Abstract
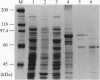
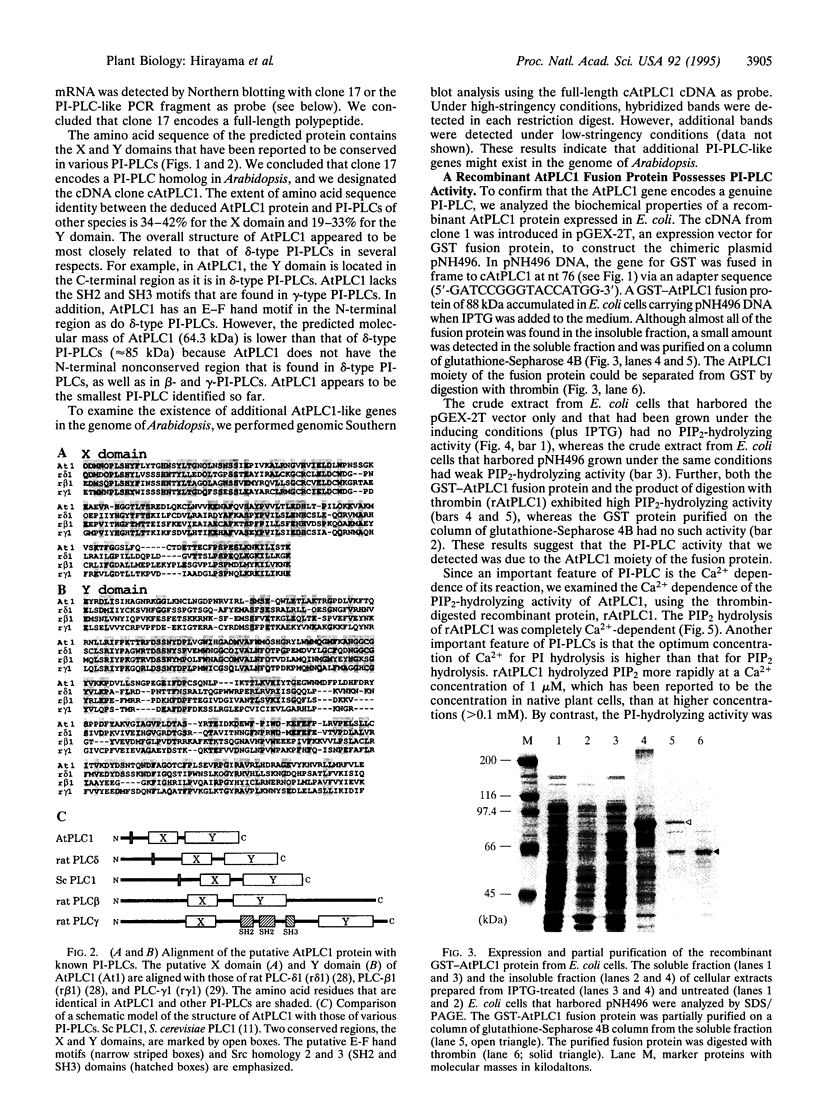
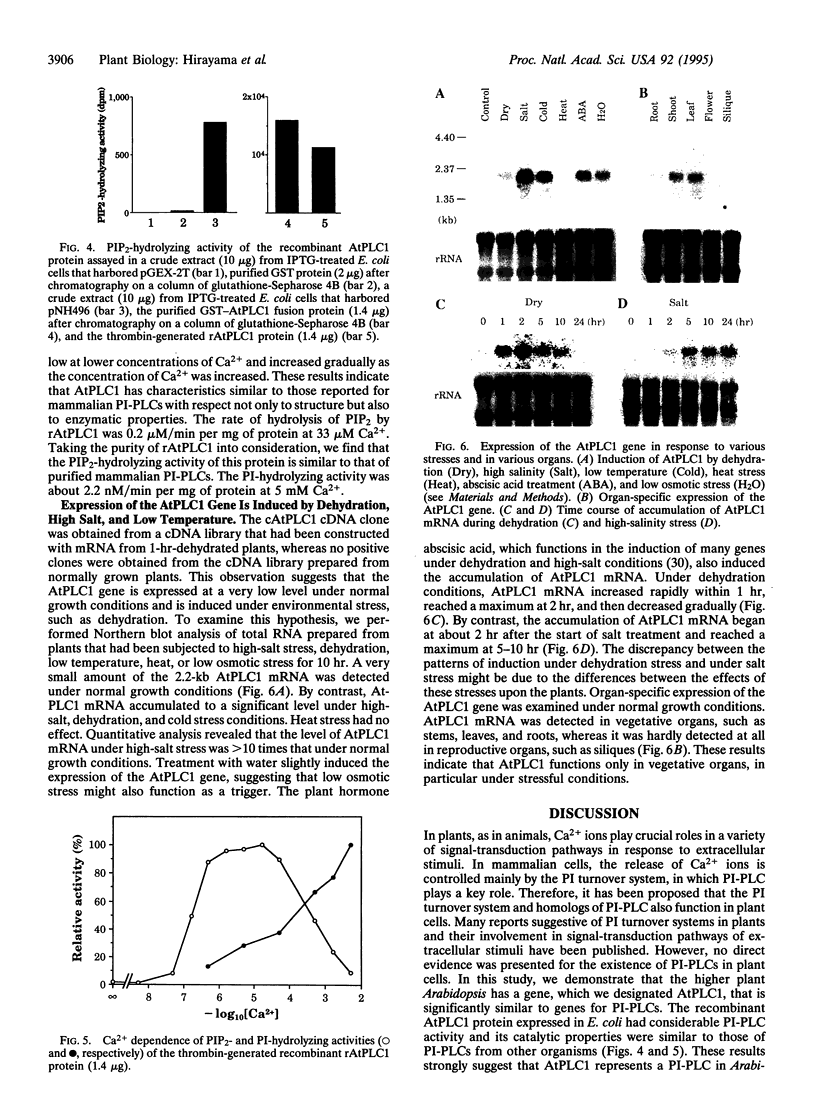
A cDNA corresponding to a putative phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) in the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana was cloned by use of the polymerase chain reaction. The cDNA, designated cAtPLC1, encodes a putative polypeptide of 561 aa with a calculated molecular mass of 64 kDa. The putative product includes so-called X and Y domains found in all PI-PLCs identified to date. In mammalian cells, there are three types of PI-PLC, PLC-beta, -gamma, and -delta. The overall structure of the putative AtPLC1 protein is most similar to that of PLC-delta, although the AtPLC1 protein is much smaller than PLCs from other organisms. The recombinant AtPLC1 protein synthesized in Escherichia coli was able to hydrolyze phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and this activity was completely dependent on Ca2+, as observed also for mammalian PI-PLCs. These results suggest that the AtPLC1 gene encodes a genuine PI-PLC of a higher plant. Northern blot analysis showed that the AtPLC1 gene is expressed at very low levels in the plant under normal conditions but is induced to a significant extent under various environmental stresses, such as dehydration, salinity, and low temperature. These observations suggest that AtPLC1 might be involved in the signal-transduction pathways of environmental stresses and that an increase in the level of AtPLC1 might amplify the signal, in a manner that contributes to the adaptation of the plant to these stresses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt M. R., Thiel G., Trentham D. R. Reversible inactivation of K+ channels of Vicia stomatal guard cells following the photolysis of caged inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):766–769. doi: 10.1038/346766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray E. A. Molecular Responses to Water Deficit. Plant Physiol. 1993 Dec;103(4):1035–1040. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.4.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer A. L., Van der Kaay J., Mayr G. W., Van Haastert P. J. Role of phospholipase C in Dictyostelium: formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and normal development in cells lacking phospholipase C activity. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 1;13(7):1601–1609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer A. L., van Haastert P. J. Molecular cloning and expression of a phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18387–18392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Peeler T. C., Thompson G. A., Jr Rapid changes in polyphosphoinositide metabolism associated with the response of Dunaliella salina to hypoosmotic shock. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5775–5779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Homma Y., Sorimachi H., Kawasaki H., Nakanishi O., Suzuki K., Takenawa T. A second type of rat phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C containing a src-related sequence not essential for phosphoinositide-hydrolyzing activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21885–21890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettlinger C., Lehle L. Auxin induces rapid changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolites. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):176–178. doi: 10.1038/331176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick J. S., Thorner J. Genetic and biochemical characterization of a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5861–5876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy S., Read N. D., Trewavas A. J. Elevation of cytoplasmic calcium by caged calcium or caged inositol triphosphate initiates stomatal closure. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):769–771. doi: 10.1038/346769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama T., Oka A. Novel protein kinase of Arabidopsis thaliana (APK1) that phosphorylates tyrosine, serine and threonine. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;20(4):653–662. doi: 10.1007/BF00046450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyosue T., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K. Cloning of cDNAs for genes that are early-responsive to dehydration stress (ERDs) in Arabidopsis thaliana L.: identification of three ERDs as HSP cognate genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Aug;25(5):791–798. doi: 10.1007/BF00028874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight M. R., Campbell A. K., Smith S. M., Trewavas A. J. Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):524–526. doi: 10.1038/352524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Ross T. S., Cunningham T. W., Caldwell K. K., Jefferson A. B., Bansal V. S. Recent insights in phosphatidylinositol signaling. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90442-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. E., Fitzgerald-Hayes M. A mutation in PLC1, a candidate phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, causes aberrant mitotic chromosome segregation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4351–4364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payrastre B., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Breton M., den Hartigh J. C., Plantavid M., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J. Phosphoinositide kinase, diacylglycerol kinase, and phospholipase C activities associated to the cytoskeleton: effect of epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):121–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shariff A., Luna E. J. Diacylglycerol-stimulated formation of actin nucleation sites at plasma membranes. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.1373523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Cloning and sequence of multiple forms of phospholipase C. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90548-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh P. G., Ryu S. H., Moon K. H., Suh H. W., Rhee S. G. Inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C: complete cDNA and protein sequences and sequence homology to tyrosine kinase-related oncogene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5419–5423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A., Gilroy S. Signal transduction in plant cells. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90255-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Jiang H., Katz A., Simon M. I. Identification of critical regions on phospholipase C-beta 1 required for activation by G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3704–3709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K. A novel cis-acting element in an Arabidopsis gene is involved in responsiveness to drought, low-temperature, or high-salt stress. Plant Cell. 1994 Feb;6(2):251–264. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoko-o T., Matsui Y., Yagisawa H., Nojima H., Uno I., Toh-e A. The putative phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C gene, PLC1, of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]