Abstract
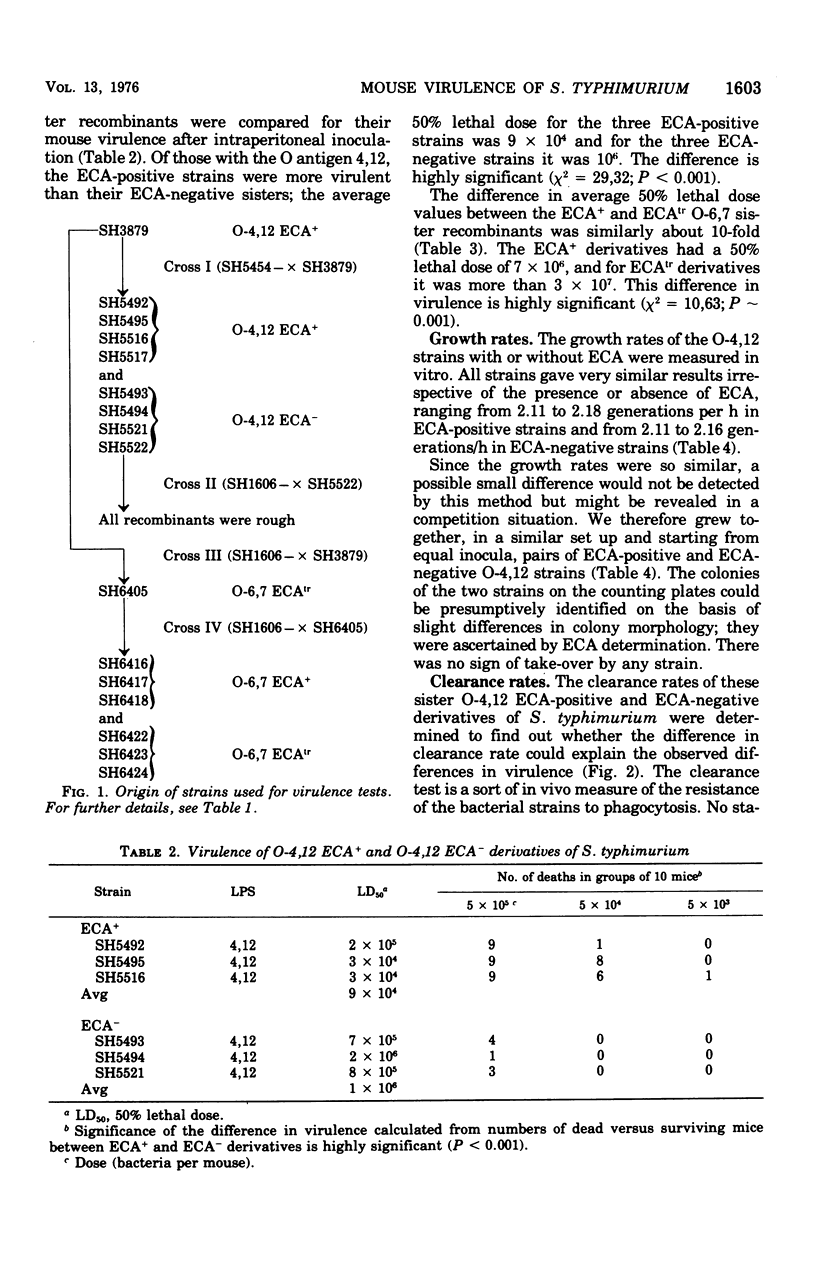
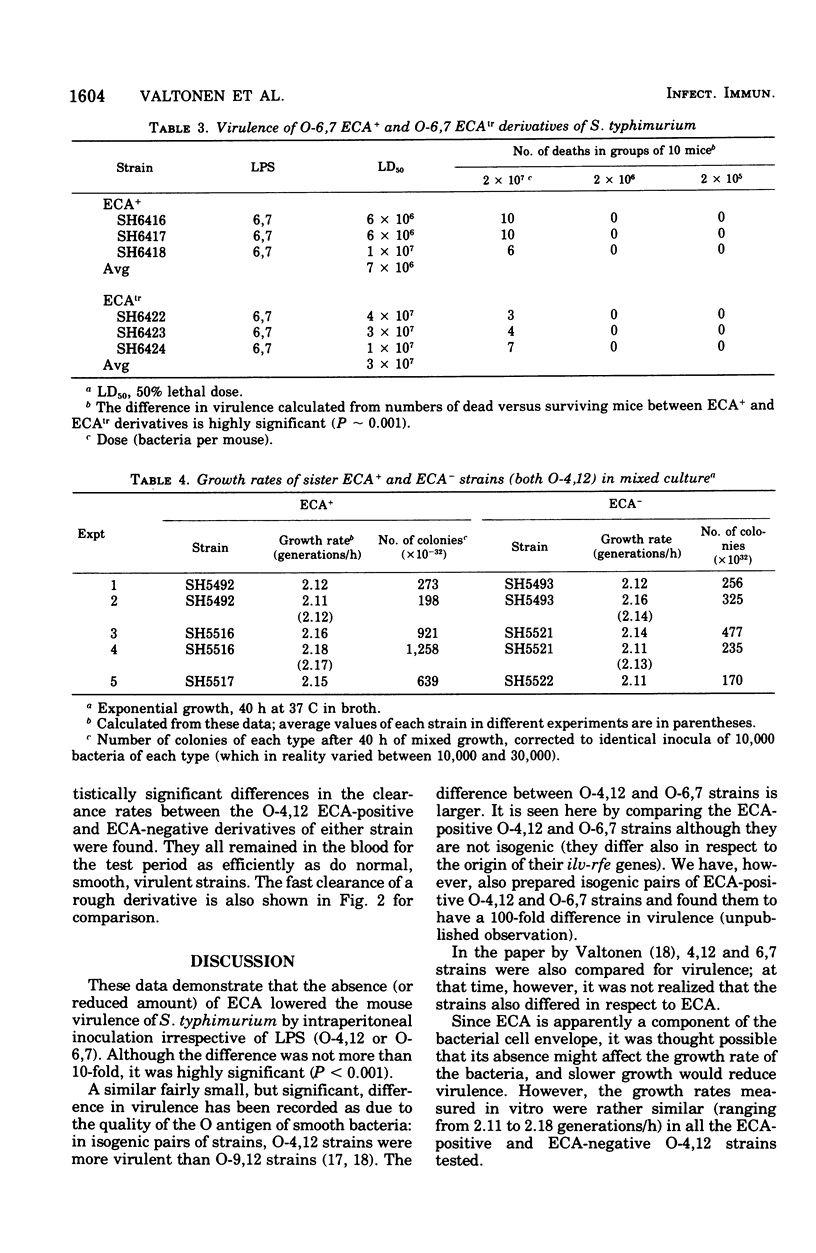
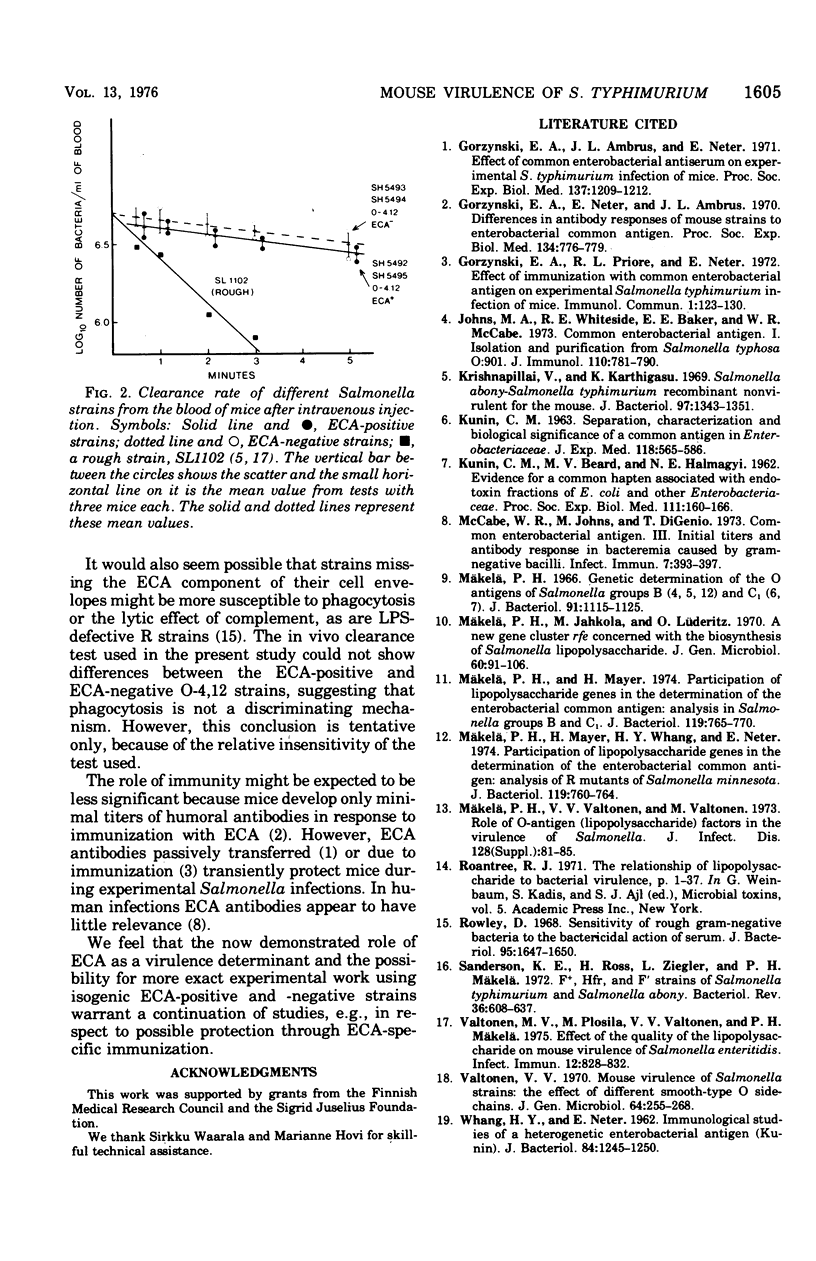
A series of nearly isogenic O4-12, and O-6,7 Salmonella typhimurium strains differing in regard to the enterobacterial common antigen (ECA) were constructed by conjugation. When tested in intraperitoneal infection of mice, the O-4,12 strains containing ECA were more virulent than their O-4,12 sister recombinants without ECA (P = less than 0.001). The same difference could be shown with ECA-positive and ECA-negative S. typhimurium derivatives, whose O antigens were of the group C type (O-6,7). The ECA-positive and ECA-negative O-4,12 strains did not differ in their growth rates in broth or clearance rates in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gorzynski E. A., Ambrus J. L., Neter E. Effect of common enterobacterial antiserum on experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection of mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1209–1212. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorzynski E. A., Neter E., Ambrus J. L. Differences in antibody responses of mouse strains to enterobacterial common antigen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jul;134(3):776–779. doi: 10.3181/00379727-134-34881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorzynski E. A., Priore R. L., Neter E. Effect of immunization with common enterobacterial antigen on experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection of mice. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(2):123–130. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Whiteside R. E., Baker E. E., McCabe W. R. Common enterobacterial antigen. I. Isolation and purification from Salmonella typhose 0:901. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):781–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. SEPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION, AND BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF A COMMON ANTIGEN IN ENTEROBACTERIACEAE. J Exp Med. 1963 Oct 1;118:565–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V., Karthigasu K. Salmonella abony-Salmonella typhimurium recombinant nonvirulent for the mouse. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1343–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1343-1351.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Johns M., DiGenio T. Common enterobacterial antigen. 3. Initial titers and antibody response in bacteremia caused by gram-negative bacilli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):393–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.393-397.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H. Genetic determination of the O antigens of Salmonella groups B (4,5,12) and C1(6,7). J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1115–1125. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1115-1125.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Jahkola M., Lüderitz O. A new gene cluster rfe concerned with the biosynthesis of Salmonella lipopolysaccharide. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jan;60(1):91–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Mayer H., Whang H. Y., Neter E. Participation of lipopolysaccharide genes in the determination of the enterobacterial common antigen: analysis of R mutants of Salmonella minnesota. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.760-764.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H. Participation of lipopolysaccharide genes in the determination of the entobacterial common antigen: analysis in Salmonella groups B and C1. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):765–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.765-770.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä P. H., Valtonen V. V., Valtonen M. Role of O-antigen (lipopolysaccharide) factors in the virulence of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):81–85. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Sensitivity of rough gram-negative bacteria to the bactericidal action of serum. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1647–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1647-1650.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Ross H., Ziegler L., Mäkelä P. H. F + , Hfr, and F' strains of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella abony. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):608–637. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.608-637.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen M. V., Plosila M., Valtonen V. V., Mäkelä P. H. Effect of the quality of the lipopolysaccharide on mouse virulence of Salmonella enteritidis. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):828–832. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.828-832.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen V. V. Mouse virulence of Salmonella strains: the effect of different smooth-type O side-chains. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(3):255–268. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-3-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHANG H. Y., NETER E. Immunological studies of a heterogenetic enterobacterial antigen (Kunin). J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1245–1250. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1245-1250.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


