Abstract
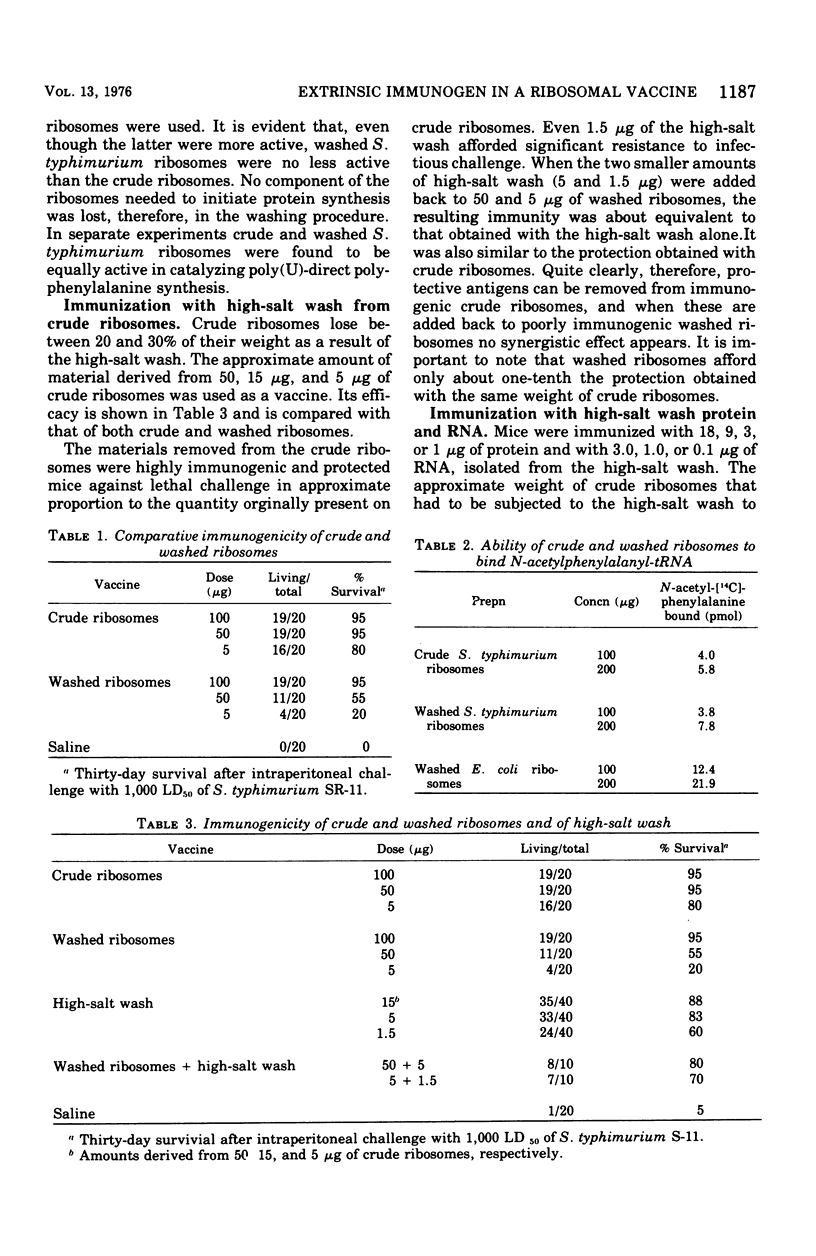
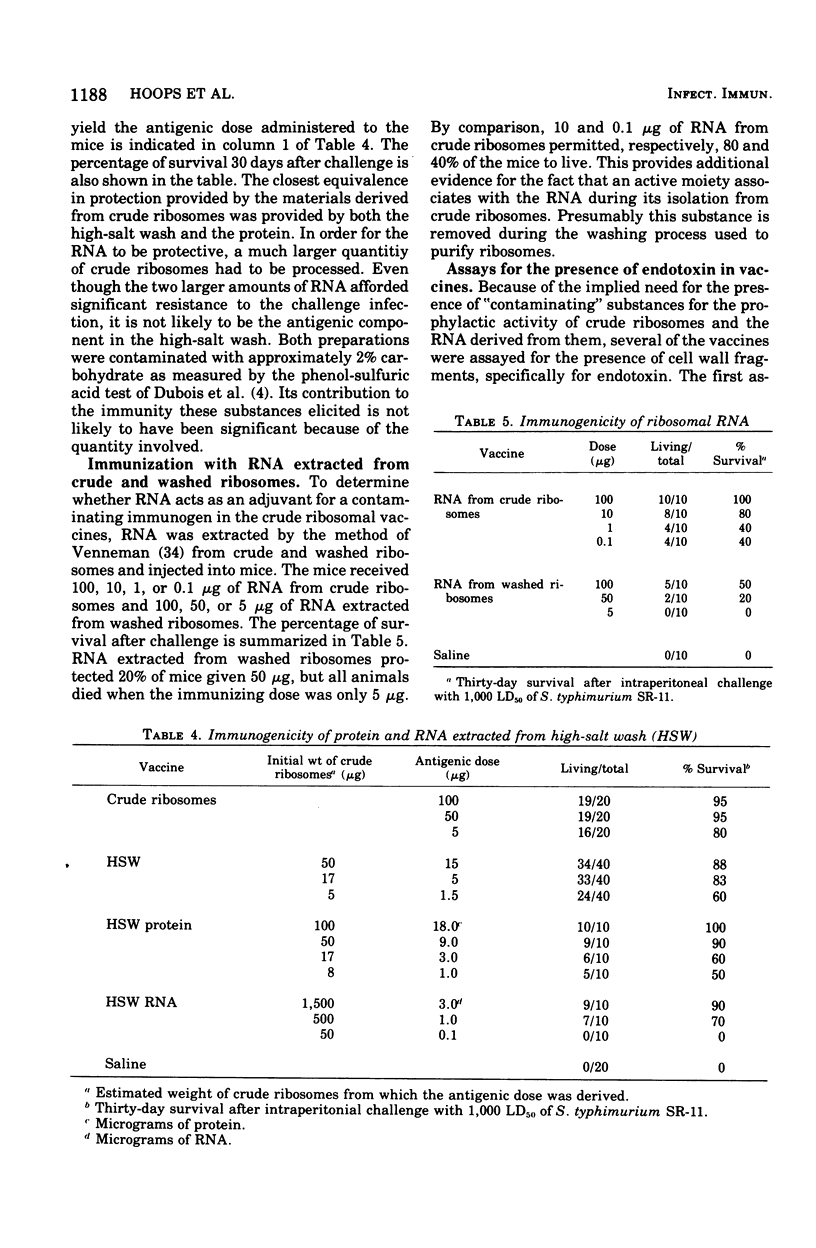
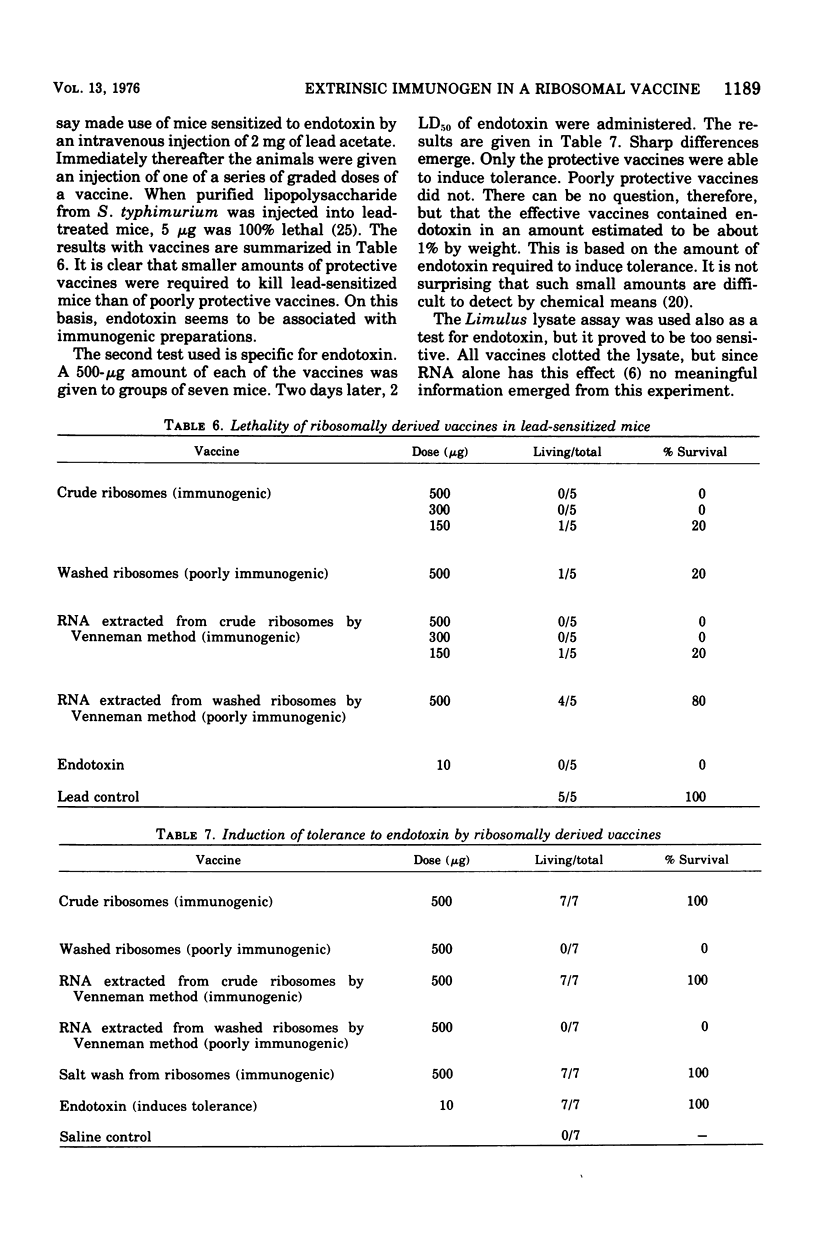
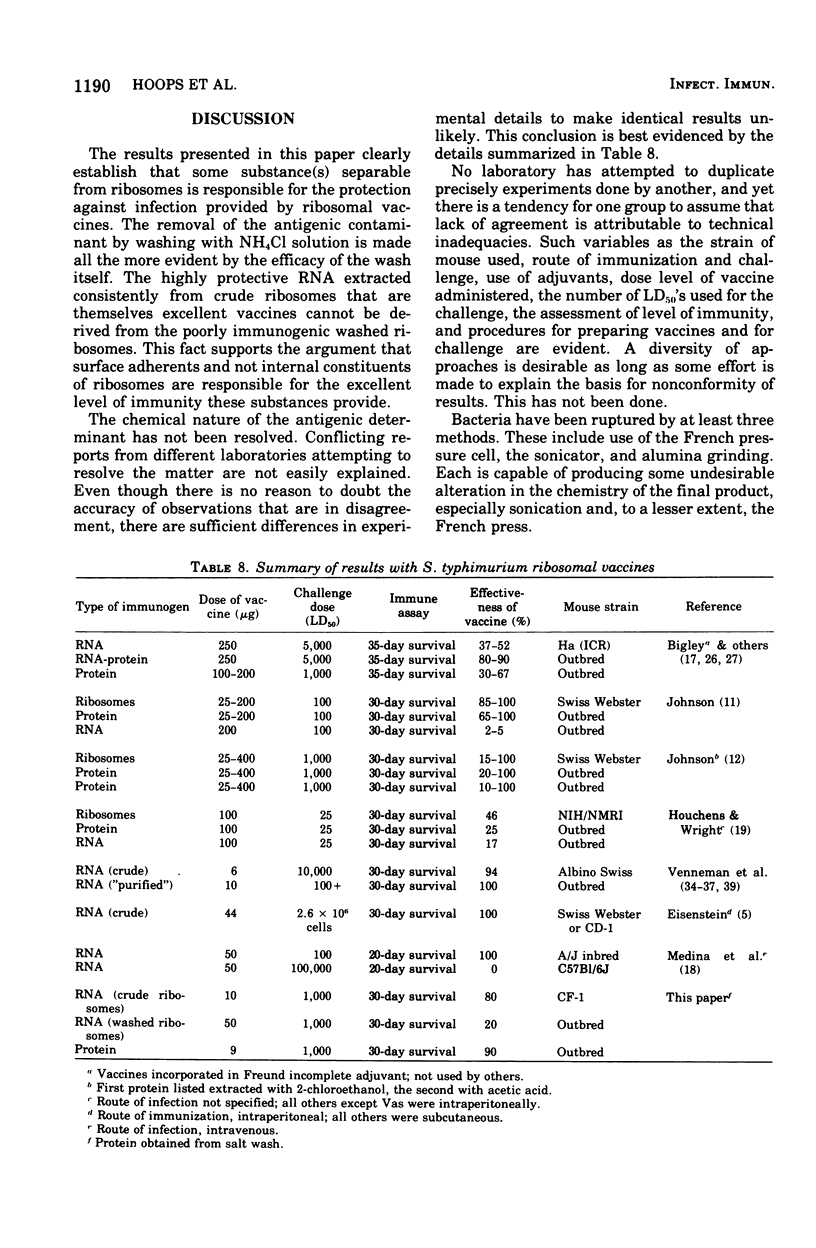
Previous work has indicated that ribosomes isolated from Salmonella typhimurium were highly immunogenic and afforded excellent protection against homologous challenge. Effective protection was obtained also when ribonucleic acid ( RNA) extracted from these ribosomes was used as a vaccine. In this investigation ribosomes prepared by another method and washed repeatedly in 1 M NH1Cl lost much of their prophylactic potency and yielded poorly protective RNA. The high-salt wash of the ribosomes was immunogenic. The RNA and the protein isolated from the salt wash of the ribosomes were effective vaccines. No intrinsic component of the ribosomes was removed by the NH4Cl wash, since the ability of both "crude" and "clean" ribosomes to function equally well in an in vitro protein synthesizing system was demonstrated. The presence of a component with toxic properties similar to those of endotoxin was found in active vaccines but not in weak ones. This was shown by the ability of effective vaccines to kill lead acetate-sensitized mice and to induce tolerance to endotoxin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Nonspecificity of the limulus amebocyte lysate test: positive reactions with polynucleotides and proteins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):349–352. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit C., Tewari R. P. Immunogenicity of Ribosomal Preparations from Yeast Cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1091-1097.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentzel M. N., Berry L. J. Protection of suckling mice from experimental cholera by maternal immunization: comparison of the efficacy of whole-cell, ribosomal-derived, and enterotoxin immunogens. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.167-172.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houchens D. P., Wright G. L., Jr Immunity to Salmonella typhimurium infection: characterization of antigens in active protection by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):507–511. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.507-511.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R., Gregory B., Naylor J., Actor P. Isolation of protective somatic antigen from Vibrio cholerae (Ogawa) ribosomal preparations. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):156–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.156-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Bang F. B. Clottable protein in Limulus; its localization and kinetics of its coagulation by endotoxin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):186–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J. M., Bigley N. J. Cytophilic macroglobulin reactive with bacterial protein in mice immunized with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):390–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.390-397.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J. M., Bigley N. J. Cytophilic macroglobulin reactive with bacterial protein in mice immunized with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):390–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.390-397.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina S., Vas S. I., Robson H. G. Effect of nonspecific stimulation on the defense mechanisms of inbred mice. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1720–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Thach R. E. A new method for the purification of initiation factor F2 in high yield, and an estimation of stoichiometry in the binding reaction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5737–5742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalla W. O., Johnson W. Immunogenicity of ribosomal vaccines isolated from group A, type 14 Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1195-1202.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selye H., Tuchweber B., Bertók L. Effect of lead acetate on the susceptibility of rats to bacterial endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):884–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.884-890.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Detection of delayed hypersensitivity in mice injected with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.384-389.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Wysocki J. A., Bruun J. N., De Courcy S. J., Jr, Blakemore W. S., Mudd S. Efficacy of ribosomal preparations from Pseudomonas aeruginosa to protect against intravenous Pseudomonas challenge in mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1974 Jan;15(1):22–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttle D. P., Haralson M. A., Ravel J. M. Initiation factor 3 requirement for the formation of initiation complexes with synthetic oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 17;51(2):376–382. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91268-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. W., Weiss E. Response of mice to injection of ribosomal fraction from group B Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):355–363. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.355-363.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson H. C., Snyder I. S. Protection against pneumococcal infection by a ribosomal preparation. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):16–23. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.16-23.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Cell-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):381–387. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.381-387.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Experimental salmonellosis: differential passive transfer of immunity with serum and cells obtained from ribosomal and ribonucleic acid-immunized mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 May;9(5):491–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Berry L. J. Serum-mediated resistance induced with immunogenic preparations of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):374–380. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.374-380.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R. Purification of immunogenically active ribonucleic acid preparations of Salmonella typhimurium: molecular-sieve and anion-exchange chromatography. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.269-282.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S. H., Berry L. J. Antibacterial immunity induced by ribosomal vaccines. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston S., Berry L. J. Immunity induced by ribosomal extracts from Staphylococcus aureus. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jul;8(1):66–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. NATURE OF THE LABILE IMMUNOGENIC SUBSTANCE IN THE PARTICULATE FRACTION ISOLATED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1030-1037.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Immunogenic mycobacterial ribosomal and ribonucleic Acid preparations: chemical and physical characteristics. Infect Immun. 1970 Nov;2(5):659–668. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.5.659-668.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



