Abstract
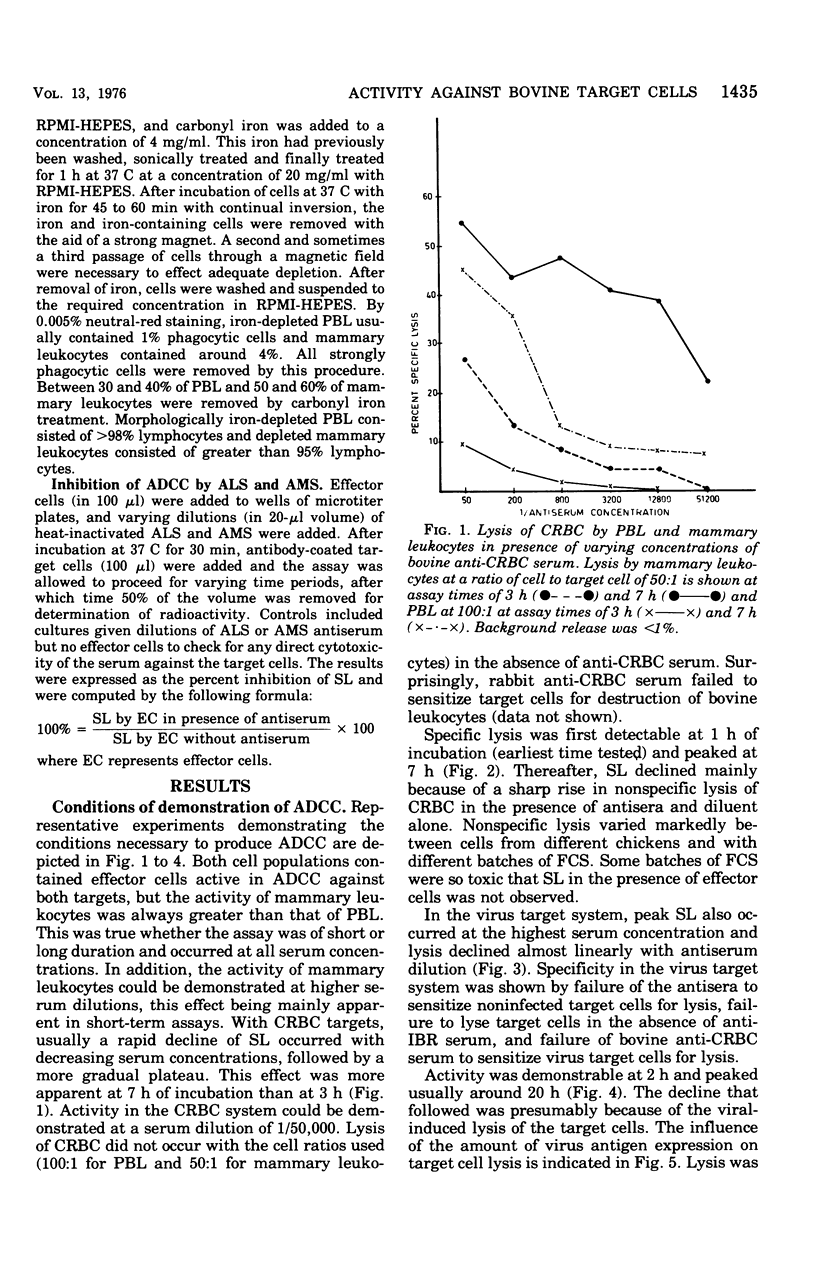
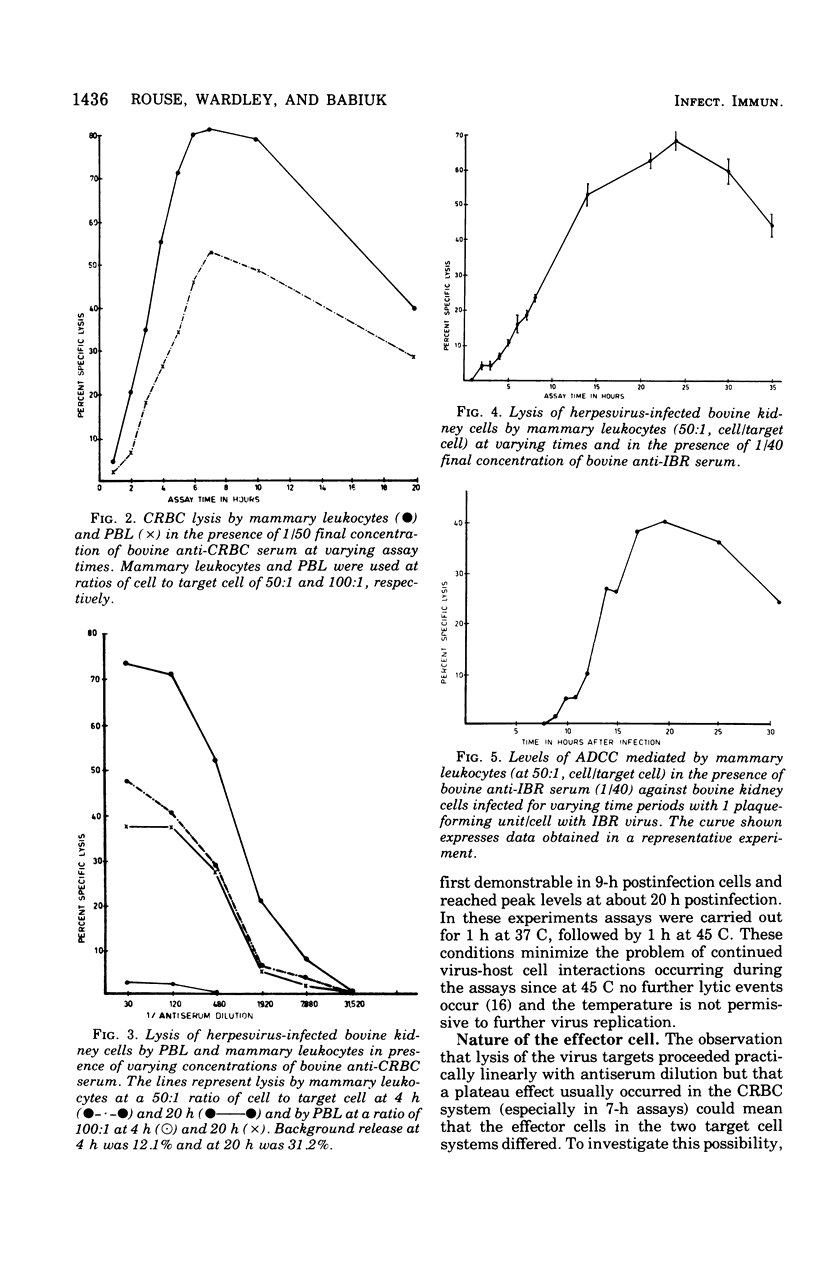
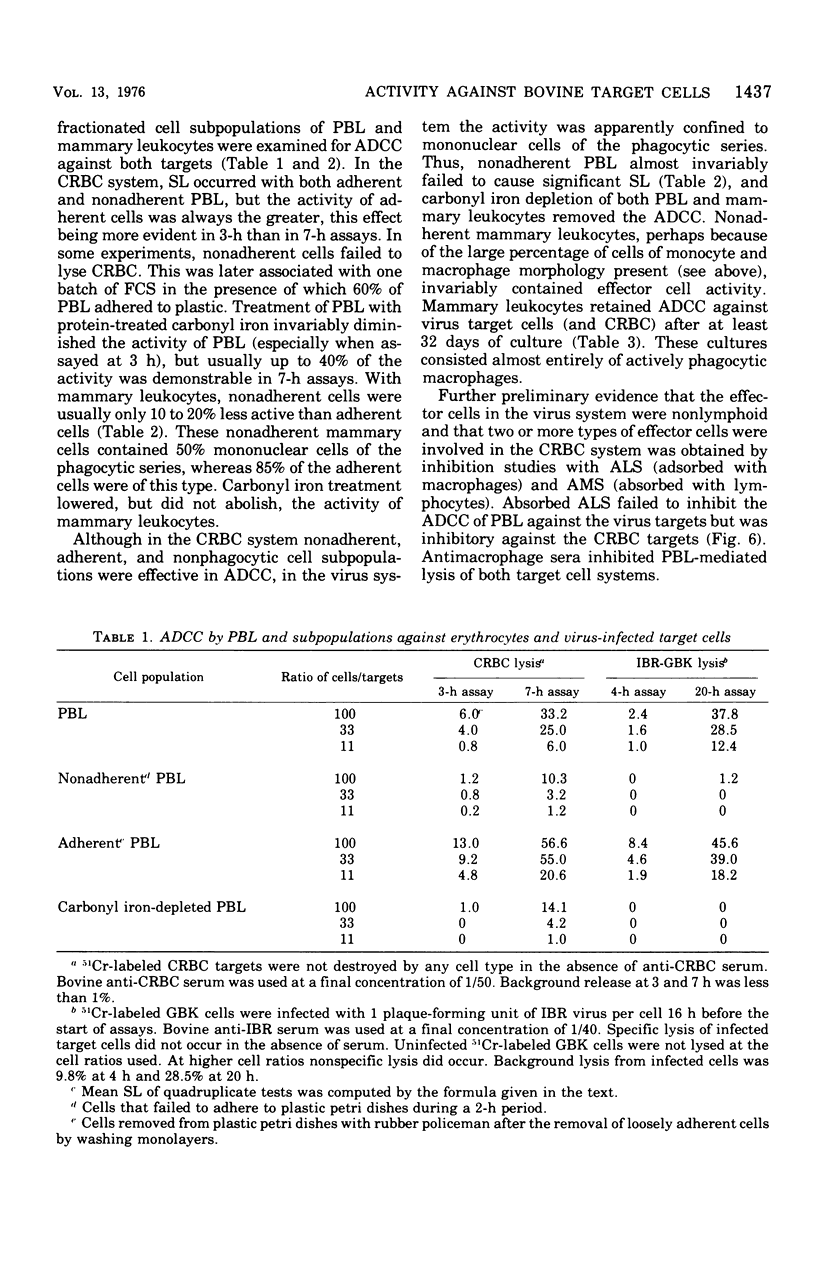
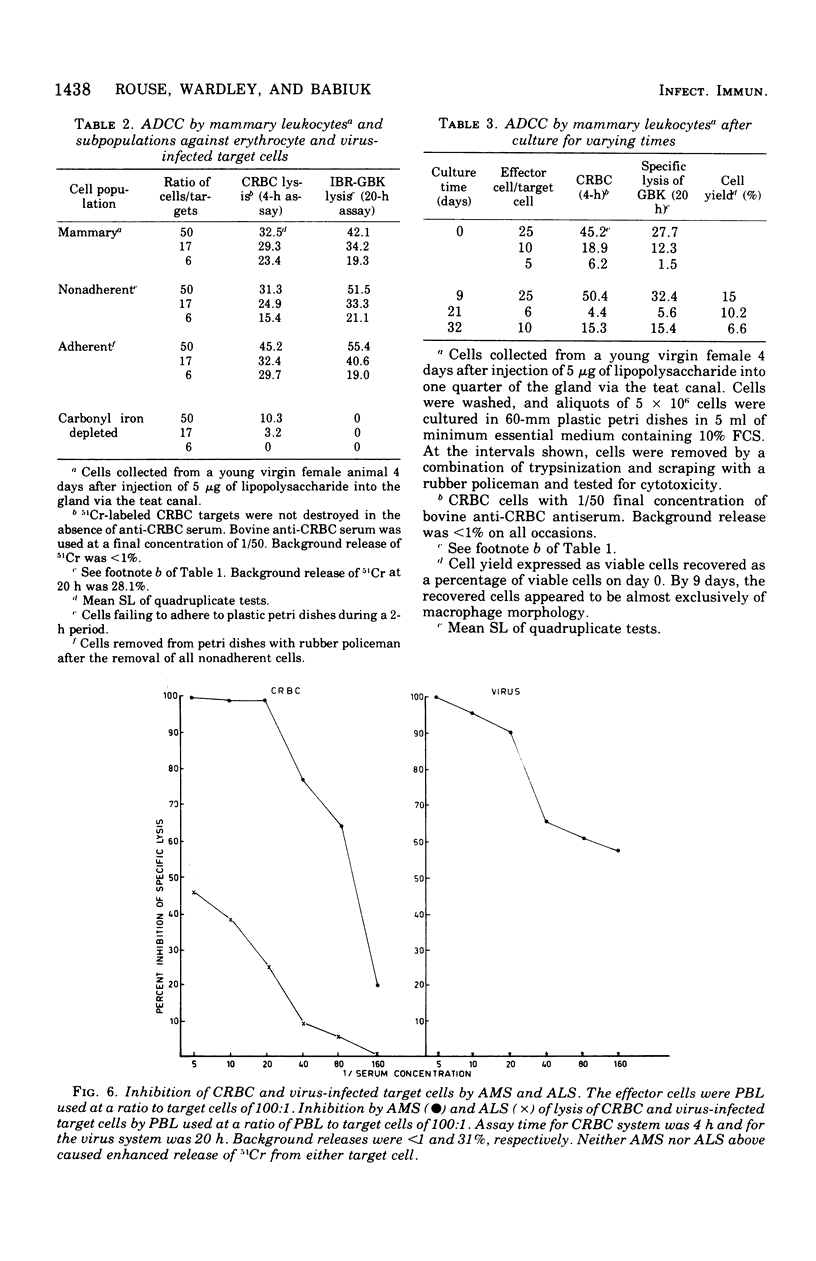
Bovine peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL) and cells collected from the bovine mammary gland were assayed for antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against chicken erythrocyte (CRBC) and bovine herpesvirus-infected bovine kidney cell targets. Bovine antisera were used to sensitize target cells. Both PBL and mammary leukocytes expressed ADCC, with the latter cell population having greater activity against both target cells. Only the CRBC target cells were killed by nonadherent PBL and phagocyte-depleted PBL. Nonadherent mammary leukocytes, rich in monocytes and macrophages, did kill virus-infected target cells. Carbonyl iron-treated mammary leukocytes failed to kill virus-infected targets but could destroy CRBC targets. Antimacrophage serum inhibited lysis of both CRBC and virus-infected targets, but antilymphocyte serum only inhibited CRBC killing. These observations indicated that at least two kinds of cells could mediate ADCC against CRBC but only cells of the mononuclear phagocytic series could kill virus-infected target cells. The herpesvirus-infected target cells became susceptible to ADCC 9 h after virus infection. A case is made for investigating the phenomenon of ADCC using in vitro systems that closely mimic the in vivo situation. The possible role of the ADCC mechanism as instrumental in causing recovery from herpesvirus infections is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiuk L. A., Wardley R. C., Rouse B. T. Defense mechanisms against bovine herpesvirus: relationship of virus-host cell events to susceptibility to antibody-complement cell lysis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):958–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.958-963.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Sturrock R. F., Houba V., Mahmoud A. A., Sher A., Rees P. H. Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):727–729. doi: 10.1038/256727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calder E. A., Penhale W. J., McLeman D., Barnes E. W., Irvine W. J. Lymphocyte-dependent antibody-mediated cytotoxicity in Hashimoto thyroiditis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jun;14(2):153–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian R. T., Ludovici P. P., Jeter W. S. Cell-to-cell transmission of herpes simplex virus in primary human amnion cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):1109–1115. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G., Lennox E. S. Phagocytic cells as effectors in a cell-mediated immunity system. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1844–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. P., Zighelboim J. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1047–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Resch K., Prester M. Antibody-mediated target cell lysis by non-immune cells. Characterization of the antibody and effector cell populations. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Oct;2(5):419–424. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Hudson L., Shen L., Roitt I. M. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity due to a "null" lymphoid cell. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):111–113. doi: 10.1038/newbio242111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Shen L., Walker L., Arnaiz-Villena A., Roitt I. M. Characteristics of the effector cells mediating cytotoxicity against antibody-coated target cells. II. The mouse nonadherent K cell. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;5(7):474–480. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Warner G. A. Increase of lymphocyte-mediated tumor-cell destruction by certain patient sera. Int J Cancer. 1973 Sep 15;12(2):348–353. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Hammarström S. Haemolytic activity of human blood monocytes. Lysis of human erythrocytes treated with anti-A serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1973 Jan;13(1):29–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G. Lysis of antibody-treated human erythrocytes by human leukocytes and macrophages in tissue culture. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(5):671–682. doi: 10.1159/000230883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson A., Perlmann P. Study of Fab and F(ab') 2 from rabbit IgG for capacity to induce lymphocyte-mediated target cell destruction in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;43(1):80–88. doi: 10.1159/000230823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J. J., Rosenberg J. C. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in prospective kidney transplant recipients. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):890–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Bonnard G. D. A comparison of the effector cells involved in cell-mediated lympholysis and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in man. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(2):129–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. G., Dunkley M. Quantitative analysis of the 51Cr release cytotoxicity assay for cytotoxic lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1974 Nov;14(2):284–302. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90212-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G., Svehag S. E. Specificiy of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity induced by in vitro antibody-coated target cells. Cell Immunol. 1972 May;4(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H. Contactual lysis of antibody-coated chicken erythrocytes by purified lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Sep;1(3):300–315. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Perlmann H., Wigzell H. Lymphocyte mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Induction and inhibition by humoral antibody and nature of effector cells. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:91–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S., Heppner G., Brawn R. J., Nelson K. Specific killing of tumor cells in vitro in the presence of normal lymphoid cells and sera from hosts immune to the tumor antigens. Int J Cancer. 1972 Mar 15;9(2):316–323. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910090209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rager-Zisman B., Allison A. C. The role of antibody and host cells in the resistance of mice against infection by coxsackie B-3 virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;19(3):329–338. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-19-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host defense mechanisms against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. II. Inhibition of viral plaque formation by immune peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host defense mechanisms against infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus: in vitro stimulation of sensitized lymphocytes by virus antigen. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):681–687. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.681-687.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A. Host responses to infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. III. Isolation and immunologic activities of bovine T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1391–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Clark I. A., Taylor G. A. Different effector cell types in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):376–377. doi: 10.1038/253376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik J. C. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. II. Early interactions between effector and target cells. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1519–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurzak H. M., Klein E., Yoshida T. O., Lamon E. W. Synergistic or antgonistic effect of different antibody concentrations on in vitro lymphocyte cytotoxicity in the Moloney sarcoma virus system. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):997–1002. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASAKI P. I., MCCLELLAND J. D. MICRODROPLET ASSAY OF HUMAN SERUM CYTOTOXINS. Nature. 1964 Dec 5;204:998–1000. doi: 10.1038/204998b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Bauman P., De Marchi M., Tökés Z. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in humans. I. Characterization of the effector cell. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., De Marchi M. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in humans. II. Energy requirement. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zighelboim J., Bonavida B., Fahey J. L. Evidence for several cell populations active in antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1737–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


