Abstract
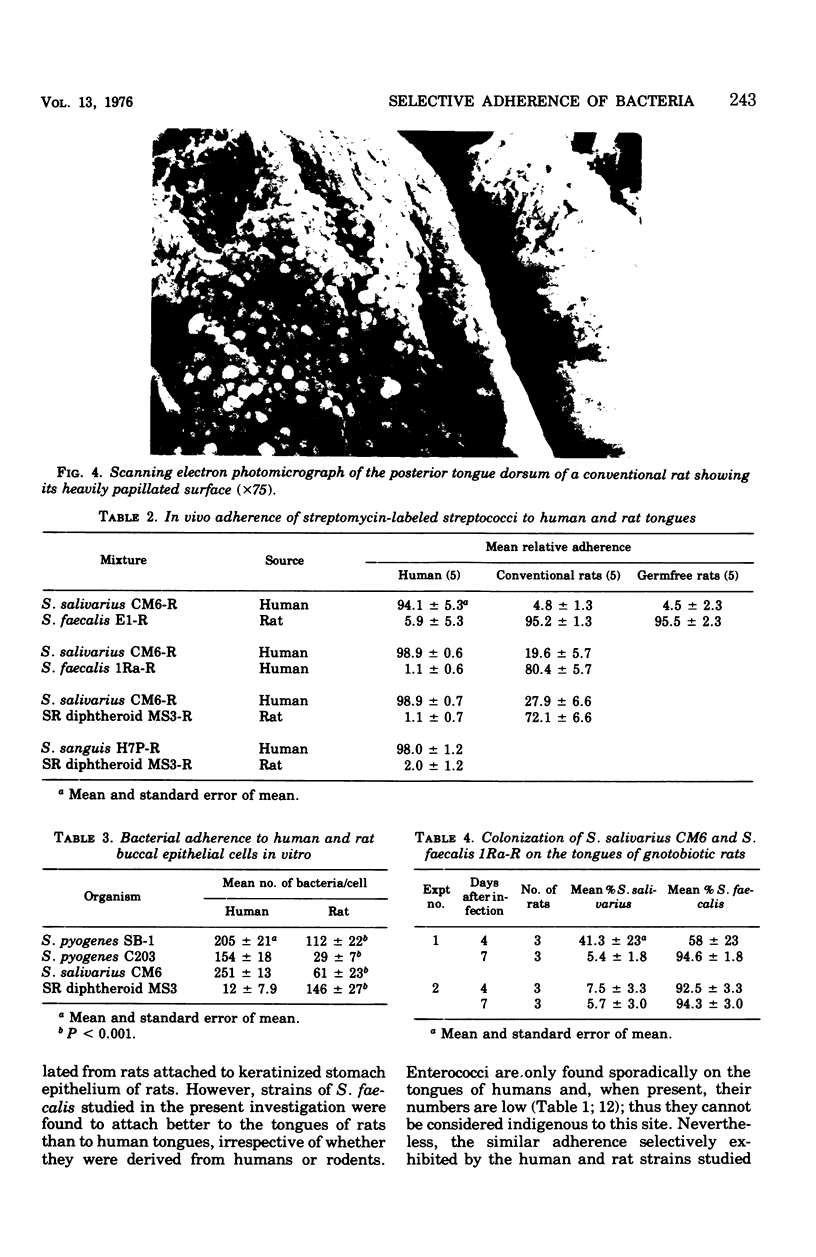
The relationship between the selective abilities of bacteria to adhere and their predilections for colonizing different mammalian hosts was investigated by using bacteria indigenous to the tongue dorsum of humans and rats as models. Streptococcus salivarius and S. sanguis averaged 22.6 and 2.8%, respectively, of the cultivable bacteria recovered from swab samples of the tonges of five humans, but these organisms were not indigenous on the tongues of rats (Charles River strain). S. faecalis and serum-requiring diphtheroids were consistently prominant on the tongues of rats, but they were not detected on the tongues of the humans examined. The ability of these organisms to adhere to the tongue surface of the hosts was compared by introducing mixtures of streptomycin-resistant strains into the mouths of human volunteers and rats. S. salivarius adhered in higher proportions to the dorsal tongue surface of humans than did strains of S. faecalis and the serum-requiring diphtheroid. S. sanguis also adhered to human tongues better than the serum-requiring diphtheroid. However, S. faecalis and the serum-requiring diphtheroid sorbed in higher proportions to the tongues of rats. In an in vivo assay, human strains of S. pyogenes and S. salivarius attached in higher numbers to buccal epithelial cells derived from humans than to those obtained from rats, whereas the reverse was observed with a serum-requiring diphtheroid derived from rats. Collectively, these studies show that bacteria sorb with a high degree of specificity to the tissues of different mammalian hosts, and the relative adherence of the organisms studied correlated with their natural host tropisms. The selective adherence of S. salvarius and S. faecalis was similar to the tongues of conventional and germ-free rats, suggesting that the presence of an indigenous bacterial flora did not significantly influence their attachment selectivity. Moreover, the ability of these organisms to colonize the tongues of gnotobiotic rats lacking an indigenous flora paralleled their adherence selectivity. Direct scanning microscopic observations indicated that the tongue dorsum of conventional rats is highly papillated but contains relatively sparse bacterial populations. Indigenous organisms colonized the bases of papillae on the anterior tip and lateral edges of the tongue as discrete microcolonies, but bacteria were rarely observed on other papillae. This localized and restricted pattern of colonization and the spatial distribution of the microcolonies of indigenous bacteria present also suggest that antagonistic interactions are unlikely to account for the bacterial tropisms observed for colonization of the tongues of rats.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immune responses of specific pathogen-free and gnotobiotic mice to antigens of indigenous and nonindigenous microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):320–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.320-329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immunological responses and microorganisms indigenous to the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1364–1371. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. M., Gray W. A., Lara-Garcia W. Localization of bacteria on the rat tongue with scanning and transmission electron microscopy. J Dent Res. 1975 Jul-Aug;54(4):777–782. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540041401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratthall D., Gibbons R. J. Changing agglutination activities of salivary immunoglobulin A preparations against oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):603–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.603-606.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil L. B., Schurig G. G., Bier P. J., Winter A. J. Bovine veneral vibriosis: antigenic variation of the bacterium during infection. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courant P. R., Gibbons R. J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1605–1613. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellen R. P., Gibbons R. J. Parameters affecting the adherence and tissue tropisms of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):85–91. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.85-91.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foo M. C., Lee A. Immunological response of mice to members of the autochthonous intestinal microflora. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):525–532. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.525-532.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Selective bacterial adherence to oral epithelial surfaces and its role as an ecological determinant. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):567–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.567-573.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold O. G., Jordan H. V., van Houte J. The prevalence of enterococci in the human mouth and their pathogenicity in animal models. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Jul;20(7):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Goldberg D., Sampson J. Laboratory studies with a selective Enterococcus medium. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Sep;20(3):433–436. doi: 10.1128/am.20.3.433-436.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAUS F. W., KONNO J. THE SALIVARY SECRETION OF ANTIBODY. Ala J Med Sci. 1965 Jan;2:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Ability of Veillonella and Neisseria species to attach to oral surfaces and their proportions present indigenously. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):264–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.264-268.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljemark W. F., Gibbons R. J. Suppression of Candida albicans by human oral streptococci in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):846–849. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.846-849.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., SOCRANSKY S., SAWYER S. A survey of the bacterial flora of the periodontium in the rice rat. Arch Oral Biol. 1959 Aug;1:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(59)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Hentges D. J. Experimental Shigella infections in laboratory animals. I. Antagonism by human normal flora components in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):168–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.168-173.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Onderdonk A. B., Baskett R. C., Hentges D. J. Shigella, indigenous flora interactions in mice. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1433–1440. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick J. D., Goldberg H. S., Sonnenwirth A. C. Human antibody to Bacteroidaceae. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1351–1356. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., JOHANSEN E., DISRAELY M. N. The relation of streptococci, lactobacilli, and the general oral and fecal flora to the progression of dental caries in the hamster. J Dent Res. 1957 Oct;36(5):695–708. doi: 10.1177/00220345570360050901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FLORA OF THE ALIMENTARY TRACT OF ANIMALS AND FACTORS AFFECTING ITS COMPOSITION. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:95–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Miller C. E. Progressive changes of Vibrio serotypes in germ-free mice infected with Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.688-695.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. D., Hall C. E., Burda K., Corbeil L. B., Duncan J. R., Winter A. J. Persistent genital tract infection with Vibrio fetus intestinalis associated with serotypic alteration of the infecting strain. Am J Vet Res. 1973 Nov;34(11):1399–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Manganiello S. D. The oral microbiota of man from birth to senility. J Periodontol. 1971 Aug;42(8):485–496. doi: 10.1902/jop.1971.42.8.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F. Blood-group and Forssman antigenic determinants shared between microbes and mammalian cells. Prog Allergy. 1971;15:9–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Pulkkinen A. J. Adherence as an ecological determinant for streptococci in the human mouth. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Oct;16(10):1131–1141. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of streptococcal attachment to receptors on human buccal epithelial cells by antigenically similar salivary glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):711–718. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.711-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






