Abstract
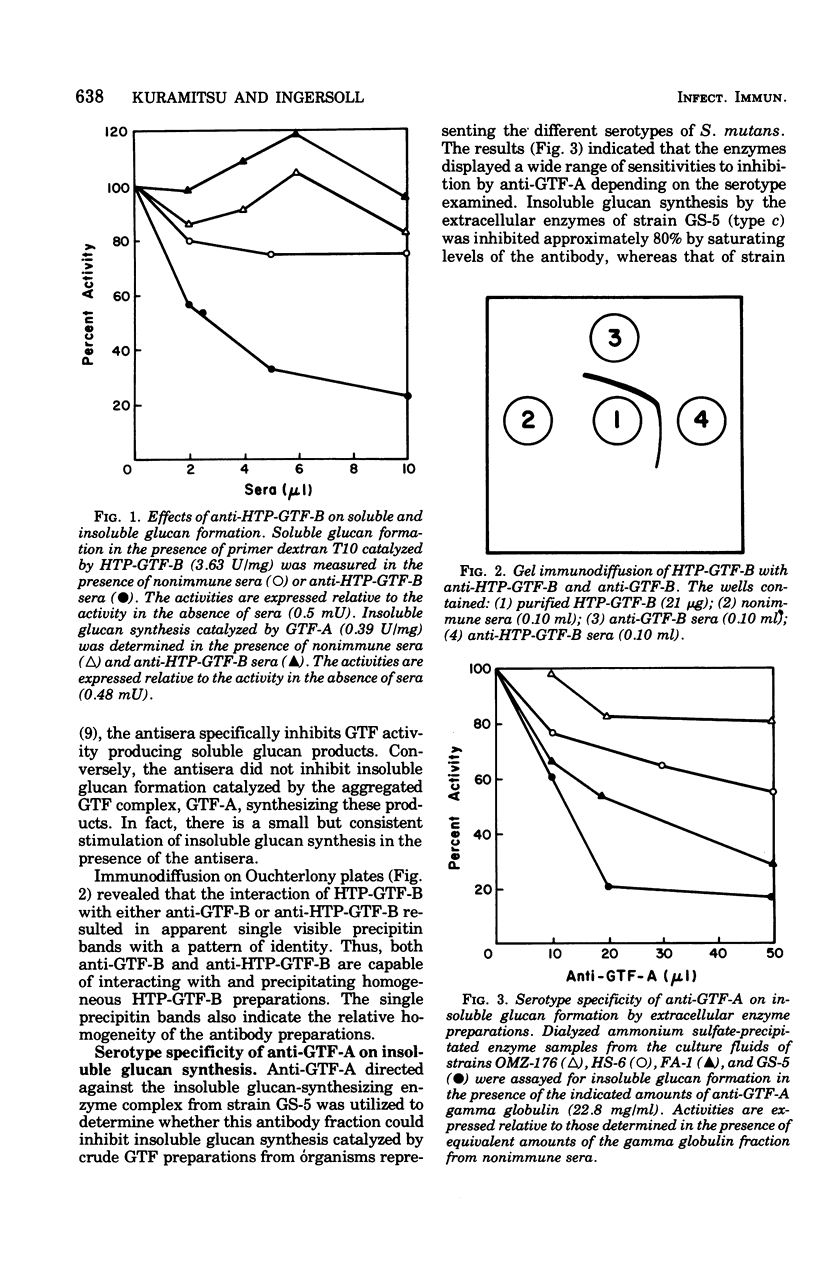
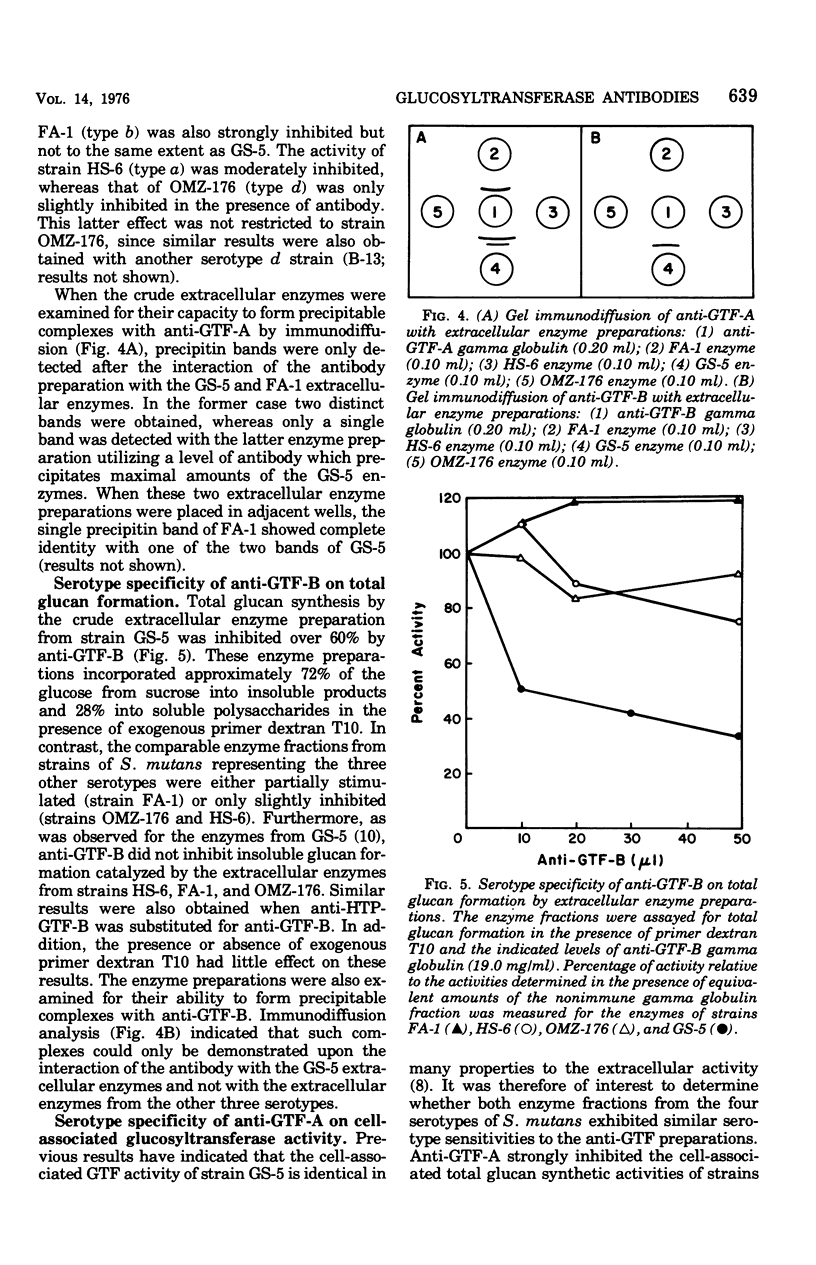
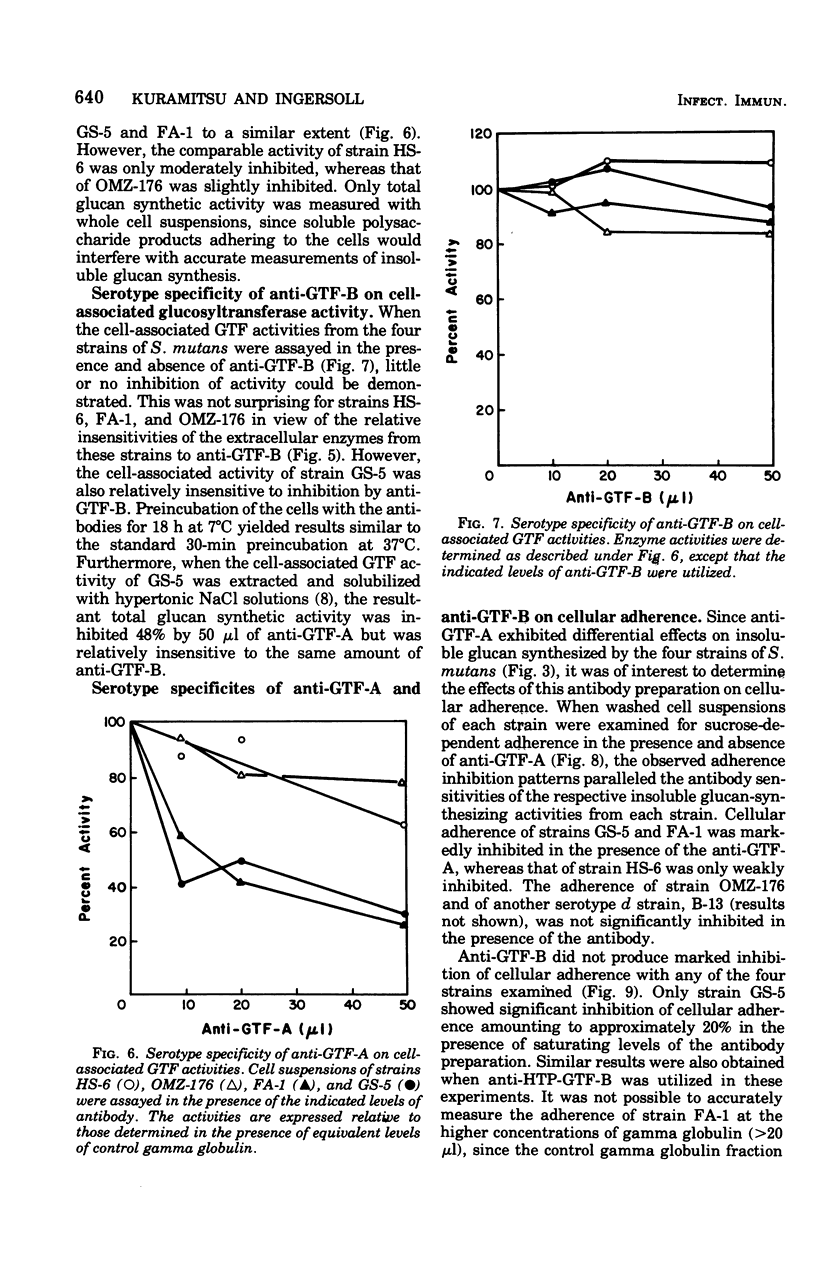
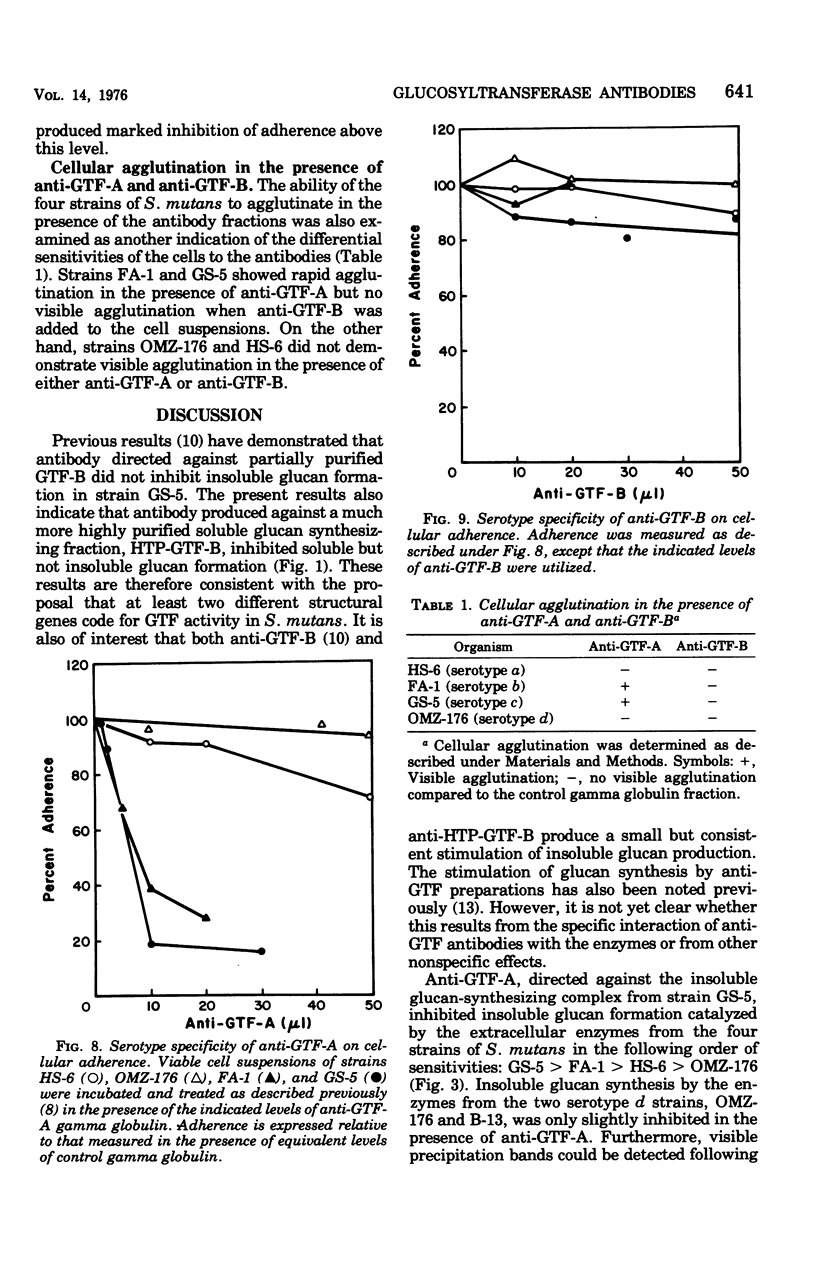
Partially purified glycosyltransferase enzymes for Streptococcus mutans GS-5 (serotype c) have been utilized to prepare antibodies directed against the soluble glucan-synthesizing activity, GTF-B, and the insoluble-soluble glucan synthetic activity, GTF-A. Anti-GTF-A inhibited insoluble glucan formation catalyzed by the extracellular enzymes from strains GS-5 and FA-1 (serotype b) to a much greater extent than that of strains HS-6 (serotype a) or OMZ-176 (serotype d). This antibody fraction also inhibited both the cell-associated glucosyltransferase activities as well as the sucrose-mediated adherence of cells to glass surfaces by strains GS-5 and FA-1 but not that of strains HS-6 and OMZ-176. Anti-GTF-B inhibited soluble glucan formation catalyzed by the extracellular enzymes of strains GS-5 but not that of strain HS-6, FA-1, or OMZ-176. However, this antibody fraction did not strongly inhibit either the cell-associated glycosyltransferase activity or cellular adherence of any of the four strains. These results with body antibody fractions were also correlated with the ability of the antibodies to agglutinate the cells and form precipitin bands after immunodiffusion with the extracellular enzymes. Antibody prepared against the homogeneous soluble glucan-synthesizing enzyme demonstrated similar effects to the anti-GTF-B fraction. These results are discussed in terms of the antigenic relationships existing between the glucosyltransferases from different serotypes of S. mutans.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ceska M., Granath K., Norrman B., Guggenheim B. Structural and enzymatic studies on glucans synthesized with glucosyltransferases of some strains of oral streptococci. Acta Chem Scand. 1972;26(6):2223–2230. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.26-2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chludzinski A. M., Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F. Purification and properties of dextransucrase from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.1-7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Fukui Y., Moriyama T. Purification and properties of dextransucrase and invertase from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Fukui Y., Moriyama T. Some Immunochemical Properties of Dextransucrase and Invertase from Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):985–990. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.985-990.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of cell-associated dextransucrase activity from glucose-grown cells of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.227-235.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of Steptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):738–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.738-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of invertase activity from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1003-1010.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K., Ingersoll L. Differential inhibition of Streptococcus mutans in vitro adherence by anti-glucosyltransferase antibodies. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1775–1777. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1775-1777.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. Immunological and bacteriological basis for vaccination against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):517–520. doi: 10.1038/254517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer R., Slade H. D. Characterization of an anti-glucosyltransferase serum specific for insoluble glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):494–500. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.494-500.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, Michalek S. M., Webb J., Navia J. M., Rahman A. F., Legler D. W. Effective immunity to dental caries: protection of gnotobiotic rats by local immunization with Streptococcus mutans. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of the Adherence of Streptococcus mutans to Smooth Surfaces III. Purification and Properties of the Enzyme Complex Responsible for Adherence. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1135–1145. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1135-1145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbman M. A., Smith D. J. Effects of local immunization with Streptococcus mutans on induction of salivary immunoglobulin A antibody and experimental dental caries in rats. Infect Immun. 1974 Jun;9(6):1079–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.6.1079-1091.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



