Abstract
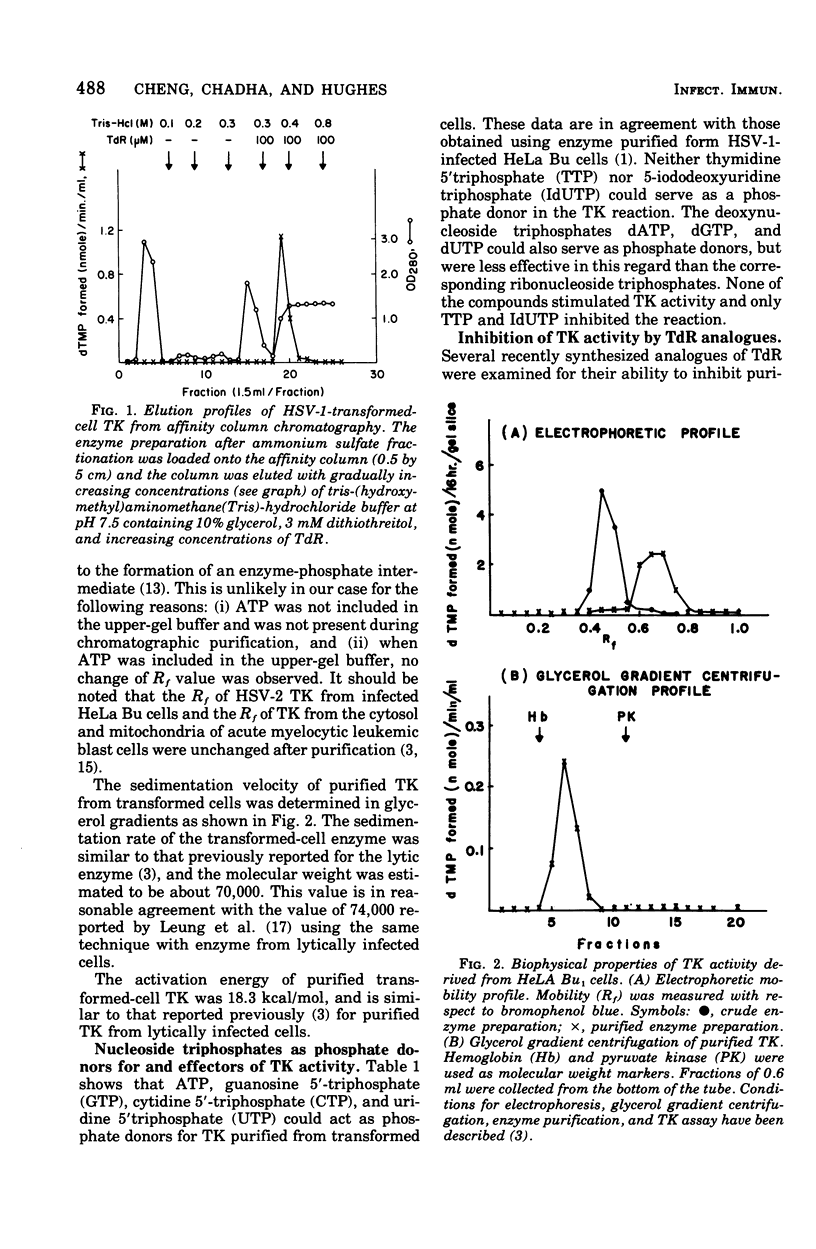
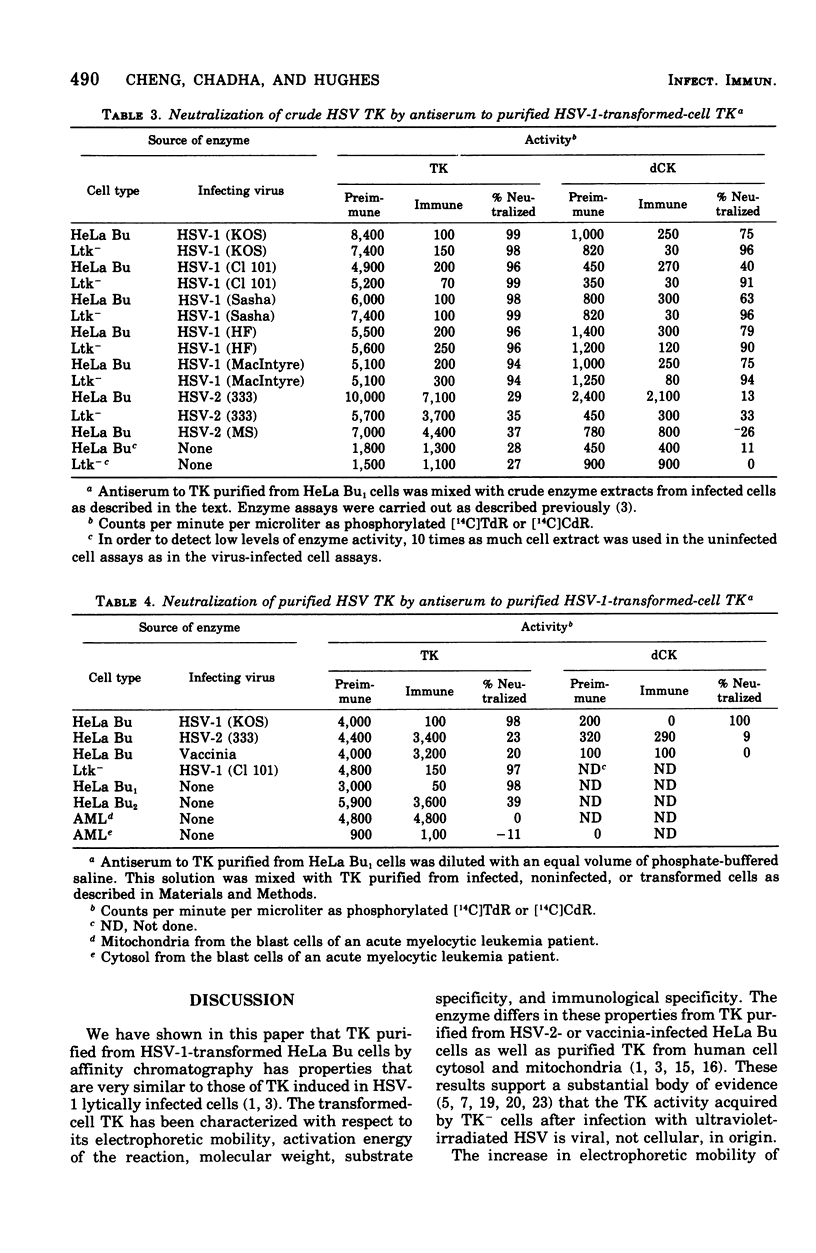
Thymidine kinase (TK) from herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) biochemically transformed HeLa cells, purified by affinity chromatography, has been characterized with respect to its electrophoretic mobility, molecular weight, activation energy, substrate specificity, and immunological specificity. TK purified from HSV-1-transformed HeLa cells has the same electrophoretic mobility as TK purified from HeLa cells lytically infected with HSV-1. The sedimentation velocity of purified TK from transformed cells was similar to that previously reported for the lytic enzyme, and its molecular weight was estimated to be 70,000. The activation energy of purified transformed-cell TK was 18.3 kcal/mol. Antiserum prepared against purified HSV-1 TK, although it showed some cross-reactivity, preferentially neutralized homologous TK. The transformed-cell TK antiserum also neutralized the deoxycytidine kinase activity of HSV-1-infected cell extracts but had no effect on deoxycytidine kinase activity of HSV-2-infected cell extract. These results further support the notion that TK acquired by HeLa cells transformed by HSV-1 is of viral and not of cellular origin.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y. C. Deoxythymidine kinase induced in the HELA TK- cells by herpes simplex virus type I and type II. Substrate specificity and kinetic behavior. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):370–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. C., Ostrander M. Deoxythymidine kinase induced in HeLa TK- cells by herpes simplex virus type I and type II. II. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2605–2610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Adelstein S. J., Oxman M. N. Herpes simplex virus as a source of thymidine kinase for thymidine kinase-deficient mouse cells: suppression and reactivation of the viral enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1912–1916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. B., Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Chawda R. Virus type-specific thymidine kinase in cells biochemically transformed by herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.140-145.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. G., Jr, Munyon W. H. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 defective in lysis but not in transformation. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):275–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.275-283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Gentry G. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Induction of both thymidine and deoxycytidine kinase activity by herpes viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):465–480. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. T., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Biochemical studies on the herpes simplex virus-specified deoxypyrimidine kinase activity. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):481–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Jorgensen G. N., Dubbs D. R., Chan S. K., Leung W. C. Biochemical and serological properties of the thymidine-phosphorylating enzymes induced by herpes simplex virus mutants temperature-dependent for enzyme formation. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Jorgensen G. N., Dubbs D. R. Distinctive properties of thymidine kinase isozymes induced by human and avian hepresviruses. Int J Cancer. 1974 Nov 15;14(5):598–610. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Trkula D., Jorgensen G. Gel electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing of mitochondrial and viral-induced thymidine kinases. Int J Cancer. 1974 Feb 15;13(2):203–218. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Leung W. C., Trkula D. Properties of mitochondrial thymidine kinases of parental and enzyme-deficient HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):503–513. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90542-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal E. P., Markus G. Affinity chromatography of thymidine kinase from a rat colon adenocarcinoma. Prep Biochem. 1976;6(5):369–385. doi: 10.1080/00327487608061625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Cheng Y. C. Human deoxythymidine kinase. I. Purification and general properties of the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial isozymes derived from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2600–2604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Cheng Y. c. Human deoxythymidine kinase II: substrate specificity and kinetic behavior of the cytoplasmic and mitochondrial isozymes derived from blast cells of acute myelocytic leukemia. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3686–3690. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung W. C., Dubbs D. R., Trkula D., Kit S. Mitochondrial and herpesvirus-specific deoxypyrimidine kinases. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):486–497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.486-497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Buchsbaum R., Paoletti E., Mann J., Kraiselburd E., Davis D. Electrophoresis of thymidine kinase activity synthesized by cells transformed by herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1972 Sep;49(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Kraiselburd E., Davis D., Mann J. Transfer of thymidine kinase to thymidine kinaseless L cells by infection with ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.813-820.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Chadha K. C., Munyon W. H. Serological specificity of thymidine kinase activity in herpes simplex virus-transformed L cells. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):350–351. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E. Serological properties of thymidine kinase produced in cells infected with type 1 or type 2 herpes virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Dec;17(3):307–315. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E., Wildy P. Deoxypyrimidine kinases of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2: comparison of serological and structural properties. J Gen Virol. 1975 Feb;26(2):159–170. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


