Abstract
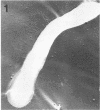
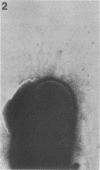
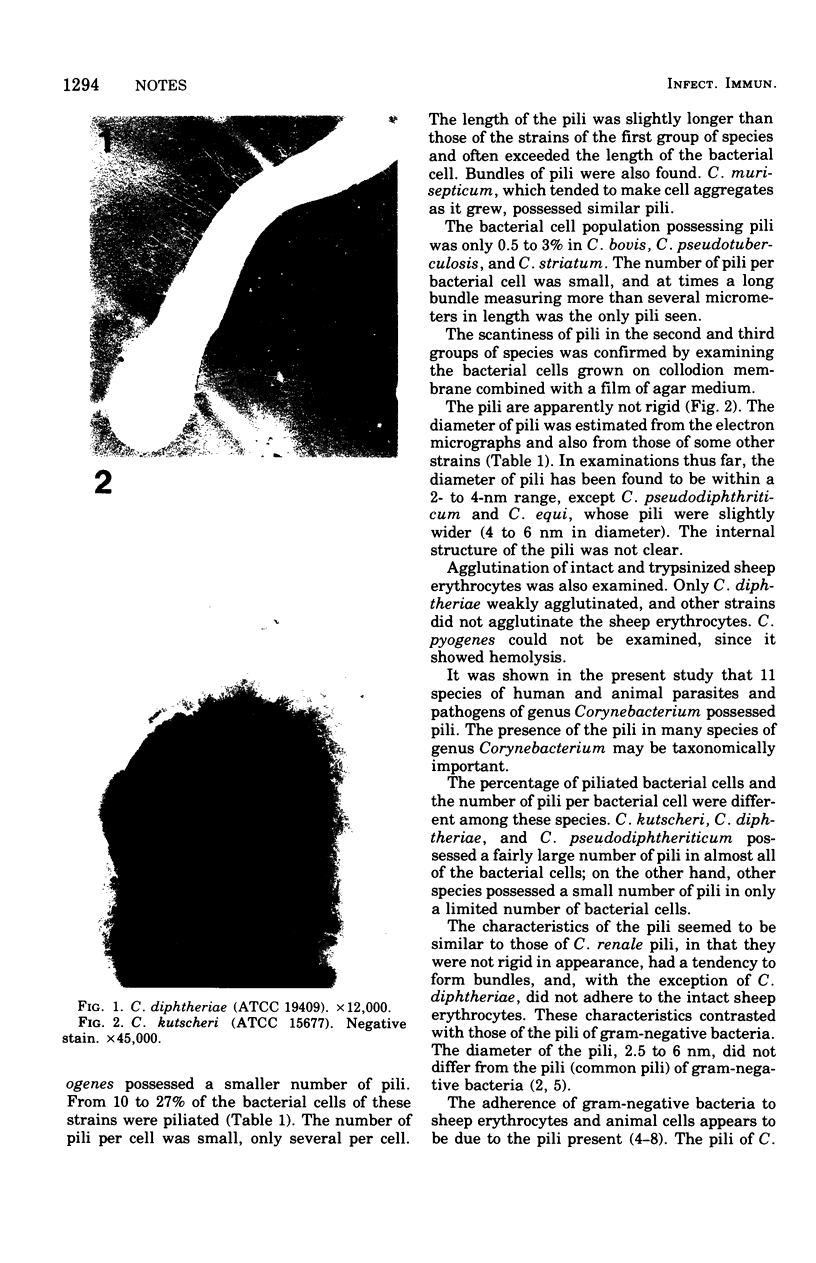
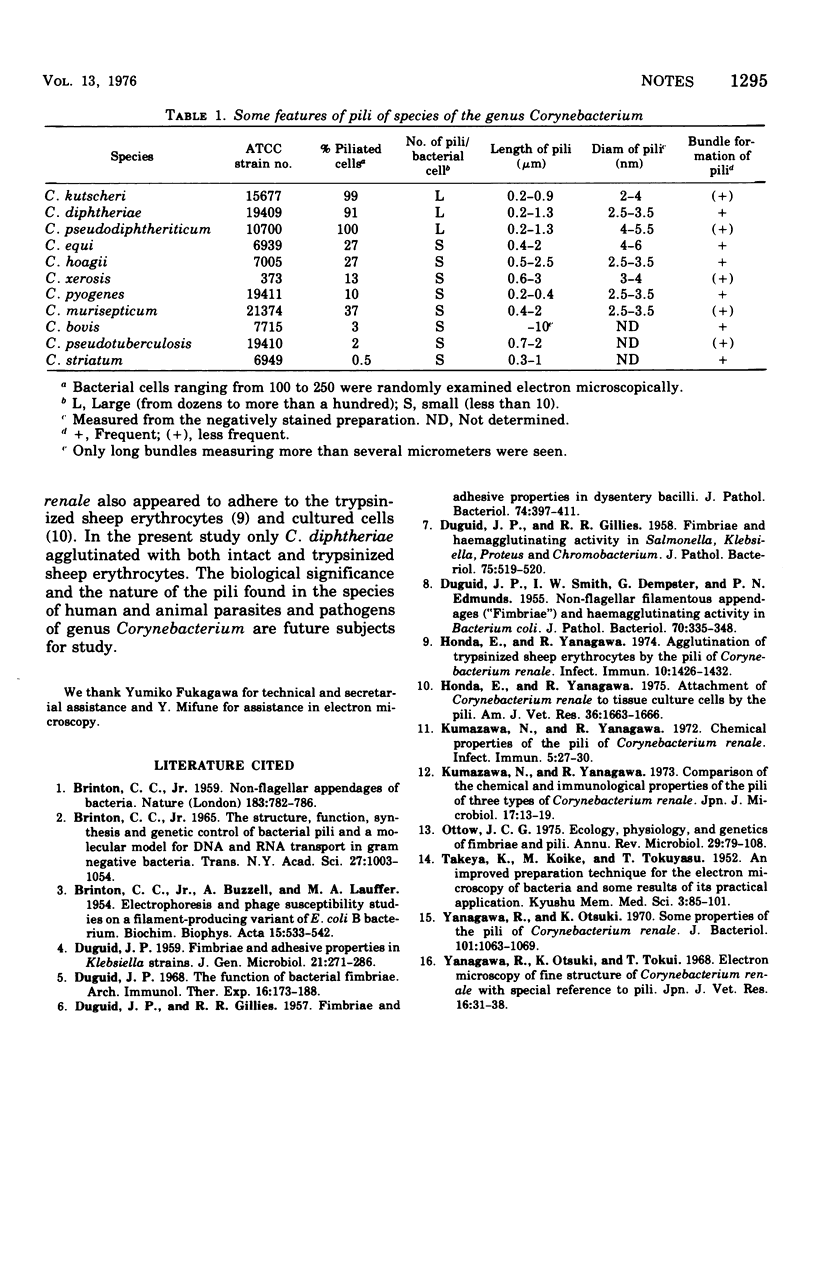
The presence of pili in human and animal parasites and pathogens of the genus Corynebacterium was examined. C. kutscheri, C. diphtheriae, and C. pseudodiphtheriticum possessed a fairly large number of pili, ranging from dozens to more than a hundred, in 91 to 100% of the bacterial cells. C. equi, C. hoagii, C. xerosis, C. pyogenes, and C. murisepticum had only a small number of pili in 10 to 37% of the bacterial cells. In C. bovis, C. striatum, and C. pseudotuberculosis, pili were detected in only 0.5% to 3% of the bacterial cells. The pili were similar to each other and to those of C. renale; they were not rigid and had a tendency to form bundles. The length of pili usually ranged from 0.2 to 3 mum, and their diameter was within a 2- to 6-nm range.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, BUZZELL A., LAUFFER M. A. Electrophoresis and phage susceptibility studies on a filament-producing variant of the E. coli B bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Dec;15(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINTON C. C., Jr Non-flagellar appendages of bacteria. Nature. 1959 Mar 21;183(4664):782–786. doi: 10.1038/183782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. Fimbriae and adhesive properties in Klebsiella strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:271–286. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P., SMITH I. W., DEMPSTER G., EDMUNDS P. N. Non-flagellar filamentous appendages (fimbriae) and haemagglutinating activity in Bacterium coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(2):335–348. doi: 10.1002/path.1700700210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid J. P. The function of bacterial fimbriae. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1968;16(2):173–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda E., Yanagawa R. Agglutination of trypsinized sheep erythrocytes by the pili of Corynebacterium renale. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1426–1432. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1426-1432.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda E., Yanagawa R. Attachment of Corynebacterium renale to tissue culture cells by the pili. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Nov;36(11):1663–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa N., Yanagawa R. Chemical properties of the pili of Corynebacterium renale. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):27–30. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.27-30.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa N., Yanagawa R. Comparison of the chemical and immunological properties of the pili of three types of Corynebacterium renale. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;17(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Otsuki K. Some properties of the pili of Corynebacterium renale. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1063-1069.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Otsuki K., Tokui T. Electron microscopy of fine structure of Corynebacterium renale with special reference to pili. Jpn J Vet Res. 1968 Mar;16(1):31–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]