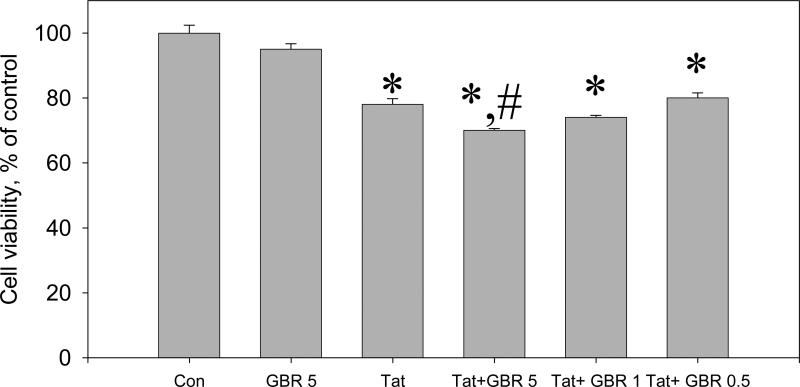
Figure 4.
The effect of the selective dopamine transporter inhibitor, GBR 12909, on the toxicity of Tat 1-86 in primary rat fetal midbrain cell culture.
Results presented as mean % of Calcein/Ethidium bromide fluorescence (Live/Dead ratio)vs non-treated control ± SEM, n of sister cultures analyzed = 7-13 per each variant of treatment. *- marks significant (P<0.05) difference between the treated group (50 nM Tat or 50 nM Tat + non-toxic dose of GBR 12909) and non-treated control group; *,#-marks that this experimental group (50 nM Tat+ non-toxic dose of GBR 12909) was significantly (P<0.05) different from non-treated control (*) and from Tat-treated group (#). Similar to cocaine, 5 μM GBR 12909 significantly enhances neurotoxicity of 50 nM Tat following 48 hour-exposure. All doses of GBR 12909 used in these experiments (0.5, 1, or 5 μM) did not cause changes of Live/Dead ratios in rat fetal midbrain cell cultures. Cell viability of a group of cultures exposed to 5 μM GBR 12909 is included in the graph.