Abstract
Soluble β-amyloid has been shown to regulate presynaptic Ca2+ and synaptic plasticity. In particular, picomolar β-amyloid was found to have an agonist-like action on presynaptic nicotinic receptors and to augment long-term potentiation (LTP) in a manner dependent upon nicotinic receptors. Here, we report that a functional N-terminal domain exists within β-amyloid for its agonist-like activity. This sequence corresponds to a N-terminal fragment generated by the combined action of α- and β-secretases, and resident carboxypeptidase. The N-terminal β-amyloid fragment is present in the brains and CSF of healthy adults as well as in Alzheimer's patients. Unlike full-length β-amyloid, the N-terminal β-amyloid fragment is monomeric and nontoxic. In Ca2+ imaging studies using a model reconstituted rodent neuroblastoma cell line and isolated mouse nerve terminals, the N-terminal β-amyloid fragment proved to be highly potent and more effective than full-length β-amyloid in its agonist-like action on nicotinic receptors. In addition, the N-terminal β-amyloid fragment augmented theta burst-induced post-tetanic potentiation and LTP in mouse hippocampal slices. The N-terminal fragment also rescued LTP inhibited by elevated levels of full-length β-amyloid. Contextual fear conditioning was also strongly augmented following bilateral injection of N-terminal β-amyloid fragment into the dorsal hippocampi of intact mice. The fragment-induced augmentation of fear conditioning was attenuated by coadministration of nicotinic antagonist. The activity of the N-terminal β-amyloid fragment appears to reside largely in a sequence surrounding a putative metal binding site, YEVHHQ. These findings suggest that the N-terminal β-amyloid fragment may serve as a potent and effective endogenous neuromodulator.
Keywords: β-amyloid, Ca regulation, fear memory, neuromodulation, synaptic plasticity
Introduction
Amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides of 38–43 aa in length are cleaved from the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by the combined action of β- and γ-secretases, with Aβ1–42 as the dominant toxic species found in fibrillar form in neuritic plaques (Golde et al., 2000). Though broadly expressed, APP is targeted to synapses (Koo et al., 1990; Schubert et al., 1991), resulting in the release of Aβ into the synaptic environment in a nerve activity-dependent manner (Cirrito et al., 2005, 2008). APP can also be cleaved by α-secretase followed by γ-secretase, yielding a different array of peptide fragments [e.g., Aβ17–42 (P3), sAPPα], and this has been termed the alternative, nonamyloidogenic pathway (Esch et al., 1990; Selkoe, 2001; Selkoe and Schenk, 2003). Previous evidence appeared to indicate that the two pathways are mutually exclusive (Skovronsky et al., 2000; Thinakaran and Koo, 2008). Recently, a third pathway has been proposed, involving successive action of α- and β-secretases (Portelius et al., 2011). This pathway was inferred following the discovery of Aβ1–15 and Aβ1–16 as prominent N-terminal Aβ fragments in brain and CSF by Portelius et al. (2007, 2010a). Under conditions of reduced γ-secretase activity, this third pathway appears to be fostered by virtue of an increase in α-secretase activity (Portelius et al., 2010b, 2011), yielding N-terminal Aβ peptide fragments to perhaps coexist at varying levels with full-length Aβ. As there are several receptor-linked means by which α-secretase activity may be regulated (e.g., via protein kinase C; Thinakaran and Koo, 2008), the production of such N-terminal Aβ fragments may be a dynamic physiological event.
Aβ1–42 has 28 residues outside of the transmembrane (TM) domain and 14 residues from within the predicted TM domain of APP. The first 28 residues have a hydrophilic nature, whereas the rest are largely hydrophobic, comprising the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of the Aβ peptide, respectively. Therefore, it is possible that the two different domains of Aβ, namely the extracellular and TM domains, have different molecular targets with which they interact, and the N-terminal fragments may represent highly soluble, active peptides.
Several putative molecular targets for soluble Aβ have been identified (Patel and Jhamandas, 2012). Two possible targets at the synapse are the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR; Wang et al., 2000; Liu et al., 2001; Pettit et al., 2001) and certain metabotropic glutamate receptors (Chin et al., 2007), both of which have been shown to be functionally regulated by Aβ. An agonist-like action of Aβ on presynaptic nAChRs has previously been observed (Dougherty et al., 2003; Mehta et al., 2009; Khan et al., 2010), regulating synaptic plasticity (Puzzo et al., 2008, 2011). We have determined that Aβ activates the α7 nAChR via the receptor's agonist-binding domain (Tong et al., 2011). To investigate the possibility that the N-terminal fragment arising from α- and β-secretase cleavage retains the agonist-like activity of Aβ, we examined its impact on presynaptic Ca2+, post-tetanic potentiation (PTP), long-term potentiation (LTP), and contextual fear conditioning compared with several Aβ mutants and N-terminal Aβ fragment mutants.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture and transfection.
The hybrid neuroblastoma cell line NG108–15 (Nelson et al., 1976) was maintained in DMEM containing 15% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 0.1 mm hypoxanthine, 1 μm aminopterin, and 16 μm thymidine. The cells were differentiated in 1% FBS-containing DMEM via exposure to dibutyryl cAMP (1 mm, Sigma-Aldrich) for 48 h until axon-like neurites and varicosities were observed (typically 2–3 d) as described previously (Khan et al., 2010). α7-nAChR was expressed in the differentiated NG108–15 cells by transfecting the mouse α7-nAChR cDNA sequence in pcDNA3.1zeo (courtesy of Dr. Jerry Stitzel, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO) using the FuGENE 6 transfection reagent (Roche Diagnostics) or the magnetofection reagent NeuroMag (OZ Biosciences). Mock cells (as controls) were treated with FuGENE 6 or NeuroMag alone. Successful expression of α7-nAChRs required another 48 h. Moderate expression levels were typically obtained, allowing for the detection of negative or positive changes (Tong et al., 2011).
Hippocampal synaptosome preparation.
Synaptosomes (isolated nerve terminals) were isolated from male mouse hippocampi according to a procedure adapted from Dunkley et al. (1986).
Confocal imaging of intracellular calcium.
Changes in Ca2+ level were monitored by the Ca2+-specific fluorescent dye Fluo-4 using confocal imaging, as previously described (Khan et al., 2010). Changes in fluorescent intensity (F) associated with individual structures (varicosities or synaptosomes) in digitized images were determined across all frames using ImageJ. Each time-series was normalized to baseline fluorescence intensity at time zero (F/F0) and corrected for photobleaching. Peak responses were F/F0 values collected during 60–180 s after the initiation of stimulation.
Extracellular field potential recording in hippocampal slices.
Hippocampal slice preparations were from 2- to 5-month-old C57BL/6 mice (The Jackson Laboratory) or 5- to 6-month-old APPswe (Tg2576) and B6/SJL (control littermates) mice (Taconic Biosciences). Extracellular recording in the slices were performed as previously described (Bellinger et al., 2002). In brief, mice were anesthetized with tribromoethanol and decapitated. Hippocampi were dissected from brains removed into ice-cold artificial CSF (aCSF) containing (in mm) 130 NaCl, 3.5 KCl, 1.5 MgSO4, 2 CaCl2, 1.25 NaH2PO4, 24 NaHCO3, and 10 glucose, bubbled with 95% O2/5% CO2, and slices were cut transversely at 350 μm using a vibrating microtome (Leica). Slices were preincubated for 30 min at room temperature before transferring to a chamber at 32°C for another 30 min before recording. Slices were stimulated at 0.1 Hz with 3 V via a bipolar stimulating electrode to produce field EPSPs (fEPSPs) at 20–40% of maximum, as monitored with a 1–5 MΩ glass recording electrode filled with 3 m NaCl. After recording stable baseline responses, LTP was induced in CA1 stratum radiatum upon Schaffer collateral stimulation, following the theta burst protocol (TBP) used by Puzzo et al. (2008) consisting of trains of four pulses at 100 Hz, with 10 trains delivered at 5 Hz, each repeated three times every 15 s (three bursts) or the high-frequency stimulation (HFS) protocol used by Ma et al. (2010), consisting of two 1 s trains of 100 Hz separated by 20 s. Individual responses were recorded as extracellular fEPSPs. PTP was recorded in response to the TBP in separate experiments.
Contextual fear conditioning.
Bilateral injections and contextual fear conditioning were performed as described previously (Sherrin et al., 2010). After acclimatization to the animal facility, C57BL/6 mice were deeply anesthetized (1.2% avertin) and cannulae were stereotaxically inserted bilaterally into the dorsal hippocampi using the following coordinates: anteroposterior, −1.5 mm; lateral, ±1 mm; depth, −2 mm; Paxinos and Franklin, 2001). Cannulated mice were allowed to recover for at least 7 d. Full-length Aβ1–42 or the Aβ1–15 fragment was bilaterally administered via microinjector into the dorsal hippocampi of C57BL/6 mice over 30 s, yielding a maximum volume of 25 μl injected in each side. Single-trial contextual conditioning was then performed, consisting of 180 s exposure to the conditioning context, followed by mild shock (0.8 mA) for 2 s. Context fear memory retention was tested 24 h later by measuring the freezing response (lack of movement observed at 10 s intervals) to re-exposure to the conditioning context. This was independently performed by two trained observers. Mean activity during conditioning and activity burst produced by the shock were automatically measured using a computer-controlled fear-conditioning system (TSE Systems). Basic locomotion was also monitored. In separate experiments, methyllycaconitine (MLA; 20 μm) was bilaterally injected into the dorsal hippocampi alone or just before the injection of the Aβ peptide or fragment, and fear conditioning was assessed as noted.
Animals.
Protocols for the use of mice in the imaging, electrophysiological, and behavioral experiments were approved by the University of Hawai'i Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee in accordance with the National Institutes of Health and Society for Neuroscience guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. Adult male mice were used for all preparations.
Tris–tricine electrophoresis, circular dichroic spectroscopy, and thioflavin-T fluorescence.
As Aβ is normally present largely in oligomeric form when suspended in aqueous solution (Bell et al., 2004; Khan et al., 2010), it was essential to assess the oligomeric state, secondary structure content, and fibril formation of Aβ, the Aβ fragments, and mutants. For assessment of monomer-oligomer status, 10–20% Tris–tricine gel electrophoresis (Bio-Rad) was used. Coomassie staining was performed by LabSafe GEL Blue (G-Biosciences). Silver Stain Plus Kit (Bio-Rad) was used for high-sensitivity (nanogram) detection (Bio-Rad). For Aβ1–15, monomeric status was confirmed using Amicon Ultra 3 kDa-cutoff spin filters. As the molecular weight of the peptide is 1827 Da, the 3 kDa cutoff filter will exclude dimers or larger. Circular dichroic (CD) spectra of Aβ peptides and fragments in 50 mm phosphate buffer, pH 7, were obtained using a Jasco J810 CD spectrometer. As Thioflavin-T (ThT) binds selectively to fibrillar-aggregated Aβ, the time courses for fibril formation were assessed fluorimetrically using a LS50B Fluorescence Spectrometer (PerkinElmer) with 440 nm excitation and 480 nm emission following incubation of the peptides with 5 μm ThT out to 72 h. All the readings were normalized to the first reading of full-length Aβ1–42 at 0 h.
Chemicals and β-amyloid preparation.
The following Aβ peptides, Aβ mutants, and Aβ peptide fragments were purchased from American Peptide (all are human sequences unless otherwise noted): Aβ1–42; Aβ42–1; Aβ1–15; Aβ1–16; Aβ1–28; Aβ17–42; Aβ33–42; Aβ1–11; [H13A] Aβ1–42; and rodent Aβ1–42. The following truncated sequences were purchased from Anaspec: Aβ1–9; Aβ4–10; Aβ1–12; Aβ1–13; and Aβ1–14. The following mutant Aβ and Aβ N-terminal fragments were synthesized by Peptide 2.0: Aβ10–15; [F4A] Aβ1–15; [R5A] Aβ1–15; [H6A] Aβ1–15; [D7A] Aβ1–15; [H13A][H14A] Aβ1–15; Aβ15–1; and rodent Aβ1–15. Purity of the peptides was confirmed using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Proteomics Core, Agricultural Sciences, University of Hawai'i at Manoa).
Stock solutions of human Aβ peptides, mutants, and fragments were prepared at 0.1–0.5 mm by dissolving the solid synthetic peptides in double-distilled H2O, as previously described (Khan et al., 2010), and stored at −20°C. The peptides were diluted for each experiment into oxygenated HEPES-buffered saline to final concentration (picomolar–nanomolar match concentrations found in vivo; Puzzo et al., 2008, 2011) and vortexed to assure full suspension.
Unless otherwise noted, all standard chemicals (e.g., buffers) were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific or Sigma.
Statistical analysis.
Each experiment was replicated at least three times. Multiple groups were compared by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple-comparison post hoc test. Two-tailed Student's t tests were used for pairwise comparison. A p value of <0.05 was used as the minimal threshold for significance.
Results
The N-terminal Aβ fragment is a highly effective and potent activator of α7-nAChRs
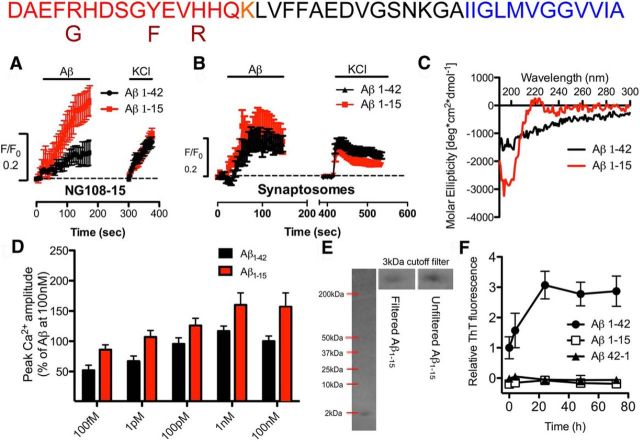
To identify the domains in Aβ essential for activating α7-nAChRs, we first compared the hydrophilic domain to the hydrophobic domain. We considered two fragments encompassing the hydrophilic domain, Aβ1–28 and Aβ1–15, the latter as a representative of α- and β-secretase cleavage, followed by carboxypeptidase cleavage (Portelius et al., 2010b). For comparison, Aβ33–42 was used to represent the core of the hydrophobic domain. As a sensitive functional screen for agonist-like activity of various Aβ peptides, relative changes in Ca2+ level on α7-nAChR activation in individual axonal varicosities of NG108–15 cells were assessed via confocal imaging (Khan et al., 2010; Tong et al., 2011). Both Aβ1–28 and Aβ1–15 retained agonist-like activity in increasing Ca2+ (Figs. 1, 2), whereas Aβ17–42 (P3) and Aβ33–42 displayed no significant activity over that found for the control Aβ42–1 peptide (39 ± 7% of Aβ1–42, n = 32; 33 ± 13% of Aβ1–42, n = 24), which was not different from that seen for Aβ1–42 or Aβ42–1 with mock-treated cells (Khan et al., 2010), both being not significant over baseline. Aβ15–1, as an additional control, was also essentially inactive (30 ± 10% of Aβ1–42; n = 38) when compared with baseline. Not only did Aβ1–15 have agonist-like activity, it was potent (EC50 ≤1 pm; Fig. 1D) and much more effective (157 ± 23%; n = 29; Fig. 2A) than Aβ1–42. The activity of Aβ1–15 was not restricted to α7-nAChRs, as α4β2-nAChRs were also activated by the peptide fragment (data not shown). This was confirmed using primary nerve endings from mouse hippocampus (Fig. 1B), which express both receptor subtypes (Mehta et al., 2009). As for the nature of the active N-terminal fragment, Aβ1–15 (molecular weight, 1827 Da) was found to exist largely as a monomer (Fig. 1E), with little secondary structure based on CD spectral analysis (Fig. 1C) and no capability of forming fibrils or other oligomeric forms (Fig. 1F), indicating that the soluble monomeric form of this N-terminal Aβ peptide fragment accounts for its agonist-like activity.
Figure 1.
A N-terminal Aβ fragment encompassing residues 1–15 is a potent and highly effective agonist at α7-nAChRs on presynaptic-like axonal varicosities. A, B, Averaged [Ca2+]i responses (F/F0) in varicosities of NG108–15 cells expressing α7-nAChRs (A) or mouse hippocampal synaptosomes (B) to 100 nm Aβ1–42 (A, n = 49; B, n = 16) were compared with responses to 100 nm Aβ1–15 (A: n = 178; p < 0.05; B: n = 26; NS), followed sequentially by K+-induced depolarization. Time-series traces are means ± SEM at individual time points. The Ca2+ responses to 100 nm Aβ1–42 are similar in magnitude to that observed with nicotine (data not shown; see Khan et al., 2010). C, Representative CD spectra for Aβ1–42 and Aβ1–15. D, Averaged peak Ca2+ responses in varicosities expressing α7-nAChRs to 100 fm (n = 22 or n = 33), 1 pm (n = 26 or n = 21), 100 pm (n = 19 or n = 32), 1 nm (n = 30 or n = 15), and 100 nm (n = 44 or n = 29) Aβ1–42 or Aβ1–15, respectively. All pairs (Aβ1–42 vs Aβ1–15) are significantly different (p < 0.05, t test). E, 4–20% gradient Tris-Tricine PAGE of Aβ1–15 (2 nmol). Positions of molecular weight standards (data not shown) are as marked in kilodaltons. Insets show a comparison of Aβ1–15 (molecular weight, 1827 kDa) before and after (from whole lane) filtration through an Amicon 3 kDa cutoff filter. Dimers and larger oligomers will be excluded by the 3 kDa filter. F, Fibril–aggregate formation of Aβ1–42, Aβ1–15, or Aβ42–1 control peptide, each at 200 nm, assessed in triplicate by a fluorimetric thioflavin (ThT) assay.
Figure 2.
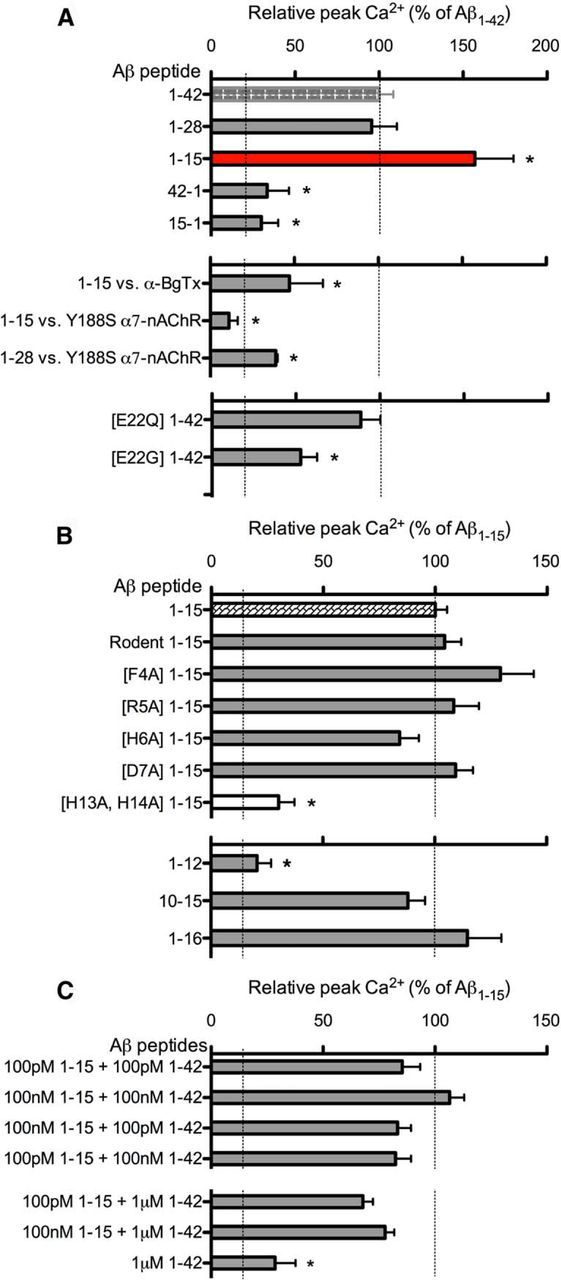
Structure–function analysis of the N-terminal Aβ domain and fragment. A, Averaged peak Ca2+ responses in varicosities of NG108–15 cells expressing α7-nAChRs to 100 nm Aβ1–42 (n = 44), Aβ1–28 (n = 10), and Aβ1–15 (n = 29), and the control peptides Aβ42–1 (n = 24) and Aβ15–1 (n = 38). Peak Ca2+ responses to Aβ1–15 in the presence of 50 nm α-bungarotoxin (α-BgTx, n = 12), Aβ1–15 (n = 20), and Aβ1–28 (n = 11) on Y188S α7-nAChRs. Peak Ca2+ responses to E22Q Aβ1–42 (n = 29) and E22G Aβ1–42 (n = 19). B, Peak Ca2+ responses via α7-nAChRs to rodent Aβ1–42 (n = 49), rodent Aβ1–15 (n = 39), F4A Aβ1–15 (n = 27), R5A Aβ1–15 (n = 46), H6A Aβ1–15 (n = 34), D7A Aβ1–15 (n = 40); H13A/H14A Aβ1–15 (n = 25), Aβ1–12 (n = 48), Aβ1–16 (n = 51), and Aβ10–15 (n = 70). C, Averaged peak Ca2+ responses to mixtures of Aβ1–15 and Aβ1–42 at various concentrations, as noted. *p < 0.05 (Bonferroni post hoc tests) NB. Dashed lines indicate the baseline (background) and respective average maximal responses for either Aβ1–42 and Aβ1–15, as indicated.
As found for Aβ1–42 (Tong et al., 2011), the agonist-like action of Aβ1–15 involved direct activation of the nAChRs, as its activity was lost when the critical Tyr-188 in the agonist binding domain of α7-nAChR was mutated to Ser (Y188S α7-nAChR; Fig. 2A). Consistent with this result, the highly selective antagonist of α7-nAChR, α-bungarotoxin, also blocked Ca2+ increases induced by Aβ1–15 (Fig. 2A). When the hairpin structure of Aβ1–42 was disrupted by the nonconservative familial mutation at Glu-22 (E22G; Morimoto et al., 2004), the agonist-like activity was also reduced (Fig. 2A), indicating that the activity of the 1–15/16 sequence within Aβ1–42 is affected by the overall structure of the full-length peptide.
As an initial indication of the structural basis for the activity of Aβ1–15, mutation of residues near the N terminus was performed, focusing first on Phe-4, Arg-5, and His-6, in particular, based on previous structural analysis of the binding of α-bungarotoxin to α1-nAChRs (Dellisanti et al., 2007; but see also Tong et al., 2011). Aβ1–15 [R5A] was as active as Aβ1–15, as was Aβ1–15 [D7A], eliminating Arg-5 and Asp-7 as possible key residues for activity. Mutation of His-6 and Phe-4 indicate opposing trends but are not significantly different from wild-type Aβ1–15. Comparison of the rodent sequence for Aβ1–15, in which three residues differ from that of the human sequence (Fig. 1), including Arg-5 (R5G), as well as Tyr-10 (Y10F) and His-13 (H13R), showed that rodent Aβ1–15 also has significant agonist-like activity compared with full-length Aβ (Fig. 2B), again eliminating Arg-5 from consideration. As for Tyr-10, the change in rodent Aβ1–15 is conservative (Y10F), whereas for His-13 the change retains a large basic residue in position (H13R). As Aβ1–42 [H13A] was found to be less active than the full-length peptide (data not shown), a nonconservative double mutation at His-13 (H13A) and His-14 (H14A) in the N-terminal fragment was examined, along with truncated sequences removing these histidines (e.g., Aβ1–12 as shown). The results show that His-13 and His-14 are key to the activity of the N-terminal Aβ fragment. These findings are consistent with the previous demonstration that Aβ12–28 has significant agonist-like activity (Wang et al., 2000; Dougherty et al., 2003). Moreover, a hexapeptide encompassing these residues, YEVHHQ at 10–15, was found to be as effective as the N-terminal Aβ fragment (Fig. 2B), localizing the primary active sequence to this region. Further analysis will be necessary, involving combinations of mutations in the N-terminal fragment to better define the critical residues for activity and their interaction with target receptors.
To evaluate the modulatory activity of the N-terminal Aβ fragment in the presence of full-length Aβ, various mixtures of the two peptides were tested. For picomolar and nanomolar concentrations, there were no additive effects, but the inclusion of Aβ1–15 showed a trend toward increased responses over that observed for Aβ1–42 alone (compare Figs. 2C, 1D). For highly elevated levels of Aβ1–42 (1 μm), the N-terminal fragment appears to partially reverse the strongly reduced response to the full-length peptide alone (Fig. 2C).
The N-terminal Aβ fragment enhanced PTP, LTP, and contextual fear conditioning
To examine the functional consequence of acute application of the N-terminal Aβ fragment, we examined its impact on synaptic plasticity and hippocampus-based memory. Changes in synaptic plasticity were assessed in mouse hippocampal slices using theta-burst induction of PTP and LTP via the Schaffer collaterals. Numerous previous studies have consistently demonstrated a strong inhibitory effect of full-length Aβ (Aβ1–42 or Aβ1–40) at high nanomolar to micromolar concentrations on LTP (Rowan et al., 2007). In contrast, picomolar Aβ was found to enhance PTP and LTP in a manner dependent upon nAChRs (Puzzo et al., 2008). Here, significant enhancement of PTP (Fig. 3B) and LTP (Fig. 3C,D; peak, 184 ± 25% of baseline; plateau, 162 ± 12% of baseline) following prior incubation with femtomolar levels of Aβ1–15 was observed, without any effect on baseline responses before the induction of LTP. Neither picomolar (Fig. 3C) nor nanomolar (data not shown) Aβ1–15 had a significant effect on LTP, which contrasts with the findings found for full-length Aβ. Interestingly, a report examining the effect of Aβ1–16 on LTP using an intermediate concentration (∼1 nm) found no significant change compared with controls (Portelius et al., 2010a). This underscores the need to examine different concentrations of the Aβ peptide N-terminal fragments, particularly down below the picomolar range. These results also indicate that the N-terminal domain of Aβ may account for the positive neuromodulatory activity of the full-length peptide (Puzzo et al., 2008, 2011).
Figure 3.
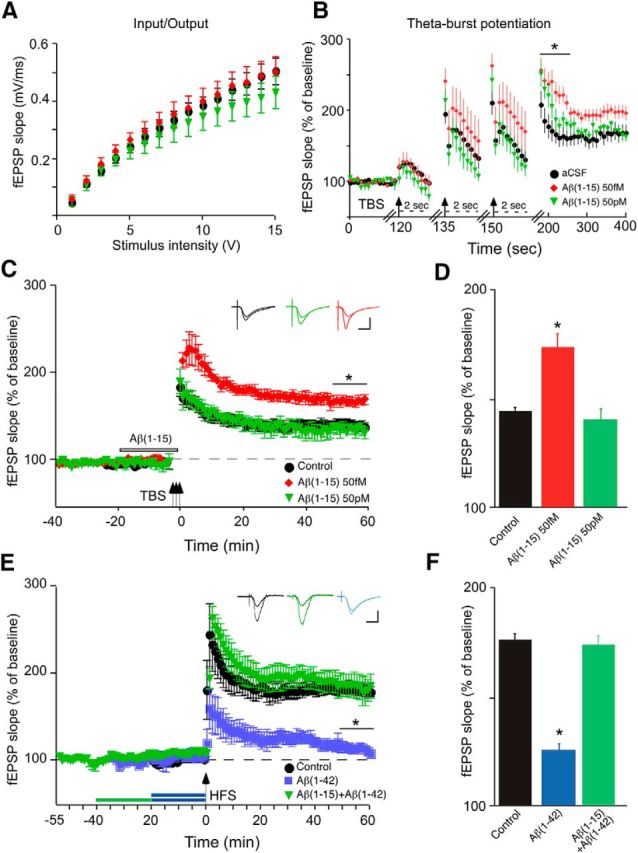
N-terminal Aβ fragment augments LTP in hippocampal slices in the absence or presence of elevated full-length Aβ. Hippocampal slices were superfused with aCSF containing vehicle (control) or various concentrations of Aβ1–15 without (B–D) or with (E, F) Aβ1–42, followed by the induction of LTP in the CA1 region via theta burst stimulation (TBP: four trains of 100 Hz pulses delivered at 5 Hz repeated three times every 15 s for a total of 3 bursts) or HFS (two 1 s trains of 100 Hz separated by 20 s) through the Schaffer collaterals and expressed as normalized fEPSP slope values. A, Control input/output curves, before treatment. B, Recording during and after the theta burst following 57 fm, 57 pm, or 100 nm Aβ1–15 for 20 min, with the start of each burst marked with an arrow. Note the change in time scale (dashed lines) for the bursts: PTP marked with a solid bar. C, TBP-induced LTP with color-coded insets showing example fEPSPs for control aCSF (black), femtomolar Aβ1–15 (red) or picomolar Aβ1–15 (green) for baseline and LTP. The period of Aβ1–15 pretreatment is marked by the open bar. D, Average fEPSP slope values for the end of the plateau (50–60 min post-tetanus), as noted by the solid bar in C (*). E, HFS-induced LTP, with color-coded insets showing example fEPSPs for control aCSF (black), 500 nm Aβ1–42 (blue), or 500 nm Aβ1–15 followed by 500 nm Aβ1–42 (green) for baseline and LTP; periods of peptide pretreatment are marked by the bars. F, Average fEPSP slope values for the end of the plateau (50–60 min post-tetanus), as noted by the solid black bar in E (*). Data are the means ± SD, n = 6 slices/group derived from three experiments. Calibration: horizontal, 10 ms; vertical, 0.4 mV. *p < 0.05 (Bonferroni post hoc tests).
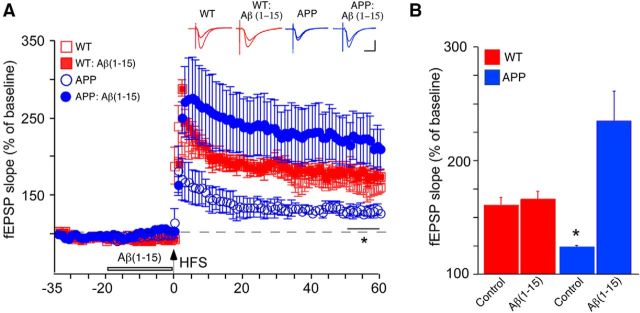
To directly assess the potential of the N-terminal Aβ fragment in the context of elevated full-length Aβ, we examined whether Aβ1–15 affected impairment of LTP by Aβ1–42 with the latter at a concentration (high nanomolar) resulting in the inhibition of LTP induced by HFS (Ma et al., 2010). Pretreatment with Aβ1–15 prevented the impairment of LTP in the presence of 500 nm Aβ1–42 (Fig. 3E,F), indicating that the N-terminal Aβ fragment can function as a strong, positive neuromodulator despite highly elevated levels of full-length Aβ. Similarly, pretreatment with Aβ1–15 led to full “rescue” of LTP in hippocampal slices from APPswe mice (Fig. 4), where the decrement in LTP also appears to be largely the result of elevated full-length Aβ (Ohno et al., 2004).
Figure 4.
N-terminal Aβ fragment rescues LTP deficits in APPswe mouse hippocampal slices. Hippocampal slices from APPswe or wild-type (WT) littermates were superfused with aCSF containing vehicle (Control) or 500 nm Aβ1–15. A, HFS-induced LTP, with color-coded insets showing example fEPSPs for slices from WT mice without or with pretreatment with Aβ1–15 (red) or slices from APPswe mice without or with pretreatment with 500 nm Aβ1–42 (blue) for baseline and LTP; period of Aβ1–15 pretreatment marked by the open bar. B, Average fEPSP slope values for the end of the plateau (50–60 min post-tetanus), as noted by the solid bar in A (*). Data are the means ± SD, n = 4 slices/group. Calibration: horizontal, 10 ms; vertical, 0.4 mV. *p < 0.05 (Bonferroni post hoc tests).
To see whether the functional impact of the N-terminal Aβ fragment extends to hippocampus-based memory, we tested the effect of Aβ1–15 on contextual fear conditioning. Bilateral injection of 100 pm Aβ1–15 into the dorsal hippocampi of mice trained under a standard single-trial contextual fear-conditioning paradigm (Sherrin et al., 2010) led to a significant enhancement of freezing compared with saline-injected control mice or mice injected with 100 nm Aβ1–15 (mean ± SEM percentage freezing: saline control, 36 ± 9% SEM; 100 pm Aβ1–15, 69 ± 8% SEM; 100 nm Aβ1–15, 24 ± 4% SEM; Fig. 5A). There was no effect of injected Aβ1–15 on basal locomotion (as mean activity) either to the new context or shock (data not shown). The enhancement of fear conditioning at a picomolar concentration was more pronounced for Aβ1–15 compared with full-length Aβ1–42 (Fig. 5B). Last, the effect of pm Aβ1–15 was blocked by coadministration of the α7-nAChR-selective blocker MLA (Fig. 5C).
Figure 5.
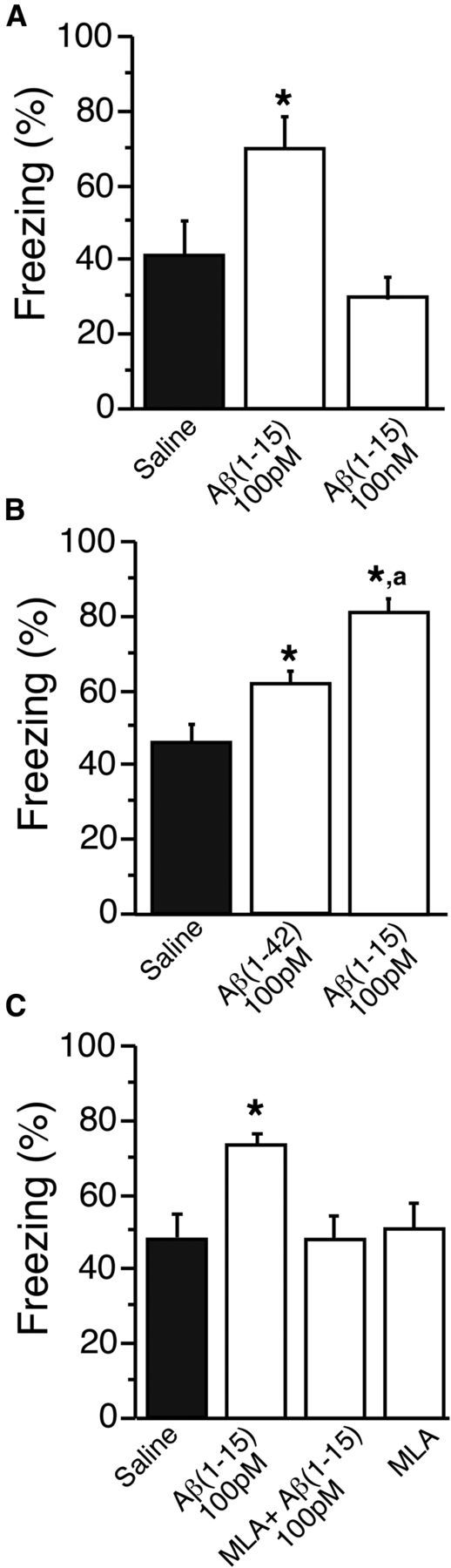
Bilateral delivery of picomolar N-terminal Aβ fragment into the dorsal hippocampus enhances contextual fear conditioning. Mice were trained for contextual fear conditioning under a single-trial paradigm using mild shock. A–C, Twenty-four hours before testing, 1.83 ng/L (100 pm) Aβ1–15 or 1.83 μg/L (100 nm) Aβ1–15 (A); 4.5 ng/L (100 pm) Aβ1–42 or 1.83 ng/L (100 pm) Aβ1–15 (B); and 1.83 ng/L (100 pm) Aβ1–15, 1.83 ng/L (100 pm) Aβ1–15 + 100 nm MLA or 100 nm MLA (C); or sterile saline were bilaterally injected into the dorsal hippocampi. Freezing was measured via TSE videotracking software. Conditioned freezing was assessed by two trained observers. Data are the means ± SEM, n = 6–9 mice/group. *p < 0.005 compared with saline control; ap < 0.05 comparing Aβ1–15 to Aβ1–42 (Bonferroni post hoc tests).
Discussion
Recent studies strongly implicate Aβ as a neuromodulator at normal picomolar concentrations (Puzzo et al., 2008, 2011), possibly involving both direct (Abramov et al., 2009) and indirect (Pirttmaki et al., 2013) regulation of synaptic function. The present findings confirm and extend this notion, identifying the N-terminal hydrophilic region of Aβ in the agonist-like activity of the peptide (Khan et al., 2010; Tong et al., 2011) and raising the intriguing possibility that N-terminal Aβ fragments resulting from the action of α- and β-secretases, first described by Portelius, Blennow, and colleagues (Portelius et al., 2007, 2010a,b, 2011), serve as highly potent synaptic regulators. As early studies of the general toxicity of Aβ peptides indicated that the N-terminal residues up to position 28 in Aβ do not contribute to the pathogenic activity of Aβ (Whitson et al., 1989), it is also likely that the N-terminal Aβ fragments are nontoxic. This would be consistent with evidence showing that residues in the hydrophobic domain at or near Gly-33 largely account for the cellular toxicity of the full-length peptide (Harmeier et al., 2009), though residues around Glu-22 are also key, at least from a structural standpoint (β-hairpin). It would therefore be of particular interest to assess the impact of the N-terminal Aβ fragments on full-length Aβ toxicity.
The activities of α- and β-secretases have been proposed to be part of separate, alternative APP processing pathways. However, ADAM10 (constitutive α-secretase) and BACE (β-secretase) appear to be coordinately expressed in brain (Marcinkeiwicz and Seidah, 2000). In view of the high potency of the N-terminal Aβ fragment, even very modest α-secretase activity might therefore result in levels, albeit picomolar or lower, which would still retain significant regulatory activity. In addition, the action of ADAM17 (regulated α-secretase) to produce the N-terminal fragment from Aβ may be induced by one or more receptor pathways (Tippmann et al., 2009). Where and to what extent α-secretase cleavage of Aβ occurs at synaptic sites remains to be determined. Moreover, the steady-state level of the N-terminal fragment in brain is, as yet, not known, but is postulated to be below the estimates for Aβ1–42 (∼200 pm; see Puzzo et al., 2008). In addition, concurrent cleavage by additional peptidases resulting in the shorter fragments (e.g., Aβ1–14) observed in CSF (Portelius et al., 2007) is as yet uncharacterized. Last, it will also be interesting to consider whether familial mutations in Aβ at positions 21 or 22 (e.g., A21G Flemish mutation, E22K Italian mutation, E22Q Dutch mutation, and E22G Arctic mutation) affect the production of the N-terminal Aβ fragment.
Structural analysis of Aβ indicates a random/weak loop structure from residues 1–14, a β-strand from residues 15 to 21, a turn in residue 22, and again, a β-strand from residues 24 to 32 (Morimoto et al., 2004). It would thus be predicted that Aβ1–15 exists in a largely random structure in the absence of the remaining 16–40/42 residues in Aβ. Indeed, Aβ1–15 displays a predominantly random structure in CD spectral analysis, though there also appears to be some β sheet. In addition, Aβ1–15 was found to be incapable of forming fibrils or other oligomeric species. At minimum, it would appear that exposure/accessibility of residues 1–15/16 in full-length Aβ are likely restricted at some level in view of the substantially lower agonist-like activity of Aβ1–42 (or Aβ1–28) compared with Aβ1–15. Nonetheless, we would suggest that residues within 1–15, specifically within positions 10–15, account for a significant portion of the activity of full-length Aβ. In addition, the 10–15 sequence is of special interest, as the two histidines at His-13 and His-14 are supposed contributors, along with His-6, to a putative metal (Cu and perhaps Zn) binding site in full-length Aβ (Shin and Saxena, 2011), and the sequence overlaps with a putative heparin-binding consensus sequence (Buée et al., 1993).
The regulatory activity of Aβ1–15 extended to positive effects on synaptic plasticity and fear conditioning in a concentration-dependent fashion. The apparent high potency of the N-terminal fragment raises some interesting questions. First, it may be the effective concentration of the active form of full-length Aβ is considerably lower than the high picomolar range, as previously reported (Dougherty et al., 2003; Puzzo et al., 2008; Tong et al., 2011), owing to the heterogeneity of full-length Aβ structures as well as the actual concentration of the active form within the solubilized preparation. Second, the aforementioned possibility of restricted accessibility of the first 15–16 N-terminal residues in full-length Aβ may affect the potency. Third, interactions between other residues in full-length Aβ (positions 17–40/42) and target receptors, or other cellular elements, could also affect its apparent effective potency. Fourth, pronounced nonspecific binding or dilution may decrease the effective concentration in hippocampal slice preparations and, especially, in intrahippocampal injections. Last, the key targets for the Aβ fragments in the regulation of synaptic plasticity and fear memory, and whether fluctuation of the levels of the fragments at the synapse fits with the potency of the Aβ fragments at such targets, remain to be determined. Our work implicates the involvement of nicotinic receptors, as does previous work examining full-length Aβ (Puzzo et al., 2008), but this does not exclude other receptor targets.
The inhibitory effect of high nanomolar to micromolar levels of Aβ on LTP is well documented (Rowan et al., 2007) and suggests a possible separate action of the peptide through entirely different pathways (Wang et al., 2008), which also may again affect the apparent potency of the peptide. In addition, relatively higher concentrations of Aβ may be desensitizing. Nonetheless, how competing pathways activated by different concentrations of the Aβ peptides result in opposing synaptic effects and the significance of this regulation as levels of the peptides change physiologically at the synapse or over the course of Alzheimer's disease are important questions for future studies. Of particular note, a high nanomolar N-terminal Aβ fragment was able to rescue the inhibitory effect of high nanomolar full-length Aβ on LTP as well as the decrement in LTP in hippocampal slices from APP mice, indicating a possible protective role. In this regard, it will be of particular interest to determine how, when, where, and at what level are the N-terminal Aβ fragments produced in brain, and whether they are regulated by nerve activity. Moreover, current (e.g., γ-secretase inhibition) and future therapeutic strategies might consider optimizing the production of the N-terminal Aβ fragments or even the direct application of the Aβ fragments or derivatives as a means to counter the neurotoxic effects of accumulating Aβ over the course of Alzheimer's disease.
Footnotes
The work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (AG21586), the American Health Assistance Foundation, and the Hawaii Community Foundation to R.A.N.; and from the IDeA Network of Biomedical Research Excellence (P20-RR016467 Junior Investigator Program) to C.T. and F.P.B. Additional support for the microscopy core at the University of Hawai'i was provided by the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities (G12MD007601), with additional funding from a Centers of Biomedical Research Excellence grant (P20RR016453). We thank Dr. Jerry Stitzel (University of Colorado) for providing the mouse nicotinic receptor sequences. We thank Margaret Ruzicka Baker for performing mass spectrometry on the β-amyloid peptides. We thank Michael Robles for help with the electrophysiology experiments. We thank Kelly Parson for help with the calcium imaging experiments. We thank Dr. Gary Landreth (Case Western Reserve University) for critical reading of the manuscript.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- Abramov E, Dolev I, Fogel H, Ciccotosto GD, Ruff E, Slutsky I. Amyloid-β as a positive endogenous regulator of release probability at hippocampal synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1567–1576. doi: 10.1038/nn.2433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell KA, O'Riordan KJ, Sweatt JD, Dineley KT. MAPK recruitment by β-amyloid in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures depends on physical state and exposure time. J Neurochem. 2004;91:349–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger FP, Wilce PA, Bedi KS, Wilson P. Long-lasting synaptic modification in the rat hippocampus resulting from NMDA receptor blockade during development. Synapse. 2002;43:95–101. doi: 10.1002/syn.10020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buée L, Ding W, Delacourte A, Fillit H. Binding of secreted human neuroblastoma proteoglycans to the Alzheimer's amyloid A4 peptide. Brain Res. 1993;601:154–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91706-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin JH, Ma L, MacTavish D, Jhamandas JH. Amyloid β protein modulates glutamate-mediated neurotransmission in the rat basal forebrain: involvement of presynaptic neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine and metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9262–9269. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1843-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirrito JR, Yamada KA, Finn MB, Sloviter RS, Bales KR, May PC, Schoepp DD, Paul SM, Mennerick S, Holtzman DM. Synaptic activity regulates interstitial fluid amyloid-β levels in vivo. Neuron. 2005;48:913–922. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.10.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirrito JR, Kang JE, Lee J, Stewart FR, Verges DK, Silverio LM, Bu G, Mennerick S, Holtzman DM. Endocytosis is required for synaptic activity-dependent release of amyloid-β in vivo. Neuron. 2008;58:42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellisanti CD, Yao Y, Stroud JC, Wang ZZ, Chen L. Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of nAChR α1 bound to α-bungarotoxin at 1.94 Å resolution. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:953–962. doi: 10.1038/nn1942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty JJ, Wu J, Nichols RA. β-amyloid regulation of presynaptic nicotinic receptors in rat hippocampus and neocortex. J Neurosci. 2003;23:6740–6747. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06740.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley PR, Jarvie PE, Health JW, Kidd GJ, Rostas JAP. A rapid method for isolation of synaptosomes on Percoll gradients. Brain Res. 1986;327:115–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch FS, Keim PS, Beattie EC, Blacher RW, Culwell AR, Oltersdorf T, McClure D, Ward PJ. Cleavage of amyloid β-peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990;248:1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde TE, Eckman CB, Younkin SG. Biochemical detection of Aβ isoforms: implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1502:172–187. doi: 10.1016/S0925-4439(00)00043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmeier A, Wozny C, Rost BR, Munter LM, Hua H, Georgiev O, Beyermann M, Hildebrand PW, Weise C, Schaffner W, Schmitz D, Multhaup G. Role of amyloid-β glycine 33 in oligomerization, toxicity, and neuronal plasticity. J Neurosci. 2009;29:7582–7590. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1336-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan GM, Tong M, Jhun M, Arora K, Nichols RA. β-amyloid activates presynaptic α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors reconstituted into a model nerve cell system: involvement of lipid rafts. Eur J Neurosci. 2010;31:788–796. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo EH, Sisodia SS, Archer DR, Martin LJ, Weidemann A, Beyreuther K, Fischer P, Masters CL, Price DL. Precursor of amyloid protein in Alzheimer disease undergoes fast anterograde axonal transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87:1561–1565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu QS, Kawai H, Berg DK. β-amyloid peptide blocks the response of α7-containing nicotinic receptors on hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:4734–4739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.081553598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma T, Hoeffer CA, Capetillo-Zarate E, Yu F, Wong H, Lin MT, Tampellini, Klann E, Blitzer RD, Gouras GK. Dysregulation of the mTOR pathway mediates impairment of synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkiewicz M, Seidah NG. Coordinated expression of β-amyloid precursor protein and the putative β-secretase BACE and α-secretase ADAM10 in mouse and human brain. J Neurochem. 2000;75:2133–2143. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta TK, Dougherty JJ, Wu J, Choi CH, Khan GM, Nichols RA. Defining pre-synaptic nicotinic receptors regulated by beta amyloid in mouse cortex and hippocampus with receptor null mutants. J Neurochem. 2009;109:1452–1458. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06070.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto A, Irie K, Murakami K, Masuda Y, Ohigashi H, Nagao M, Fukuda H, Shimizu T, Shirasawa T. Analysis of the secondary structure of β-amyloid (Aβ42) fibrils by systematic proline replacement. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:52781–52788. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406262200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P, Christian C, Nirenberg M. Synapse formation between clonal neuroblastoma X glioma hybrid cells and striated muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976;73:123–127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M, Sametsky EA, Younkin LH, Oakley H, Younkin SG, Citron M, Vassar R, Disterhoft JF. BACE1 deficiency rescues memory deficits and cholinergic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2004;41:27–33. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00810-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel AN, Jhamandas JH. Neuronal receptors as targets for the action of amyloid-beta protein (Aβ) in the brain. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012;14:e2. doi: 10.1017/S1462399411002134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ. The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Ed 2. San Diego: Academic; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit DL, Shao Z, Yakel JL. β-amyloid1–42 peptide directly modulates nicotinic receptors in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurosci. 2001;21:RC120. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-j0003.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirttimaki TM, Codadu NK, Awni A, Pratik P, Nagel DA, Hill EJ, Dineley KT, Parri HR. α7 nicotinic receptor-mediated astrocytic gliotransmitter release: Aβ effects in a preclinical Alzheimer's mouse model. PLoS One. 2013;8:e81828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelius E, Tran AJ, Andreasson U, Persson R, Brinkmalm G, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Westman-Brinkmalm A. Characterization of amyloid β peptides in cerebrospinal fluid by an automated immunoprecipitation procedure followed by mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:4433–4439. doi: 10.1021/pr0703627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelius E, Andreasson U, Ringman JM, Buerger K, Daborg J, Buchhave P, Hansson O, Harmsen A, Gustavsson MK, Hanse E, Galasko D, Hampel H, Blennow K, Zetterberg H. Distinct cerebrospinal fluid amyloid β peptide signatures I sporadic and PSEN1 A431E-associated familial Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegen. 2010a;5:2. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelius E, Dean RA, Gustavsson MK, Andreasson U, Zetterberg H, Siemers E, Blennow K. A novel Aβ isoform pattern in CSF reflects γ-secretase inhibition in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2010b;2:7. doi: 10.1186/alzrt30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portelius E, Price E, Brinkmalm G, Stiteler M, Olsson M, Persson R, Westman-Brinkmalm A, Zetterberg H, Simon AJ, Blennow K. A novel pathway for amyloid precursor protein processing. Neurobiol Aging. 2011;32:1090–1098. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puzzo D, Privitera L, Leznik E, Fà M, Staniszewski A, Palmeri A, Arancio O. Picomolar amyloid-β positively modulates synaptic plasticity and memory in hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14537–14545. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2692-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puzzo D, Privitera L, Fa' M, Staniszewski A, Hashimoto G, Aziz F, Sakurai M, Ribe EM, Troy CM, Mercken M, Jung SS, Palmeri A, Arancio O. Endogenous amyloid-β is necessary for hippocampal synaptic plasticity and memory. Ann Neurol. 2011;69:819–830. doi: 10.1002/ana.22313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan MJ, Klyubin I, Wang Q, Hu NW, Anwyl R. Synaptic memory mechanisms: Alzheimer's disease amyloid β-peptide-induced dysfunction. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:1219–1223. doi: 10.1042/BST0351219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert W, Prior R, Weidemann A, Dircksen H, Multhaup G, Masters CL, Beyreuther K. Localization of Alzheimer βA4 amyloid precursor protein at central and peripheral synaptic sites. Brain Res. 1991;563:184–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91532-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:742–766. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe DJ, Schenk D. Alzheimer's disease: molecular understanding predicts molecular-based therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:545–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.140248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrin T, Blank T, Hippel C, Rayner M, Davis RJ, Todorovic C. Hippocampal c-Jun-N-terminal kinases serve as negative regulators of associative learning. J Neurosci. 2010;30:13348–13361. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3492-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shin BK, Saxena S. Substantial contribution of the two imidazole rings of His13-His14 dyad to Cu(II) binding in amyloid-β(1–16) at physiological pH and its significance. J Phys Chem A. 2011;115:9590–9602. doi: 10.1021/jp200379m. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skovronsky DM, Moore DB, Milla ME, Doms RW, Lee VM. Protein kinase C-dependent α-secretase competes with β-secretase for cleavage of amyloid-β precursor protein in the trans-Golgi network. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:2568–2575. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.4.2568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thinakaran G, Koo EH. Amyloid precursor protein trafficking, processing and function. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:29615–29619. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800019200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tippmann F, Hundt J, Schneider A, Endres K, Fahrenholz F. Up-regulation of the α-secretase ADAM10 by retinoic acid receptors and acitretin. FASEB J. 2009;23:1643–1654. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-121392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong M, Arora K, White MM, Nichols RA. Role of key aromatic residues in the ligand-binding domain of α7 nicotinic receptors in the agonist action of β-amyloid. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:34373–34381. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang HY, Lee DH, D'Andrea MR, Peterson PA, Shank RP, Reitz AB. β-amyloid1–42 binds to α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with high affinity: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5626–5632. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q, Klyubin I, Wright S, Griswold-Prenner I, Rowan MJ, Anwyl R. αv integrins mediate beta-amyloid induced inhibition of long-term potentiation. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29:1485–1493. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitson JS, Selkoe DJ, Cotman CW. Amyloid β protein enhances the survival of hippocampal neurons in vitro. Science. 1989;243:1488–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2928783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]