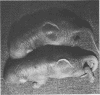
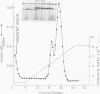
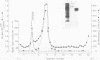Abstract
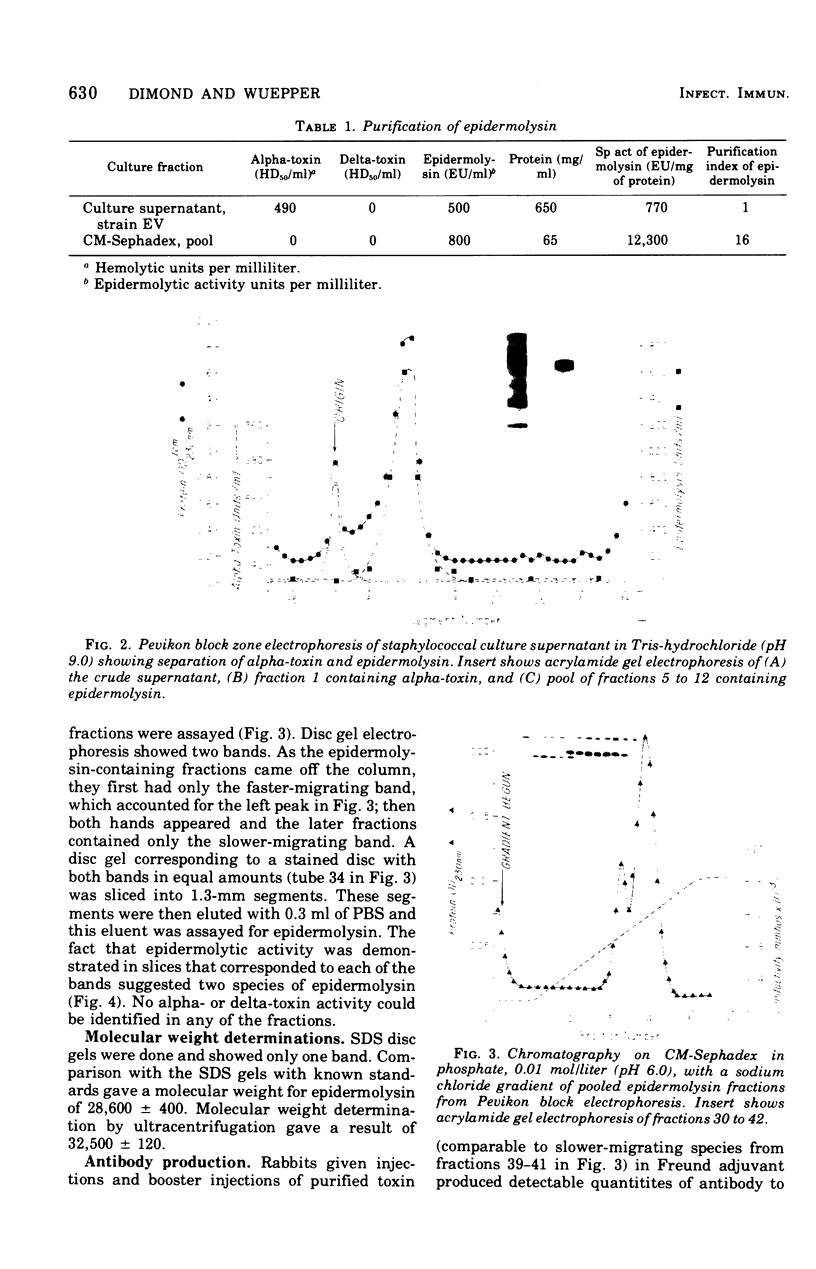
A staphylococcal exotoxin that causes epidermolysis when injected into the skin of the newborn mouse and man was highly purified by coventional biochemical techniques. With Staphylococcus aureus EV, the epidermolytic toxin was a major protein component of supernatant culture fluids. The initial step in purification was zone electrophoresis in Pevikon carried out at pH 9.0, the isoelectric point of alpha-hemolytic toxin, which remained near the origin. Fractions containing the epidermolytic toxin, but free of alpha-toxin, were then subjected to cation exchange chromatography on carboxymethyl-Sephadex C-50 to remove trace contaminants. A major highly purified epidermolytic toxin migrated as a single band in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, sedimented as a single component in the analytical ultracentrifuge, and elicited a single precipitating antibody after injection into rabbits. A smaller amount of a second epidermolytic toxin, identical in molecular weight and antigenicity but differing in electrophoretic behavior from the major molecular species, was also identified. The epidermolytic factor had a molecular weight of 28,600 +/- 400 by sodium dodecyl sulfate-acrylamide electrophoresis and 32,500 +/- 120 by approach to sedimentation equilibrium.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B., Thompson W. D. Isoelectric focusing studies of staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):92–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Kent J., Lyell A., Gemmell C. G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis produced by an extracellular product of Staphylococcus aureus. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEINING P. R., KENNEDY E. R. CHARACTERISTICS OF A STRAIN OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS GROWN IN VIVO AND IN VITRO. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:732–741. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.732-741.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCamelli R. F., Holohan P. D., Basinger S. F., Lebowitz J. Molecular weight determinations by low-speed sedimentation equilibrium. A combined use of the Nazarian equation and the Griffth rapid equilibrium technique. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):470–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Miller M. M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):541–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.541-545.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. New type of exfoliatin obtained from staphylococcal strains, belonging to phage groups other than group II, isolated from patients with impetigo and Ritter's disease. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):851–861. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.851-861.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Sakurai S., Sarai Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):156–164. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.156-164.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J. A new supporting medium for preparative electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12:33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A., Turner M. D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J Infect Dis. 1972 Feb;125(2):129–140. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]