Abstract
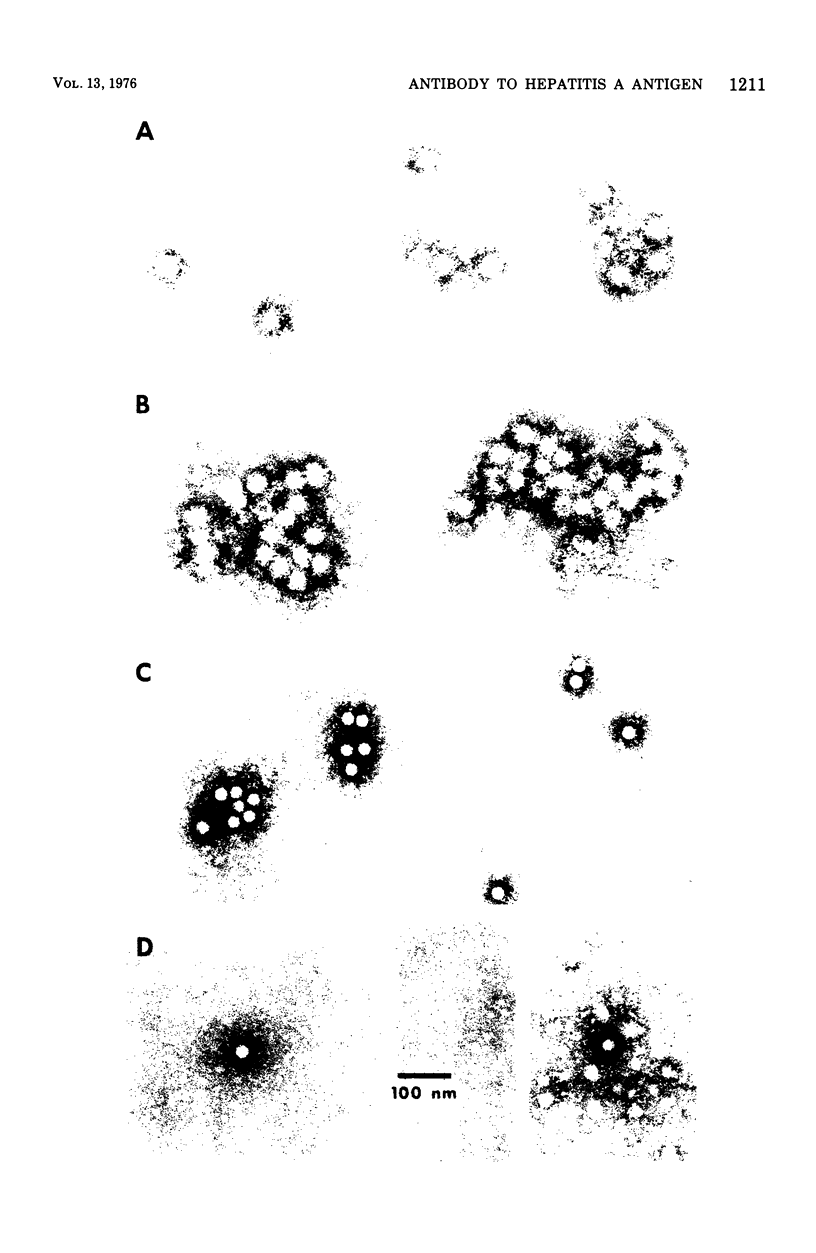
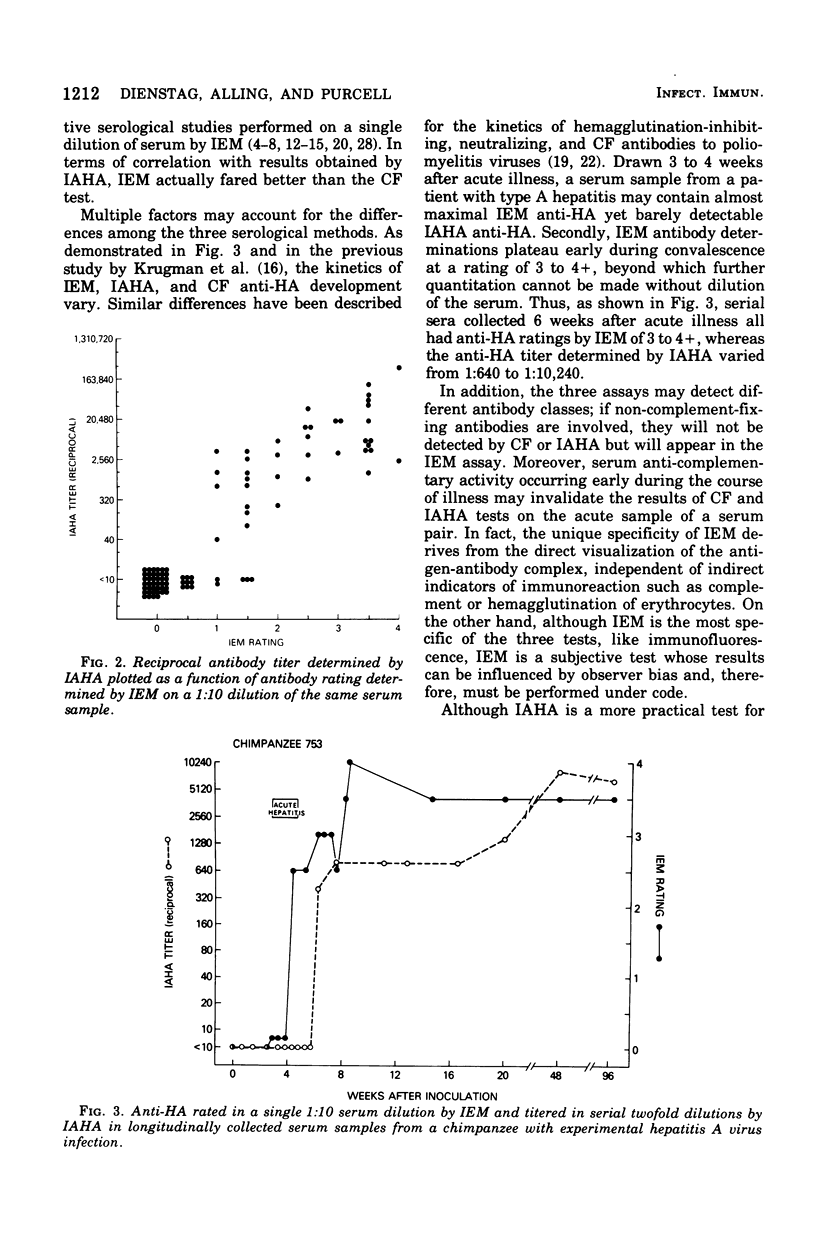
A set of precipitin reactions was performed by immune electron microscopy (IEM) with hepatitis A antigen (HA Ag) and varying quantities of antibody to HA A q (anti-HA). Serial dilution of anti-HA resulted in progressive diminution in IEM antibody rating. These data, together with a highly significant correlation between IEM ratings and immune adherence hemagglutination (IAHA) titers on 92 coded serum samples, confirm that quantitative serology development can be performed by IEM. To demonstrate the different kinetics of antibody development by IEM and IAHA, we used both techniques to test for anti-HA in longitudinally collected sera from a chimpanzee experimentally infected with hepatitis A virus. Detection of anti-HA was possible by IEM during acute hepatitis, but IAHA anti-HA was not observed until approximately 4 weeks later. Six weeks after acute illness, IEM ratings reached a plateau beyond which IAHA titers continued to rise gradually. Peak titers were achieved 11 months after inoculation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida J. D., Gay F. W., Wreghitt T. G. Pitfalls in the study of hepatitis A. Lancet. 1974 Sep 28;2(7883):748–751. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90943-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. The morphology of virus-antibody interaction. Adv Virus Res. 1969;15:307–338. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. D., Melnick J. L., Conrad M. E., Felsher B. F. Viral hepatitis. Clinical and tissue culture studies. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1041–1046. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Hoofnagle J. H., Barker L. F., London W. T., Popper H., Peterson J. M., Kapikian A. Z. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):532–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Purcell R. H., Hooper R. R., Harrison W. O. Foodhandler-associated outbreak of hepatitis type A. An immune electron microscopic study. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Nov;83(5):647–650. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-5-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purcell R. H., Alter H. J., Holland P. V. Transfusion-associated hepatitis not due to viral hepatitis type A or B. N Engl J Med. 1975 Apr 10;292(15):767–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197504102921502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravelle C. R., Hornbeck C. L., Maynard J. E., Schable C. A., Cook E. H., Bradley D. W. Hepatitis A: report of a common-source outbreak with recovery of a possible etiologic agent. II. Laboratory studies. J Infect Dis. 1975 Feb;131(2):167–171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. W., Deinhardt F., Wolfe L., Froesner G., Paterson D., Casto B., Conrad M. E. Specific neutralization of human hepatitis type A in marmoset monkeys. Nature. 1973 Jun 15;243(5407):419–420. doi: 10.1038/243419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Dolin R., Thornhill T. S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Visualization by immune electron microscopy of a 27-nm particle associated with acute infectious nonbacterial gastroenteritis. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1075–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1075-1081.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knodell R. G., Conrad M. E., Dienstag J. L., Bell C. J. Etiological spectrum of post-transfusion hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1278–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Friedman H., Lattimer C. Viral hepatitis, type A. Identification by specific complement fixation and immune adherence tests. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 29;292(22):1141–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505292922201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugman S., Giles J. P., Hammond J. Infectious hepatitis. Evidence for two distinctive clinical, epidemiological, and immunological types of infection. JAMA. 1967 May 1;200(5):365–373. doi: 10.1001/jama.200.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., SCHMIDT N. J. Studies on the development and persistence of complement-fixing and neutralizing antibodies in human poliomyelitis. Am J Hyg. 1957 Mar;65(2):210–238. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander J. J., Alter H. J., Purcell R. H. Frequency of antibody to hepatitis-associated antigen as measured by a new radioimmunoassay technique. J Immunol. 1971 May;106(5):1166–1171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Stott A. C., Gust I. D. The relationship between a 27-nm virus-like particle and hepatitis A as demonstrated by immune electron microscopy. Intervirology. 1974;4(2):110–118. doi: 10.1159/000149849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., RAMOS-ALVAREZ M., BLACK F. L., GIRARDI A. J., NAGAKI D. Poliomyelitis viruses in tissue culture. VII. Experiences with viral and serological diagnostic procedures. Yale J Biol Med. 1954 Jun;26(6):465–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayumi M., Okochi K., Nishioka K. Detection of Australia antigen by means of immune adherence haemagglutination test. Vox Sang. 1971 Feb;20(2):178–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb00549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. J., Provost P. J., McAleer W. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Hilleman M. R. Specific immune adherence assay for human hepatitis A antibody application to diagnostic and epidemiologic investigations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 May;149(1):254–261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Valdesuso J., Wong D. C., Wagner J., Routenberg J. A., Purcell R. H. Purification of hepatitis A antigen from feces and detection of antigen and antibody by immune adherence hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):898–908. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.898-908.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. J., Bryan J. A., Hurley J. P., Murphy J. F., O'Brien T. F., Wacker W. E. The Holy Cross college football team hepatitis outbreak. JAMA. 1972 Feb;219(6):706–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Arguedas J. A., Hilleman M. R. Etiologic relationship of marmoset-propagated CR326 hepatitis A virus to hepatitis in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provost P. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Hilleman M. R. A specific complement-fixation test for human hepatitis a employing CR326 virus antigen. Diagnosis and epidemiology. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Apr;148(4):962–969. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z. Relationship of hepatitis A antigen to viral hepatitis. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):61–71. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., HAGENS S. J., LENNETTE E. H. Studies on the antibody responses of patients infected with ECHO viruses. Am J Hyg. 1962 Mar;75:168–182. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]