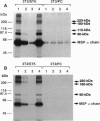
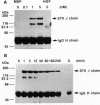
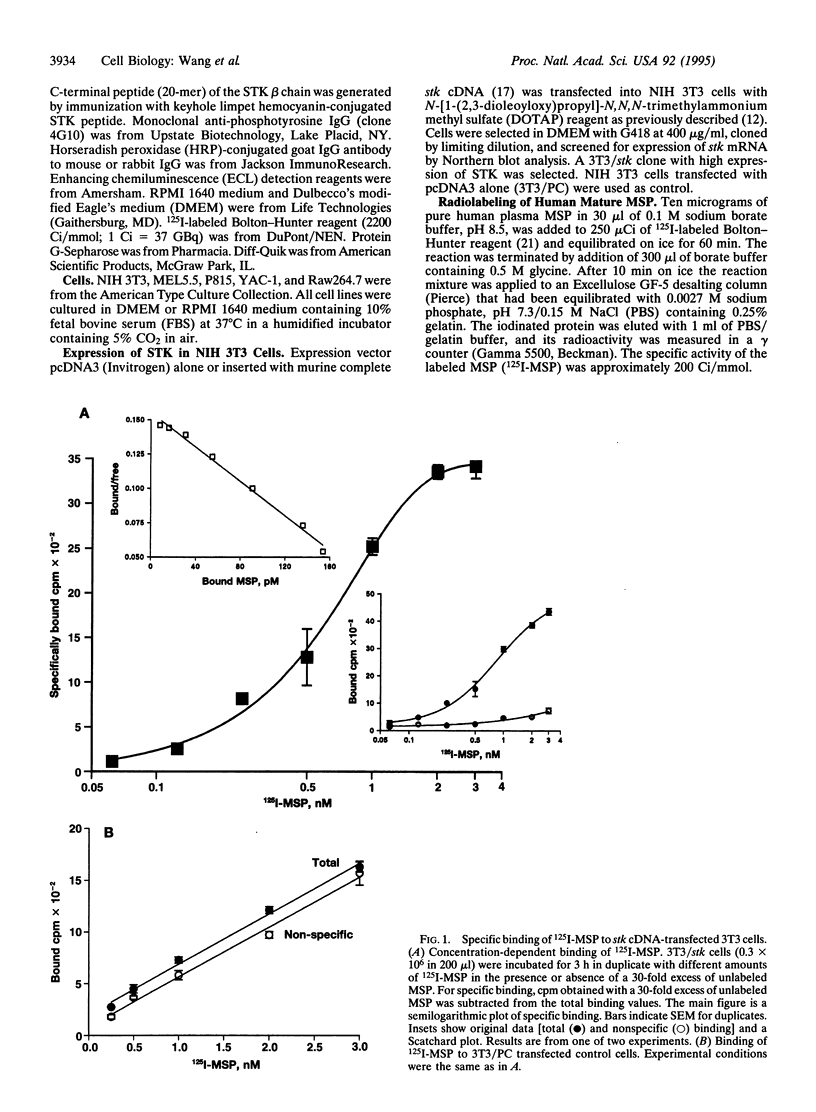
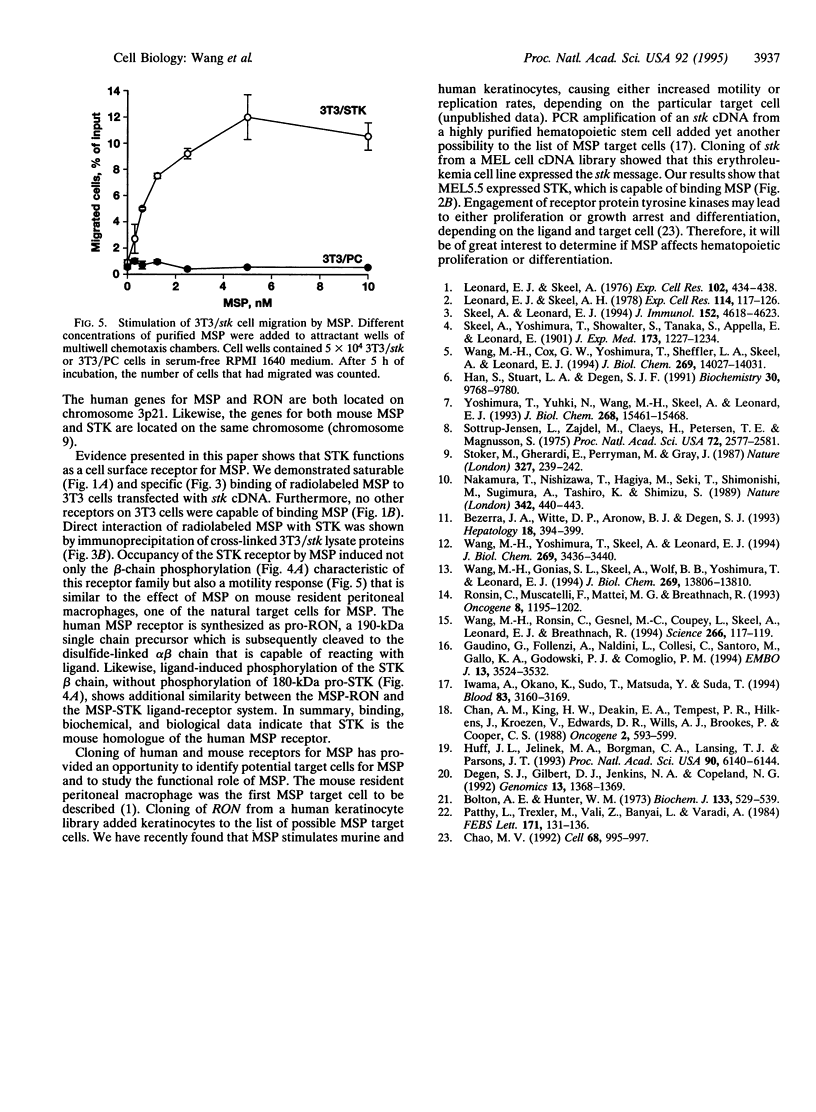
Abstract
Macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP) was originally identified as an inducer of murine resident peritoneal macrophage responsiveness to chemoattractants. We recently showed that the product of RON, a protein tyrosine kinase cloned from a human keratinocyte library, is the receptor for MSP. Similarity of murine stk to RON led us to determine if the stk gene product is the murine receptor for MSP. Radiolabeled MSP could bind to NIH 3T3 cells transfected with murine stk cDNA (3T3/stk). Binding was saturable and was inhibited by unlabeled MSP but not by structurally related proteins, including hepatocyte growth factor and plasminogen. Specific binding to STK was demonstrated by cross-linking of 125I-labeled MSP to membrane proteins of 3T3/stk cells, which resulted in a protein complex with a molecular mass of 220 kDa. This radiolabeled complex comprised 125I-MSP and STK, since it could be immunoprecipitated by antibodies to the STK beta chain. Binding of MSP to stk cDNA-transfected cells induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the 150-kDa STK beta chain within 1 min and caused increased motile activity. These results establish the murine stk gene product as a specific transmembrane protein tyrosine kinase receptor for MSP. Inasmuch as the stk cDNA was cloned from a hematopoietic stem cell, our data suggest that in addition to macrophages and keratinocytes, a cell in the hematopoietic lineage may also be a target for MSP.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezerra J. A., Witte D. P., Aronow B. J., Degen S. J. Hepatocyte-specific expression of the mouse hepatocyte growth factor-like protein. Hepatology. 1993 Aug;18(2):394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. M., King H. W., Deakin E. A., Tempest P. R., Hilkens J., Kroezen V., Edwards D. R., Wills A. J., Brookes P., Cooper C. S. Characterization of the mouse met proto-oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):593–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V. Growth factor signaling: where is the specificity? Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):995–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90068-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Assignment of the gene coding for hepatocyte growth factor-like protein to mouse chromosome 9. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1368–1369. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino G., Follenzi A., Naldini L., Collesi C., Santoro M., Gallo K. A., Godowski P. J., Comoglio P. M. RON is a heterodimeric tyrosine kinase receptor activated by the HGF homologue MSP. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3524–3532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Stuart L. A., Degen S. J. Characterization of the DNF15S2 locus on human chromosome 3: identification of a gene coding for four kringle domains with homology to hepatocyte growth factor. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9768–9780. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. L., Jelinek M. A., Borgman C. A., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. The protooncogene c-sea encodes a transmembrane protein-tyrosine kinase related to the Met/hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6140–6144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama A., Okano K., Sudo T., Matsuda Y., Suda T. Molecular cloning of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase gene, STK, derived from enriched hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3160–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. H. Isolation of macrophage stimulating protein (MSP) from human serum. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. A serum protein that stimulates macrophage movement, chemotaxis and spreading. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 15;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nishizawa T., Hagiya M., Seki T., Shimonishi M., Sugimura A., Tashiro K., Shimizu S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):440–443. doi: 10.1038/342440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L., Trexler M., Váli Z., Bányai L., Váradi A. Kringles: modules specialized for protein binding. Homology of the gelatin-binding region of fibronectin with the kringle structures of proteases. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 4;171(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80473-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronsin C., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Breathnach R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1195–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Action and target cell specificity of human macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP). J Immunol. 1994 May 1;152(9):4618–4623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeel A., Yoshimura T., Showalter S. D., Tanaka S., Appella E., Leonard E. J. Macrophage stimulating protein: purification, partial amino acid sequence, and cellular activity. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1227–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Zajdel M., Claeys H., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Amino-acid sequence of activation cleavage site in plasminogen: homology with "pro" part of prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M., Gherardi E., Perryman M., Gray J. Scatter factor is a fibroblast-derived modulator of epithelial cell mobility. Nature. 1987 May 21;327(6119):239–242. doi: 10.1038/327239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Cox G. W., Yoshimura T., Sheffler L. A., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Macrophage-stimulating protein inhibits induction of nitric oxide production by endotoxin- or cytokine-stimulated mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14027–14031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Gonias S. L., Skeel A., Wolf B. B., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J. Proteolytic activation of single-chain precursor macrophage-stimulating protein by nerve growth factor-gamma and epidermal growth factor-binding protein, members of the kallikrein family. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13806–13810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Ronsin C., Gesnel M. C., Coupey L., Skeel A., Leonard E. J., Breathnach R. Identification of the ron gene product as the receptor for the human macrophage stimulating protein. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):117–119. doi: 10.1126/science.7939629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Yoshimura T., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Proteolytic conversion of single chain precursor macrophage-stimulating protein to a biologically active heterodimer by contact enzymes of the coagulation cascade. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3436–3440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Yuhki N., Wang M. H., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, MST1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15461–15468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]