Abstract
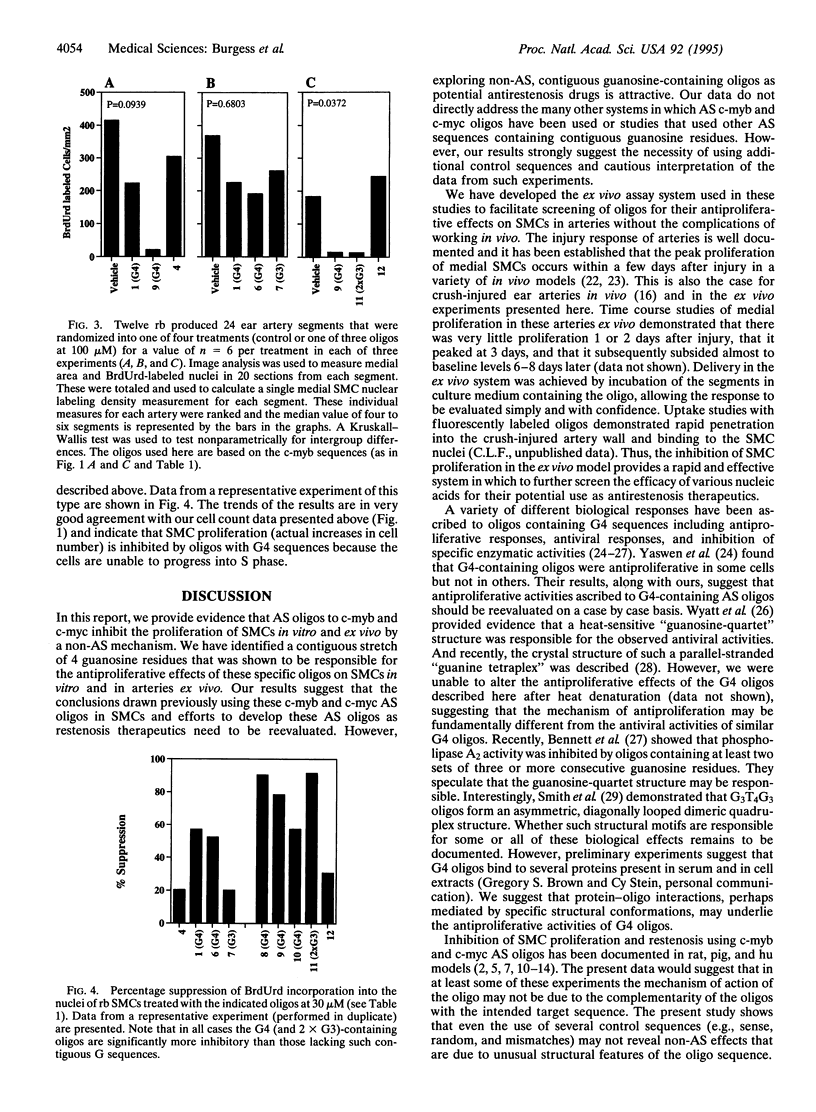
Smooth muscle cell (SMC) proliferation is thought to play a major role in vascular restenosis after angioplasty and is a serious complication of the procedure. Developing antisense (AS) oligonucleotides as therapeutics is attractive because of the potentially high specificity of binding to their targets, and several investigators have reported inhibition of SMC proliferation in vitro and in vivo by using AS strategies. We report here the results of our experiments on vascular SMCs using AS oligonucleotides directed toward c-myb and c-myc. We found that significant inhibition of SMC proliferation occurred with these specific AS sequences but that this inhibition was clearly not via a hybridization-dependent AS mechanism. Rather, inhibition was due to the presence of four contiguous guanosine residues in the oligonucleotide sequence. This was demonstrated in vitro in primary cultures of SMCs and in arteries ex vivo. The ex vivo model developed here provides a rapid and effective system in which to screen potential oligonucleotide drugs for restenosis. We have further explored the sequence requirements of this non-AS effect and determined that phosphorothioate oligonucleotides containing at least two sets of three or four consecutive guanosine residues inhibit SMC proliferation in vitro and ex vivo. These results suggest that previous AS data obtained using these and similar, contiguous guanosine-containing AS sequences be reevaluated and that there may be an additional class of nucleic acid compounds that have potential as antirestenosis therapeutics.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe J., Zhou W., Taguchi J., Takuwa N., Miki K., Okazaki H., Kurokawa K., Kumada M., Takuwa Y. Suppression of neointimal smooth muscle cell accumulation in vivo by antisense cdc2 and cdk2 oligonucleotides in rat carotid artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jan 14;198(1):16–24. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banai S., Shou M., Correa R., Jaklitsch M. T., Douek P. C., Bonner R. F., Epstein S. E., Unger E. F. Rabbit ear model of injury-induced arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Kinetics, reproducibility, and implications. Circ Res. 1991 Sep;69(3):748–756. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.3.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender T. P., Kuehl W. M. Murine myb protooncogene mRNA: cDNA sequence and evidence for 5' heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Chiang M. Y., Chan H., Shoemaker J. E., Mirabelli C. K. Cationic lipids enhance cellular uptake and activity of phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;41(6):1023–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. F., Chiang M. Y., Wilson-Lingardo L., Wyatt J. R. Sequence specific inhibition of human type II phospholipase A2 enzyme activity by phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):3202–3209. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.3202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Anglin S., McEwan J. R., Jagoe R., Newby A. C., Evan G. I. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by c-myc antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):820–828. doi: 10.1172/JCI117036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biro S., Fu Y. M., Yu Z. X., Epstein S. E. Inhibitory effects of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeting c-myc mRNA on smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):654–658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. E., Kindy M. S., Sonenshein G. E. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene in bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4625–4630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Reidy M. A., Clowes M. M. Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I. Smooth muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):327–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebbecke M., Unterberg C., Buchwald A., Stöhr S., Wiegand V. Antiproliferative effects of a c-myc antisense oligonucleotide on human arterial smooth muscle cells. Basic Res Cardiol. 1992 Nov-Dec;87(6):585–591. doi: 10.1007/BF00788668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecker D. J., Vickers T. A., Hanecak R., Driver V., Anderson K. Rational screening of oligonucleotide combinatorial libraries for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1853–1856. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein S. E., Speir E., Unger E. F., Guzman R. J., Finkel T. The basis of molecular strategies for treating coronary restenosis after angioplasty. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994 May;23(6):1278–1288. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke H., Strohschneider T., Oberhoff M., Betz E., Karsch K. R. Time course of smooth muscle cell proliferation in the intima and media of arteries following experimental angioplasty. Circ Res. 1990 Sep;67(3):651–659. doi: 10.1161/01.res.67.3.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughlan G., Murchie A. I., Norman D. G., Moore M. H., Moody P. C., Lilley D. M., Luisi B. The high-resolution crystal structure of a parallel-stranded guanine tetraplex. Science. 1994 Jul 22;265(5171):520–524. doi: 10.1126/science.8036494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majello B., Kenyon L. C., Dalla-Favera R. Human c-myb protooncogene: nucleotide sequence of cDNA and organization of the genomic locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9636–9640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Single intraluminal delivery of antisense cdc2 kinase and proliferating-cell nuclear antigen oligonucleotides results in chronic inhibition of neointimal hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8474–8478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morishita R., Gibbons G. H., Ellison K. E., Nakajima M., von der Leyen H., Zhang L., Kaneda Y., Ogihara T., Dzau V. J. Intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury is inhibited by antisense cdk 2 kinase oligonucleotides. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1458–1464. doi: 10.1172/JCI117123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. F., Yanagihara D., Klopchin K., Danilenko D. M., Hsu E., Kenney W. C., Morris C. F. Stimulation of all epithelial elements during skin regeneration by keratinocyte growth factor. J Exp Med. 1994 Mar 1;179(3):831–840. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.3.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San Antonio J. D., Karnovsky M. J., Ottlinger M. E., Schillig R., Pukac L. A. Isolation of heparin-insensitive aortic smooth muscle cells. Growth and differentiation. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 May;13(5):748–757. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.5.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Fard A., Galeo A., Hutchinson H. G., Vermani P., Dodge G. R., Hall D. J., Shaheen F., Zalewski A. Transcatheter delivery of c-myc antisense oligomers reduces neointimal formation in a porcine model of coronary artery balloon injury. Circulation. 1994 Aug;90(2):944–951. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.2.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Hutchinson H. G., Hall D. J., Zalewski A. Downregulation of c-myc expression by antisense oligonucleotides inhibits proliferation of human smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 1993 Sep;88(3):1190–1195. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.88.3.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Edelman E. R., DeKeyser J. L., Langer R., Rosenberg R. D. Antisense c-myb oligonucleotides inhibit intimal arterial smooth muscle cell accumulation in vivo. Nature. 1992 Sep 3;359(6390):67–70. doi: 10.1038/359067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons M., Rosenberg R. D. Antisense nonmuscle myosin heavy chain and c-myb oligonucleotides suppress smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro. Circ Res. 1992 Apr;70(4):835–843. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. W., Lau F. W., Feigon J. d(G3T4G3) forms an asymmetric diagonally looped dimeric quadruplex with guanosine 5'-syn-syn-anti and 5'-syn-anti-anti N-glycosidic conformations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10546–10550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cheng Y. C. Antisense oligonucleotides as therapeutic agents--is the bullet really magical? Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1004–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.8351515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Krieg A. M. Problems in interpretation of data derived from in vitro and in vivo use of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Antisense Res Dev. 1994 Summer;4(2):67–69. doi: 10.1089/ard.1994.4.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. R., Vickers T. A., Roberson J. L., Buckheit R. W., Jr, Klimkait T., DeBaets E., Davis P. W., Rayner B., Imbach J. L., Ecker D. J. Combinatorially selected guanosine-quartet structure is a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus envelope-mediated cell fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaswen P., Stampfer M. R., Ghosh K., Cohen J. S. Effects of sequence of thioated oligonucleotides on cultured human mammary epithelial cells. Antisense Res Dev. 1993 Spring;3(1):67–77. doi: 10.1089/ard.1993.3.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




