Abstract
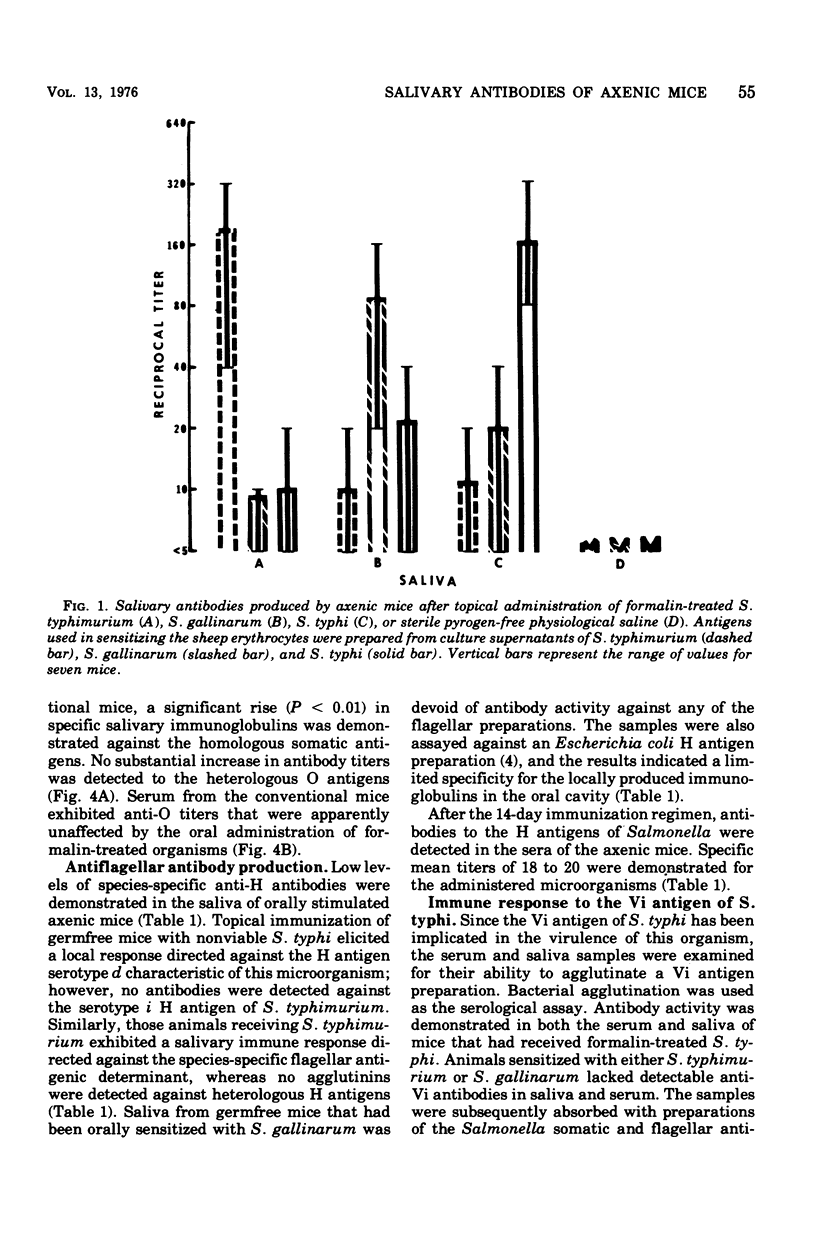
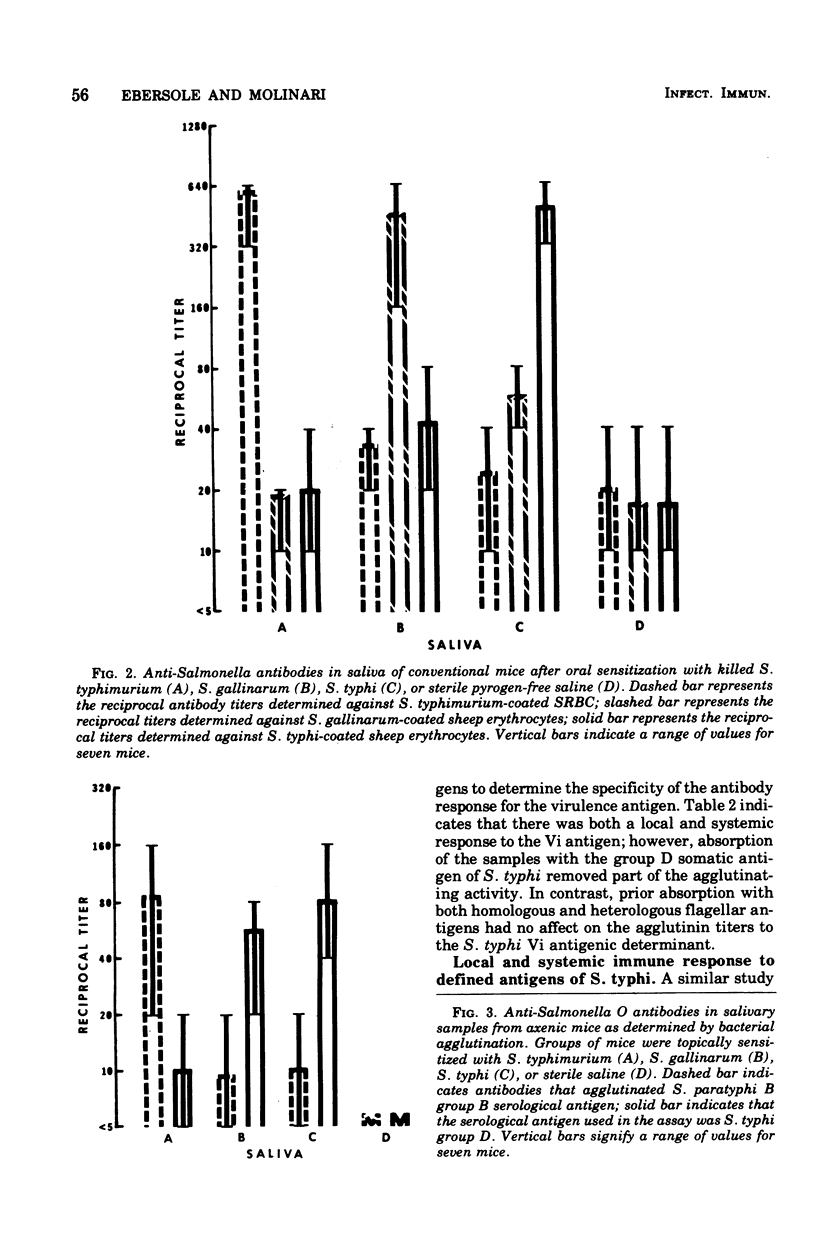
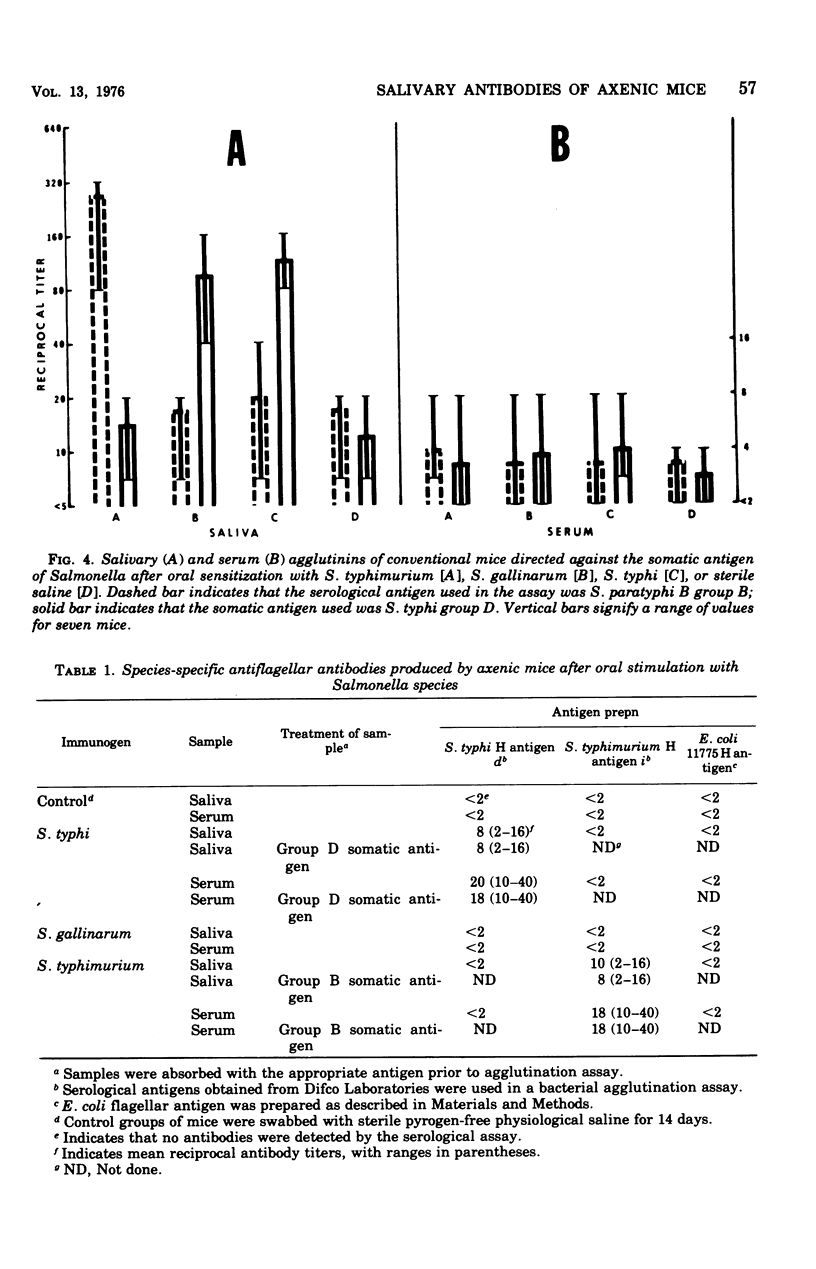
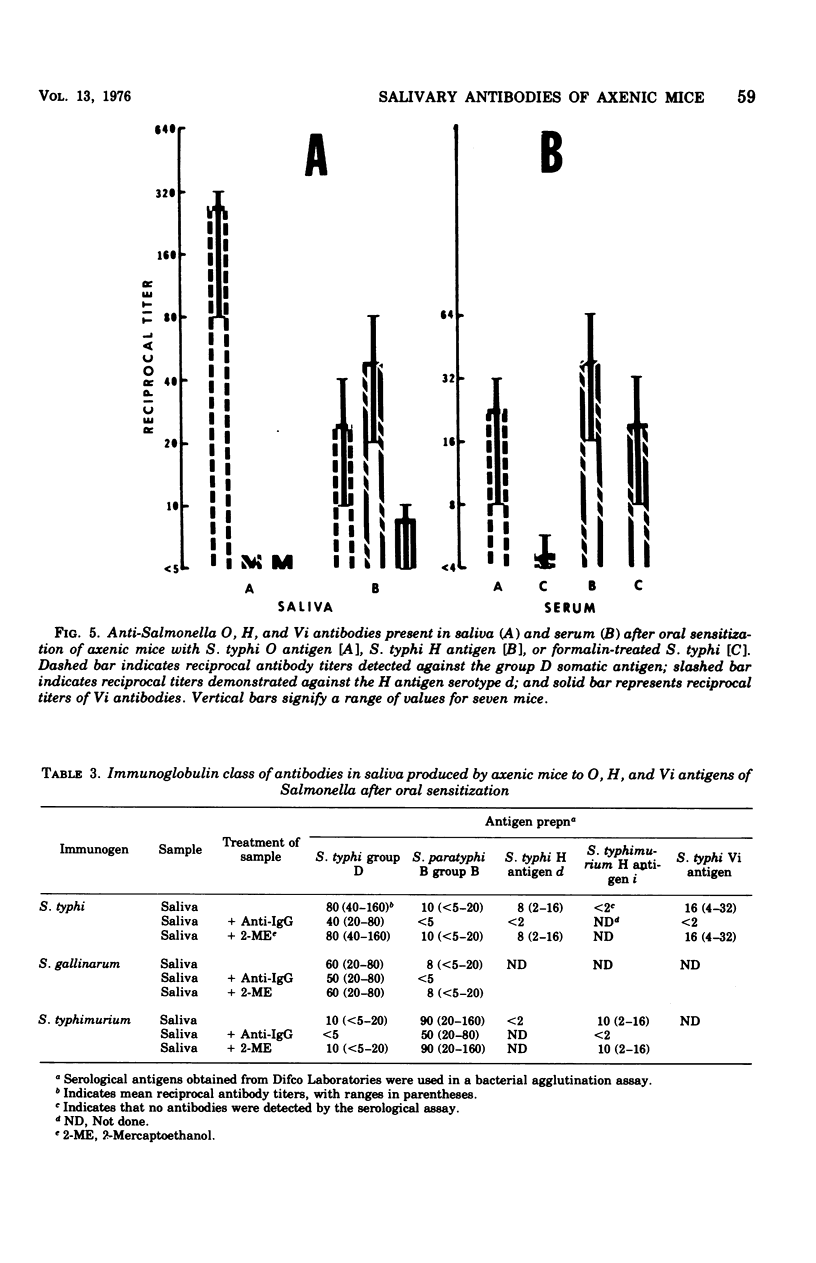
The present investigation examined the specificity of the salivary immune response of axenic and conventional mice to topically administered Salmonella typhi, S. gallinarum, and S. typhimurium. Specific antibacterial antibodies were determined by passive hemagglutination and bacterial agglutination. Reciprocal antibody titers up to 320 were detected in saliva from mice immunized and assayed with homologous antigens. Antibodies to heterologous immunogens exhibited lower mean titers of 10 to 20 under identical conditions. High concentrations of specific antibodies to the somatic (O) antigen were detected in the saliva of mice administered these microorganisms; however, no significant differences in serum antibody levels were detectable after oral immunization. Only low levels of specific antiflagellar (H) antibodies were demonstrated in the saliva of immunized mice, whereas mean reciprocal titers of 20 were observed in the serum. Antibodies to the Vi antigen of S. typhi were detected in the saliva and serum of only those mice administered formalin-treated S. typhi. Examination of the classes of antibody elicited by these organisms indicated that immunoglobulin A (IgA) was the predominant class in saliva against the O antigens. The salivary response to the H antigens was comprised of both IgG and IgA, whereas the specific serum immunoglobulins were consistent with a primary humoral immune reaction. Local antibodies formed in response to the Vi antigen were exclusively IgG. Serum immunoglobulins produced after peroral administration of the somatic and virulence antigens were limited to the IgM class.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAUER D. C., MATHIES M. J., STAVITSKY A. B. Sequences of synthesis of gamma-1 macroglobulin and gamma-2 globulin antibodies during primary and secondary responses to proteins, salmonella antigens, and phage. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:889–907. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Nash D. R., Bazin H., Eyssen D. V., Heremans J. F. Antibodies of the IgA type in intestinal plasma cells of germfree mice after oral or parenteral immunization with ferritin. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):723–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Molinari J. A., Platt D. Sequential appearance of salivary antibodies after oral immunization of axenic mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):353–359. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.353-359.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Availability of locally synthesized and systemic antibodies in the intestine. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):965–981. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.965-981.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genco R. J., Taubman M. A. Secretory gamma-A antibodies induced by local immunization. Nature. 1969 Feb 15;221(5181):679–681. doi: 10.1038/221679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. 2. N Engl J Med. 1970 Oct 1;283(14):739–746. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197010012831406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornick R. B., Greisman S. E., Woodward T. E., DuPont H. L., Dawkins A. T., Snyder M. J. Typhoid fever: pathogenesis and immunologic control. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):686–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenblat P. E., Rothberg R. M., Minden P., Farr R. S. Immune responses of human adults after oral and parenteral exposure to bovine serum albumin. J Allergy. 1968 Apr;41(4):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(68)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy M., Sanderson R. P., Jackson A. L. Humoral and cellular aspects of the immune response to the somatic antigen of Salmonella enteritidis. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):483–504. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie G. A., Waldman R. H. Anti-hapten antibodies in the serum and bronchial secretions of dogs following respiratory tract immunization. Experientia. 1969 Oct 15;25(10):1096–1097. doi: 10.1007/BF01901453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Arsić B. L., Nikolić B. D., Radovanić M. L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 4. Oral immunization with live monotypic and combined vaccines. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):375–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mel D. M., Papo R. G., Terzin A. L., Vuksić L. Studies on vaccination against bacillary dysentery. 2. Safety tests and reactogenicity studies on a live dysentery vaccine intended for use in field trials. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):637–645. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinari J. A., Ebersole J. L., Platt D. Investigation of secretory immunoglobulins in saliva from germfree mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1207–1212. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1207-1212.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb R. W., Ishizaka K., DeVald B. L. Human IgG and IgA diphtheria antitoxins in serum, nasal fluids and saliva. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):215–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M., Kraft S. C., Farr R. S. Similarities between rabbit antibodies produced following ingestion of bovine serum albumin and following parenteral immunization. J Immunol. 1967 Feb;98(2):386–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strannegård O., Yurchision A. Formation of agglutinating and reaginic antibodies in rabbits following oral administration of soluble and particulate antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(6):579–590. doi: 10.1159/000230211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Bencic Z., Sinha R., Deb B. C., Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Mukerjee S., Ganguly R. Cholera immunology. II. Serum and intestinal secretion antibody response after naturally occurring cholera. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):401–407. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. Immunity to infections on secretory surfaces. J Infect Dis. 1974 Oct;130(4):419–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Grunspan R., Ganguly R. Oral immunization of mice with killed Salmonella typhimurium vaccine. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.58-61.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Wigley FM Small P. A., Jr Specificity of respiratory secretion antibody against influenza virus. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigley F. M., Wood S. H., Waldman R. H. Aerosol immunization of humans with tetanus toxoid. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):1096–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


