Abstract
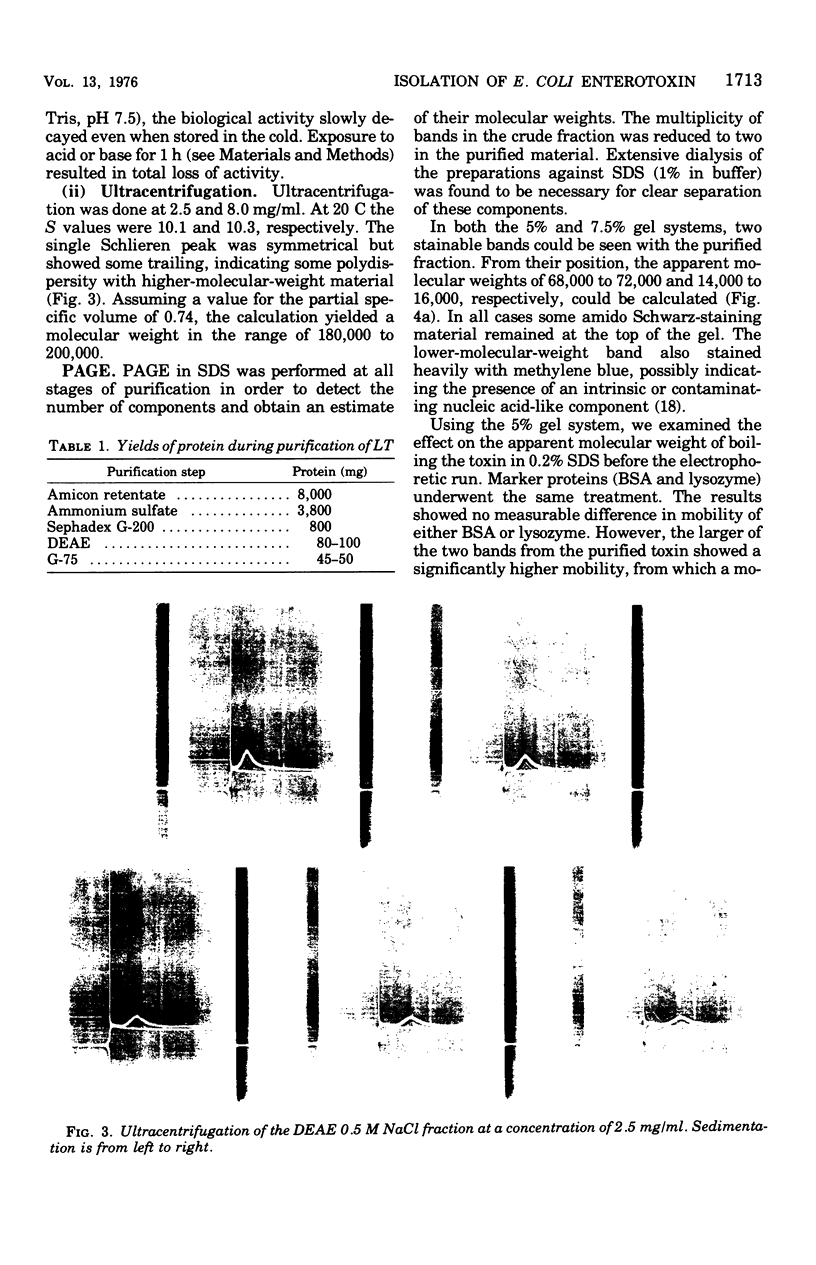
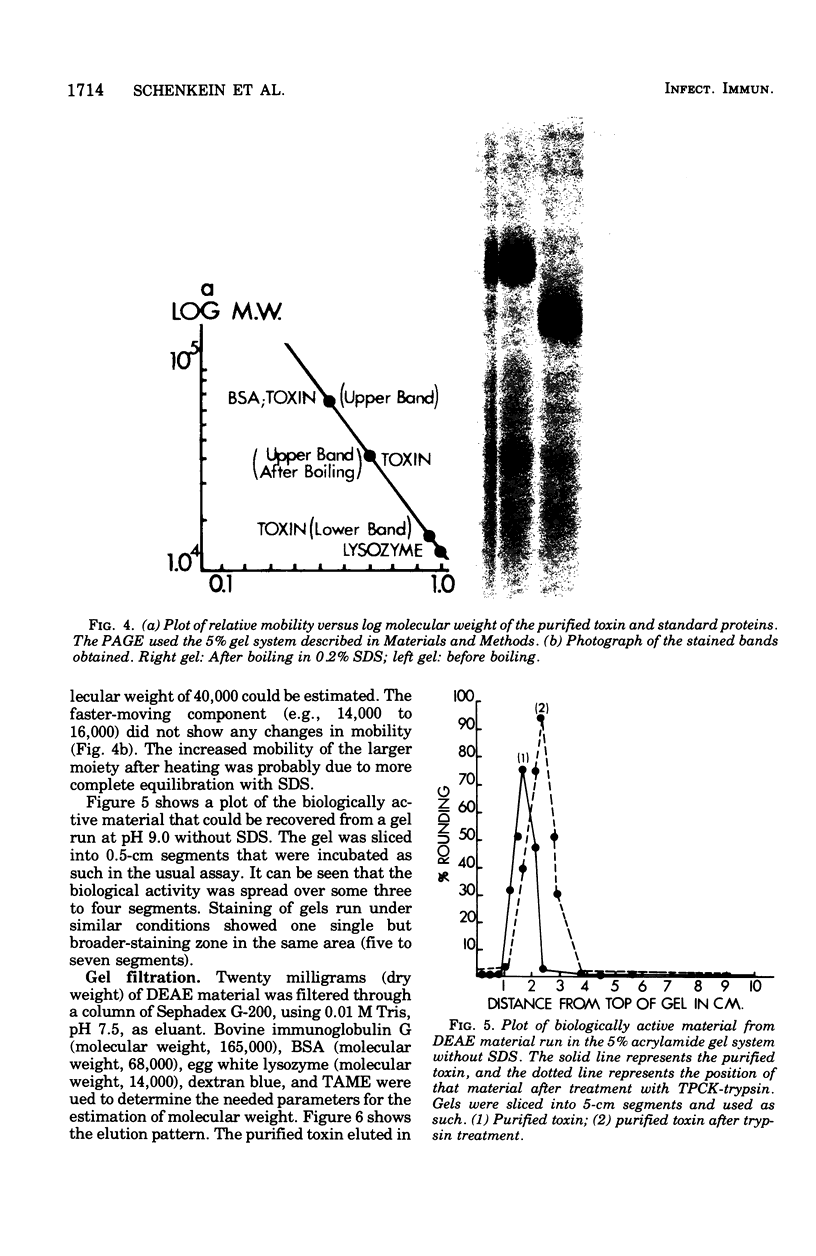
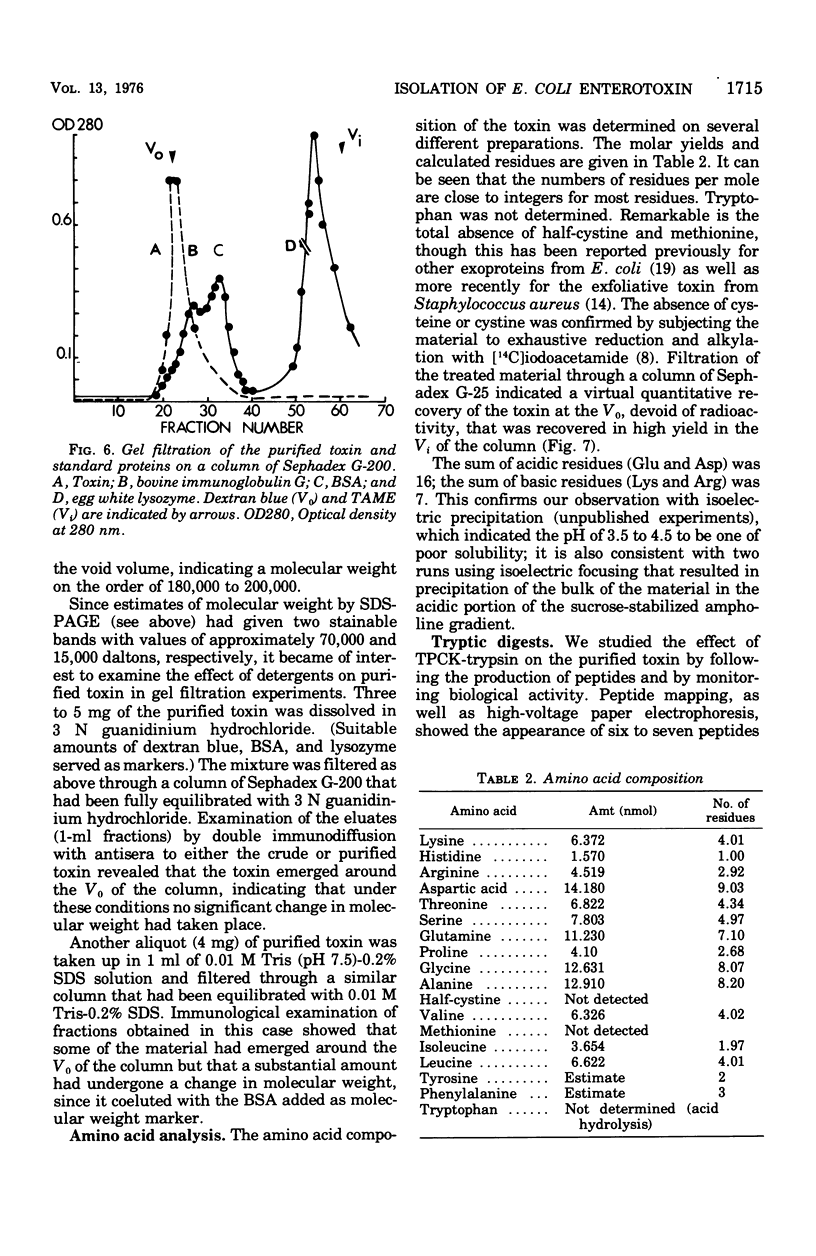
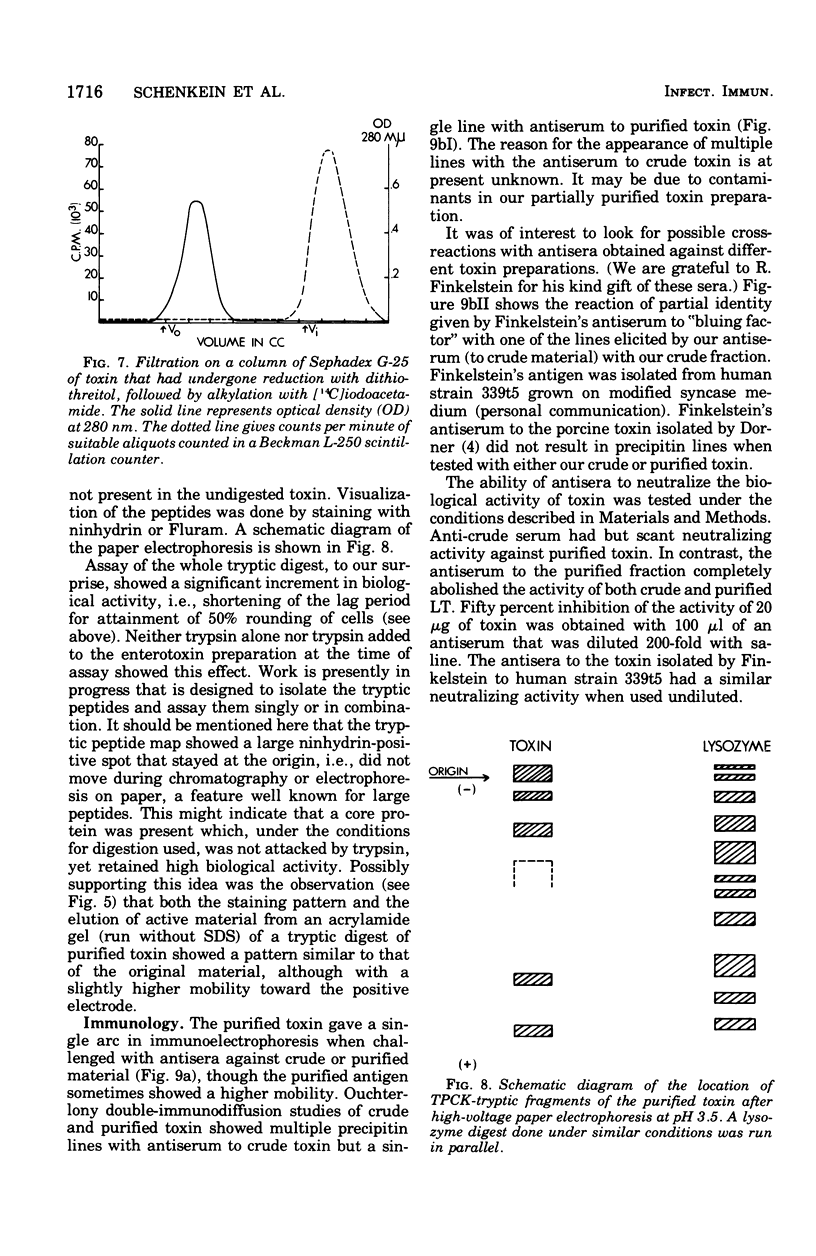
A partially purified enterotoxin was obtained from the growth medium of Escherichia coli strain 711 (P307), a derivative of E. coli K-12, by ultrafiltration, precipitation with ammonium sulfate, molecular sieving, and anion exchange column chromatography. The active moiety, which is heat-labile, behaved like a protein particle of 180,000 to 200,000 daltons during molecular sieving and ultracentrifugation. During polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS-PAGE), it dissociated into two subunits with apparent molecular weights of 68,000 to 70,000 and 14,000 to 15,000. SDS-PAGE after heating in SDS changed the larger subunit to an apparent molecular weight of about 40,000; the smaller subunit did not change. The intact particle induced rounding of the cells in Y-1 mouse adrenal tumor cells used for assay. The detergent-dissociated molecules were not active. Proteolysis of the purified toxin by tolylsulfonyl phenylalanyl chloromethyl ketone-trypsin appeared to enhance its activity. The addition of serum to the assay medium resulted in partial depression of the activity. Activity was also abolished by preincubation of the toxin with either a rabbit antiserum to it or solutions containing GM1 ganglioside. The length of time needed to evoke a response in the assay system by fractions from different stages in the purification of the enterotoxin was a useful parameter in the evaluation of specific activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahlberg A. E., Dingman C. W., Peacock A. C. Electrophoretic characterization of bacterial polyribosomes in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):139–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Smith D. M. Stimulation of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and its neutralization by specific antiserum. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.500-505.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner F. Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8712–8719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Gorbach S. L. Production of vascular permeability factor by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from man. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):725–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.725-730.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PAIN R. H., PORTER R. R. Reduction of gamma-globulins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C., So M., Falkow S. The enterotoxin plasmids of Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):40–49. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Fixation and inactivation of cholera toxin by GM1 ganglioside. Scand J Infect Dis. 1973;5(1):77–78. doi: 10.3109/inf.1973.5.issue-1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J., Braemer A. C., Bidlack D. E. Properties of the enterotoxic component in Escherichia coli enteropathogenic for swine. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):178–189. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.178-189.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Metzger J. F., Spero L. Production, purification, and chemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1206–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1206-1210.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan C. N., Wishnow R. M. Escherichia coli enterotoxin-induced steroidogenesis in cultured adrenal tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):146–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.146-151.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lariviére S., Gyles C. L., Barnum D. A. Preliminary characterization of the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli F11(P155). J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):312–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos D. S., Palchaudhuri S., Maas W. K. Genetic and physical characteristics of an enterotoxin plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1240-1247.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The effect of cell-free fluids prepared from cultures of human and animal enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli on ligated intestinal segments of rabbits and pigs. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):403–409. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Gyles C. L. The relationship between two apparently different enterotoxins produced by enteropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli of porcine origin. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Aug;3(3):387–401. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlind O., Möllby R., Wadström T. Purification and some properties of a heat-labile enterotoxin from escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1974;229(2):190–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E., Carpenter C. C., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Deactivation of cholera toxin by ganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):415–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]