Abstract
The secondary organic aerosol (SOA) mass yields from NO3 oxidation of a series of biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs), consisting of five monoterpenes and one sesquiterpene (α-pinene, β-pinene, Δ-3-carene, limonene, sabinene, and β-caryophyllene), were investigated in a series of continuous flow experiments in a 10 m3 indoor Teflon chamber. By making in situ measurements of the nitrate radical and employing a kinetics box model, we generate time-dependent yield curves as a function of reacted BVOC. SOA yields varied dramatically among the different BVOCs, from zero for α-pinene to 38–65% for Δ-3-carene and 86% for β-caryophyllene at mass loading of 10 μg m–3, suggesting that model mechanisms that treat all NO3 + monoterpene reactions equally will lead to errors in predicted SOA depending on each location’s mix of BVOC emissions. In most cases, organonitrate is a dominant component of the aerosol produced, but in the case of α-pinene, little organonitrate and no aerosol is formed.
Introduction
Secondary organic aerosol (SOA), formed in situ from the conversion of gas-phase volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to oxidized products that partition preferentially to the particle phase, is an important source of aerosol mass both regionally and globally. It is estimated that approximately 70% of total global organic aerosol production is secondary (∼150 TgC/yr),1 but formation mechanisms remain uncertain.
A large fraction of total organic aerosol is thought to originate from the oxidation products of biogenic VOC emissions.1,2 These naturally emitted compounds constitute the majority of VOC emissions to the atmosphere globally,3−5 with a diverse and regionally varied mixture of isoprenoid chemical structures, depending on regional plant species distributions. The gas-phase oxidation of VOCs to condensable products is initiated by reaction with O3 or the OH or NO3 radicals. The relative importance of each competing oxidant depends on the relevant rate constants (which depends on the VOC molecular structure) and ambient concentrations. For example, NO3-initiated reactions with biogenic alkenes have large rate constants,6 and will be most important at night (when photolysis and NO reaction sinks for NO3 radical are minimized), and in regions that contain both high biogenic emissions and elevated NOx such as downwind of urban areas or industrial point sources. SOA yields from OH and O3 oxidation of BVOC have been studied extensively,7 but less is known about reactions involving NO3-induced oxidation.
Because partitioning to the aerosol phase depends on molecular weight and polarity,8 the precursor VOC generally needs to contain a minimum number of carbon atoms (or undergo condensed phase oligomerization reactions) to produce condensable oxidation products and thus form SOA. Isoprene (C5H8) is the globally dominant BVOC, comprising ∼50% of total global nonmethane VOC emissions by mass5 with total emissions estimated at approximately 500 Tg yr–1. However, isoprene and its NO3-induced oxidation products are quite volatile, and thus have relatively low NO3 SOA yields of 4–24%.9 The larger monoterpenes (C10H16) and sesquiterpenes (C15H24), which are much more prevalent in coniferous forests, are more efficient SOA precursors via their production of extremely low-volatility organic compounds.10
The NO3 oxidation of some terpenes has been studied in laboratory experiments, summarized in Table 1. Wängberg et al.,11 Hallquist et al.,12 and Spittler et al.13 all observed substantially higher ketone yields and lower organonitrate yields for α-pinene than for the other terpenes; where SOA yield measurements are available they roughly correlate with organonitrate yields, showing lower yield for α-pinene. We note that these chamber experiments may preclude further oxidation of initial products, which could produce additional SOA in the real atmosphere (e.g., photo-oxidation of pinonaldehyde14).
Table 1. Oxidation Products and SOA Yields Observed in Previous Studies of NO3 + Terpenes.
| BVOC | ketone molar yielda | organonitrate molar yield | SOA mass yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-pinene | 58–66% Wängberg
et al.11 65–72% Hallquist et al.12 39–58% Spittler et al.13 |
14% Wängberg et al.11 18–25% Hallquist et al.12 11–29% Spittler et al.13 |
7% Hallquist
et al.12 0.3–0.7% Moldanova and Ljungstrom15 4–16% Spittler et al.13 |
| β-pinene | 0–2% Hallquist et al.12 | 51–74% Hallquist
et al.12 40% Fry et al.16 |
>39% Hallquist et al.12 50% Fry et al.16 18–35% Moldanova and Ljungstrom15 |
| Δ-carene | 0–3% Hallquist et al.12 | 68–74% Hallquist et al.12 | >15% Hallquist et al.12 >13% Moldanova and Ljungstrom15 |
| limonene | 69% Hallquist et al.12 25–33% Spittler et al.13 |
48% Hallquist et
al.12 63–72% Spittler et al.13 30% Fry et al.17 |
17% Hallquist et al.12 20–40% Spittler et al.;13 Fry et al.17 18% Moldanova and Ljungstrom15 |
In Hallquist et al.,12 these ketone yields refer to the dominant single ketone product, e.g. in the case of α-pinene, pinonaldehyde.
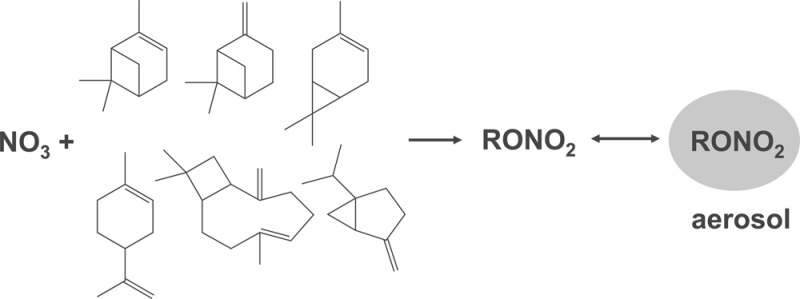
A systematic controlled chamber study of SOA production from six mono- and sesquiterpenes is the focus of the work presented here. We measured the SOA yield from NO3 reacting with the individual monoterpenes α-pinene, β-pinene, Δ-3-carene, limonene, sabinene, and with the sesquiterpene β-caryophyllene (structures shown in Supporting Information (SI) Figure S6 and in the abstract). Since the nitrato-peroxy radicals produced from these terpenes are all tertiary, we expect no HO2 production in the chamber. Hence, these experiments explore RO2—RO2 and RO2—NO3 chemistry only, omitting RO2—HO2 chemistry that would contribute in the real nighttime atmosphere. These experiments were performed in continuous-flow mode in a dark chamber at the Atmospheric Chemistry Division of the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Fall 2011. We monitored particle size distributions and total alkyl nitrate concentrations to enable determination of SOA mass yields and alkyl nitrate yields. We interpreted key observations based on chemical structure and proposed mechanisms.
Experimental and Theoretical Methods
NCAR Chamber Facility
A detailed description of the NCAR Chamber Facility instrumentation and cleaning and operating procedures for the experiments described herein are provided in the SI. Figure SI shows the chamber diagram, and Table SI the instrumentation employed in these experiments. Briefly, the 10 m3 chamber18,19 was run with all reagents input continuously under dark conditions, with an average chamber residence time of 4 h. The NO3 and N2O5 concentrations were alternately measured either before entering the chamber, or from the chamber itself. Flows were adjusted to give initial [N2O5 + NO3] and [BVOC] of 10–100 ppb in dry zero air. SOA experiments were initiated by injecting BVOC (∼50 ppm in N2) into the N2O5 + NO3 filled chamber, delivered from the standard cylinders using flow restrictors and added to the zero air flow to obtain the final desired mixing ratios (Table 2). This results in decay of chamber N2O5 + NO3 as the BVOC reacts away.
Table 2. Experimental Conditionsa.
| expt # | date | BVOC | [BVOC]I (ppb) | [N2O5]I (ppb) | kNO3+BVOC @298 K (cm3 molec-1 s–-1) | [N2O5]i/[BVOC]i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9/15/11 | α-pinene (seeded) | 48 | 54 | 6.16 × 10–12 | 1.1 |
| 2 | 9/28/11 | β-pinene “high” | 41 | 60 | 2.51 × 10–12 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 10/18/11 | β-pinene “low” | 10 | 10 | 2.51 × 10–12 | 1.0 |
| 4 | 9/19/11 | Δ-3-carene “high” | 16 | 42 | 9.1 × 10–12 | 2.6 |
| 5 | 10/21/11 | Δ-3-carene “low” | 10 | 9 | 9.1 × 10–12 | 0.9 |
| 6 | 10/3/11 | limonene “high” | 40 | 60 | 1.22 × 10–11 | 1.5 |
| 7 | 10/11/11 | limonene “low” | 10 | 10 | 1.22 × 10–11 | 1.0 |
| 8 | 10/15/11 | limonene (+ O3 + NO2) | 10 | [O3]i = 12 ppb; [NO2]i= 6.3 ppb | 1.22 × 10–11 | 1.2 |
| 9 | 9/22/11 | β-caryophyllene “high” | 109 | 40 | 1.9 × 10–11 | 0.4 |
| 10 | 10/26/11 | β-caryophyllene “low” | 3 | 10 | 1.9 × 10–11 | 3.0 |
| 11 | 11/11/11 | sabinene | 9 | 10 | 1 × 10–11 | 1.1 |
Except α-pinene, all experiments were conducted without seed aerosol. Rate constants at 298 K are taken from Calvert et al. (2000).21 For the “low” experiments, the ratio of N2O5 to BVOC in the inlet line was approximately 1:1; for the “high” experiments, the oxidant was generally in slight excess (with the exception of Expt # 9). The highest purity sabinene source available was 80%, and contained 20% β-pinene. No correction was applied for this, so sabinene SOA reflects this mixture.
A series of 11 experiments were conducted with the six BVOC, in most cases with two levels of oxidant and BVOC concentrations: a nominally “high” (∼50 ppb) and a “low” (∼10 ppb) concentration of each (see Table 2). For the high concentration experiments only (Expts. 1, 2, 4, 6, and 9), organic nitrate measurements are available. In these experiments, total alkyl + peroxy nitrate mixing ratios (ΣANs + PNs), subsequently referred to collectively as organonitrates, are determined in the gas and aerosol phases by sampling directly or through a charcoal denuder.20
Instrumentation
The following measurements were made during each experiment: (1) NO3 and N2O5 concentrations on both inlet and outlet flows by cavity ringdown spectroscopy (CRDS, Wagner et al.;22 Dube et al.23), and on the outlet side only: (2) NO and NO2 by chemiluminescence, (3) O3 by absorption spectroscopy, (4) particle number and size distribution by a scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS), and (5) organonitrates by thermal dissociation–laser-induced fluorescence (TD-LIF, Rollins et al.20). The specifications of each instrument used in these experiments are shown in Table S1 in the SI.
Wall Losses
In order to interpret observed aerosol formation, it is essential to understand the effect of chamber wall losses on measured aerosol size distributions. Following the methods of Van Reken et al.,24 we measured the size-dependent wall loss of ammonium sulfate aerosol at steady-state flow. Results and additional analysis details are shown in the SI (Figure S2). Average input and output size distributions were analyzed to derive the first-order size-dependent wall loss coefficient, β(dp), with the chamber considered to behave as a continuously stirred tank reactor:25,26
| 1 |
The losses are applied cumulatively, so that corrected aerosol mass timeseries include all particles lost since the start of the experiment, following the method of McMurry and Grosjean,27 and we find values consistent with previous chamber studies.24
Recent work has shown that vapor-phase wall losses may also substantially contribute to underestimation of chamber SOA yields,28,29 suggesting that the yields reported here may be lower limits. The implications of this unconstrained process for observed relative organonitrate yields is discussed in below.
Results
Qualitative Differences in Aerosol Formation
Particle formation and growth was observed for all BVOCs except α-pinene, although with widely varying yields. The observed time evolution of the particle size distribution function of a representative experiment (Experiment 3, β-pinene at low concentration) is shown in Figure 1, illustrating the new particle formation and growth that occurred in each experiment (except α-pinene).
Figure 1.
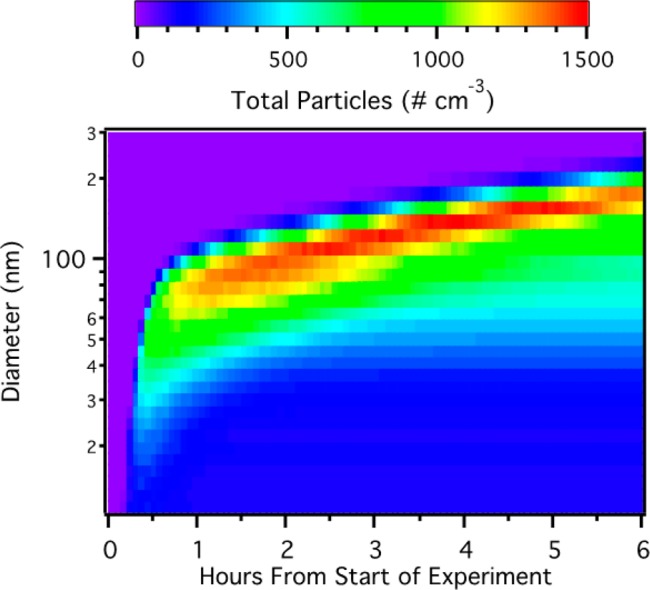
Wall loss corrected SOA growth curve for Experiment 3 (β-pinene low concentration).
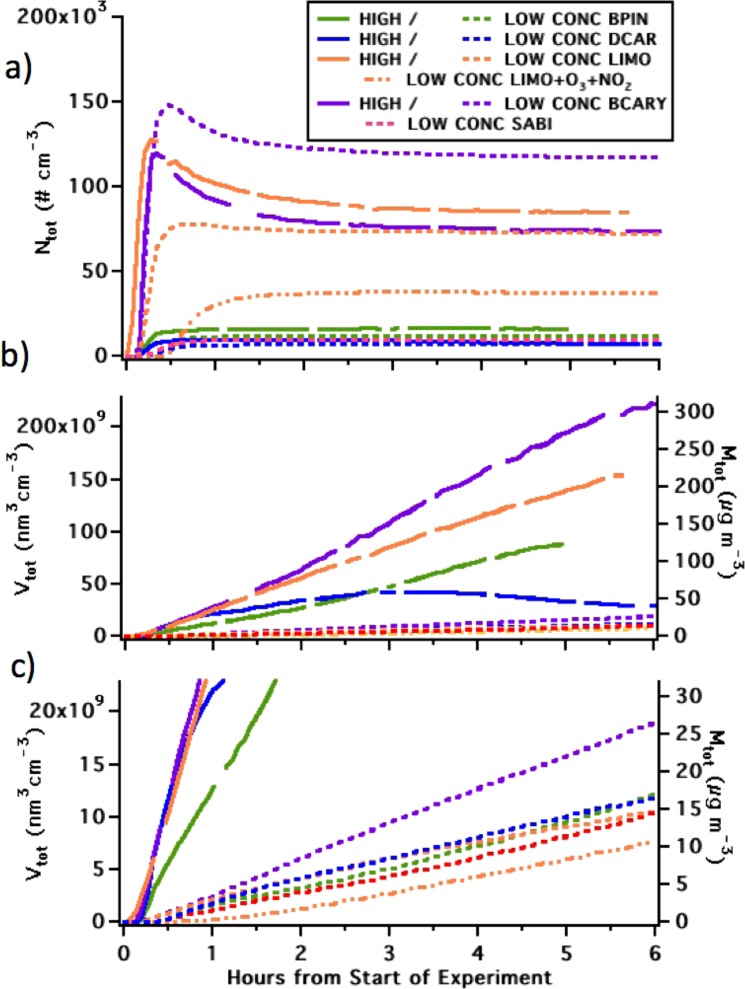
Figure 2 shows the time evolution of aerosol number (Ntot, Figure 2a) and volume concentration (Vtot, Figure 2b,c). These plots show the comparison of SOA growth from different BVOC precursors, including both concentration conditions for each precursor (nominally 50 and 10 ppb for both NO3 and BVOC). Generally, we observe the largest peaks in Ntot from the oxidation of the BVOCs with two double bonds, β-caryophyllene and limonene, regardless of low or high concentration. Hence, for example, the peak Ntot from limonene at 10 ppb initial concentration is larger than the peak Ntot for all the monoterpenes with a single double bond, even at the higher concentration initial conditions. In contrast, the Vtot curves grow fastest for the higher concentration experiments of all terpene precursors. In the case of β-caryophyllene, the faster volume growth at low loading may be due to differing chemical regime; higher NO3/BVOC ratio could lead to more second-generation products.
Figure 2.
Time series of total wall-loss corrected aerosol (a) particle number concentration, and (b) volume and mass concentration, from all experiments producing SOA. Panel (c) repeats (b), zoomed in on the lowest 30 μg m–3 of the y axis to show that the same pattern in volume growth is observed for the low-concentration series as for the high. LOW and HIGH indicate the nominal concentrations of BVOC and oxidant in each experiment; BPIN denotes β-pinene; DCAR, Δ-3-carene, LIMO, limonene; BCARY, β-caryophyllene; and SABI, sabinene.
Aerosol Yield Determination
We determined the unitless time-dependent SOA mass yields over the course of the experiments, defined as Y = ΔM/ΔVOC, based on wall-loss corrected change in aerosol mass ΔM (μg m–3) divided by amount of VOC reacted ΔVOC (μg m–3), referenced to the beginning of the experiment when both aerosol mass (M) and VOC were zero.
Since each experiment was initiated with VOC injection into a chamber already filled with oxidant, the VOC began to react immediately, preventing measurement of its concentration during initial reaction. Therefore, the ΔVOC in each experiment must be calculated. Since there are uncertainties in both the reaction kinetics and chamber mixing, we employ two separate strategies to bracket the possible range of ΔVOC: (1) a simple observationally constrained method that more accurately captures mixing dynamics due to the high precision and time resolution measurement of [NO3], and (2) a free-running kinetics box model assuming a well-mixed chamber, that may more accurately capture subsequent RO2 chemistry, but is subject to large uncertainties in RO2 rate constants for these systems and cannot capture mixing.
For the first method, we use the known amount of VOC injected and the observed [NO3] in each time step (Δt) to determine the amount of VOC consumed via eq 2:
| 2 |
where rate constants k are taken from Calvert et al. (2000),21 [NO3] is the instantaneous observed concentration
(and hence includes NO3 produced from N2O5 added at each time step), and [VOC] is the sum of concentration
added to the chamber and the unreacted concentration in the chamber
from the previous time step. If this calculation of ΔVOC results
in a reacted amount less than the VOC injected during that time step,
then the residual VOC builds up in the chamber and contributes to
the instantaneous rate calculation for the next timsestep. In this
way, a ΔVOC 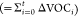 timeseries is derived that
depends only on observed NO3 consumption, assuming a one-to-one
NO3 to VOC stoichiometry. This method ignores any reactions
of NO3 with first-generation oxidation products (NO3 + RO2 reactions), thus rendering it an upper limit
on the amount of VOC reacted, which leads to lower limit SOA yields.
However, it has the advantage of allowing our most precise, highest
time-resolution measurement to directly incorporate the time scale
of chamber mixing into the calculation of ΔVOC. Thus, for each
experiment we determine a complete ΔVOC time series that is
constrained until NO3 concentration decreases to zero,
as shown in the SI (Figure S3). Often,
the usable SMPS data is truncated before this occurs, because the
aerosol size distribution grows to diameters beyond the measurement
range (∼350 nm).
timeseries is derived that
depends only on observed NO3 consumption, assuming a one-to-one
NO3 to VOC stoichiometry. This method ignores any reactions
of NO3 with first-generation oxidation products (NO3 + RO2 reactions), thus rendering it an upper limit
on the amount of VOC reacted, which leads to lower limit SOA yields.
However, it has the advantage of allowing our most precise, highest
time-resolution measurement to directly incorporate the time scale
of chamber mixing into the calculation of ΔVOC. Thus, for each
experiment we determine a complete ΔVOC time series that is
constrained until NO3 concentration decreases to zero,
as shown in the SI (Figure S3). Often,
the usable SMPS data is truncated before this occurs, because the
aerosol size distribution grows to diameters beyond the measurement
range (∼350 nm).
In the second method of ΔVOC calculation, we employ a free-running kinetics box model constrained only by the known addition rates of N2O5 and VOC. The cumulative VOC reacted over time is determined, by iterative solution of coupled kinetic equations for all X molecules:
| 3 |
where [X]in is the concentration of X in the inlet flow (only N2O5 and VOC are added, at known concentrations shown in Table 2), [X]ch is the concentration in the chamber, Q is the flow rate through the chamber (40 lpm), and V the chamber volume (10 000 L), Y are all chemical losses (for NO3, reactions with VOC, RO2, and NO2; for VOC, only reaction with NO3), Z are all chemical sources (N2O5 decomposition for NO3; none for VOC), and kwall,X is the rate of loss of X to chamber walls. The complete set of reactions and rate constants used are described in the SI Figure S4 and Table S2. The cumulative ΔVOC is obtained by summing cumulative reacted VOC in this model.
This method is superior in its chemical complexity, explicitly including RO2 + NO3, RO2 + RO2, and RO2 + NO2 reactions after the initial NO3 + VOC → RO2. However, because these reaction rates are poorly known for monoterpene nitrato-RO2, this introduces some uncertainty. Further, since we are no longer constrained by NO3 data, we must invoke wall losses for NO3 and N2O5. In order to run this model consistently across experiments and with the minimum number of arbitrarily tunable variables, we “spun up” the model with continuous N2O5 addition to the initial conditions of each chamber experiment, determining NO3 and N2O5 wall loss rate constants that best fit all available data. Each experiment then proceeds by continuous addition of VOC and N2O5 at the known injection rates, which we model free-running, with no tuning to match observed NO3 decay. This model assumes a well-mixed chamber at all times, so we interpret discrepancies with observed NO3 decay to be due to mixing inhomogeneity or uncertainties in RO2 rate constants (see SI Figure S5 for an exemplary model fit of NO3 decay). Because this method incorporates additional losses of NO3, resulting VOC consumption is slower, leading to higher apparent SOA yields.
Both methods of ΔVOC determination ignore reaction with the second double bonds in limonene or β-caryophyllene, which would deplete NO3 further and enhance SOA yields.30 The rate of NO3 reaction at the second, exocyclic double bond is predicted to be 30-fold slower in the case of limonene, so this is not expected to be a large effect,17 although it may be more competitive in the low β-caryophyllene experiment, where N2O5 concentration greatly exceeded BVOC.
Each wall-loss corrected SMPS size distribution in the time series was converted to ΔM as follows. First, we iteratively applied the size-dependent wall loss corrections to the full SMPS time series to derive a complete time series of the size distributions that would have been observed had no particles been lost the walls. Then, number concentration data from each size bin were converted to SOA mass concentration in μg m–3 using the mean bin diameter and assumed organic aerosol density of 1.4 g cm–3.7 Since no seed particles were used, all observed aerosol is organic, and the wall-loss corrected aerosol mass gives cumulative ΔM. The ratio of this ΔM to cumulative VOC consumed is the unitless mass yield, (Y = ΔM/ΔVOC).
We observe differences between high and low concentration mass yield curves (Figure 3) that vary with BVOC, suggesting that the experiments differ in more than simply the total aerosol mass loading. We note from the kinetics modeling that in all experiments, the ratio of RO2—NO3 to RO2—RO2 rates is highest initially and decreases, in the case of the low concentration experiments crossing over so that after several hours of reaction, RO2—RO2 reactions are predicted to be dominant, while in the high concentration experiments, RO2—NO3 reactions dominate throughout. Because these rate constants are quite uncertain and not known for specific BVOC precursors, we simply conclude that some of the explanation of the higher yields for the high concentration experiments may lie in the differences in RO2 radical fate. We note here again an important difference between these experiments and what would be observed in the atmosphere: HO2 radicals were nonexistent in these chamber experiments, but are expected to be a significant reaction partner for RO2 in the real atmosphere.
Figure 3.
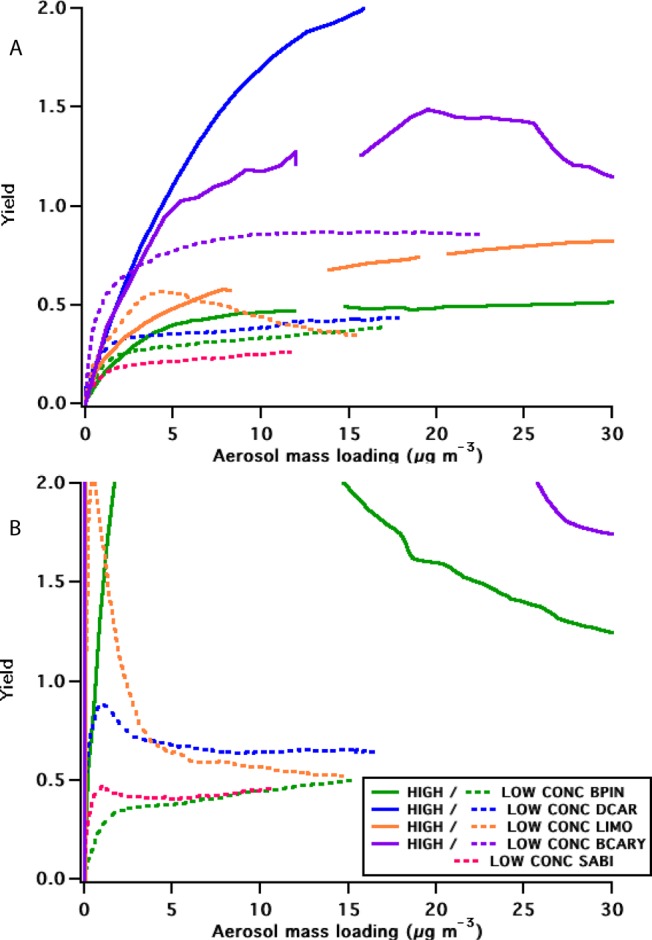
Yield curves for high and low NO3 + BVOC SOA experiments, using (a) observed NO3 decay, or (b) complete kinetics model to determine reacted BVOC. BVOC labeling is as in Figure 2.
In all low concentration experiments, due to the slower reaction, the ΔVOC is better constrained for longer periods, and the mixing time scale is faster relative to reactions, resulting in yield curves with less uncertainty but with the same inter-BVOC trend observed at both concentration conditions. Due to these differences, subsequent discussion will focus only on these low concentration experiments. As is apparent in Figure 3, the high concentration experiments (and early stages of some low concentration experiments) produce unrealistically high yields, especially in the full kinetics model, suggesting that in these cases, reactions were faster than chamber mixing and that this box model may be inaccurate. According to absorptive partitioning theory,31−34 yields should increase with aerosol mass loading, assuming a constant product distribution over time. If, however, the product distribution is changing over time as RO2 reactive fate changes, then mass yields could appear to decrease as an artifact of a shift from early high molecular weight products to later lower molecular weight products. As a result of these uncertainties at early times, we do not fit the mass-dependent yield for these experiments, but rather report yields at 10 μg m–3 for each low concentration experiment (Table 3). We choose 10 μg m–3 because it is sufficiently late in the low concentration experiments (generally ∼1.5 h) that irregularities in the yield curve have subsided.
Table 3. Aerosol Yields (=ΔM/ΔVOC) Observed at 10 μg m–3 in the Low-Concentration NO3 Oxidation Experiments, Using Two Alternative Methods of Determining ΔVOC to Bracket Uncertainties Due to Mixing and RO2 Fatea.
| BVOC | yield @ 10 μg m–3 ΔVOC calculated from NO3 loss alone (Method 1) | yield @ 10 μg m–3 ΔVOC calculated by complete kinetics model with RO2 reactions (Method 2) |
|---|---|---|
| β-pinene | 0.33 | 0.44 |
| Δ-3-carene | 0.38 | 0.65 |
| limonene | 0.44 | 0.57 |
| sabinene | 0.25 | 0.45 |
| β-caryophyllene | 0.86 | n/ab |
| α-pinene | 0 | 0 |
Method 1 represents a lower limit yield, since no other RO2 reactions are included, while Method 2’s uncertainty lies in the uncertainty of rate constants (see SI discussion around Figures S3–S6).
For β-caryophyllene, extremely rapid modeled RO2 + NO3 reactions result in predicted very slow BVOC consumption and thus unreasonably high yields. This may be indicative of the rate constants being different for sequiterpene RO2. Because the predicted relative excess of RO2 + NO3 reactions is greatest for β-caryophyllene, it is likely that the reported yield from the first method (which neglects these pathways entirely) is an underestimate.
Mechanistic Hypotheses for Observed Differences in SOA Formation
Although we observe different yields for the high and low concentration experiments for each BVOC (Figure 3), the inter-BVOC trend of volume growth observed at the higher oxidant + BVOC concentrations follows a similar pattern seen in the lower concentration experiments (Figure 2). This suggests that the mechanism responsible for this behavior corresponds to the chemical nature of each individual BVOC. Among the monoterpenes with one double bond, Δ-3-carene’s initial volume growth (Figure 2b) exceeds both β-pinene and sabinene for both high and low concentration experiments, not matching the trend in reaction rate constants (sabinene’s rate of reaction with NO3 is faster than Δ-3-carene’s). Sabinene was included in these experiments to assess whether the instability of the three-membered ring was responsible for Δ-3-carene’s high SOA yield; sabinene’s relatively low yield suggests that this is not the explanatory difference.
A possible mechanism for the observed SOA formation trends emerges when examining the structural differences of these monoterpenes. The NO3 radical preferentially adds to the double bond in such a way as to make the more substituted alkyl radical, which will quickly react with O2 to become an alkyl peroxy radical, and then upon reaction with another NO3 or RO2, will produce the alkoxy radical (mechanism shown the SI Figure S6). In the subsequent reaction forming a ketone, the bond that is broken can be predicted via structure activity relationships (e.g., Table 3 in Vereecken and Peeters,35 shown in black in SI Figure S6). Because a β-alkyl substitution destabilizes the adjacent bond more than a β-nitrate, the ketones predicted to be formed from breaking the weakest C—C bond in α-pinene and Δ-3-carene are structurally very different. In α-pinene, the predicted product has the radical at the opposite end of the molecule from a terminal nitrate. In Δ-3-carene, limonene, and β-caryophyllene, the radical ends up adjacent to the nitrate group, a structure which will stabilize the radical, possibly making it more likely to undergo subsequent radical-initiated oligomer formation rather than decomposition, and explaining high organonitrate and aerosol yields. However, we note that the predicted pathway of α-pinene bond scission is inconsistent with the observed dominant product channel of pinonaldehyde (Table 1), which is consistent with our observed low nitrate yield from α-pinene and potentially explanatory of low aerosol yield. Additional observations of NOy balance relevant to the understanding this subsequent radical chemistry are discussed below.
The importance of the nitrate radical in initiating rapid SOA growth was tested by conducting another limonene experiment (Expt. 8), where NO3 was generated by O3 + NO2 (more typical in the atmosphere) rather than N2O5 dissociation. In this case, limonene was oxidized by a mixture of O3 and NO3, rather than only the NO3 radical. No OH scrubber was used, so OH recycling may have also contributed to oxidative chemistry in this case, given the 86% OH yield from ozonolysis of limonene.36 We observed in this mixed-oxidant case both a 3-fold lower peak number concentration and slower initial volume growth than in the case of NO3 alone at nominally the same initial oxidant concentration ([N2O5]i = 10 ppb vs [O3]i = 12 ppb and [NO2]i = 6.3 ppb, in both cases with [limonene]i = 10 ppb). These nominally similar concentrations do not imply similar rates–the rate constant of O3 + limonene is 2.1 × 10–16 cm3 molec–1 s–1,6 in contrast to NO3 + limonene’s 1.22 × 10–11 cm3 molec–1 s–1.21 In the observed volume growth curves, later in the experiment the total SOA volume in the mixed-oxidant case “catches up” to the NO3-only experiment. Hence, limonene ozonolysis and nitrate oxidation produce similar eventual SOA mass yields at comparable initial concentrations, but NO3-initiated chemistry appears more effective at nucleating new particles. This is consistent with the initial nitrate oxidation products being higher mass and lower-volatility than their ozone and OH counterparts under dry conditions, but both reactions producing substantial yields of products of intermediate volatility that begin to condense as aerosol loading increases.
The Exceptional BVOC: α-Pinene Forms No Aerosol upon NO3 Oxidation
The wide range of observed SOA yields from NO3 oxidation of various BVOC is provocative, but perhaps most surprising is the observation that α-pinene reacting with NO3 produced no SOA. Because α-pinene is frequently used as a model monoterpene in chamber studies, this exceptional behavior relative to all other monoterpenes tested is particularly important. We seek an explanation in the initial oxidation steps of this reaction, and note that α-pinene could be expected to produce an internal nitrate rather than a terminal nitrate, such as would be expected in β-pinene, Δ-3-carene, or sabinene (see SI Figure S6). It has been shown that terminal functional groups result in lower vapor pressure than internal, but this observation would seem to be a very extreme manifestation of that trend. We note that the NO3 + α-pinene reaction forms little organonitrate (Table 4), and this organonitrate was not observed to partition to the aerosol phase. Most of the NO3 returns to the gas phase as NO2, consistent with previous observations that α-pinene chemistry instead produces the diketone pinonaldehyde (SI Figure S6, red pathway), which is expected to be more volatile than the organonitrate alternatives.37
Table 4. Observed Organic Nitrate Yields and Gas/Aerosol Partitioning, and Nitrogen Balancea.
| BVOC | molar organic nitrate yield (Δ[ANs + PNs]/ Δ[VOC]) | fraction of organonitrates in aerosol phase (Δ[ANs + PNs]aero/Δ[ANs + PNs] | organonitrate fraction of total aerosol mass (MANsaero/Mo) | N-balance: NO2 release (Δ[NO2]/ −Δ[N2O5]) | N-balance: organonitrate formation (Δ[ANs + PNs]/–Δ[N2O5]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-pinene | 0.22 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 1.04 1.15 | 0.08 0.23 |
| Δ-3-carene | 0.77 | 0.50 | 0.56 | 1.14 | 0.22 |
| limonene | 0.54 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.76 0.96 | 0.31 0.41 |
| β-caryophyllene | n/a | 1 | 0.80 | n/ab | n/ab |
| α-pinene | 0.10 | 0 | 0 | 1.54 1.75 | 0.03 0.10 |
BVOC-based molar organic nitrate yield, aerosol fraction of organonitrates, and organonitrate fraction of total aerosol mass are all evaluated at 2 h after chamber experiment initiation (data are all from the high-concentration experiments, when the TD-LIF instrument was available); N2O5-based NO2 and ANs + PNs production are evaluated at 30 min after chamber experiment initiation. For β-pinene, limonene, and α-pinene, NO3 decays slowly enough that this N balance analysis can be reliably repeated at 2 h. These are the numbers reported in italics.
Several parameters are not available for β-caryophyllene, because the N2O5 decay was very rapid and not well-characterized.
Organonitrate Yields for Various BVOC
An example of observed gas- and aerosol-phase organonitrate production is shown in the SI (Figure S7). The nitrogen balance of all high concentration experiments, for which organonitrate measurements were available, are reported in Table 4 and described below.
We determined molar organonitrate yields from BVOC (Δ[ANs + PNs]/Δ[VOC] in ppb units, using “method 1” ΔVOC), fraction of total organonitrates in the aerosol phase (Δ[ANs + PNs]−aero/Δ[ANs + PNs] in ppb units), and the fraction of total aerosol mass that is due to organonitrates (MANs,aero/Mo in μg m–3), all evaluated at 2 h into the experiment to capture longer-term trends. The calculation of total organonitrates requires subtraction from the total TD-LIF ANs + PNs signal the fraction of chamber N2O5 that is detected in this channel (empirically determined by comparison to CRDS to be 11%), and if dinitrates are present, then they would appear as 2 nitrates. The calculation of total and organonitrate aerosol mass concentrations require (a) the conversion of gas phase organonitrates to mass concentration, using assumed values for the average organonitrate molecular weight; and (b) assumptions about average density of SMPS-measured aerosol and the average organonitrate molecular weight to convert mixing ratios to mass concentrations for comparison to SMPS-derived total aerosol mass concentration. We assume an aerosol density of 1.4 g cm–3, and that ANs+PNs are on average hydroxynitrates of molecular weight 214 g mol–1 (286 g mol–1 for β-caryophyllene), hence at the experiments’ ambient pressure (Patm = 0.8 atm), 1 ppb = 7.0 μg m–3 (9.4 μg m–3 for β-caryophyllene).
In addition, we investigate the observed nitrogen balance in these high-concentration experiments by comparing molar NO2 release from N2O5 (Δ[NO2]/−Δ[N2O5] in ppb units) and organonitrate formation (Δ[ANs + PNs]/−Δ[N2O5] in ppb units) to assess closure. For these measurements, we use data 30 min after initiation of the chamber experiment, to ensure that −Δ[N2O5] is still well-constrained.
Several key similarities and differences among BVOC emerge in this comparison. First, we note that in all experiments except α-pinene, organonitrates constitute a substantial fraction of total aerosol mass (greater than 60%), and a large fraction (50–100%) of observed organonitrates are in the aerosol phase. This indicates that the organonitrates produced in NO3 + monoterpene or sesquiterpene reactions tend to be of low volatility, with the largest aerosol-phase fraction (lowest volatility) nitrate arising from the oxidation of the single sesquiterpene tested, β-caryophyllene. This is consistent with expectation based on the sesquiterpene’s larger molecular weight.
There is a correlation between organic nitrate molar yields and aerosol mass yields (see Table 3), with α-pinene’s low organonitrate yield corresponding to no SOA production, while Δ-3-carene and limonene have both larger organonitrate yields and SOA yields. However, the correlation is not strong (consistent with previous observations by Hallquist et al.12). For example, β-caryophyllene does not fit the trend: despite the largest SOA yield, it has the second-lowest organonitrate yield. We note that the β-caryophyllene experiment differed from others in terms of initial conditions, with [BVOC] ≫ [N2O5], which may explain this discrepancy. In addition, as a sesquiterpene (C15), β-caryophyllene starts at a lower volatility than other precursors, which may also affect the degree to which non-nitrate products might also partition to the aerosol phase. Its larger size also may affect vapor-phase wall losses, which are observed to be faster for larger carbon number molecules,29 potentially depressing apparent SOA yield relative to the monoterpenes (C10). All of the organonitrates produced from β-caryophyllene are observed in the condensed phase.
The nitrogen balance provides additional indications of differences among precursors (a schematic of N balance is shown in SI Figure S8). NO2 release greater than 1 indicates that some of the NO3 + BVOC products fragment to rerelease NO2 (the first NO2 molar equivalent comes from the initial dissociation of N2O5). This NO2 release is greatest for α-pinene, which does not produce SOA, suggesting that the non-nitrate/fragmentation products are less condensable.
In all cases, the total N balance after 30 min reaction time sums to less than two total, the total that would be expected for closure (as there are two molar equivalents of N in each N2O5 precursor upon which the N balance is based). This shortfall could be due to faster wall losses of organonitrates, or to the production of NOy species not measured, most notably, HNO3. Previous chamber studies of NO3 + β-pinene and limonene have demonstrated substantial HNO3 formation;16,17 in these experiments, β-pinene and limonene exhibit the least total N closure. Furthermore, as can be seen in the three available time-dependent N balances, the N shortfall is largest at the beginning of the experiments, when [NO3] most dramatically exceeds [BVOC], resulting in the greater likelihood of other later-generation NO3 reactions such as H abstraction to produce HNO3.
In summary, SOA yield is greater for the sesquiterpene than monoterpenes, and within the monoterpenes is roughly correlated with the production of low-volatility nitrates. SOA formation is hindered by excessive fragmentation and NO2 release (as observed in α-pinene).
Implications for Modeling SOA Formation
The observed SOA yields range widely, from 0 to 86% at 10 μg m–3 background aerosol, but display consistent trends across experiments at different initial concentrations, suggesting that differences are a function of BVOC precursor molecular structure. In past global modeling efforts, a single yield has been applied for aggregate NO3 + terpenes, for example, Pye et al.38 use a parametrization based on Griffin et al.,39 which gives SOA yield at 10 μg m–3 of 26% and find that adding in NO3 oxidation of terpenes increased global SOA production by 3 Tg/yr. If we apply our speciated yields to the case of a Rocky Mountain front range forest, where the mix of BVOC is 1:1:1 α-pinene/β-pinene/Δ-carene,40 then we obtain a BVOC-weighted yield of 24%–36% (range based on yields from two ΔVOC methods), which falls in line with the Pye et al. aggregate model because high yield from some BVOC outweighs zero yield from α-pinene. However, in parts of the country where α-pinene is dominant among terpenes (coastal Pacific northwest, deep south41), this aggregate number may overestimate NO3-initiated SOA production, while areas where other terpenes dominate (central plains, northeastern U.S.), the aggregate may underestimate NO3-initiated SOA production.
An additional factor to note when comparing to the real atmosphere is that the relative importance of NO3 oxidation vs O3 varies among these molecules: at 10 ppt NO3 and 30 ppb O3, nitrate reaction rates proceed 20–90 times faster than ozonolysis for all the monoterpenes, but for β-caryophyllene, only half as fast.6 Thus, β-caryophyllene will be relatively less likely to be oxidized by NO3. A true assessment of the role of these reactions requires more detailed regional modeling that can capture the spatial overlap of speciated natural BVOC emissions with anthropogenic NOx plumes and resulting oxidation chemistry.
Acknowledgments
J.L.F. gratefully acknowledges sabbatical support from the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Science (CIRES) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research Visiting Scholars Program, and J.L.F. and S.S.B. acknowledge funding from the NOAA Climate Program Office’s AC4 program (Grant No. NA13OAR4310070). We thank Serena Chung, Peter McMurry, Paul Ziemann, and John Orlando for helpful discussions. J.N.S. acknowledges funding from the Finnish Academy (Grant No. 251007) and U.S. Department of Energy (Grant No. DE-SC0006861). P.M.W. acknowledges financial support from the Austrian Science Fund (FWF, Project No. J3198-N21). The National Center for Atmospheric Research is sponsored by the National Science Foundation.
Supporting Information Available
NCAR chamber facility description; schematic of the NCAR environmental chamber facility (Figure S1); instruments used in chamber experiments (Table S1); wall loss analysis; wall loss characterization for the NCAR chamber (Figure S2); determination of ΔVOC; derivation of cumulative β-pinene FVOC time series (Figure S3); kinetics box model mechanism (Figure S4); rate constants used in the above model (Table S2); wall loss characterization for the NCAR chamber; exemplary model run for β-pinene high concentration experiment (Figure S5); molecular structural effects on alkoxy radical fate; proposed initial steps of nitrate oxidation (Figure S6); Full time series of organonitrate measurements (Figure S7); schematic of nitrogen balance (Figure S8); and additional references. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org/.
Author Present Address
¶ Department of Physics, University of Vienna, Austria.
Author Present Address
▲ Department of Chemistry, University of York, York, United Kingdom.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Hallquist M.; Wenger J. C.; Baltensperger U.; Rudich Y.; Simpson D.; Claeys M.; Dommen J.; Donahue N. M.; George C.; Goldstein A. H.; Hamilton J. F.; Herrmann H.; Hoffmann T.; Iinuma Y.; Jang M.; Jenkin M. E.; Jimenez J. L.; Kiendler-Scharr A.; Maenhaut W.; McFiggans G.; Mentel T. F.; Monod A.; Prévôt A. S. H.; Seinfeld J. H.; Surratt J. D.; Szmigielski R.; Wildt J. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5235. [Google Scholar]
- Spracklen D. V.; Jimenez J. L.; Carslaw K. S.; Worsnop D. R.; Evans M. J.; Mann G. W.; Zhang Q.; Canagaratna M. R.; Allan J.; Coe H.; McFiggans G.; Rap A.; Forster P. Aerosol mass spectrometer constraint on the global secondary organic aerosol budget. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 112312109–12136. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther A.; Hewitt C. N.; Erickson D.; Fall R.; Geron C.; Graedel T.; Harley P.; Klinger L.; Lerdau M.; McKay W. A.; Pierce T.; Scholes B.; Steinbrecher R.; Tallamraju R.; Taylor J.; Zimmerman P. A global model of natural volatile organic compound emissions. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 8873–8892. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther A.; Karl T.; Harley P.; Wiedinmyer C.; Palmer P. I.; Geron C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther A.; Jiang X.; Heald C. L.; Sakulyanontvittaya T.; Duhl T.; Emmons L.; Wang X. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2. 1): An extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions. Geosci. Model Dev. Dis. 2012, 521503–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson R.; Arey J. Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of biogenic volatile organic compounds: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 370197–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. R.; Boy M.; Donahue N. M.; Fry J. L.; Glasius M.; Guenther A.; Hallar A. G.; Huff Hartz K.; Petters M. D.; Petäjä T.; Rosenoern T.; Sullivan A. P. A review of the anthropogenic influence on biogenic secondary organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 111321–343. [Google Scholar]
- Pankow J. F.; Barsanti K. C. The carbon number-polarity grid: A means to manage the complexity of the mix of organic compounds when modeling atmospheric organic particulate matter. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43172829–2835. [Google Scholar]
- Ng N.; Kwan A.; Surratt J.; Chan A.; Chhabra P.; Sorooshian A.; Pye H.; Crounse J.; Wennberg P.; Flagan R.; Seinfeld J. Secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation from reaction of isoprene with nitrate radicals (NO3). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8144117–4140. [Google Scholar]
- Ehn M.; Thornton J. A.; Kleist E.; Sipila M.; Junninen H.; Pullinen I.; Springer M.; Rubach F.; Tillmann R.; Lee B.; Lopez-Hilfiker F.; Andres S.; Acir I.-H.; Rissanen M.; Jokinen T.; Schobesberger S.; Kangasluoma J.; Kontkanen J.; Nieminen T.; Kurten T.; Nielsen L. B.; Jorgensen S.; Kjaergaard H. G.; Canagaratna M.; Maso M. D.; Berndt T.; Petaja T.; Wahner A.; Kerminen V.-M.; Kulmala M.; Worsnop D. R.; Wildt J.; Mentel T. F. A large source of low-volatility secondary organic aerosol. Nature 2014, 5067489476–479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wangberg I.; Barnes I.; Becker K. H. Product and mechanistic study of the reaction of NO3 radicals with α-pinene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 3172130–2135. [Google Scholar]
- Hallquist M.; Wangberg I.; Ljungstrom E.; Barnes I.; Becker K. H. Aerosol and product yields from NO3 radical-initiated oxidation of selected monoterpenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 334553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Spittler M.; Barnes I.; Bejan I.; Brockmann K. J.; Benter T.; Wirtz K. Reactions of NO3 radicals with limonene and α-pinene: Product and SOA formation. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40Suppl. 1S116–S127. [Google Scholar]
- Chacon-Madrid H. J.; Henry K. M.; Donahue N. M. Photo-oxidation of pinonaldehyde at low NOx: from chemistry to organic aerosol formation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 1363227–3236. [Google Scholar]
- Moldanova J.; Ljungstrom E. Modelling of particle formation from NO3 oxidation of selected monoterpenes. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31111317–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. L.; Kiendler-Scharr A.; Rollins A. W.; Wooldridge P. J.; Brown S. S.; Fuchs H.; Dube W.; Mensah A.; dal Maso M.; Tillmann R.; Dorn H. P.; Brauers T.; Cohen R. C. Organic nitrate and secondary organic aerosol yield from NO3 oxidation of β-pinene evaluated using a gas-phase kinetics/aerosol partitioning model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 941431–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. L.; Kiendler-Scharr A.; Rollins A. W.; Brauers T.; Brown S. S.; Dorn H.-P.; Dube W. P.; Fuchs H.; Mensah A.; Rohrer F.; Tillmann R.; Wahner A.; Wooldridge P. J.; Cohen R. C. SOA from limonene: role of NO3 in its generation and degradation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 1183879–3894. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler P. M.; Ortega J.; Karl T.; Cappellin L.; Friedli H. R.; Barsanti K.; McMurry P. H.; Smith J. N. Identification of the biogenic compounds responsible for size-dependent nanoparticle growth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 3920L20815. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J.; Smith J. N.; Eisele F. L.; Chen M.; Kuang C.; McMurry P. H. Observation of neutral sulfuric acid-amine containing clusters in laboratory and ambient measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 112110823–10836. [Google Scholar]
- Rollins A. W.; Pusede S.; Wooldridge P.; Min K. E.; Gentner D. R.; Goldstein A. H.; Liu S.; Day D. A.; Russell L. M.; Rubitschun C. L.; Surratt J. D.; Cohen R. C. Gas/particle partitioning of total alkyl nitrates observed with TD-LIF in Bakersfield. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2013, 118126651–6662. [Google Scholar]
- Calvert J. G.; Atkinson J. A.; Kerr J. A.; Madronich S.; Moortgat G. K.; Wallington T. J.; Yarwood G.. Mechanisms of the Atmospheric Oxidation of the Alkenes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner N. L.; Dube W. P.; Washenfelder R. A.; Young C. J.; Pollack I. B.; Ryerson T. B.; Brown S. S. Diode laser-based cavity ring-down instrument for NO3, N2O5, NO, NO2 and O3 from aircraft. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Dube W. P.; Brown S. S.; Osthoff H. D.; Nunley M. R.; Ciciora S. J.; Paris M. W.; McLaughlin R. J.; Ravishankara A. R., Aircraft instrument for simultaneous, in situ measurement of NO3 and N2O5 via pulsed cavity ring-down spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77 (3). [Google Scholar]
- VanReken T. M.; Greenberg J. P.; Harley P. C.; Guenther A. B.; Smith J. N. Direct measurement of particle formation and growth from the oxidation of biogenic emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6124403–4413. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs N. A.The Mechanics of Aerosols, Rev Engl ed. ed.; Dover: Mineola, NY, 1989; p 408. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel O.Chemical Reaction Engineering; Wiley: New York, 1972; p 578. [Google Scholar]
- McMurry P. H.; Grosjean D. Gas and aerosol wall losses in Teflon film smog chambers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19121176–1182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X.; Cappa C. D.; Jathar S. H.; McVay R. C.; Ensberg J. J.; Kleeman M. J.; Seinfeld J. H. Influence of vapor wall loss in laboratory chambers on yields of secondary organic aerosol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111165802–5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga A.; Ziemann ‡ P. J. Gas-wall partitioning of organic compounds in a teflon film chamber and potential effects on reaction product and aerosol yield measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 4410881–892. [Google Scholar]
- Rollins A. W.; Browne E. C.; Min K.-E.; Pusede S. E.; Wooldridge P. J.; Gentner D. R.; Goldstein A. H.; Liu S.; Day D. A.; Russell L. M.; Cohen R. C. Evidence for NOx control over nighttime SOA formation. Science 2012, 33760991210–1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue N. M.; Robinson A. L.; Stanier C. O.; Pandis S. N. Coupled partitioning, dilution, and chemical aging of semivolatile organics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 4082635–2643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odum J. R.; Hoffmann T.; Bowman F.; Collins D.; Flagan R. C.; Seinfeld J. H. Gas/partitioning and secondary organic aerosol yields. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar]
- Pankow J. F. An absorption model of gas/particle partitioning of organic compounds in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 282185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh R.; Donahue N. M.; Robinson A. L. Time scales for gas-particle partitioning equilibration of secondary organic aerosol formed from α-pinene ozonolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47115588–5594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vereecken L.; Peeters J. Decomposition of substituted alkoxy radicals-part I: A generalized structure-activity relationship for reaction barrier heights. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11409062–9074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson R.; Aschmann S. M.; Arey J.; Shorees B. Formation of OH radicals in the gas phase reactions of O3 with a series of terpenes. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 1992, 97D56065–6073. [Google Scholar]
- Pankow J. F.; Asher W. E. SIMPOL.1: A simple group contribution method for predicting vapor pressures and enthalpies of vaporization of multifunctional organic compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8102773–2796. [Google Scholar]
- Pye H. O. T.; Chan A. W. H.; Barkley M. P.; Seinfeld J. H. Global modeling of organic aerosol: The importance of reactive nitrogen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Disscuss. 2010, 10, 21259–21301. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin R. J.; Flagan R. C.; Seinfeld J. H. Organic aerosol formation from the oxidation of biogenic hydrocarbons. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 3555–3568. [Google Scholar]
- Fry J. L.; Draper D. C.; Zarzana K. J.; Campuzano-Jost P.; Day D. A.; Jimenez J. L.; Brown S. S.; Cohen R. C.; Kaser L.; Hansel A.; Cappellin L.; Karl T.; Hodzic Roux A.; Turnipseed A.; Cantrell C.; Lefer B. L.; Grossberg N. Observations of gas- and aerosol-phase organic nitrates at BEACHON-RoMBAS 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8585–8605. [Google Scholar]
- Geron C.; Rasmussen R.; R. Arnts R.; Guenther A. A review and synthesis of monoterpene speciation from forests in the United States. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34111761–1781. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.