Abstract
Germ-line genetic control of gene expression occurs via expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs). We present a large, exon-specific eQTL data set covering ten human brain regions. We found that cis-eQTL signals (within 1 Mb of their target gene) were numerous, and many acted heterogeneously among regions and exons. Co-regulation analysis of shared eQTL signals produced well-defined modules of region-specific co-regulated genes, in contrast to standard coexpression analysis of the same samples. We report cis-eQTL signals for 23.1% of catalogued genome-wide association study hits for adult-onset neurological disorders. The data set is publicly available via public data repositories and via http://www.braineac.org/. Our study increases our understanding of the regulation of gene expression in the human brain and will be of value to others pursuing functional follow-up of disease-associated variants.
Neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders are among the most complex and poorly understood conditions affecting the human body. In recent years there has been a major research effort to improve our understanding of these disorders. First, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been used with great success to identify genetic variants that affect the likelihood of suffering from a wide range of neurological and psychiatric conditions, including Parkinson’s disease1, Alzheimer’s disease2 and schizophrenia3 (reviewed in ref. 4). Many of these recently identified loci have not previously been implicated in any neurologic or psychiatric disease and therefore should generate insights into disease pathways. Second, genome-wide transcriptome analysis has been used to obtain insights into the human CNS during normal development, in adult life and in the presence of disease. Much of the information obtained from both approaches has been via microarray-based technologies (genotyping panels for GWAS and array-based expression panels for transcriptomics), but high-volume sequencing technologies have recently been introduced to both arenas. Together these research strands allow researchers to use an unbiased approach to identify and then study genes or even transcripts of interest in disease.
eQTL analysis interrogates genome-wide gene expression measurements in a given tissue along with genotyping information to find genetic variation associating with changes in gene expression. The most immediate application of eQTL analysis lies in the interpretation of GWAS risk loci. Because most GWAS signals do not appear to act via protein coding changes5, their functional effects are likely to be mediated via regulation of gene expression. One obvious use of eQTL data is to identify the likely causal gene of interest in an associated region in which several genes may lie. Given that some eQTLs appear to be tissue specific and many disease phenotypes manifest themselves only in certain tissues, this approach has been most successful when eQTL analyses have been performed in the disease-relevant tissue. Examples include eQTLs from adipose tissue that have shed light on obesity-related risk loci6 and eQTLs from lymphoblastoid cell lines that have helped explain genetic risk loci for immunity-related diseases7.
The generation of large eQTL data sets in human brain can also provide insights into the regulatory architecture underlying gene expression in human brain and thus shed light on the well-recognized differences in disease susceptibility among brain regions. For example, selective loss of dopaminergic neurons from the substantia nigra is characteristic of Parkinson’s disease8, while the selective loss of CA1 neurons of the hippocampus is characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease9. Additionally, it is now well recognized that alternative splicing is both extremely common in human brain, with present estimates suggesting that 92–94% of multi-exon genes are alternatively spliced10, and also of functional significance11,12.
To address these issues, the UK Brain Expression Consortium (UKBEC) has generated genotype and exon-specific expression data for several human brain regions from 134 neuropathologically confirmed control individuals of European descent. In comparison to previous eQTL studies in the human brain13-22, our study is distinguished either by larger samples sizes, by more brain regions sampled from the same individual or by greater detail in characterizing exon-level rather than gene-level expression patterns. This has resulted in the generation of a single, comprehensive data set that provides the opportunity to look robustly at the regional specificity of gene regulation across the human brain. We have taken advantage of large whole-genome and whole-exome sequencing repositories to apply stringent quality control procedures to our data and reduce false positive results that may arise from polymorphisms lying in probe regions23. We have used the resulting high-quality eQTL data set to provide insights into the specificity of gene regulation in the human brain with a particular focus on the interpretation of GWAS signals. Our data set is available online as a resource for the exploration of the regulatory significance of genetic variants in the human brain (http://www.braineac.org/).
RESULTS
eQTL discovery
We assayed DNA and RNA from 134 post-mortem brains from individuals of European descent free of known neurological disorders. In all samples control status was confirmed by the lack of any significant pathology as judged by a senior neuropathologist. Exon-specific RNA expression was quantified using Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST arrays in 10 brain regions: cerebellar cortex, frontal cortex, hippocampus, inferior olivary nucleus (sub-dissected from the medulla), occipital cortex, putamen (at the level of the anterior commissure), substantia nigra, temporal cortex, thalamus (at the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus) and intralobular white matter. DNA was genotyped using Illumina Omni1-quad and Immunochip arrays followed by imputation using the 1000 Genomes Project (March 2012 release) as reference. The quality control of the RNA preparation from this brain series and the reliability of the quantification of expression have been previously documented24. Further details on the data set generation, quality control and analysis are provided in the Online Methods and by Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Figure 1.
We searched for eQTL associations of ~5.88 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and ~577 thousand indels (collectively referred to as markers) with 291,705 exon-level and 26,493 gene-level expression profiles (collectively referred to as expression IDs) in each brain region, plus the average across all available regions (referred to as average-all). Using a false discovery rate (FDR) of 1% and defining sentinels as the most associated marker in a set of markers in high linkage disequilibrium (r2 > 0.8), we found 30,333 cis-eQTL and 59,470 trans-eQTL signals (defined as significant sentinel marker–transcript ID pairs). The cis-eQTL signals comprised 90,885 sentinelized subsignals (sentinel marker–expression ID–tissue combinations; Supplementary Table 2) or 2.2 million unsentinelized subsignals. cis-eQTL signals implicated 27,258 sentinel markers (17,814 SNPs plus 9,444 indels) and 21,617 expression IDs corresponding to 8,573 transcript IDs.
eQTL discovery was aided by elements of our study design. Between 60 and 70% of our cis-eQTL signals were found only from exon-specific expression, 55% were found only by averaging expression across regions and 13% only by including indels from 1000 Genomes data imputation.
Replication of cis-eQTL signals in three independent data sets
To assess the reliability of our proposed eQTL signals, we sought replication in three independent published data sets (Supplementary Table 3 and Online Methods). Heinzen et al.14 featured the same expression array but a small sample size (n = 84) from a single brain region (frontal cortex). The North American Brain Expression Consortium (NABEC)16,20 featured a different expression array but a larger sample size (n = 304) for two brain regions (cerebellum and frontal cortex) from each individual. Zeller et al.25 featured a different array and a single non-brain cell type (monocytes) but a very large sample size (n = 1,490), and therefore this data set might replicate ubiquitous eQTL signals found across human tissues.
cis-eQTL replication rates in all data sets were considerably greater than the applied type 1 error rates (Supplementary Table 3), despite the reduced power to replicate implied either by the reduced sample size (Heinzen et al.14) or the different expression array (NABEC and Zeller et al.25) or different tissue (Zeller et al.25). Region-specific replication patterns were also compelling (see below). We found these replication rates to compare favorably to other published replication rates for eQTL data sets26,27. For example, the published replication rate for two cis-eQTL data sets using the same array platform on a shared single cell type (monocytes) was 63.8% (refs. 25,26). In our data set, the replication rate using the same array platform in the same brain region was 48.8%, despite the challenges arising from the use of post-mortem tissue containing a mixture of cell types. We note that this does not mean that the remaining 51.2% are all false positives. The false positive rate in the set of non-overlapping cis-eQTL signals depends on various unknown factors, which include the power to detect cis-eQTL signals of different strengths in both our data set and the comparison data set and, crucially, the proportion of eQTL signals in the human brain that remain undiscovered. If the latter proportion is large and the power of current studies is low, then two studies of equal power can both discover largely non-overlapping sets of true eQTL signals. This scenario is supported by the recent demonstration of large numbers of protein QTLs of small effect in yeast28.
cis-eQTL replication rates were similar between exon-specific and gene-level signals but were reduced for signals where the marker was further away from its target gene (Supplementary Table 3), a phenomenon we attribute to the larger number of tests that belong to this group. Therefore, to increase confidence in our analyses of eQTL location, we considered only those signals that replicated in one of our replication data sets.
For trans-eQTL signals, we achieved low replication rates. The best result was for the Heinzen et al.14 data set, where 11.2% of trans-eQTL signals were replicated at a 5% type 1 error rate. Thus, while we did find evidence for the existence of true trans-eQTLs, we conclude that many of our trans-eQTL signals are likely to be false positives and therefore focus our attention here on our cis-eQTL signals. We expect that reliable trans-eQTL analysis will require the accrual of larger data sets.
cis-eQTL signals cluster in biologically meaningful ways
The large number of cis-eQTL signals identified in this study (90,885 unique sentinel marker–expression ID–tissue combinations), across ten brain regions, allowed us to explore the organization of cis-eQTLs in the human brain. We note that a gene that is ubiquitously expressed in human brain may still display region-specific patterns if, as recent studies illustrate26, cis-eQTLs act in a context-specific manner. We used unsupervised hierarchical clustering (Pearson’s linear dissimilarity measure applied to absolute z scores of all cis-eQTL signals across all ten brain regions) to group cis-eQTL signals and brain regions into clusters of interest (Fig. 1a). Consistent with expectation, this approach identified shared cis-regulation among cortical brain regions, and in particular between frontal and temporal cortex. This approach also identified a striking number of distinctively region-specific cis-eQTL clusters. Notably, this clustering pattern was not apparent from the results of unsupervised hierarchical clustering of equivalent gene expression data (all expression IDs targeted by cis-eQTL signals; Fig. 1b). This suggests a more nuanced relationship between gene regulation and expression, which allows a gene to be the target of different cis-eQTLs in different brain regions and yet have similar expression levels across brain regions (Supplementary Fig. 2). Thus, co-regulated cis-eQTL modules provide separate biological insights into the underlying regulatory architecture in human brain as compared to those from expression data alone.
Figure 1. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of cis-eQTL signals and related expression data.
(a) Heat plot and dendrograms based on unsupervised hierarchical clustering of absolute z scores of all cis-eQTL signals across all ten brain regions. (b) Heat plot and unsupervised hierarchical clustering of mean expression in a brain region for the equivalent expression data (expression IDs targeted by all cis-eQTL signals identified). Column dendrograms for the two panels were very similar, so b has been ordered according to the column dendrogram in a. The row dendrogram in b was indistinct, so it has not been colored by clade. SNIG, substantia nigra; PUTM, putamen (at the level of the anterior commissure); MEDU, the inferior olivary nucleus (sub-dissected from the medulla); THAL, thalamus (at the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus); OCTX, occipital cortex; HIPP, hippocampus; FCTX, frontal cortex; TCTX, temporal cortex; WHMT, intralobular white matter; CRBL, cerebellar cortex.
To investigate the biological function of these co-regulated modules, we looked for enrichment of gene ontology terms and involvement in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways among the genes in cis-eQTL clusters. Among the 10 major cis-eQTL clusters identified, we found evidence for significant enrichment of 60 gene ontology terms or KEGG pathways in 6 clusters (Supplementary Table 4). We found significant enrichment of cation-binding genes (gene ontology GO:0043169, cation binding; Benjamini-corrected modified Fisher’s exact P = 1.1 × 10−5) among genes targeted by the cerebellum-specific cis-eQTL cluster. This finding is in keeping with existing data suggesting that calcium homeostasis and, in particular, ITPR1-dependent signaling are central to Purkinje cell function and that disruption of this signaling system results in ataxia29. We identified six genes in this cluster that when disrupted are known to give rise to ataxia, including ITPR1 itself and CACNA1A. Thus, the cerebellum-specific regulation of these genes may provide an explanation for why, despite being ubiquitously expressed in human brain, mutations in these genes give rise to cerebellar ataxia. We also identified a significant enrichment of genes implicated in lysosome function (hsa04142, lysosome; Benjamini-corrected P = 0.019 in a cis-eQTL cluster specific to frontal and temporal cortex. Given that lysosome function is increasingly being implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and fronto-temporal dementia30, this finding may provide some insight into why other brain regions, and in particular the occipital cortex (a highly related structure), are relatively protected in these diseases.
Regionally heterogeneous cis-eQTL signals
Supplementing the results of hierarchical clustering, we found evidence for both region-specific and pan-regional cis-eQTL signals. In favor of the latter, the majority (55%) of our signals were found only by averaging expression values across all ten brain regions, indicating that there was sufficient sharing of weak eQTL signals among regions to benefit from an increase in signal-to-noise ratio through averaging. Almost all regional cis-eQTL signals seen in more than one brain region were also identified from the average-all analysis (Fig. 2a). Figure 3a gives one example of a pan-regional signal.
Figure 2. Regional characterization of cis-eQTL signals.
(a) cis-eQTL signals identified in multiple brain regions, and the proportion of these also identified using average-all (aveALL). (b) cis-eQTL signals classified by brain region. See Figure 1 legend for brain region codes.
Figure 3. Regional characterization examples.
(a) Example of a pan-regional cis-eQTL signal. ATP5G2 transcript 3456313 was highly expressed in all brain regions (left) and rs12818213 was a consistent eQTL signal (right). (b) Example of a region-specific cis-eQTL signal. PPAPDC1A transcript 3267563 was highly expressed in all brain regions, including cerebellum (left), but rs10788102 was an eQTL signal in cerebellum only (right). (c) Second example of a region-specific cis-eQTL signal. ADAMTS18 transcript 3700158 was highly expressed in all brain regions, especially cerebellum (left), but rs4888622 was seen as an eQTL signal in all regions except cerebellum (right). See Figure 1 legend for brain region codes.
We also found cis-eQTL signals that were only detected in a specific brain region, varying from 936 in substantia nigra to 4,642 in cerebellum (Fig. 2b). We note that some of these single-region cis-eQTL signals will result from the chance detection of a weak pan-regional signal in one region only. We therefore investigated the statistical evidence for regional heterogeneity using a modified test of heterogeneity (see Online Methods). This test was specifically used to distinguish between the absence of a cis-eQTL signal in a brain region and the failure of a cis-eQTL signal to reach statistical significance in the presence of expression. We found 42.6% of the 17,374 tested cis-eQTL subsignals to be heterogeneous (Supplementary Table 5). The regional heterogeneity of these eQTL signals could not be explained by absence of gene expression in some regions, as regions with no detectable expression above background were excluded from the test-of-heterogeneity analysis.
Further support for region-specific cis-eQTL signals was provided by a comparison of our signals with those from other region-specific data sets. We separated our cis-eQTL signals into those with more evidence for region-specific effects (found in the tissue specified and significantly heterogeneous across tissues in our data set) and those with more evidence for pan-regional effects (found in the tissue specified but not significantly heterogeneous across tissues) (Supplementary Table 3). For pan-regional signals, we found roughly equal replication rates in each comparison data set when comparing the cerebellum to the frontal cortex, although there was still a tendency for replication rates to be higher when comparing same-tissue data sets. For region-specific signals, the difference in replication rates became much more pronounced, with performance noticeably better in the same-tissue comparisons. Finally, using monocytes as an outside comparison that may pick up pan-tissue eQTL signals, we noted that replication rates were noticeably better in our tissue-common signals (32.9%) than our tissue-complex ones (23.2%).
We did not find any examples of cis-eQTL subsignals that significantly reversed slopes in different brain regions, a phenomenon that has been reported in pure cell types26, perhaps because our brain samples comprised mixtures of cell types. Statistically significant heterogeneity generally manifested itself as a significant slope in some regions and a lack of a slope in others. In some cases, as demonstrated by the example of rs10788102, a significantly heterogeneous cis-eQTL for PPADC1A (Fig. 3b), the eQTL signal was only evident in a single brain region (cerebellum). Conversely, significant regional heterogeneity in cis-eQTL signals could also arise by the detection of cis-eQTL signals in all but one brain region. One such example is rs48888622, a significantly heterogeneous cis-eQTL for ADAMTS18 (Fig. 3c). Although ADAMTS18 was most highly expressed in cerebellum, this was the only brain region where a cis-eQTL signal was not evident. This last example also illustrates that eQTL detection is not purely driven by differences in overall gene expression.
We identified significant differences in the location and gene targets of regionally heterogeneous and pan-regional cis-eQTL signals. We found that, while the distribution of regionally heterogeneous and pan-regional cis-eQTLs were both centered around the transcription start site, regionally heterogeneous cis-eQTLs were more dispersed, and this change in distribution was statistically significant (two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test P = 1.6 × 10−9). Notably, we also found that the gene targets of regionally heterogeneous cis-eQTL signals systematically differed from the gene targets of pan-regional cis-eQTL signals in biologically relevant ways. Using gene ontology enrichment analysis, genes regulated by regionally heterogeneous cis-eQTL signals were significantly enriched for terms related to synaptic transmission (GO:0007268, synaptic transmission; Bonferroni-corrected modified Fisher’s exact P = 0.018), while genes regulated by pan-regional cis-eQTL signals were related to more basic cellular functions, including Golgi apparatus and organelle lumen (GO:0005794, Golgi apparatus; Bonferroni-corrected modified Fisher’s exact P = 0.00130; GO:0070013, intracellular organelle lumen; Bonferroni-corrected modified Fisher’s exact P = 0.0182). These findings suggest that regionally heterogeneous control of gene regulation is predominantly directed at genes involved in specialized cellular functions, as within the human brain the most specialized of functions would be predicted to be synaptic transmission.
We found that regional heterogeneity in the action of cis-eQTL signals was evident not only from variable signal strength, but also from variability in their target of action. Excluding average-all signals, our data set contained 44,270 cis-eQTL subsignals (sentinel–expression ID–region combinations) involving 12,748 sentinels. 9,384 of these sentinels (73.6%) regulated a single gene in a single brain region only, while 2,762 (21.6%) regulated a single gene across multiple brain regions. Intriguingly, 602 of these sentinels cis-regulated multiple genes, with a maximum of 10 genes regulated by the same marker (Supplementary Table 6). 312 of these regulated different genes with at least one marker–gene relationship being unique to a single brain region, and 96 of these sentinels regulated multiple gene targets all of which were region specific (as based on the absence of a significant cis-eQTL signal in another brain region and on significant regional heterogeneity using our modified test of heterogeneity). One of the most interesting examples of such markers is rs73009150, which was a cis-eQTL signal for RNF214 in medulla, for PAFAH1B2 in cerebellum and putamen, and for SIK3 in putamen (Fig. 4a-c). We note that one explanation for these results could be the existence of multiple functional variants in linkage disequilibrium. Nevertheless, taken together with the regional heterogeneity of cis-eQTL signals, these findings highlight the potential dangers of extrapolating eQTL findings from one tissue type to another, even if they are highly related.
Figure 4. Region-specific gene switching example.
rs73009150 was a cis-eQTL signal with (a) RNF214 probe set 3350857 in medulla, (b) PAFAH1B2 probe set 3350766 in cerebellum and (c) IK3 probe set 3393006 in putamen. See Figure 1 legend for brain region codes.
The majority of cis-eQTL signals operate at the exon level
By assaying gene expression using the Affymetrix exon array platform, we were able to differentiate between cis-eQTL signals regulating all expressed exons in a gene from those regulating a subset of exons. Consistent with growing evidence for the widespread nature and functional importance of alternative splicing in the human brain, we found that most of our cis-eQTL signals were only apparent using exon-level data. Only 29.6–39.2% of our cis-eQTL signals were reflected in a significant gene-level signal, but almost all were represented by at least one exon-level signal (Supplementary Table 5). The majority of signals would therefore have not been identified without exon-level information. This finding is not explained by differing false positive rates among groups of cis-eQTL signals, as replication rates for gene-level and exon-level signals were similar (Supplementary Table 3).
We further investigated the extent to which cis-eQTL signals operate in an exon-specific manner using a modified test of heterogeneity that accounts for the dependency structure arising from within-individual and within-gene correlations. We found that 86.45% of testable cis-eQTL subsignals were significantly heterogeneous across exons (Supplementary Table 5). We accept that this figure may be inflated by probe-specific artifacts. To moderate this, we only tested for heterogeneity among exons with evidence of expression, and we also performed rigorous quality control to remove array probes that might be influenced by sequence variation (see Online Methods for details). We anticipate that RNA-seq data will provide a more accurate figure for between-exons signal heterogeneity.
rs4753547 exemplifies a non-heterogenous gene-level cis-eQTL signal characterized by a similar effect on expression across all exons within a gene (GPR83; Fig. 5a). Conversely, rs10986468 is a significantly heterogeneous cis-eQTL signal evident in only a subset of probe sets, in this case coinciding with one of the three known alternatively spliced variants for this gene (ARPC5L; Fig. 5b). These findings implicate alternative splicing as an important mechanism in the genetic control of gene expression.
Figure 5. Exon-level characterization of cis-eQTL signals.
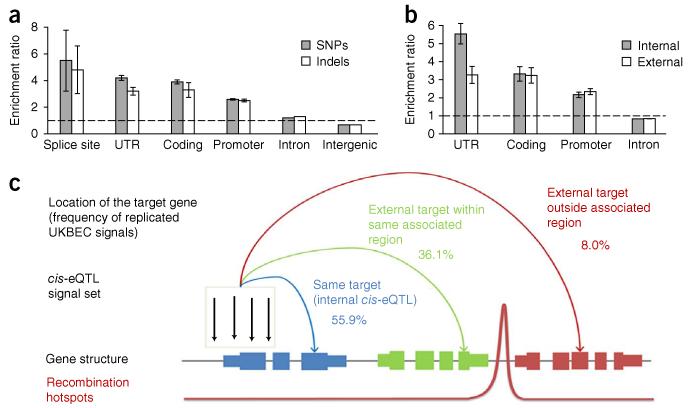
(a) Example of a consistent gene-level cis-eQTL signal. rs4753547 was a significant eQTL for all five probe sets in GPR83, which has two recognized alternatively spliced isoforms. (b) Example of a significantly heterogeneous exon-specific cis-eQTL signal. The cis-eQTL signal for rs10986468 was evident for three probe sets out of nine covering ARPC5L in cerebellum (CRBL). These probe sets mapped to three consecutive exons and were unique to one of the three recognized alternatively spliced isoforms from this gene, namely ARPC5L-002. (c) Distribution of gene-level and exon-level cis-eQTL signals by distance from the target transcription start site. (d) Enrichment of gene-level and exon-specific cis-eQTL signals, stratified by their location with respect to their gene of action. Error bars represent s.e.m.
We speculated that the locations of exon-specific and gene-level cis-eQTL signals may differ as a result of the different regulatory mechanisms that may be involved. We found that gene-level cis-eQTL signals were symmetrically distributed around the transcription start site, while exon-specific signals tended to be located within the gene itself, as indicated by a positive shift in the marker distribution (Fig. 5c; two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov P = 1.6 × 10−10). However, we did not find any significant differences in the genic location of variants involved in gene-level cis-eQTL signals as compared to exon-specific cis-eQTL signals (Fig. 5d).
Functional characterization of cis-eQTL signals
We investigated the enrichment of cis-eQTL signals with respect to sentinel marker type and genic location. Sentinels do not necessarily represent true causal variants, and this introduces noise into our analyses. However, to the extent that we do find some significant relationships, these can only arise from there being some overlap of true causal variants with sentinels. Furthermore, we imputed to the 1000 Genomes data set before performing eQTL analyses, which increases the likelihood of overlap between sentinels and true causal variants.
We found significant enrichment of sentinels in exons and promoters, but not introns and non-promoter intergenic regions (Fig. 6a). There were no significant differences in the location of gene-level as compared to exon-level cis-eQTL signals. We observed the highest enrichment in splice sites and note that this may be a consequence of the ability of our exon-specific array to pick up splicing-level eQTL signals. There was no evidence that the locations were distributed differently between SNPs and indels (data not shown).
Figure 6. Functional characterization by location of sentinel in relation to its target gene.
Data were restricted to cis-eQTL signals that showed evidence of replication in independent data sets (Supplementary Table 3). (a) Enrichment of cis-eQTL signals relative to all markers in the data set, stratified by their location with respect to their gene of action. (b) Enrichment of cis-eQTL signals located within their target gene (internal) or within a different gene (external), stratified by their location within the gene. (c) The relationship of cis-eQTL signal locations to their target genes.
We were particularly motivated to investigate the relationship of sentinel location to their target gene. This is because follow-up of GWAS hits typically proceeds by defining an associated region that spans the hit and is bounded by recombination hotspots on either side. All genes in this region are then explored for potential causality. We note that recombination hotspots vary in their strength, and this further adds to the arbitrary nature of this procedure. Furthermore, there is no biological reason for linkage disequilibrium patterns to have a direct bearing on the location of external regulators of transcription. To explore the validity of GWAS follow-up via associated intervals, we classified our cis-eQTL signals according to whether the sentinel marker resided inside (internal eQTL signal) or outside its target gene (external eQTL signal). External cis-eQTL signals were further classified according to whether the transcript being regulated was inside or outside the hotspot-bounded associated region of the marker. To account for uncertainty in the location of the true causal variant due to linkage disequilibrium, we redefined cis-eQTL signals according to the location of all markers in high linkage disequilibrium (r2 > 0.8) with the sentinel marker (Fig. 6c and Supplementary Table 3). Even when we restricted our attention to signals that replicated in one of our three replication data sets, we found that 44.1% of cis-eQTL signals lay entirely outside their target gene, and 88.0% lay entirely outside the associated region of the target gene. These findings point to one possible explanation for why functional characterization of some GWAS hits has been difficult.
We examined the enrichment of internal cis-eQTL signals within genic regions (promoter, coding, intronic or untranslated regions (UTRs)) relative to external cis-eQTL signals that were also annotated to a gene (though by definition not the gene they regulate). We found a relative increase in the frequency of internal cis-eQTL signals mapping to promoter or coding regions but, most prominently, UTRs (P = 0.0026; Fig. 6b). This pattern suggests that internal cis-eQTL signals may act more by changing the rate of mRNA degradation than by changing the rate of transcription per se. To investigate this further, we looked at whether the gene targets of internal cis-eQTL signals were enriched for specific sequence features that are already known to influence mRNA decay, such as AU-rich elements and microRNA binding site densities. We found a significant enrichment of genes containing AU-rich elements (as defined by the AREsite database31, http://rna.tbi.univie.ac.at/cgi-bin/AREsite.cgi) among the gene targets of internal cis-eQTL signals (Fisher’s exact P = 7.46 × 10−10) but no significant difference in miRNA binding site densities (two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov P = 0.072). Therefore, while complexity in the relationship between cis-eQTL signals and their gene targets undoubtedly makes interpretation of GWAS hits more challenging, it can also be used to provide insights into the mechanisms underlying gene regulation by cis-eQTLs.
Using cis-eQTL signals to interpret GWAS hits
A primary motivation for our study was to investigate eQTLs as plausible modes of action for association hits from GWAS. To this purpose, we looked for overlap of our cis-eQTL signals with known GWAS association signals (Table 1 and Supplementary Table 7). The US National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) GWAS catalog (accessed 7 March 2014), when restricted to SNPs in our 1000 Genomes imputed SNP data set, revealed 385 genome-wide significant SNPs (P < 5 × 10−8) associated with brain-related traits, such as multiple sclerosis, bipolar disorder and Parkinson’s disease, and 3,949 SNPs associated with other traits, such as height, type 2 diabetes and Crohn’s disease. Of these, 17.4% and 20.8% respectively matched cis-eQTL signals in our data set. When we restricted the analysis to SNPs associated specifically with adult-onset neurological disorders, we found that 23.1% of risk SNPs matched cis-eQTL signals. A substantial percentage of brain-related GWAS-eQTL signals acted at a distance, including many cases where the GWAS-signal eQTL signal set (GWAS-eQTL plus all markers with r2 >0.8) resided in a different gene or even a different associated region as defined by recombination hotspots (Table 1). Of the 149 implicated cis-eQTL signals, 61 (1616.7%) lay entirely outside of the associated region of their target gene, reinforcing our results for cis-eQTL signals in general (Fig. 6 and Supplementary Table 3). These findings highlight the value of eQTL information in guiding the functional follow-up of GWAS hits.
Table 1. Coincidence of SNPs from the GWAS catalog and the UKBEC data set.
| Phenotype investigated in the GWAS |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Not related to brain | Any brain-related traits | Only adult-onset neurological disorders | |
| SNPs in NHGRI GWAS catalog with P <5 × 10−8 | 4,227 | 430 | 230 |
| SNPs in NHGRI GWAS catalog with P <5 × 10−8 and found in UKBEC | 3,949 | 385 | 212 |
| SNPs with any significant cis-eQTL | 689 (17.4%) | 80 (20.8%) | 49 (23.1%) |
| Implicated cis-eQTL subsignals (average per SNP with cis-eQTL) | 2,074 (3.0) | 366,366 (4.66) | 209 (4.3) |
| Implicated cis-eQTL signals | 958 | 149 | 94 |
| Location of GWAS-eQTL signal set (sentinel + markers with r2 >0.8) | |||
| All within target gene (including gene promoter and UTRs) | 288 (13.9%) | 81 (22.1%) | 23 (11.0%) |
| Some (not all) outside target gene, but all in same associated region as target | 727 (35.1%) | 80 (21.9%) | 50 (23.9%) |
| All outside target gene, but all in same associated region as target | 664 (32.0%) | 112 (30.6%) | 87 (41.6%) |
| Some (not all) outside the associated region of the target gene | 45 (2.2%) | 32 (8.7%) | 16 (7.7%) |
| All outside the associated region of the target gene | 350 (16.9%) | 61 (16.7%) | 33 (15.8%) |
We illustrate the value of our eQTL data set for some important brain-related GWAS signals. rs2395163 is a risk SNP for Parkinson’s disease32, but is challenging to interpret given that it is an intergenic SNP located in the major histocompatibility complex region of chromosome 6, a highly gene-rich region with high levels of linkage disequilibrium. In our data this SNP is a significant gene-level and exon-level cis-eQTL for HLA-DQA2 (P = 1.29 × 10−6 in the inferior olivary nucleus of the medulla and P = 1.82 × 10−12 in average-all for expression ID 2903265; Fig. 7a) and a more moderate exon-level cis-eQTL for BAT3 (P = 3.64 × 10−6 in average-all for expression ID 2949194). Both HLA-DQA2 and BAT3 are located on the other side of a recombination hotspot, and we note that the cis-eQTL signal for HLA-DQA2 is significantly stronger.
Figure 7. Examples of GWAS hits that were cis-eQTL signals.
(a) Association of local markers (left) and specifically rs2395163 (right), a risk SNP for Parkinson’s disease32, with exon 3 (probe set 2903265) of HLA-DQA2 in average-all (aveALL). (b) Association of local markers (left) and specifically rs12608932 (right), a risk SNP for ALS33, with the 3′ UTR (probe set 3824686) of KCNN1 in frontal cortex (FCTX). (c) Association of local markers (left) and specifically rs1051730 (right), a synonymous coding SNP located in CHRNA3 and a risk SNP for lung cancer, smoking behavior and nicotine dependence, with CHRNA5 (transcript 3603436) in average-all. (d) Association of local markers (left) and specifically rs3768716 (right), a risk SNP for neuroblastoma, with BARD1 (transcript 2598099) in average-all.
rs12608932 is a risk SNP for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)33 located in an intronic region of UNC13A. This has led some to consider UNC13A as a candidate gene in ALS pathology30. We find that rs12608932 is a significant exon-level cis-eQTL for KCNN1 in frontal cortex only (P = 7.11 × 10−7 for expression ID 3824686; Fig. 7b). Both UNC13A and KCNN1 are highly expressed in healthy human brain. UNC13A is implicated in the regulation of neurotransmitter release34,35, and KCNN1 (a voltage-independent calcium-activated potassium channel gene) is implicated in the regulation of neuronal excitability by contributing to the slow component of synaptic after hyperpolarization36. Thus, both genes represent plausible a priori functional candidates, but our region-specific eQTL data weigh in in favor of KCNN1.
rs1051730 is a risk SNP for the interlinked phenotypes of lung cancer, smoking behavior and nicotine dependence37-42. It is a synonymous exonic SNP located in CHRNA3 in a region of high linkage disequilibrium that covers the related genes CHRNA5 and CHRNB4. In our data it is a significant gene-level and exon-level cis-eQTL for CHRNA5 alone (P = 5.11 × 10−6 for expression ID 3603447 in occipital cortex; P = 4.10 × 10−10 for expression ID t3603436 in average-all; Fig. 7c), a finding that potentially clarifies the mechanism of action of this well-established locus.
Many of the GWAS-eQTL signals we examined did act in an expected fashion, regulating the genes in which they are located. For example, rs3768716 is a risk SNP for neuroblastoma43 located in and regulating BARD1 (P = 3.58 × 10−7 in temporal cortex and P = 1.02 × 10−11 in average-all for expression ID t2598099; Fig. 7d). The BARD1 gene product heterodimerizes with the product of the familial breast cancer gene BRCA1 and is considered essential for BRCA1’s tumor suppressive function. Similarly, rs3818361 is a risk SNP for Alzheimer’s disease2,44,45 located in and regulating the complement receptor 1 gene CR1 (P = 1.11 × 10−6 in white matter and P = 1.11 × 10−6 in average-all for expression ID t2377332).
DISCUSSION
Our understanding of the scale and complexity of gene regulation has grown with the ever-increasing size and diversity of eQTL studies. This study represents one of the most powerful eQTL studies yet for its combination of sample size, exon-level expression data and multiregional sampling. We have taken advantage of these features to substantially increase the number of brain-related eQTL signals and to reveal and provide functional insight into their exon-specific and regional-specific heterogeneity. Using these data, we show that eQTL signals in human brain are frequent, widespread and complex both in terms of their effects on individual genes and across the human brain. We show that an appreciation of this complexity can provide insights into the basic processes underlying gene regulation in human brain and, perhaps most significantly, the interpretation of disease-associated loci. For close to 10% of known GWAS hits, we provide cis-eQTL evidence for a role in gene regulation, in many cases in previously unlooked-for targets such as ones across a recombination hotspot boundary. These signals will aid the functional characterization of these GWAS hits.
There are, however, limitations to our findings. The majority of GWAS hits, including ones for brain-related traits, have no matching eQTL signal in our data. We also find tantalizing evidence for trans-eQTLs in our data, and we anticipate that larger sample sizes will allow these to be detected with sufficient power. Finally, the enhanced quality and dynamic range of RNA sequencing will reveal new isoform-level and noncoding RNA-level eQTL signals. Nevertheless, despite these shortcomings, we have shown that the core product of this analysis, namely the identification of 30,333 cis-eQTL signals and their detailed characterization, represents a uniquely valuable resource of benefit to the neuroscience community.
ONLINE METHODS
Collection and dissection of post-mortem human brain tissues
Brain samples were obtained from 134 individuals of European descent. All individuals were neurologically normal during life and confirmed to be neuropathologically normal by a consultant neuropathologist using histology performed on sections prepared from paraffin-embedded brain tissue blocks. The individuals sampled had a mean age at death of 59 years old (range 16–102), were mostly men (74.5%) and the most common cause of death was ischemic heart disease (44.7%).
The brains were collected by the Medical Research Council Sudden Death Brain and Tissue Bank, Edinburgh, UK47, and the Sun Health Research Institute an affiliate of Sun Health Corporation, USA48. Ten brain regions were sampled per individual for RNA analyses. The regions studied were cerebellar cortex, frontal cortex, hippocampus, inferior olivary nucleus (sub-dissected from the medulla), occipital cortex, putamen (at the level of the anterior commissure), substantia nigra, temporal cortex, thalamus (at the level of the lateral geniculate nucleus) and intralobular white matter. The choice of brain regions was driven by relevance to human disease and previous evidence to suggest high variance in expression profiles18,49,50.
A detailed description of the samples used in the study, tissue processing and dissection is provided in Trabzuni et al.24, and summary information is provided in Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Figure 1. All samples had fully informed consent for retrieval and were authorized for ethically approved scientific investigation (Research Ethics Committee number 10/H0716/3).
RnA isolation and processing brain samples on Affymetrix Human exon 1.0 ST arrays
Total RNA was isolated from human post-mortem brain tissues (randomized for extraction) by the single-step method of RNA isolation using the miRNeasy 96 kit (Qiagen). All RNA extractions were performed by a single individual and, in the main, two sample plates were processed on each occasion (186 samples in a batch). The quality of total RNA was evaluated by the 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) and RNA 6000 Nano Kit (Agilent). Total RNA samples were randomized across individuals and brain regions for processing for array analysis on 96-well plates, in large batches (four 96-well plates). All subsequent sample processing was performed on 96-well plates in the microarray facility (AROS Biotechnology, Denmark) within a specified timeframe. Processing with the Ambion WT Expression Kit and Affymetrix GeneChip Whole Transcript Sense Target Labeling Assay and hybridization to the Affymetrix Exon 1.0 ST arrays were performed in accordance with the manufacturers’ protocols. Hybridized arrays were scanned on an Affymetrix GeneChip Scanner 3000 7G and visually inspected for hybridization artifacts. Further details regarding RNA isolation, quality control and processing are reported in Trabzuni et al.24. There were a total of 1,231 arrays that pass quality control checks (Supplementary Table 1).
Analysis of Affymetrix Human exon 1.0 ST array data
All arrays were pre-processed using robust multi-array average (RMA) normalization51 and log2 transformation in Affymetrix Power Tools version 1.14-3. We applied RMA normalization in two different ways: one in which all expression values, regardless of tissue of origin, were used together and one in which RMA normalization was applied separately on a tissue-by-tissue basis. We found no evidence for any method-dependent bias or heterogeneity in our test results, either in the estimated eQTL signal strengths (β regression coefficients) or the P values for association (Supplementary Fig. 3). For all subsequent analysis, we used RMA normalization applied once across all tissues.
We also calculated the detection above background (DABG) metric for each probe set. After remapping the Affymetrix probe sets onto human genome build 19 (GRCh37) and using Netaffx annotation file Release 31 (HuEx-1_0-st-v2 Probeset Annotations), we restricted analysis to 291,705 exon-level probe sets that were annotated to have gene names according to NCBI Reference Sequence build 36 and contained at least three uniquely hybridizing probes that were free of the polymorphism-in-probe problem23 (SNP and indel frequency >1% according to the European panel 1000 Genomes Interim Phase v3, March 2012).
Gene-level expression was estimated for 26,493 transcripts by calculating the Winsorized mean (below 10% and above 90%) signal of all probe sets corresponding to each gene. We added the prefix “t” to the expression ID of gene-level expression probes to easily distinguish them from exon-level probes. The resulting expression data were residual-adjusted for brain bank, gender and batch effects in Partek’s Genomics Suite v6.6 (Partek Incorporated, USA). For each donor, we also calculated the mean expression profile (denoted as average-all) across the available brain regions for each expression ID. This was aimed at finding weaker but ubiquitous signals in the human brain.
DNA extraction, genotyping, imputation and cnV calling
Genomic DNA was extracted from sub-dissected samples (100–200 mg) of human postmortem brain tissue using Qiagen’s DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, UK). All samples were genotyped on the Illumina Infinium Omni1-Quad BeadChip and on the Immunochip, a custom genotyping array designed for the fine mapping of autoimmune disorders1,52. The BeadChips were scanned using an iScan (Illumina, USA) with an AutoLoader (Illumina, USA). GenomeStudio v.1.8.X (Illumina, USA) was used for analyzing the data and generating SNP calls.
After standard quality controls (removal of samples from individuals of suspected non-European descent, samples with call rate <95% and checks on reported sex status, cryptic relatedness, autosomal heterozygosity rate check, monomorphic SNPs or call rate <95%, no genomic position info or redundant SNPs, P value for deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium <0.0001, genotyping call rate <95%, fewer than two heterozygotes present, mismatching alleles with the 1000 Genomes Project (even after allowing for strand), imputation was performed using MaCH53,54 and minimac (http://genome.sph.umich.edu/wiki/Minimac) using the European panel of the 1000 Genomes Project (March 2012: Integrated Phase I haplotype release version 3, based on the 2010 November data freeze and 14 March 2012 haplotypes). We used the resulting 5,878,211 SNPs and 576,942 indels with good postimputation quality (Rsq > 0.50) and minor allele frequency (MAF) of at least 5%.
Intensity data from the Illumina genotyping platform (namely log R ratio (LRR) and B allele frequency (BAF)) were first normalized by correcting for GC content and Loess normalization, and then copy number variant (CNV)-calling was performed using the cnvHap software55. We analyzed all large CNVs (>100 kb) with a frequency >5% for any significant associations with gene expression.
eQTL analysis, FDR calculation and marker sentinelization
The eQTL analysis was run for each expression profile (either exon-level probe set ID or gene-level transcript ID) against every genetic marker (either SNP, indel or CNV) in every tissue (plus average-all). There are ~2.2 × 1013 tests involved, and we call any significant combinations of marker-expression ID-tissue ’unsentinelized subsignals’. The eQTL search was conducted using the R package Matrix EQTL56 on a high-performance Linux-based computer cluster. Matrix EQTL tests the linear model of marker genotype (imputed expected counts of minor allele) against normalized expression values using standard asymptotic methods that are equivalent to the usual likelihood ratio test for linear models. To guard against possible false positives that might arise from breakdown of the usual asymptotic assumptions, we subjected all our declared eQTL signals to permutation testing. All declared asymptotic P values were consistent with our empirical permuted P values (data not shown).
The results were classified by the marker type (SNP or indel), expression type (exon or gene-level) and distance of marker to transcription start site (cis or trans). CNVs were not included as a marker type because an analysis for common CNVs (MAF >5%) of >100 kb associated with gene expression did not identify any significant associations (at 1% FDR). We consider an eQTL signal to be cis-acting if the lead marker (or ‘sentinel’) is located within 1 Mb of the transcription start site of the associated transcript. For each of these eight classification groups in each tissue (plus average-all), we calculated the number of tests conducted and converted the nominal P values into FDRs using the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure57. We defined associations with FDR <1% as significant.
To resolve multiple associations due to haplotype effects as one signal, we calculated the linkage disequilibrium between markers and clustered them such that the markers in a cluster had a pairwise linkage disequilibrium of r2 > 0.5 with each other. Then for a given transcript ID-cluster pairing, we chose the marker with the lowest P value for association across all relevant tests as the sentinel marker. On average, there were 13.7 markers per sentinel marker among the significant results, and we refer to the resulting significant sentinelized marker-expression ID-tissue combinations as ‘subsignals’. Finally, we refer to the grouping of subsignals into significant sentinelized marker-transcript ID combinations as eQTL ‘signals’.
Modified test of heterogeneity
We applied a mixed-model approach to test for heterogeneity in eQTL signal strength. We assume that expression data from the same individual, and from the same exon within a gene, may be correlated. To test for heterogeneity among probe sets in a gene, we fitted a no-heterogeneity model containing a SNP allele dosage main effect and two random effects terms indexing each individual in the data set and each exon in the gene. We then fitted a heterogeneity model containing the same terms plus a set of fixed-effect SNP dosage × exon ID interaction terms. Both models were fitted via restricted maximum likelihood using the lmer() function in the lme4 R package. A likelihood ratio test was used to determine significance. To ensure that significant heterogeneity was not being driven by the absence of expression in all but one probe set, the test was only conducted in transcripts with at least three probe sets that either had a significant eQTL signal or were considered to be expressed above background (significant DABG).
We applied a similar mixed model test of heterogeneity test across brain regions. We only tested eQTL signals where at least three brain regions either had a significant eQTL signal or displayed significant DABG.
Identification of brain-related GWAS SNPS and functional annotation
The NHGRI GWAS catalog58 was downloaded on accessed on 7 March 2014 from http://www.genome.gov/gwastudies/. After removing duplicate entries, there were 4,887 SNPs with genome-wide significant P values (P < 5 × 10−8), of which 4,546 (93%) were also in the imputed genetic data set of UKBEC after quality control (MAF >5% and imputation R2 >0.50). The disease or trait for each GWAS study was checked and classified as either associated with brain-related phenotypes or not by two of us (M.R. and A.R). Brain-related phenotypes were additionally subclassified according to whether they were an adult-onset neurological disorder or not. For the sentinel marker of each cis-eQTL signal, we calculated the linkage disequilibrium with each of the GWAS SNPs (within a 10-Mb or 1,000-SNP moving window) using the vcftools utility (version 0.1.9) and haplotype data of the European panel (n = 379) from the 1000 Genomes Project (March 2012). If a linkage disequilibrium, r2 ≥ 0.50, was observed, the corresponding GWAS SNP along with the linkage disequilibrium measure was recorded in Supplementary Table 2.
We use the R package Variant Annotation59 to functionally annotate the SNPs and indels. We considered only the relationship between the marker and its target gene in a cis-eQTL signal and not the functional property of the SNP in relation to other genes. For example, the relationship for a cis-eQTL signal between a SNP located outside the transcribed region of the target gene X was marked as “none” even if the SNP sat in the intron of gene Y. For a small proportion of the markers, no functional annotation was available.
Replication of eQTL signals in independent data sets
Heinzen et al. (2008)14
RNA was extracted using standard Qiagen protocols from the frontal cortex of 93 adult individuals of European ancestry with no defined neuropsychiatric conditions. We downloaded the CEL files for this brain region from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) using the accession code GSE30483. We excluded nine individuals who showed evidence of non-European ancestry on the basis of a principal component analysis of the genotypes with respect to HapMap3 populations. Since this study used the same array as our study (Affymetrix Human Exon 1.0 ST), we processed the expression data in the same way as for our data. The DNA for the Heinzen et al.14 study was extracted and analyzed using standard Qiagen protocols using Illumina Infinium HumanHap550 chips, and again we carried out imputation to ~6 million markers in the same way as for our data.
North American Brain Expression Consortium (NABEC)
Cerebellar and frontal cortex samples originating from 304 adult individuals of European ancestry, confirmed free of any neuropathological disorder on the basis of histology and examination by a senior neuropathologist, were collected as previously described1,16,20. Total RNA was extracted from sub-dissected samples (100–200 mg) and amplified using the Illumina TotalPrep-96 RNA amplification kit before being directly hybridized onto Human HT12v3 Expression BeadChips (50-mer probes 3′-UTR targeted). The expression data from Illumina Human HT12v3 arrays were analyzed using the Gene Expression Module 3.2.7 in Illumina BeadStudio. Raw intensity values for each probe were transformed using the cubic spline normalization method and then log2 transformed. We remapped the annotation for probes according to ReMOAT60 onto Human Genome Build 19 and restricted the analysis to genes that were reliable, uniquely hybridized, associated with gene descriptions and free of common polymorphisms (MAF >1%). Before use in eQTL analyses, the expression data were corrected for gender, age, post-mortem interval and batch effects (hybridization batch effects and brain bank) as described previously. We successfully mapped ~40% of the Affymetrix transcript IDs to Illumina probe IDs using good quality sequence similarity matches. The DNA for individuals from NABEC was extracted and analyzed using the Illumina Infinium HumanHap550 v3 chips and subsequently imputed to ~5.3 million markers.
Zeller et al. (2010)25
RNA was extracted from monocytes from 1,490 healthy, unrelated German individuals and profiled on Illumina HT12v3 arrays. We downloaded the summary results provided by the authors’ software, which provides all cis-eQTL signals with P <5 × 10−5. The raw expression and genotype data were not publicly available. We removed any signals where the probe failed to be reannotated using ReMOAT (12.1% of signals excluded) or arising from probes containing common polymorphisms (MAF >1%, 10.5% of signals excluded). Results from ~670,000 genotyped SNPs were available for comparison.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to the Banner Sun Health Research Institute Brain and Body Donation Program of Sun City, Arizona for the provision of human biospecimens. The Brain and Body Donation Program is supported by the US National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (U24 NS072026 National Brain and Tissue Resource for Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders), the National Institute on Aging (P30 AG19610 Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Core Center), the Arizona Department of Health Services (contract 211002, Arizona Alzheimer’s Research Center), the Arizona Biomedical Research Commission (contracts 4001, 0011, 05-901 and 1001 to the Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium) and the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. We would like to thank AROS Applied Biotechnology AS company laboratories and Affymetrix for their input. H. Jonvik, L. Stanyer, J. Toombs and M. Gaskin provided invaluable assistance in helping with our computer infrastructure and in sample handling and databasing. We thank A. Pittman for discussions. This work was supported by the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) through the MRC Sudden Death Brain Bank (C.S.), a Project Grant (G0901254 to J.H. and M.E.W.) and Training Fellowship (G0802462 to M.R.). D.T. was supported by the King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Saudi Arabia. This work was also supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the US National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services; project ZO1 AG000947. We acknowledge support from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre based at Guy’s and St Thomas’ National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Appendix
Other contributing authors are as follows:
The UK Brain Expression Consortium (UKBEC): John Hardy, Mina Ryten, Daniah Trabzuni, Sebastian Guelfi11, Michael E Weale, Adaikalavan Ramasamy, Paola Forabosco12, Colin Smith & Robert Walker13
The North American Brain Expression Consortium (NABEC): Sampath Arepalli, Mark R Cookson, Allissa Dillman, J Raphael Gibbs, Dena G Hernandez, Michael A Nalls, Andrew B Singleton, Bryan Traynor, Marcel van der Brug14, Luigi Ferrucci15, Robert Johnson, Ronald Zielke16, Dan L Longo17, Juan Troncoso18, Marcel van der Brug19 & Alan Zonderman20
11Department of Molecular Neuroscience, UCL Institute of Neurology, London, UK. 12Department of Medical & Molecular Genetics, King’s College London, London, UK. 13Department of Pathology, The University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK. 14Laboratory of Neurogenetics, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. 15Clinical Research Branch, National Institute on Aging, Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 16NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders, University of Maryland Medical School, Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 17Lymphocyte Cell Biology Unit, Laboratory of Immunology, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 18Brain Resource Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 19ITGR Biomarker Discovery Group, Genentech, South San Francisco, California, USA. 20Research Resources Branch, National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.
Footnotes
Accession codes: Gene Expression Omnibus: microarray CEL files and processed data, GSE46706. SNP data are also available through dbGAP. The eQTL data can also be queried through our web tool BRAINEAC (http://www.braineac.org/). The server provides visualization tools as well as allowing users to download small sections of the raw data (for example, expression profiles for a gene with all markers within a 1-Mb window) for further in-depth analyses (for example, colocalization analysis46).
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References
- 1.International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC) Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2) A two-stage meta-analysis identifies several new loci for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hollingworth P, et al. Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:429–435. doi: 10.1038/ng.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hamshere ML, et al. Genome-wide significant associations in schizophrenia to ITIH3/4, CACNA1C and SDCCAG8, and extensive replication of associations reported by the Schizophrenia PGC. Mol. Psychiatry. 2013;18:708–712. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hardy J, Singleton A. Genomewide association studies and human disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;360:1759–1768. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0808700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Visscher PM, Brown MA, McCarthy MI, Yang J. Five years of GWAS discovery. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;90:7–24. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Emilsson V, et al. Genetics of gene expression and its effect on disease. Nature. 2008;452:423–428. doi: 10.1038/nature06758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Moffatt MF, et al. Genetic variants regulating ORMDL3 expression contribute to the risk of childhood asthma. Nature. 2007;448:470–473. doi: 10.1038/nature06014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jellinger K. Recent Developments in Parkinson’s Disease. Raven; 1986. pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hyman BT, Van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL. Alzheimer’s disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984;225:1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang ET, et al. Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature. 2008;456:470–476. doi: 10.1038/nature07509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li Q, Lee JA, Black DL. Neuronal regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;8:819–831. doi: 10.1038/nrn2237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Norris AD, Calarco JA. Emerging roles of alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulation in neuronal development and function. Front. Neurosci. 2012;6:122. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2012.00122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Myers AJ, et al. A survey of genetic human cortical gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:1494–1499. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Heinzen EL, et al. Tissue-specific genetic control of splicing: implications for the study of complex traits. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e1. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Webster JA, et al. Genetic control of human brain transcript expression in Alzheimer disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;84:445–458. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gibbs JR, et al. Abundant quantitative trait loci exist for DNA methylation and gene expression in human brain. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu C, et al. Whole-genome association mapping of gene expression in the human prefrontal cortex. Mol. Psychiatry. 2010;15:779–784. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kang HJ, et al. Spatio-temporal transcriptome of the human brain. Nature. 2011;478:483–489. doi: 10.1038/nature10523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Colantuoni C, et al. Temporal dynamics and genetic control of transcription in the human prefrontal cortex. Nature. 2011;478:519–523. doi: 10.1038/nature10524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hernandez DG, et al. Integration of GWAS SNPs and tissue specific expression profiling reveal discrete eQTLs for human traits in blood and brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012;47:20–28. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.03.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim S, Cho H, Lee D, Webster MJ. Association between SNPs and gene expression in multiple regions of the human brain. Transl. Psychiatry. 2012;2:e113. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zou F, et al. Brain expression genome-wide association study (eGWAS) identifies human disease-associated variants. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ramasamy A, et al. Resolving the polymorphism-in-probe problem is critical for correct interpretation of expression QTL studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:e88. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Trabzuni D, et al. Quality control parameters on a large dataset of regionally dissected human control brains for whole genome expression studies. J. Neurochem. 2011;119:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07432.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zeller T, et al. Genetics and beyond—the transcriptome of human monocytes and disease susceptibility. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e10693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fairfax BP, et al. Genetics of gene expression in primary immune cells identifies cell type-specific master regulators and roles of HLA alleles. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:502–510. doi: 10.1038/ng.2205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grundberg E, et al. Mapping cis- and trans-regulatory effects across multiple tissues in twins. Nat. Genet. 2012;44:1084–1089. doi: 10.1038/ng.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Albert FW, Treusch S, Shockley AH, Bloom JS, Kruglyak L. Genetics of single-cell protein abundance variation in large yeast populations. Nature. 2014;506:494–497. doi: 10.1038/nature12904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schorge S, van de Leemput J, Singleton A, Houlden H, Hardy J. Human ataxias: a genetic dissection of inositol triphosphate receptor (ITPR1)-dependent signaling. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33:211–219. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nixon RA. The role of autophagy in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Med. 2013;19:983–997. doi: 10.1038/nm.3232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gruber AR, Fallmann J, Kratochvill F, Kovarik P, Hofacker IL. AREsite: a database for the comprehensive investigation of AU-rich elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:D66–D69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pankratz N, et al. Meta-analysis of Parkinson’s disease: identification of a novel locus, RIT2. Ann. Neurol. 2012;71:370–384. doi: 10.1002/ana.22687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van Es MA, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 19p13.3 (UNC13A) and 9p21.2 as susceptibility loci for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1083–1087. doi: 10.1038/ng.442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Augustin I, Rosenmund C, Sudhof TC, Brose N. Munc13-1 is essential for fusion competence of glutamatergic synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1999;400:457–461. doi: 10.1038/22768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Varoqueaux F, et al. Total arrest of spontaneous and evoked synaptic transmission but normal synaptogenesis in the absence of Munc13-mediated vesicle priming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:9037–9042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122623799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Köhler M, et al. Small-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from mammalian brain. Science. 1996;273:1709–1714. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5282.1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McKay JD, et al. Lung cancer susceptibility locus at 5p15.33. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:1404–1406. doi: 10.1038/ng.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thorgeirsson TE, et al. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature. 2008;452:638–642. doi: 10.1038/nature06846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thorgeirsson TE, et al. Sequence variants at CHRNB3-CHRNA6 and CYP2A6 affect smoking behavior. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:448–453. doi: 10.1038/ng.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tobacco and Genetics Consortium Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:441–447. doi: 10.1038/ng.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Liu JZ, et al. Meta-analysis and imputation refines the association of 15q25 with smoking quantity. Nat. Genet. 2010;42:436–440. doi: 10.1038/ng.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Landi MT, et al. A genome-wide association study of lung cancer identifies a region of chromosome 5p15 associated with risk for adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009;85:679–691. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Capasso M, et al. Common variations in BARD1 influence susceptibility to high-risk neuroblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:718–723. doi: 10.1038/ng.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Naj AC, et al. Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:436–441. doi: 10.1038/ng.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lambert JC, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:1094–1099. doi: 10.1038/ng.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Plagnol V, Smyth DJ, Todd JA, Clayton DG. Statistical independence of the colocalized association signals for type 1 diabetes and RPS26 gene expression on chromosome 12q13. Biostatistics. 2009;10:327–334. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/kxn039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Millar T, et al. Tissue and organ donation for research in forensic pathology: the MRC Sudden Death Brain and Tissue Bank. J. Pathol. 2007;213:369–375. doi: 10.1002/path.2247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Beach TG, et al. The Sun Health Research Institute Brain Donation Program: description and experience, 1987-2007. Cell Tissue Bank. 2008;9:229–245. doi: 10.1007/s10561-008-9067-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hawrylycz MJ, et al. An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature. 2012;489:391–399. doi: 10.1038/nature11405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Roth RB, et al. Gene expression analyses reveal molecular relationships among 20 regions of the human CNS. Neurogenetics. 2006;7:67–80. doi: 10.1007/s10048-006-0032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Irizarry RA, et al. Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 2003;4:249–264. doi: 10.1093/biostatistics/4.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nalls MA, et al. Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet. 2011;377:641–649. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62345-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Li Y, Willer C, Sanna S, Abecasis G. Genotype imputation. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009;10:387–406. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.9.081307.164242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li Y, Willer CJ, Ding J, Scheet P, Abecasis GR. MaCH: using sequence and genotype data to estimate haplotypes and unobserved genotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2010;34:816–834. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Coin LJ, et al. cnvHap: an integrative population and haplotype-based multiplatform model of SNPs and CNVs. Nat. Methods. 2010;7:541–546. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shabalin AA. Matrix eQTL: ultra fast eQTL analysis via large matrix operations. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1353–1358. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 1995;57:289–300. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hindorff LA, et al. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:9362–9367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903103106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Obenchain V, Morgan M, Lawrence M. R Package Version 1.4.8. Bioconductor; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Barbosa-Morais NL, et al. A re-annotation pipeline for Illumina BeadArrays: improving the interpretation of gene expression data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:e17. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.