Abstract
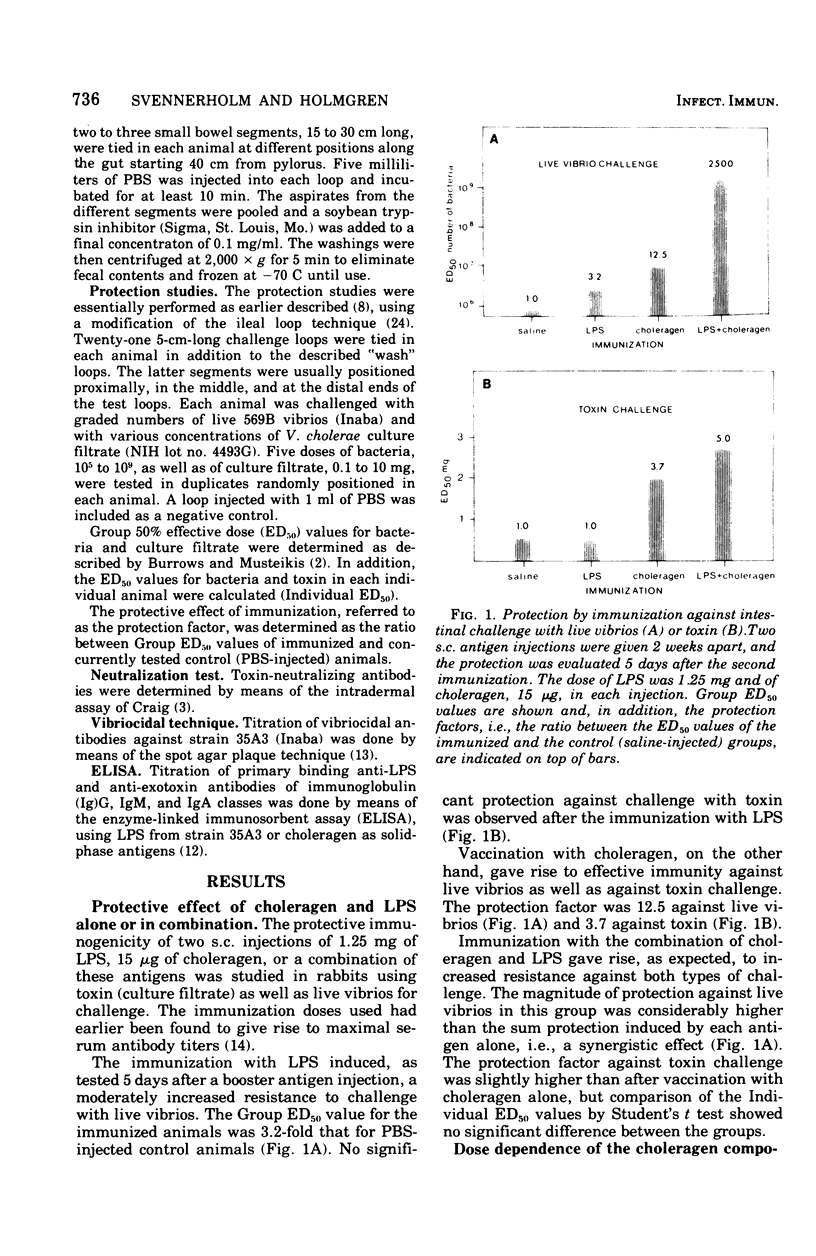
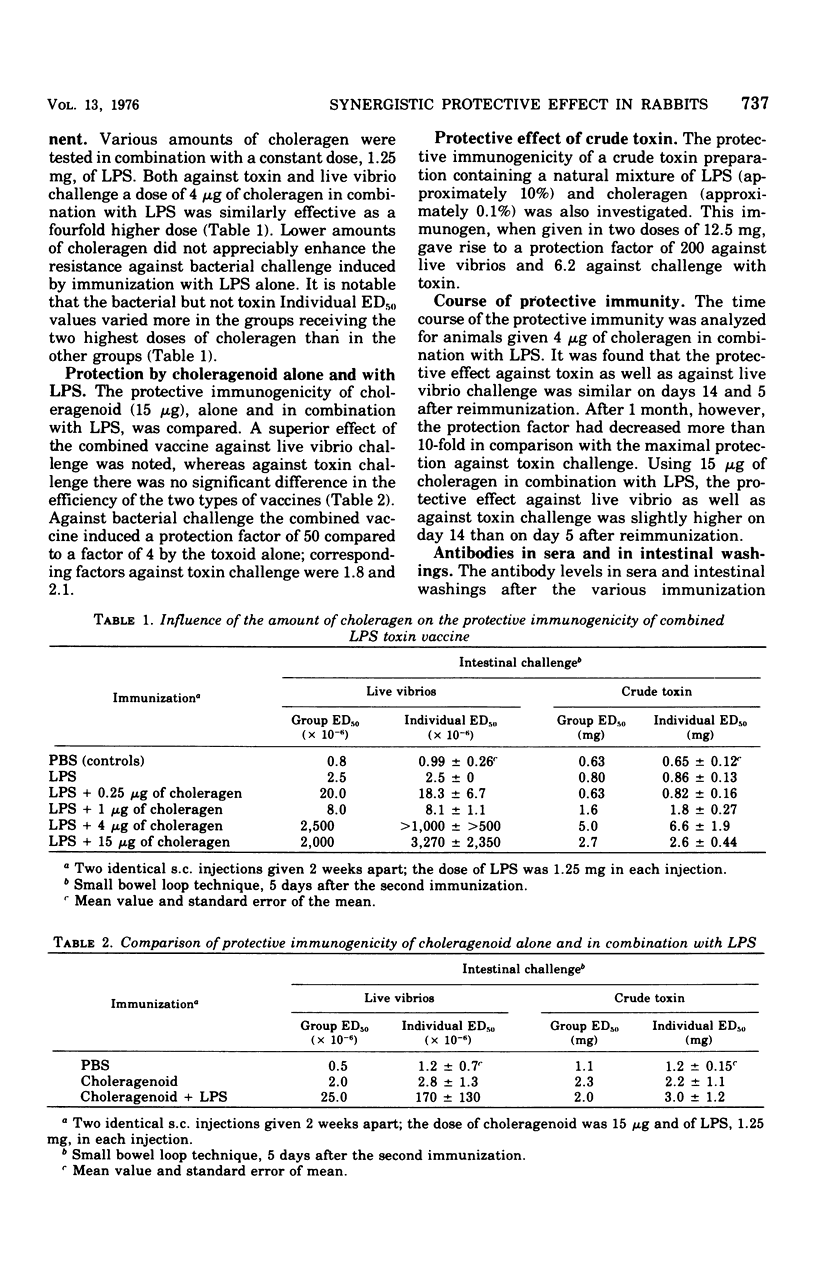
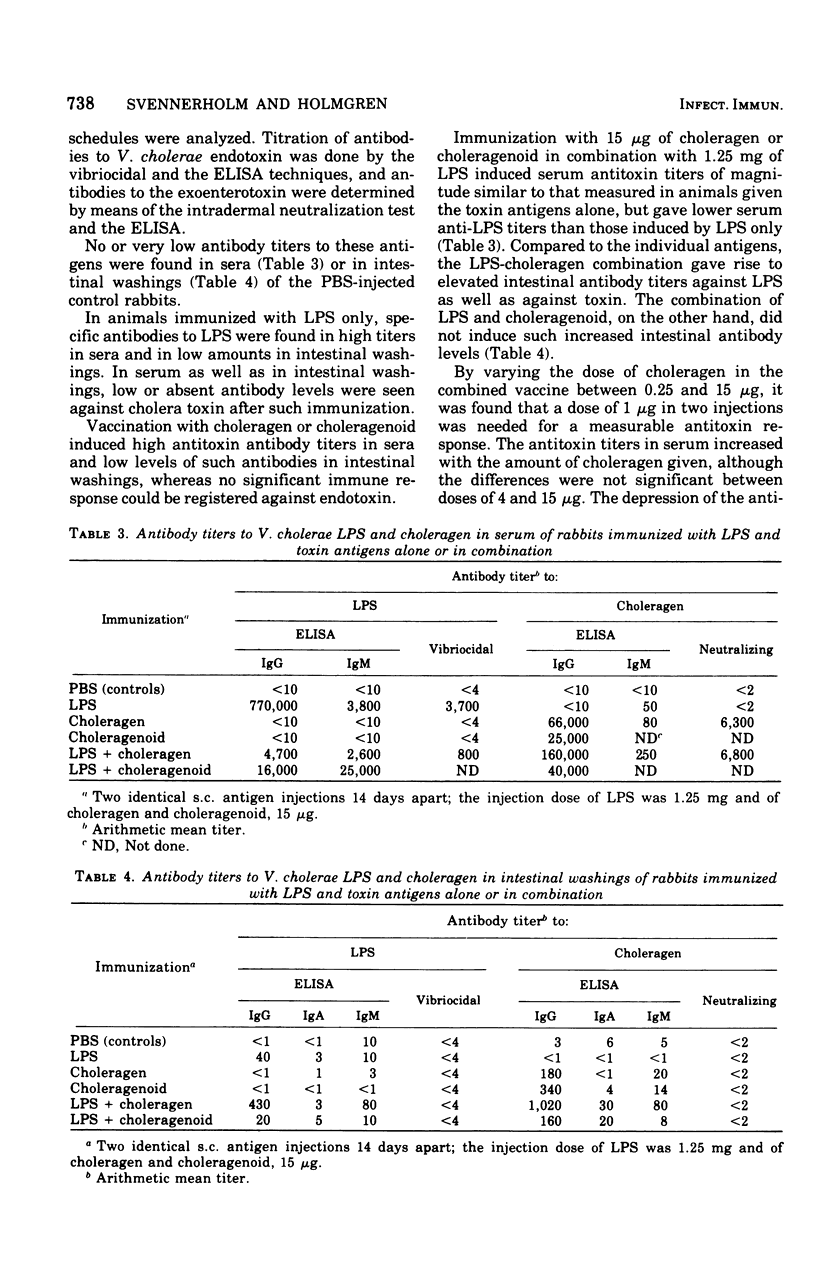
Subcutaneous immunization of rabbits with a combination of Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and enterotoxin induced a more than 100-fold-higher degree of protection against intestinal challenge with live cholera vibrios than did vaccination with either of the two antigens alone. Such a synergistic effect was also obtained by immunization with a combination of LPS and choleragenoid. The immunization with LPS and toxin (or toxoid) in combination did not enhance the reistance to toxin challenge above that induced by the toxin component alone. This, together with data from titrations of anti-LPS and antitoxin antibodies in serum and in intestinal washings, contradicts enhanced immune responses due to adjuvant action of the two antigens as the explanation for the synergistic effect of the combined vaccines. A more likely explanation would be that the antibacterial and antitoxic immune responses, without being increased in themselves, function synergistically by interfering with two separate events in cholera pathogensis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benenson A. S., Mosley W. H., Fahimuddin M., Oseasohn R. O. Cholera vaccine field trials in east Pakistan. 2. Effectiveness in the field. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(3):359–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows W., Musteikis G. M. Cholera infection and toxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Apr;116(2):183–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.2.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita K., Finkelstein R. A. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: comparison of immunity induced perorally and parenterally in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):647–655. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Andersson A., Wallerstrom G., Ouchterlony O. Experimental studies on cholera immunization. II. Evidence for protective antitoxic immunity mediated by serum antibodies as well as local antibodies. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):662–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.662-667.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lindholm L., Lönnroth I. Interaction of cholera toxin and toxin derivatives with lymphocytes. I. Binding properties and interference with lectin-induced cellular stimulation. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):801–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lonnroth I. Oligomeric structure of cholera toxin: characteristics of the H and L subunits. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jan;86(1):49–65. doi: 10.1099/00221287-86-1-49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Ouchterlony O. Immunochemical Studies of Two Cholera Toxin-Containing Standard Culture Filtrate Preparations of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):747–755. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.747-755.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ouchterlony O., Anderson A., Walletström G., Westerberg-Berndtsson U. Antitoxic immunity in experimental cholera: protection, and serum and local antibody responses in rabbits after enteral and parenteral immunization. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1331–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1331-1340.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ouchterlony O. Experimental studies on cholera immunization. 1. The response of neutralizing and vibriocidal antibodies in rabbits after immunization with culture filtrate material from V. cholerae. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(4):489–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Svennerholm A. M., Ouchterlony O. Quantitation of vibriocidal antibodies using agar plague techniques. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(5):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lönnroth I., Holmgren J. Protein reagent modification of cholera toxin: characterization of effects on antigenic, receptor-binding and toxic properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):263–277. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neter E. Endotoxins and the immune response. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;47:82–124. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46160-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M. Experimental studies on cholera immunization. 4. The antibody response to formalinized Vibrio cholerae and purified endotoxin with special reference to protective capacity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;49(4):434–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


