-[2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)ethyl]-4-methyl-piperazine. These results indicate that the tested steroid sulfate esters differentially affected the NMDA response in vitro and suggest that DHEA S acts as a sigma agonist, that PREG S acts as a sigma inverse agonist, and that progesterone may act as a sigma antagonist. Pertussis toxin, which inactivates the Gi/o types of guanine nucleotide-binding protein (Gi/o protein) function, suppresses both effects of DHEA S and PREG S. Since sigma 1 but not sigma 2 receptors are coupled to Gi/o proteins, the present results suggest that DHEA S and PREG S control the NMDA response via sigma 1 receptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: a new function in the brain. Biol Cell. 1991;71(1-2):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0248-4900(91)90045-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowlby M. R. Pregnenolone sulfate potentiation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in hippocampal neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 May;43(5):813–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. R., Creese I., Snyder S. H. Antischizophrenic drugs: chronic treatment elevates dopamine receptor binding in brain. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):326–328. doi: 10.1126/science.847477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church J., Lodge D. Failure of sigma-receptor ligands to reduce the excitatory actions of N-methyl-DL-aspartate on rat spinal neurons in-vivo. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;42(1):56–57. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb05350.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connick J. H., Addae J. I., Nicholson C. D., Stone T. W. The sigma ligand 1,3-di-o-tolylguanidine depresses amino acid-induced excitation non-selectively in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 22;214(2-3):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90115-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demirgören S., Majewska M. D., Spivak C. E., London E. D. Receptor binding and electrophysiological effects of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, an antagonist of the GABAA receptor. Neuroscience. 1991;45(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink K., Bönisch H., Göthert M. Presynaptic NMDA receptors stimulate noradrenaline release in the cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 21;185(1):115–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90219-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Fink K. Inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)- and L-glutamate-induced noradrenaline and acetylcholine release in the rat brain by ethanol. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):516–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00260606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn K., White T. D. N-methyl-D-aspartate, kainate and quisqualate release endogenous adenosine from rat cortical slices. Neuroscience. 1990;39(2):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90280-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. Y., Bourreau E., Jung-Testas I., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8215–8219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin R. P., Maragakis N. J., Rogawski M. A., Purdy R. H., Farb D. H., Paul S. M. Pregnenolone sulfate augments NMDA receptor mediated increases in intracellular Ca2+ in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jul 6;141(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y. Multiple affinity binding states of the sigma receptor: effect of GTP-binding protein-modifying agents. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;36(4):512–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Dilworth V. M., Mick S. J., Contreras P. C., Monahan J. B., Rao T. S., Wood P. L. Sigma receptors modulate both A9 and A10 dopaminergic neurons in the rat brain: functional interaction with NMDA receptors. Brain Res. 1990 Aug 6;524(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90709-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Mick S., Dilworth V., Michel J., Rao T. S., Farah J. M., Wood P. L. Sigma receptors modulate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis centrally: evidence for a functional interaction with NMDA receptors, in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 1990 Mar;29(3):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(90)90017-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar S., Wood P. L., Mick S. J., Dilworth V. M., Gray N. M., Farah J. M., Rao T. S., Contreras P. C. (+) 3-[3-hydroxyphenyl-N-(1-propyl) piperidine] selectively differentiates effects of sigma ligands on neurochemical pathways modulated by sigma receptors: evidence for subtypes, in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Aug;30(8):915–922. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90127-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. M., Snell L. D., Johnson K. M. Phencyclidine selectively inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced hippocampal [3H]norepinephrine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Feb;240(2):492–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Hu Z. Y., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in primary cultures of rat glial cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2083–2091. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Demirgören S., Spivak C. E., London E. D. The neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate is an allosteric antagonist of the GABAA receptor. Brain Res. 1990 Aug 27;526(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Mienville J. M., Vicini S. Neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes electrophysiological responses to GABA in neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 1;90(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Schwartz R. D. Pregnenolone-sulfate: an endogenous antagonist of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex in brain? Brain Res. 1987 Feb 24;404(1-2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis C., Paul S. M., Crawley J. N. The neurosteroid pregnenolone sulfate blocks NMDA antagonist-induced deficits in a passive avoidance memory task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994 Oct;116(2):201–206. doi: 10.1007/BF02245063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. H., Gruol D. L. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate alters synaptic potentials in area CA1 of the hippocampal slice. Brain Res. 1994 Jan 7;633(1-2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)91546-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Blier P., Debonnel G., de Montigny C. Modulation by sigma ligands of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced [3H]noradrenaline release in the rat hippocampus: G-protein dependency. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;346(1):32–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00167567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., Bergeron R., Gronier B., de Montigny C. The effects of sigma ligands and of neuropeptide Y on N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation of CA3 dorsal hippocampus neurones are differentially affected by pertussin toxin. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun;112(2):709–715. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., Junien J. L., De Montigny C. N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation is selectively modulated by sigma receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr 25;179(3):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90186-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnet F. P., Debonnel G., de Montigny C. In vivo electrophysiological evidence for a selective modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation in rat CA3 dorsal hippocampus by sigma ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Apr;261(1):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Purdy R. H. Neuroactive steroids. FASEB J. 1992 Mar;6(6):2311–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J., U'Prichard D. C., Greenberg D. A., Snyder S. H. Neuroleptic drug interactions with norepinephrine alpha receptor binding sites in rat brain. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Sep;16(9):549–556. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittaluga A., Raiteri M. Release-enhancing glycine-dependent presynaptic NMDA receptors exist on noradrenergic terminals of hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 27;191(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94153-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Bowen W. D., Itzhak Y., Junien J. L., Musacchio J. M., Rothman R. B., Su T. P., Tam S. W., Taylor D. P. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):85–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90030-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raiteri M., Garrone B., Pittaluga A. N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) and non-NMDA receptors regulating hippocampal norepinephrine release. II. Evidence for functional cooperation and for coexistence on the same axon terminal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):238–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. S., Cler J. A., Emmett M. R., Mick S., Iyengar S., Wood P. L. BMY-14802 antagonizes harmaline- and D-serine-induced increases in mouse cerebellar cyclic GMP: neurochemical evidence for a sigma receptor-mediated functional modulation of responses mediated by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex in vivo. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):978–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao T. S., Mick S. J., Cler J. A., Emmett M. R., Dilworth V. M., Contreras P. C., Gray N. M., Wood P. L., Iyengar S. Effects of sigma ligands on mouse cerebellar cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) levels in vivo: further evidence for a functional modulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex-mediated events by sigma ligands. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 4;561(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90747-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman F. J., Pascaud X., Martin B., Vauché D., Junien J. L. JO 1784, a potent and selective ligand for rat and mouse brain sigma-sites. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;42(6):439–440. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1990.tb06588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz S., Pohl P., Zhou G. Z. Steroid binding at sigma-"opioid" receptors. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1635–1638. doi: 10.1126/science.2556797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P., London E. D., Jaffe J. H. Steroid binding at sigma receptors suggests a link between endocrine, nervous, and immune systems. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):219–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2832949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Cook L. Sigma opiates and certain antipsychotic drugs mutually inhibit (+)-[3H] SKF 10,047 and [3H]haloperidol binding in guinea pig brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5618–5621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. M., Bowen W. D., Walker F. O., Matsumoto R. R., De Costa B., Rice K. C. Sigma receptors: biology and function. Pharmacol Rev. 1990 Dec;42(4):355–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Sonders M., Quarum M., McLean S., Pou S., Keana J. F. 1,3-Di(2-[5-3H]tolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M., Moss R. L. Patch-clamp analysis of direct steroidal modulation of glutamate receptor-channels. J Neuroendocrinol. 1994 Jun;6(3):347–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.1994.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F. S., Gibbs T. T., Farb D. H. Pregnenolone sulfate: a positive allosteric modulator at the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):333–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin R. S., Zukin S. R. Demonstration of [3H]cyclazocine binding to multiple opiate receptor sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;20(2):246–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


