Abstract
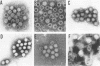
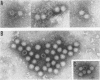
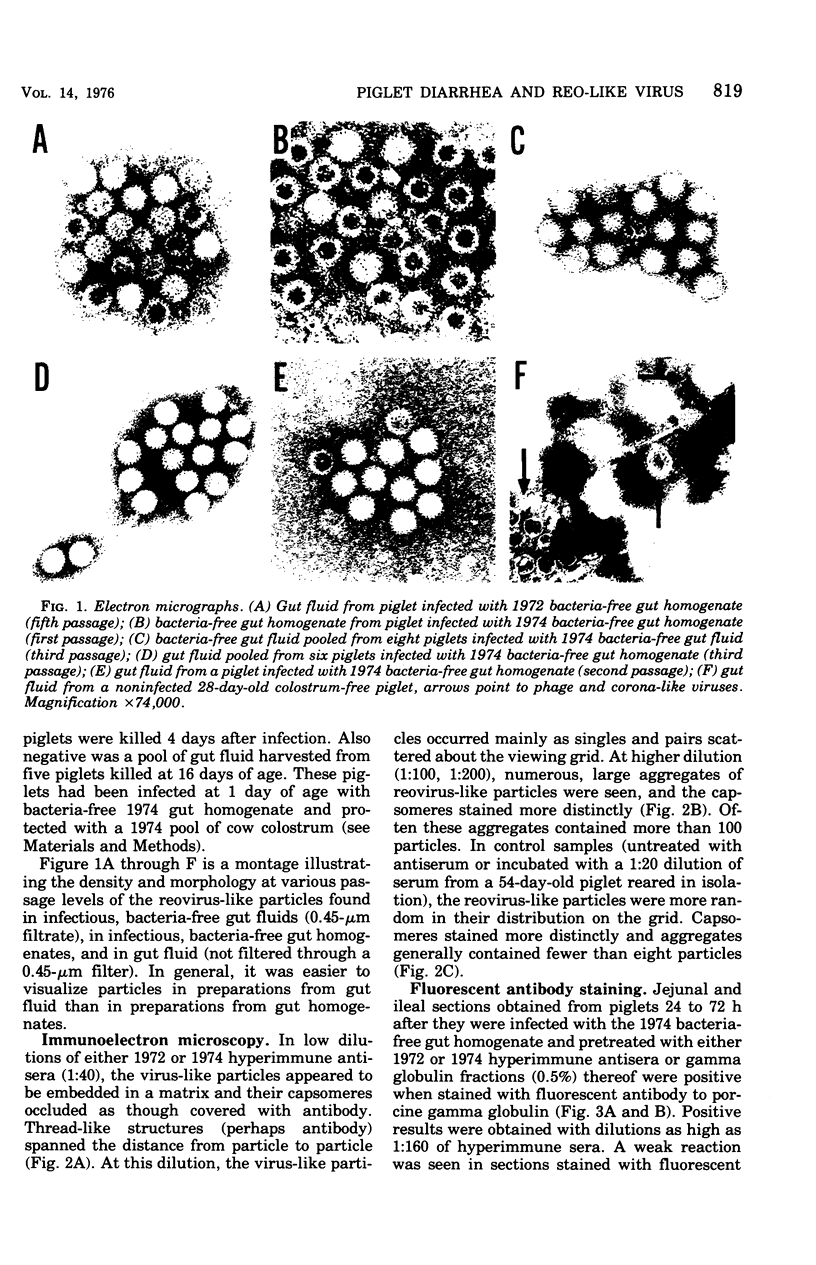
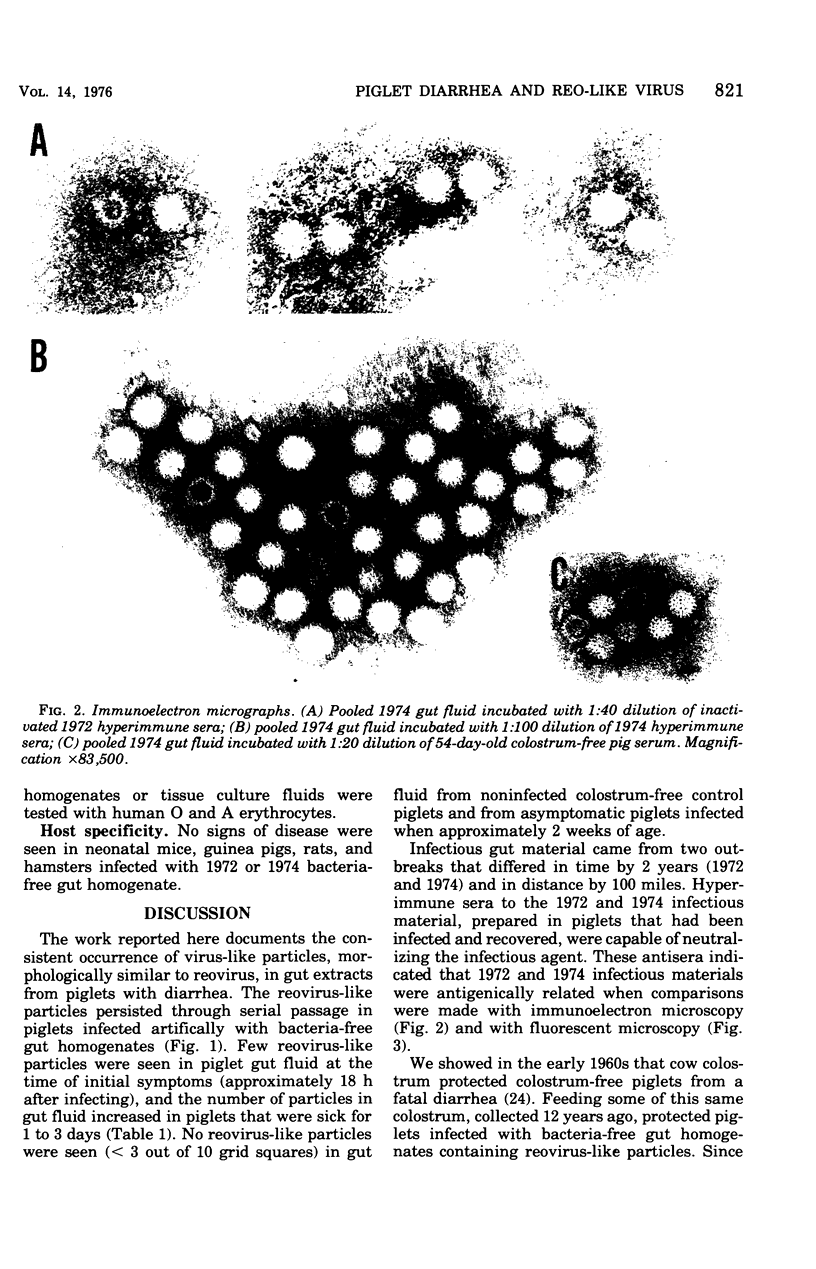
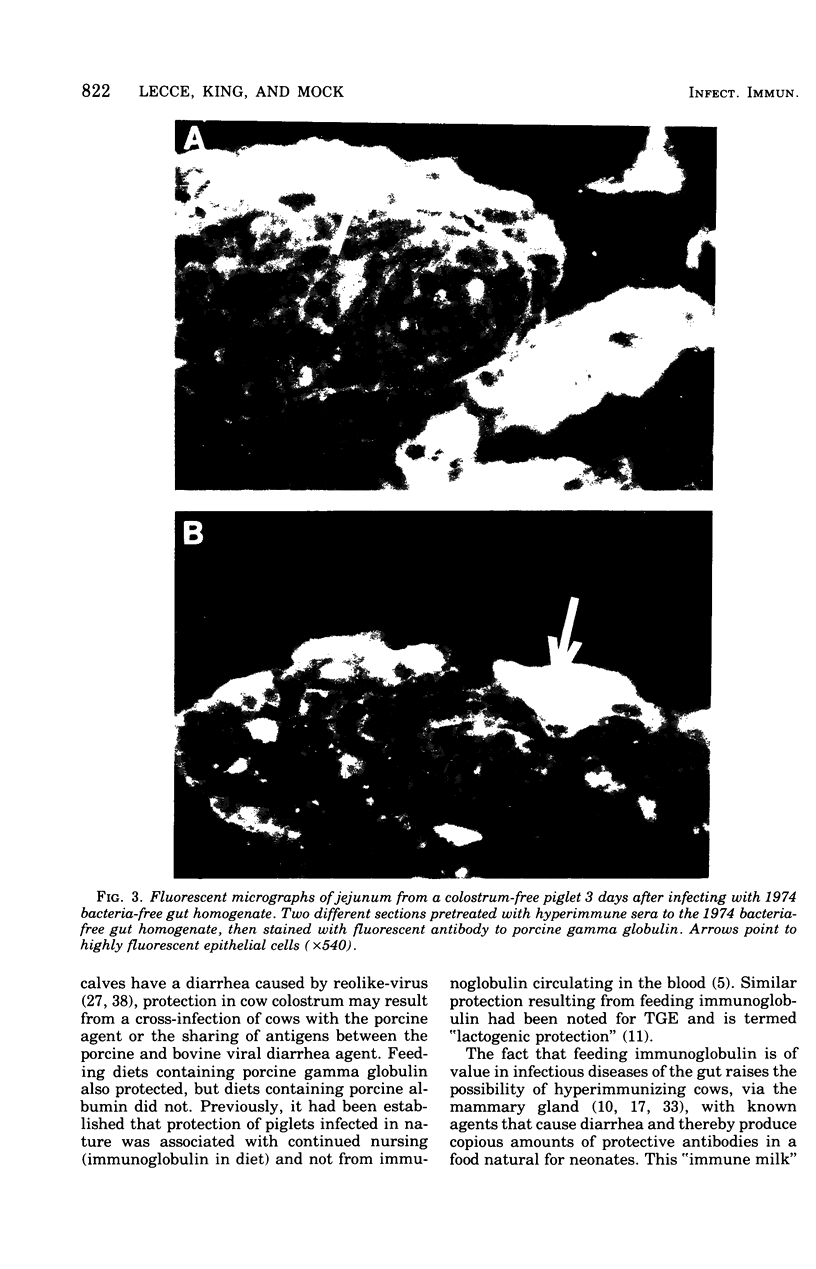
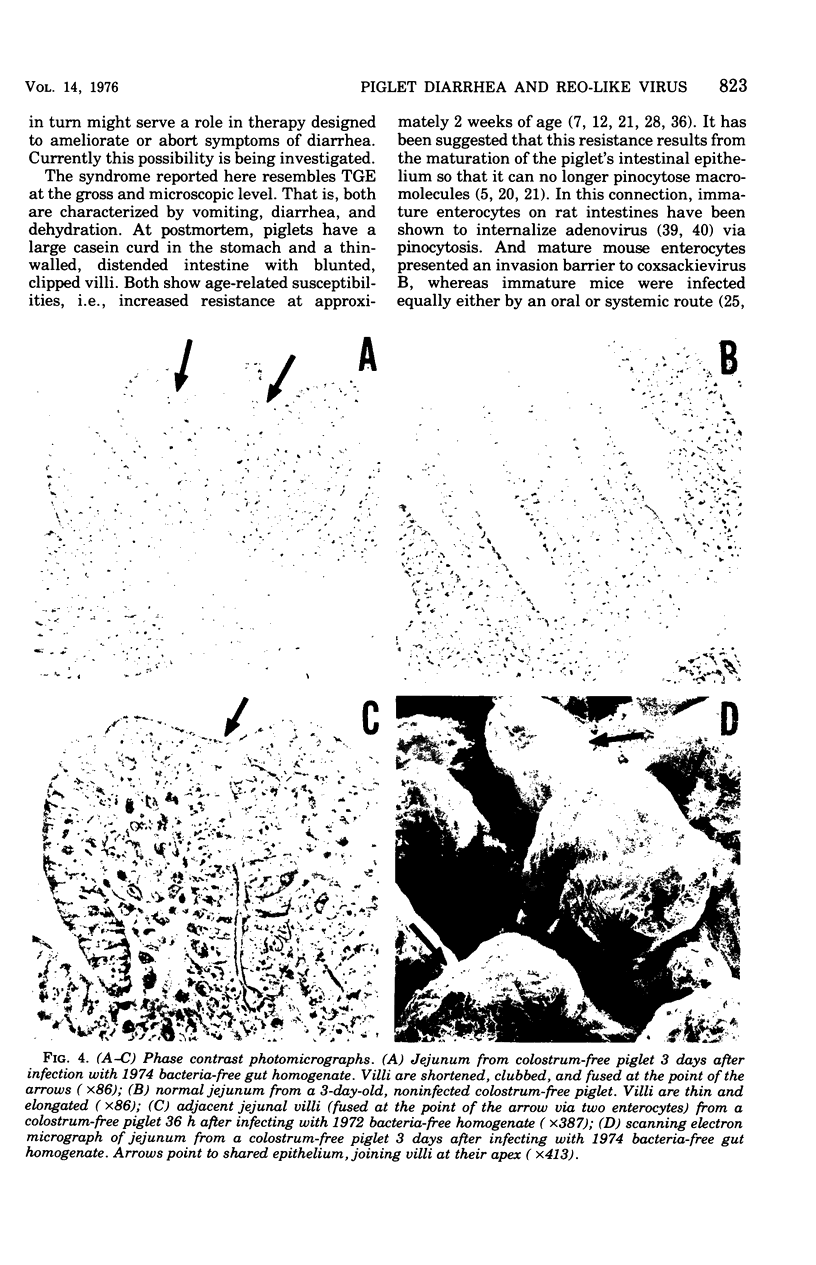
Large numbers of a reovirus-like agent were visualized with electron microscopy in bacteria-free gut homogenates obtained from piglets with a fatal diarrhea resembling transmissible gastroenteritis. The syndrome, of vomiting, diarrhea, dehydration, and death, was reproduced in piglets artificially infected with these bacteria-free gut homogenates. Reovirus-like particles persisted in serial piglet passage and none was seen in uninfected, asymptomatic controls. Hyperimmune sera (made in recovered piglets) aggregated the reovirus-like particles, as judged by immunoelectron microscopy, and neutralized the infectious agent. The cytoplasm in enterocytes on infected intestinal epithelium fluoresced when this hyperimmune sera was used in an indirect fluorescent antibody test. Feeding cow colostrum or diets containing porcine gamma globulin protected infected piglets. No cytopathogenic effect was noted in infected tissue cultures, nor did this agent affect neonatal guinea pigs, hamsters, mice, and rats. The agent did not agglutinate human O or A erythrocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams W. R., Kraft L. M. Electron-Microscopic Study of the Intestinal Epithelium of Mice Infected with the Agent of Epizootic Diarrhea of Infant Mice (EDIM Virus). Am J Pathol. 1967 Jul;51(1):39–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almeida J. D., Waterson A. P. The morphology of virus-antibody interaction. Adv Virus Res. 1969;15:307–338. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60878-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryden A. S., Davies H. A., Hadley R. E., Flewett T. H. Rotavirus enteritis in the West Midlands during 1974. Lancet. 1975 Aug 9;2(7928):241–243. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(75)90959-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. A., Lecce J. G. Herd differences in the expression of fatal diarrhea in artificially reared piglets weaned after 12 hours vs. 36 hours of nursing. J Anim Sci. 1973 Jun;36(6):1114–1121. doi: 10.2527/jas1973.3661114x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coalson J. A., Lecce J. G. Influence of nursing intervals on changes in serum proteins (immunoglobulins) in neonatal pigs. J Anim Sci. 1973 Feb;36(2):381–385. doi: 10.2527/jas1973.362381x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson G. P., Goller I., Bishop R. F., Townley R. R., Holmes I. H., Ruck B. J. Immunofluorescence in duodenal mucosa of children with acute enteritis due to a new virus. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Apr;28(4):263–266. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.4.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GONZAGA A. J., WARREN R. J., ROBBINS F. C. ATTENUATED POLIOVIRUS INFECTION IN INFANTS FED COLOSTRUM FROM POLIOMYELITIS IMMUNE COWS. Pediatrics. 1963 Dec;32:1039–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haelterman E. O. On the pathogenesis of transmissible gastroenteritis of swine. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):534–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infantile enteritis viruses: morphogenesis and morphology. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.937-943.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Kim H. W., Wyatt R. G., Rodriguez W. J., Ross S., Cline W. L., Parrott R. H., Chanock R. M. Reoviruslike agent in stools: association with infantile diarrhea and development of serologic tests. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler E. M. Pathogenesis of neonatal enteric colibacillosis of pigs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Feb 15;160(4):574–582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECCE J. G., MATRONE G., MORGAN D. O. The effect of diet on the maturation of the neonatal piglet's serum protein profile and resistance to disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Aug 31;94:250–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb35545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECCE J. G. Porcine polyserositis with arthritis: isolation of a fastidious pleuropneumonialike organism and Hemophilus influenzae suis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Jan 15;79:670–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb42741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECCE J. G., REEP B. R. Escherichia coli associated with colostrum-free neonatal pigs raised in isolation. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:491–501. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles A. K., McDowell G. H. Localized humoral immunity with particular reference to ruminants. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):170–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G. Absorption of macromolecules by neonatal intestine. Biol Neonat. 1965;9(1):50–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., Coalson J. A. Diets for rearing colostrum-free piglets with an automatic feeding device. J Anim Sci. 1976 Mar;42(3):622–629. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.423622x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G. Rearing piglets artificially in a farm environment: a promise unfulfilled. J Anim Sci. 1975 Aug;41(2):659–666. doi: 10.2527/jas1975.412659x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leece J. G. Effect of dietary regimen on cessation of uptake of macromolecules by piglet intestinal epithelium (closure) and transport to the blood. J Nutr. 1973 May;103(5):751–756. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loria R. M., Kibrick S., Broitman S. A. Peroral infection with group B coxsackievirus in the adult mouse: protective functions of the gut. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):539–543. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loria R. M., Kibrick S., Broitman S. A. Peroral infection with group B coxsackievirus in the newborn mouse: a model for human infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):225–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. W., Norman J. O., Lambert G. Age dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine (TGE). I. Clinical signs and some mucosal dimensions in small intestine. Can J Comp Med. 1973 Apr;37(2):157–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Much D. H., Zajac I. Purification and characterization of epizootic diarrhea of infant mice virus. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1019–1024. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1019-1024.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pensaert M. B., Haelterman E. O., Burnstein T. Diagnosis of transmissible gastroenteritis in pigs by means of immunofluorescence. Can J Comp Med. 1968 Oct;32(4):555–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petric M., Szymanski M. T., Middleton P. J. Purification and preliminary characterization of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbivirus group). Intervirology. 1975;5(3-4):233–238. doi: 10.1159/000149919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillip J. I., Cartwright S. F., Scott A. C. The size and morphology of T.G.E. and vomiting and wasting disease viruses of pigs. Vet Rec. 1971 Mar 20;88(12):311–312. doi: 10.1136/vr.88.12.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M. Morphology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus of pigs. A possible member of coronaviruses. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):105–108. doi: 10.1007/BF01253886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. E., Beamer P. D., Ristic M. Electron microscopy of intestinal epithelial cells of piglets infected with a transmissible gastroenteritis virus. Can J Comp Med. 1973 Apr;37(2):177–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte K. H., Tajima M., Easterday B. C. Morphologic characteristics and nucleic acid type of transmissible gastroenteritis virus of pigs. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(1):53–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01242114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woode G. N., Bridger J. C. Viral enteritis of calves. Vet Rec. 1975 Jan 25;96(4):85–88. doi: 10.1136/vr.96.4.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington B. B., Graney D. O. Uptake of adenovirus by intestinal absorptive cells of the suckling rat. II. The neonatal jejunum. Anat Rec. 1973 Jan;175(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091750106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthington B. B., Graney D. O. Uptake of adenovirus by intestinal absorptive cells of the suckling rat. II. The neonatal jejunum. Anat Rec. 1973 Jan;175(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091750106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]