Abstract
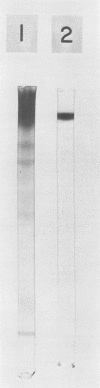
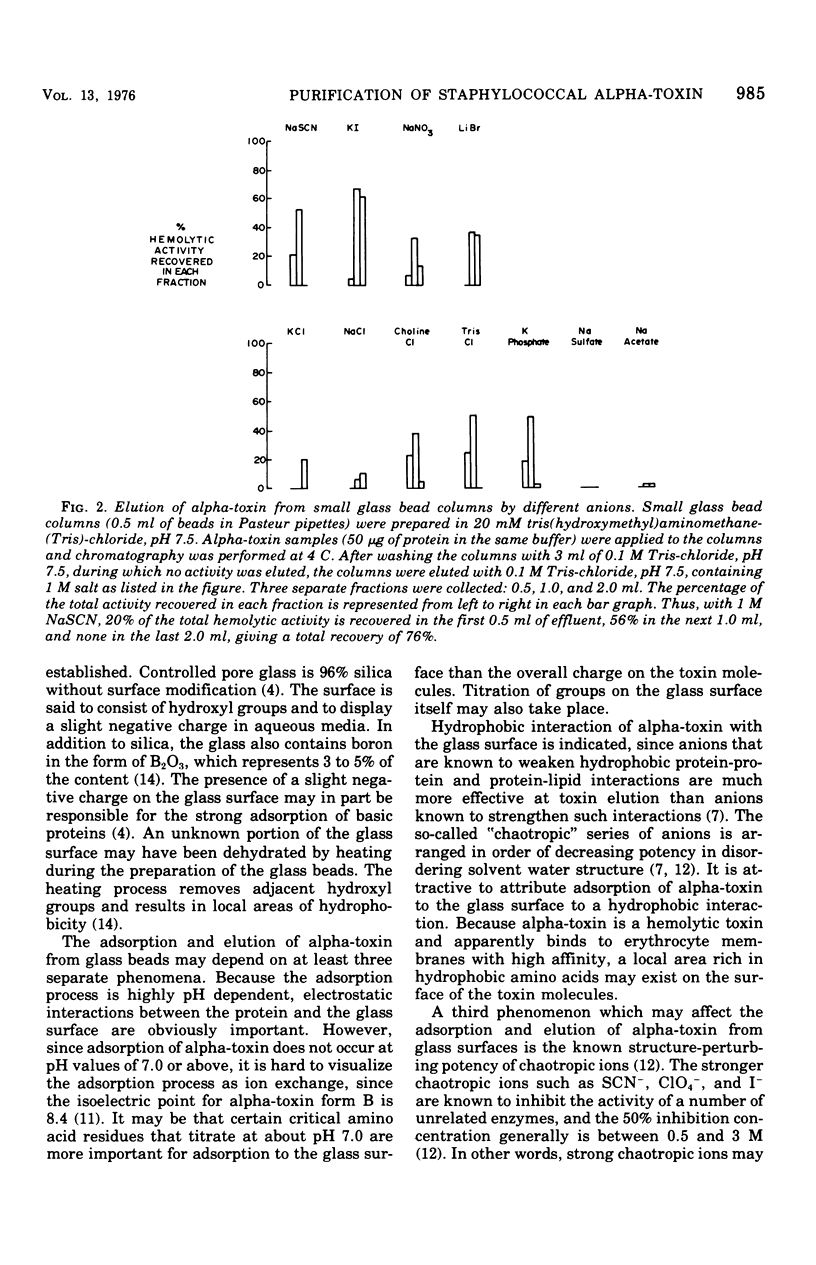
Staphylococcal alpha-toxin was purified from Staphylococcus aureus growth medium using adsorption chromatography on controlled pore glass beads. Elution of alpha-toxin from the unmodified glass surface of the beads with various anions generally followed the chaotropic series. Alpha-toxin, purified by glass bead chromatography, is composed of a single electrophoretic form, containing less than 2% of other forms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock H. O., Fleischer S. Purification of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate apodehydrogenase, a lecithin-requiring enzyme. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:374–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Hanstein W. G. Destabilization of membranes with chaotropic ions. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:770–790. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawk G. L., Cameron J. A., Dufault L. B. Chromatography of biological materials on polyethylene glycol-treated controlled-pore glass. Prep Biochem. 1972;2(2):193–203. doi: 10.1080/00327487208061469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcinka K. Application of permeation chromatography on controlled-pore glass in the purification of plant viruses. Acta Virol. 1972 Jun;16(1):53–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Physical and chemical studies on staphylococcal -toxins A and B . Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Purification and properties of two forms of staphylococcal toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2672–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T., Möllby R. Some biological properties of purified staphylococcal haemolysins. Toxicon. 1972 Aug;10(5):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Kato I. Purification and some properties of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Jpn J Exp Med. 1974 Apr;44(2):165–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]