Abstract
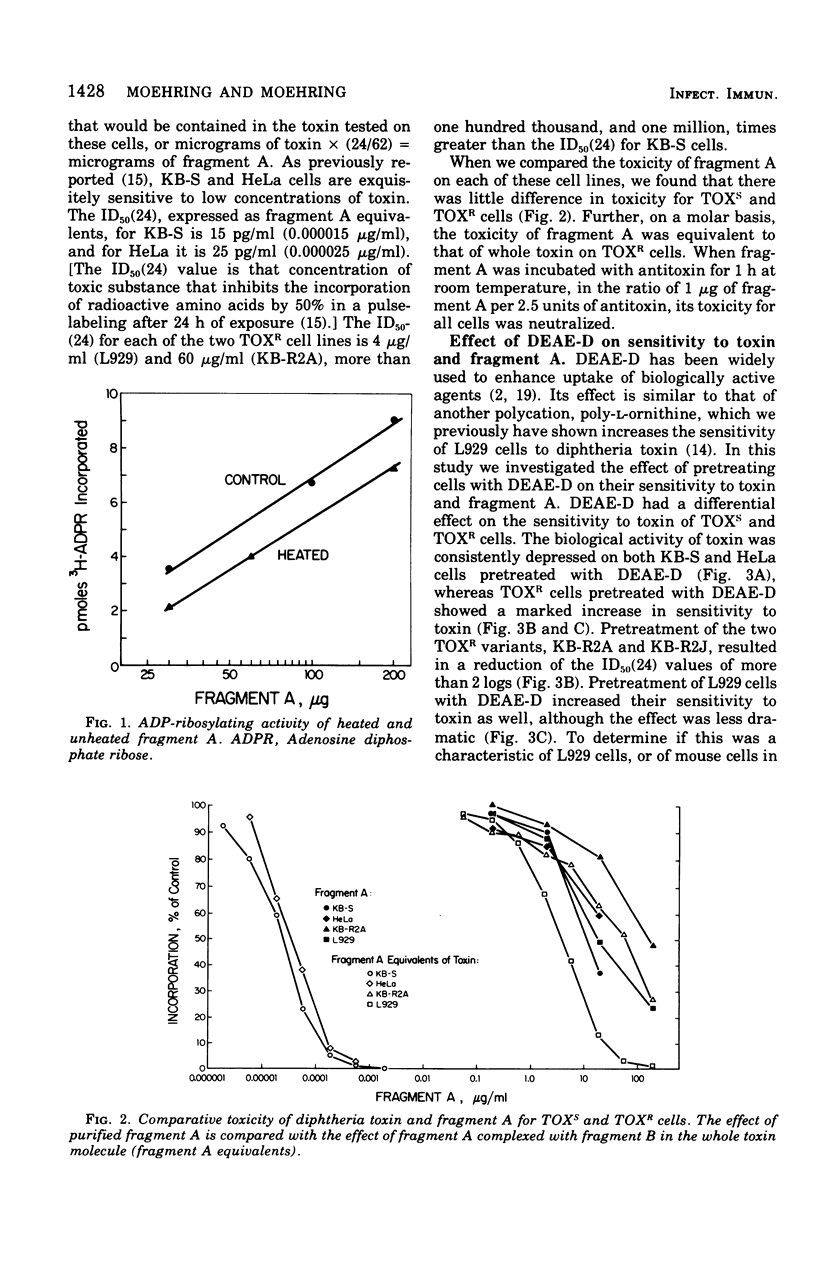
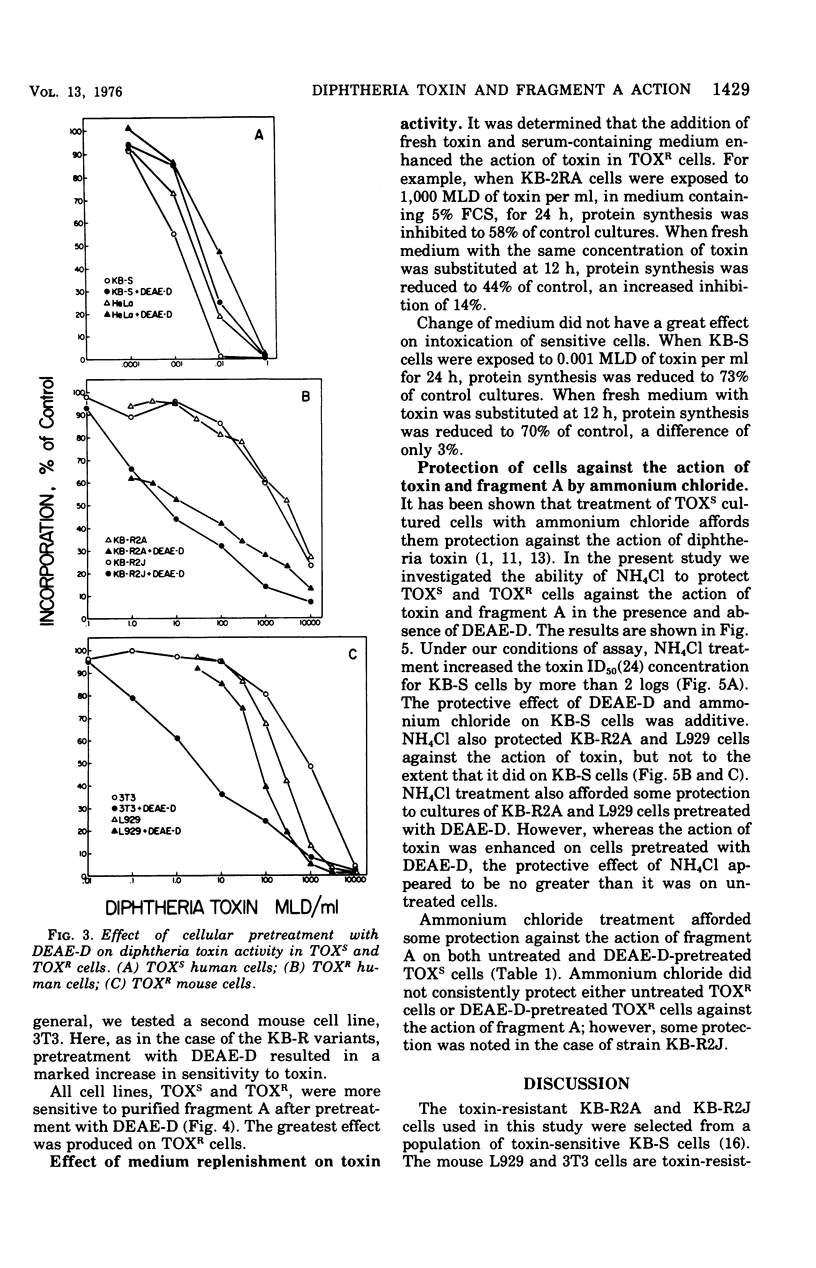
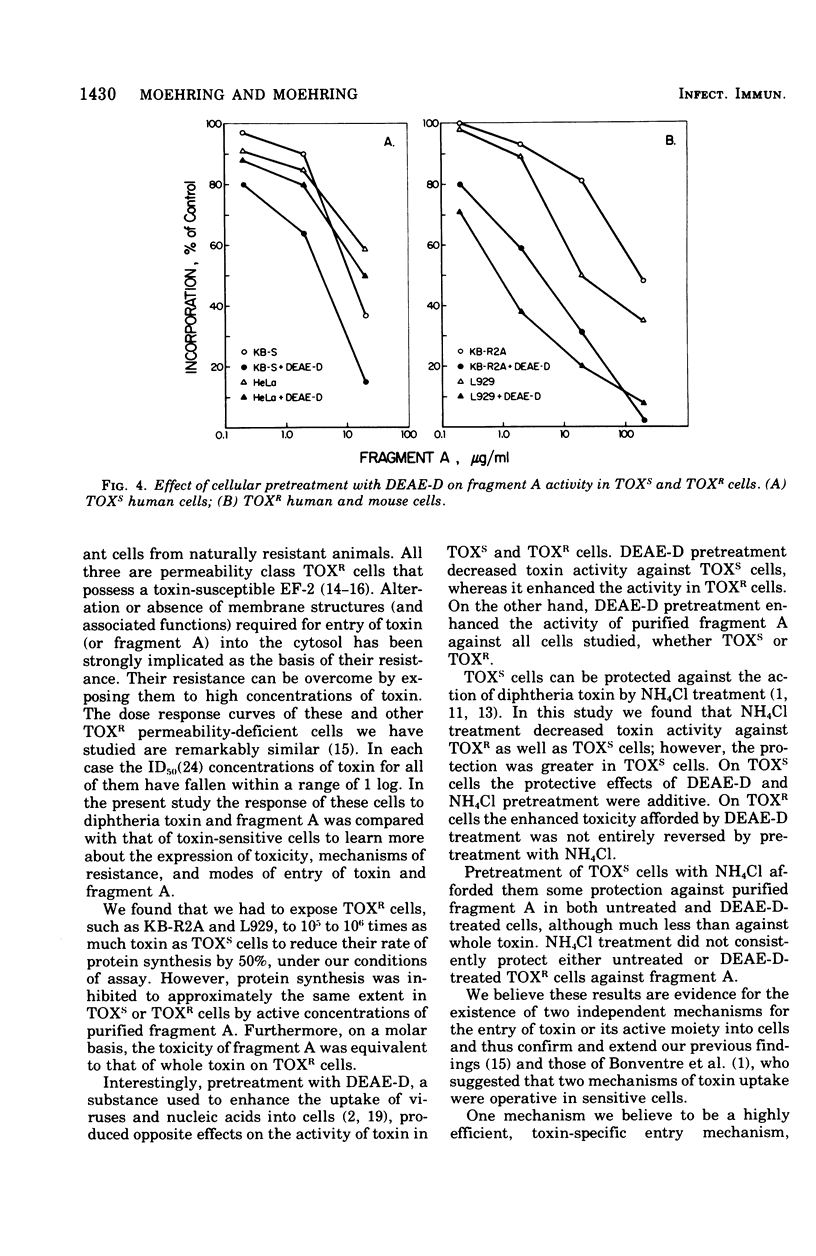
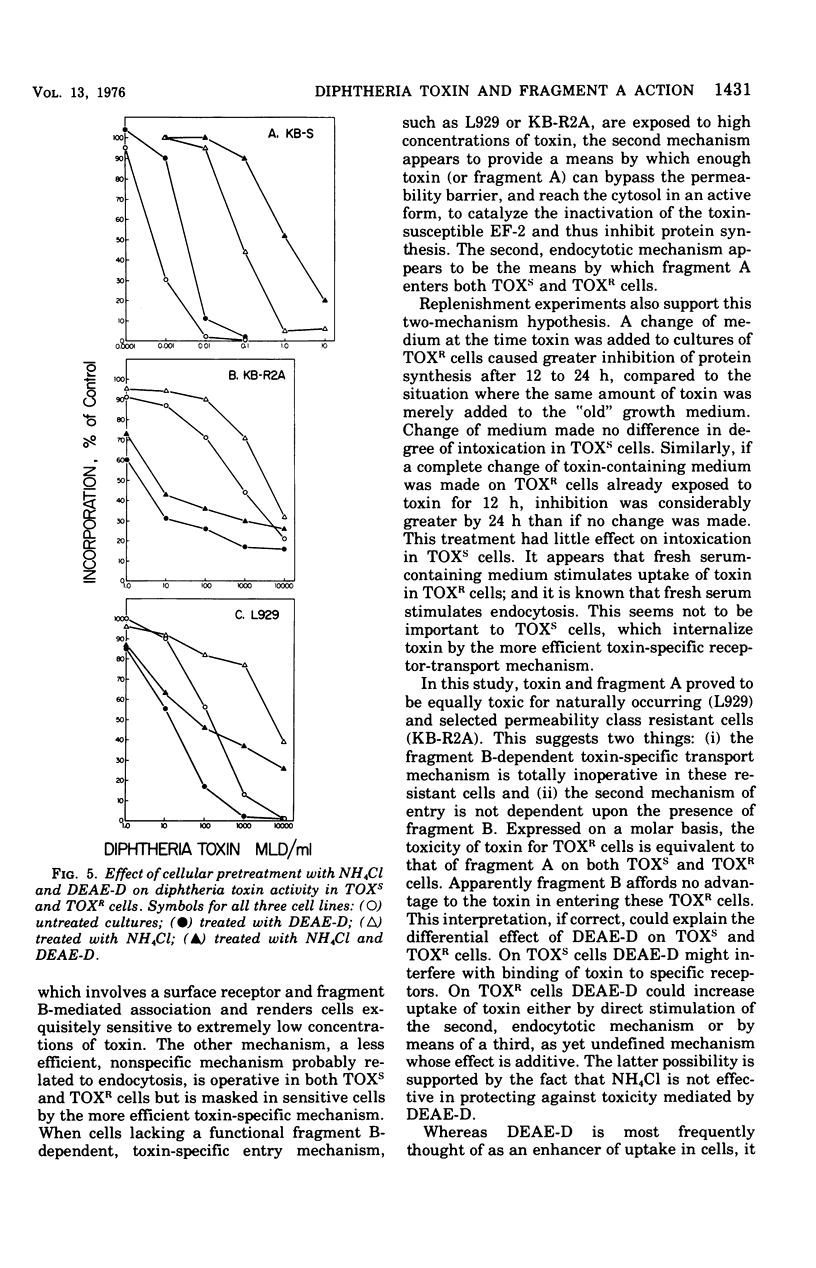
Diphtheria toxin and purified fragment A, the active subunit of the toxin, were tested on toxin-sensitive and permeability class toxin-resistant cultured mammalian cells. Protein synthesis was inhibited to the same degree in sensitive or resistant cells by active concentrations of purified fragment A. In contrast, resistant cells required a concentration of whole toxin 5 to 6 logs greater than that required by sensitive cells to achieve the same degree of inhibition. On a molar basis, the toxicity of fragment A was equivalent to that of whole toxin on resistant cells. These results are evidence for the existence of two independent mechanisms for the entry of toxin or its active moiety into cells. One mechanism is a highly efficient, toxin-specific entry mechanism, involving surface receptor and fragment B-mediated association, and is active in sensitive cells. The other is a less efficient, nonspecific mechanism, probably related to endocytosis, which is operative in sensitive and resistant cells but is inapparent in sensitive cells when they are exposed to whole toxin because of the action of the specific mechanism.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonventre P. F., Saelinger C. B., Ivins B., Woscinski C., Amorini M. Interaction of cultured mammalian cells with [125I] diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):675–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.675-684.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenfreund E., Steinglass M., Korngold G. C., Bendich A. Brief communication: Diethylaminoethyl-dextran and uptake of nucleic acids by mammalian cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Oct;51(4):1391–1392. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.4.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T. Diphtheria toxin, protein synthesis, and the cell. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Kato I., Hayaishi O. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis by diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4251–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B., Saelinger C. B., Bonventre P. F., Woscinski C. Chemical modulation of diphtheria toxin action on cultured mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):665–674. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.665-674.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Collier R. J., Chung D. W. Interaction of fragment A from diphtheria toxin with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2088–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Groman N. B. In vitro inhibition of diphtheria toxin action by ammonium salts and amines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1552–1556. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1552-1556.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. Comparison of diphtheria intoxication in human and nonhuman cell lines and their resistant variants. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):221–228. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.221-228.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring J. M., Moehring T. J. The response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. II. The resistant cell: enhancement of toxin action by poly-L-ornithine. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):541–554. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehring T. J., Moehring J. M. Response of cultured mammalian cells to diphtheria toxin. IV. Isolation of KB cells resistant to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):487–492. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.487-492.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Kumagai K. Effects of polyions on Japanese encephalitis virus: difference in interaction of virus with DEAE dextran and dextran sulfate between PS cell adapted and non-adapted virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;39(1):83–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01241531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Gill D. M. Diphtheria. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):353–358. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


