Abstract
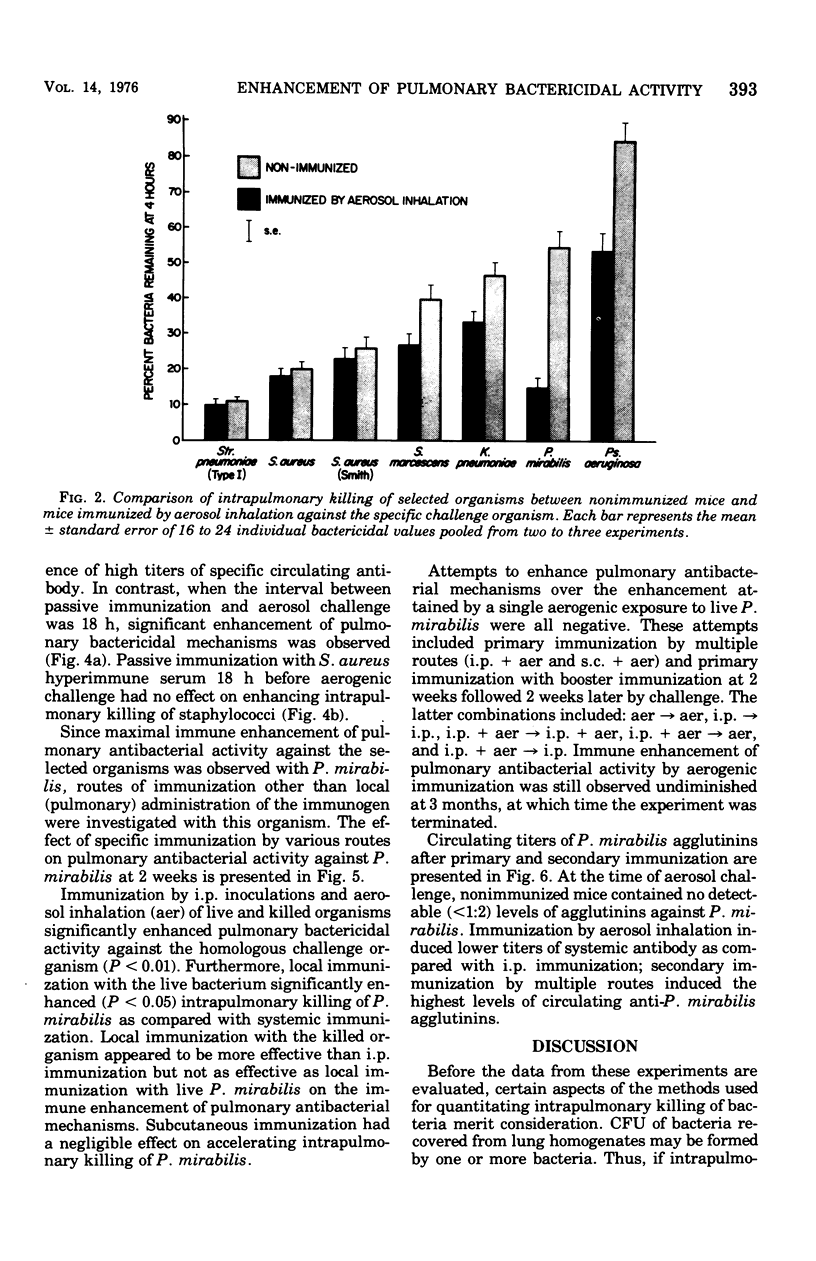
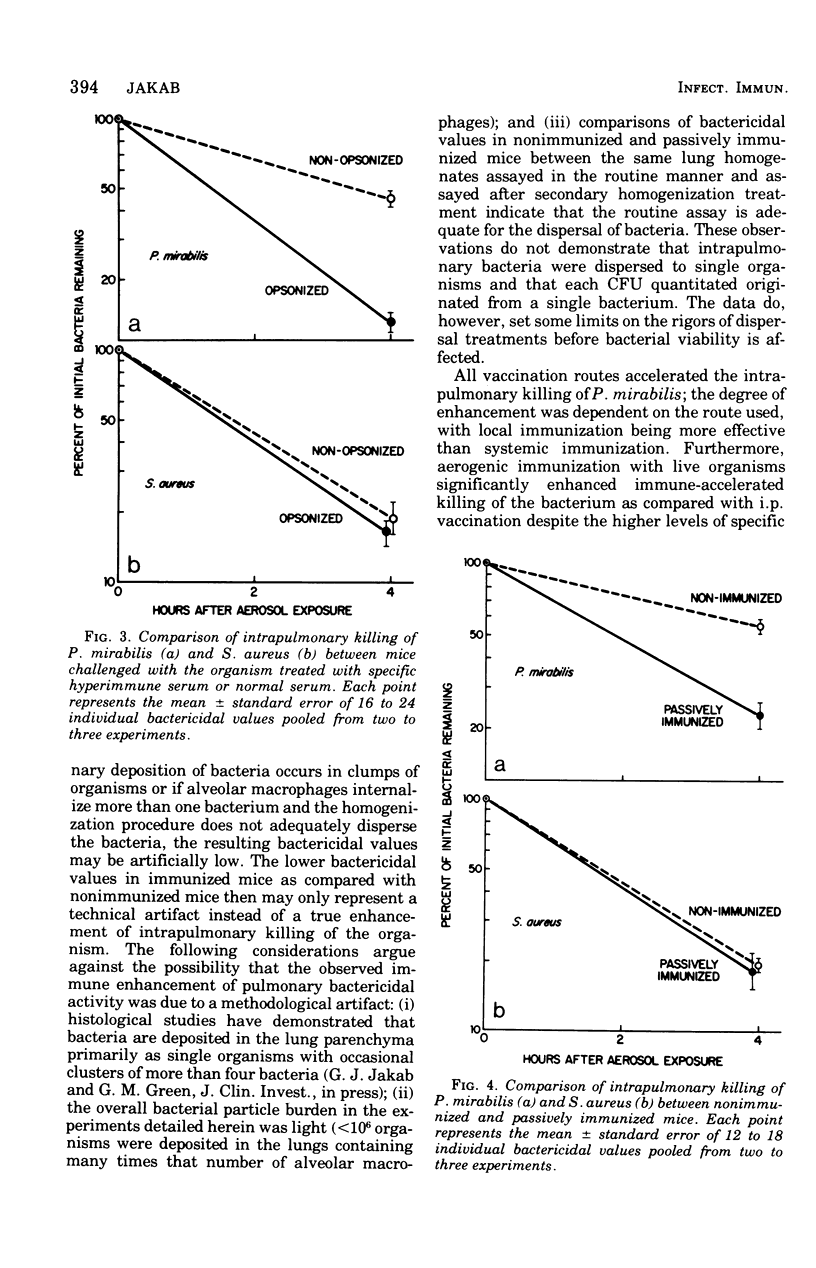
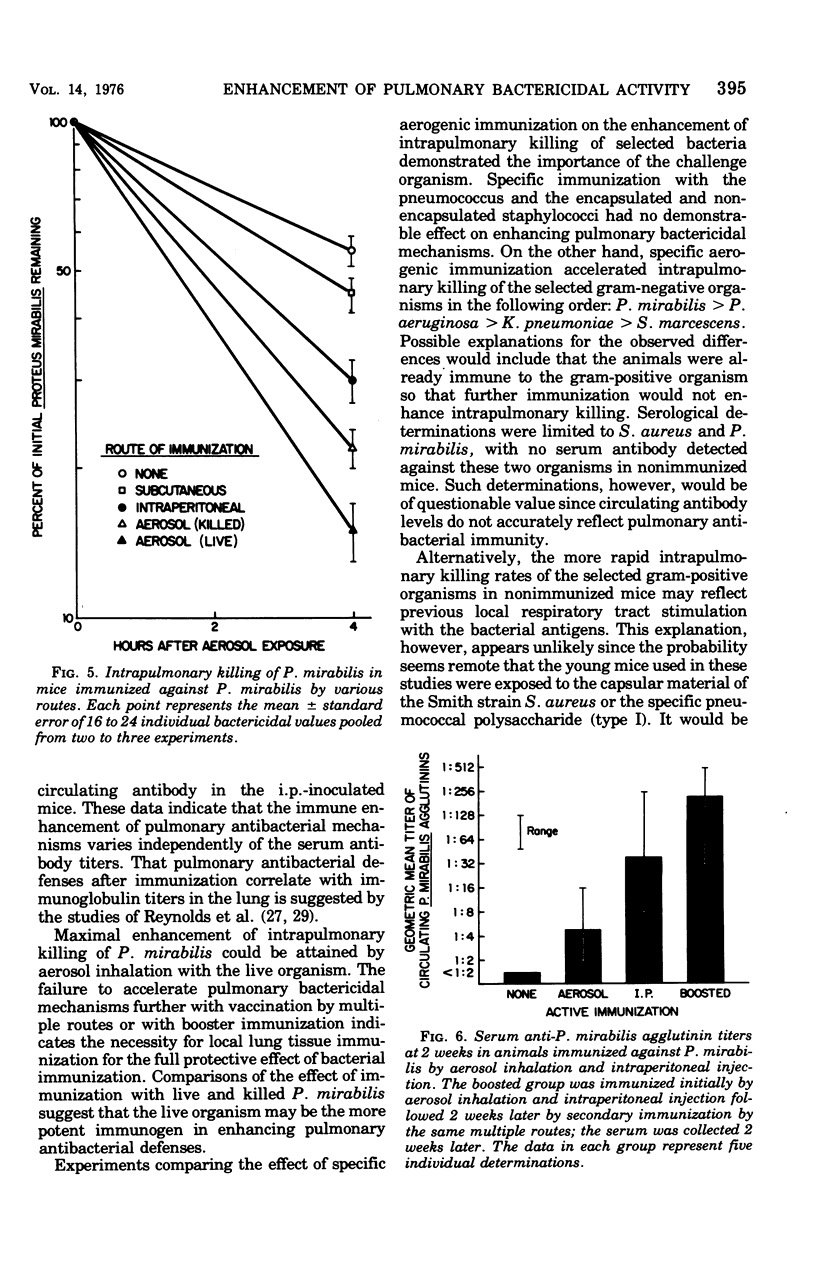
The effect of specific immunization on the antibacterial defense mechanisms of the murine lung was assessed against Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus aureus (Smith), Serratia marcescens, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Immunization by aerosol inhalation significantly enhanced the intrapulmonary killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus mirabilis but not the remaining organisms. With P. mirabilis, systemic immunization induced higher titers of specific serum agglutinins as compared with local respiratory tract immunization; however, local immunization was more effective in enhancing pulmonary bactericidal activity than was parenteral vaccination. Passive immunity against P. mirabilis or aerogenic challenge with preopsonized P. mirabilis significantly enhanced intrapulmonary killing of the homologous organism. With S. aureus, pulmonary bactericidal activity was not accelerated by aerosol challenge with the preopsonized organism, nor was it accelerated in passively immunized mice. These data demonstrate that the immune enhancement of pulmonary bactericidal activity is governed by the bacterium used for challenge and the route of immunization. The results further demonstrate that with P. mirabilis, antibody-mediated mechanisms are involved in the immune enhancement of pulmonary bactericidal activity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach-Rubin F., Ottolenghi-Nightingale E. Effect of ethanol on the clearance of airborne pneumococci and the rate of pneumococcal transformations in the lung. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):688–693. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.688-693.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R., Hand W. L. Cell-mediated immunity after bacterial infection of the lower respiratory tract. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1125–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI107856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele J. H., Goldstein E., Martucci R. W., Eagle C. The influence of acute respiratory acidosis on the pulmonary defense mechanisms in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Aug;108(2):218–224. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA BY THE LUNG. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:769–776. doi: 10.1172/JCI104961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. THE ROLE OF THE ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE IN THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA FROM THE LUNG. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:167–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Eagle M. C., Hoeprich P. D. Effect of nitrogen dioxide on pulmonary bacterial defense mechanisms. Arch Environ Health. 1973 Apr;26(4):202–204. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1973.10666256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Green G. M. The effect of acute renal failure on the bacterial clearance mechanisms of the lung. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Oct;68(4):531–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Lewis J. P. Patterns of pulmonary alveolar macrophage function following radiation injury. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Aug;82(2):276–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E., Lippert W., Warshauer D. Pulmonary alveolar macrophage. Defender against bacterial infection of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):519–528. doi: 10.1172/JCI107788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Carolin D. The depressant effect of cigarette smoke on the in vitro antibacterial activity of alveolar macrophages. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 23;276(8):421–427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702232760801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Goldstein E. A method for quantitating intrapulmonary bacterial inactivation in individual animals. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Oct;68(4):669–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M., Kass E. H. The influence of bacterial species on pulmonary resistance to infection in mice subjected to hypoxia, cold stress, and ethanolic intoxication. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Jun;46(3):360–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M. Lung defense mechanisms. Med Clin North Am. 1973 May;57(3):547–562. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. M. Patterns of bacterial clearance in murine influenza. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., Cantey J. R. Antibacterial mechanisms of the lower respiratory tract. I. Immunoglobulin synthesis and secretion. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):354–362. doi: 10.1172/JCI107567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. E., Southern P. M., Pierce A. K., Fallis B. D., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of gram-negative bacilli. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 May;69(5):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab G. J., Green G. M. Immune enhancement of pulmonary bactericidal activity in murine virus pneumonia. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2878–2884. doi: 10.1172/JCI107484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakab G. J., Green G. M. The effect of Sendai virus infection on bactericidal and transport mechanisms of the murine lung. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1989–1998. doi: 10.1172/JCI107005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanson W. G., Jr, Kennedy M. G., Bonte F. J. Use of technetium ( 99m Tc) as a bacterial label in lung clearance studies. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):592–594. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.592-594.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Hand W. L., King N. L., Hughes C. G. Activation of alveolar macrophages after lower respiratory tract infection. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):80–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M., Goldstein E., Lewis J. P., Lippert W., Warshauer D. Murine pulmonary alveolar macrophages: rates of bacterial ingestion, inactivation, and destruction. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):310–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaForce F. M., Kelly W. J., Huber G. L. Inactivation of staphylococci by alveolar macrophages with preliminary observations on the importance of alveolar lining material. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Oct;108(4):784–790. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.4.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The phagocytosis and inactivation of staphylococci by macrophages of normal rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:35–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y. Pulmonary host defenses in rabbits after immunization with Pseudomonas antigens: the interaction of bacteria, antibodies, macrophages, and lymphocytes. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S134–S142. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Thompson R. E., Devlin H. B. Development of cellular and humoral immunity in the respiratory tract of rabbits to Pseudomonas lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1351–1358. doi: 10.1172/JCI107683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Thompson R. E. Pulmonary host defenses. I. Analysis of protein and lipids in bronchial secretions and antibody responses after vaccination with pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):358–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Thompson R. E. Pulmonary host defenses. II. Interaction of respiratory antibodies with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppert D., Jakab G. J., Sylwester D. L., Green G. M. Sources of variance in the measurement of intrapulmonary killing of bacteria. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Mar;87(3):544–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. M., Jr, Mays B. B., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


