Abstract
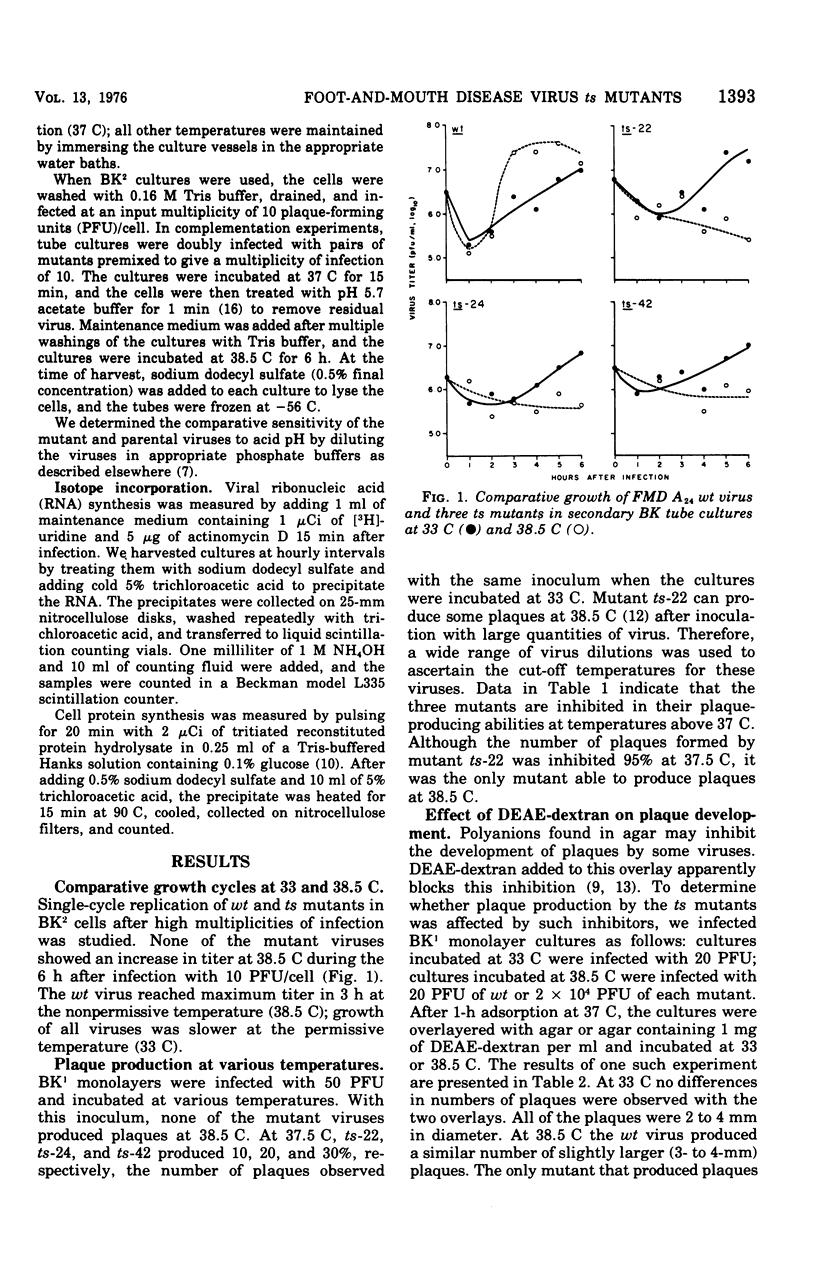
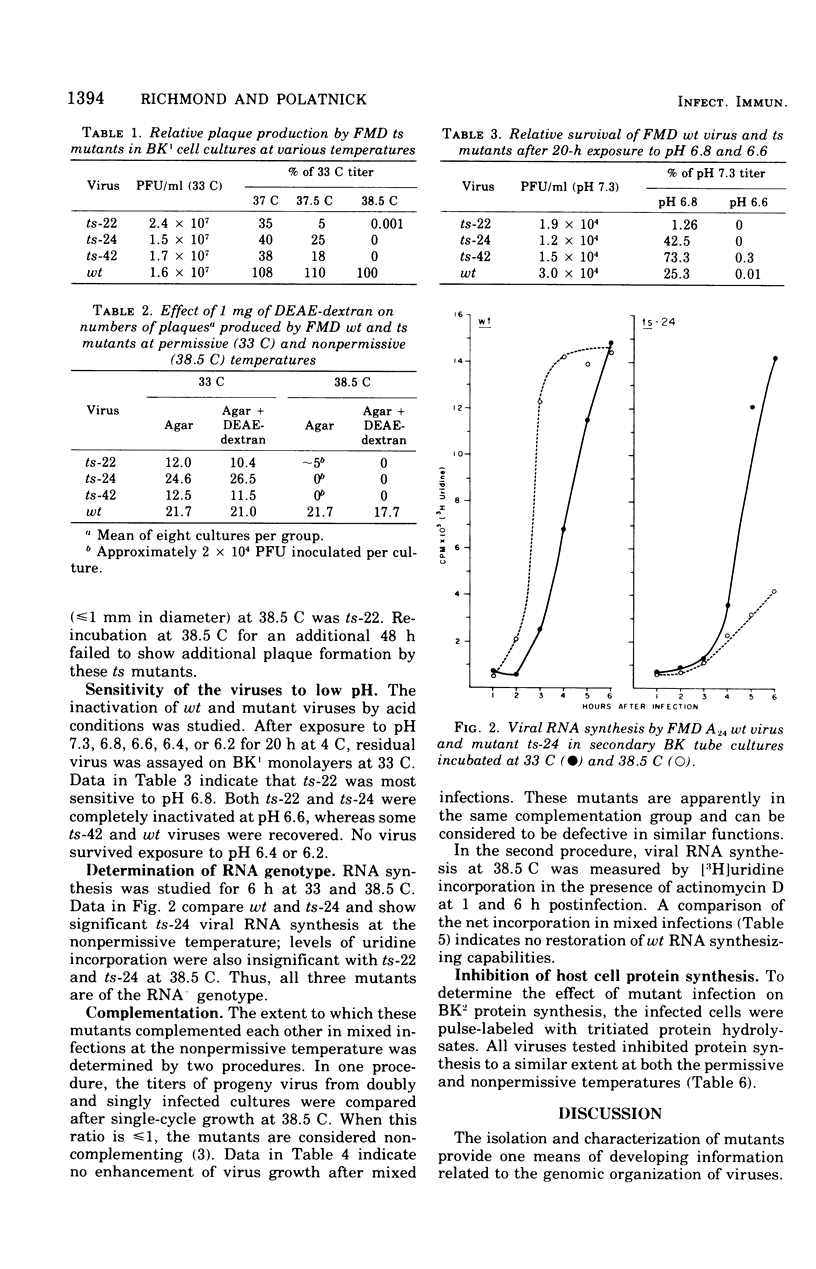
Three temperature-sensitive (ts) mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus were classified as ribonucleic acid negative and as belonging to the same complementation group when measured by virus yields and [3H] uridine incorporation in paired, mixed infections at the nonpermissive temperature (38.5C). Mutant ts-22, the only mutant able to produce plaques at 38.5 C, was more sensitive to acid than were the parental wild-type or other mutant viruses. Diethylaminoethyl-dextran did not enhance the plaque-forming ability of the mutant viruses at 38.5C. All of the viruses inhibited host cell protein syntehsis at both permissive (33C) and nonpermissive (38.5C) temperatures.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHRACH H. L., BREESE S. S., Jr, CALLIS J. J., HESS W. R., PATTY R. E. Inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus by pH and temperature changes and by formaldehyde. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):147–152. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., CALLIS J. J., HESS W. R., PATTY R. E. A plaque assay for foot-and-mouth disease virus and kinetics of virus reproduction. Virology. 1957 Oct;4(2):224–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burge B. W., Pfefferkorn E. R. Complementation between temperature-sensitive mutants of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):214–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBHABER H., TAKEMOTO K. K. Alteration plaque morphology of EMC virus with polycations. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:502–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Priston A. J., Slade W. R. A genetic recombination map of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):355–367. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie J. S., Slade W. R., Lake J., Priston R. A., Bisby J., Laing S., Newman J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of foot-and-mouth disease virus: the isolation of mutants and observations on their properties and genetic recombination. J Gen Virol. 1975 Apr;27(1):61–70. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor D., Goldblum N. Isolation and partial characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of the SAT-1 strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Feb;9(2):145–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinsen J. S. The effect of diethylaminoethyl dextran and agar overlay pH on plaque formation by two plaque-size variants of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Can J Comp Med. 1970 Jan;34(1):13–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Vande Woude G. F., Arlinghaus R. B. Changes in protein and nucleic acid metabolism in baby hamster kidney cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(3):218–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01241894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. Y. Production, isolation, and partial characterization of three foot-and-mouth disease virus temperature-sensitive mutants. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1291–1295. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1291-1295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLERS R. F., STEWART D. L. Factors affecting the formation of plaques by the virus of foot-and-mouth disease on pig kidney monolayer tissue cultures. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1960;9:594–605. doi: 10.1007/BF01242146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORNE H. V. Kinetics of cell infection and penetration by the virus of foot-and-mouth disease. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:929–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.929-942.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K. Plaque mutants of animal viruses. Prog Med Virol. 1966;8:314–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G. G., Card J. L., Cowan K. M. Immunochemical studies of foot-and-mouth disease. VII. Characterization of foot-and-mouth disease virus concentrated by polyethylene glycol precipitation. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;30(4):343–352. doi: 10.1007/BF01258364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Mechanism of plaque inhibition of poliovirus possessing the d marker. J Gen Virol. 1968 Dec;3(3):349–357. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-3-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


