Abstract
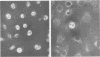
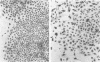
Monolayer cultures of LLC-MK2 rhesus monkey kidney cells became persistently infected with simian virus 40 (SV40) when infected at a multiplicity of infection of 100 plaque-forming units/cell. A stable carrier state developed characterized by extensive viral proliferation without obvious cytopathic effect other than the slow growth of these cultures. By 11 weeks all cells produced the SV40 T antigen. In contrast, less than 5% of the cells produced V antigen. Virus-free clonal isolates were obtained by cloning in SV40 antiserum. Continuous cultivation in antiserum resulted in a temporary cure of unclone cultures. When virus did eventually reappear in the "cured" cultures the titers remained low. The virus produced by the carrier culture was defective at both 31 and 37% c, and it interfered with the growth of standard s40 during mixed infection of CV-1 green monkey kidney cells. All of the interfering activity in carrier culture homogenates could be sedimented by centrifugation at 109,000 x g for 3 h. These cultures were completely susceptible to vesicular stomatitis virus. Extensive viral deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis occurred in CV-1 cells infected with carrier culture virus. Carrier culture homogenates are only slightly less cytopathic to CV-1 cells than standard SV40. The carrier culture express several properties of SV40 transformation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbanti-Brodano G. Molecular events accompanying slow virus infections at the cellular level. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Oct;123(4):553–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Elkington J. Conditions limiting multiplication of fibroblastic and epithelial cells in dense cultures. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):197–199. doi: 10.1038/246197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. N. Genetic manipulation of reovirus--a model for modification of disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 16;287(20):1026–1033. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211162872007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE W. INTERFERENCE AND INTERFERON IN PERSISTENT VIRAL INFECTIONS OF CELL CULTURES. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:145–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Knight P. R., Duff R. G., Rapp F. Activation of a latent measles virus infection in hamster cells. J Virol. 1973 Oct;12(4):690–695. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.4.690-695.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Rapp F. Measles virus: an unwanted variant causing hydrocephalus. Science. 1975 Feb 7;187(4175):450–451. doi: 10.1126/science.1111114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D. Defective viral particles and viral disease processes. Nature. 1970 Apr 25;226(5243):325–327. doi: 10.1038/226325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Croce C. M., Koprowski H. Isolation of defective viruses from SV40-transformed human and hamster cells. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):570–573. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90467-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner K., Santoli D., Croce C. M., Koprowski H. Characterization of defective SV40 isolated from SV40-transformed cells. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):512–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Gelb L. D., Garon C., Takemoto K. K., Lee T. N., Sack G. H., Jr, Nathans D. Characterization of "heavy" and "light" SV40-like particles from a patient with PML. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):179–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata I., Kimura Y., Ito Y., Tanaka T. Temperature-sensitive phenomenon of viral maturation observed in BHK cells persistently infected with HVJ. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):453–461. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkin L. C., Ouellette J. Cell killing by simian virus 40: variation in the pattern of lysosomal enzyme release, cellular enzyme release, and cell death during productive infection of normal and simian virus 40-transformed simian cell lines. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):48–57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.48-57.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Eckroade R. J., Dessel B. H. Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Lancet. 1971 Jun 19;1(7712):1257–1260. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney J. B., Jr, Narayan O. Studies of the antigenic relationships of the new human papovaviruses by electron microscopy agglutination. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):299–300. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.299-300.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preble O. T., Youngner J. S. Selection of temperature-sensitive mutants during persistent infection: role in maintenance of persistent Newcastle disease virus infections of L cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.481-491.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEET B. H., HILLEMAN M. R. The vacuolating virus, S.V. 40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Nov;105:420–427. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr, Narayan O., Danna K. J., Weiner L. P., Nathans D. The nucleic acid of an SV40-like virus isolated from a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Virology. 1973 Feb;51(2):345–350. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simizu B., Takayama N. Relationship between neurovirulence and temperature sensitivity of an attenuated western equine encephalitis virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;35(2):242–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01249716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P., Herndon R. M., Narayan O., Johnson R. T., Shah K., Rubinstein L. J., Preziosi T. J., Conley F. K. Isolation of virus related to SV40 from patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med. 1972 Feb 24;286(8):385–390. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197202242860801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M. Association of papova-virions with a human demyelinating disease (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy). Prog Med Virol. 1969;11:185–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]