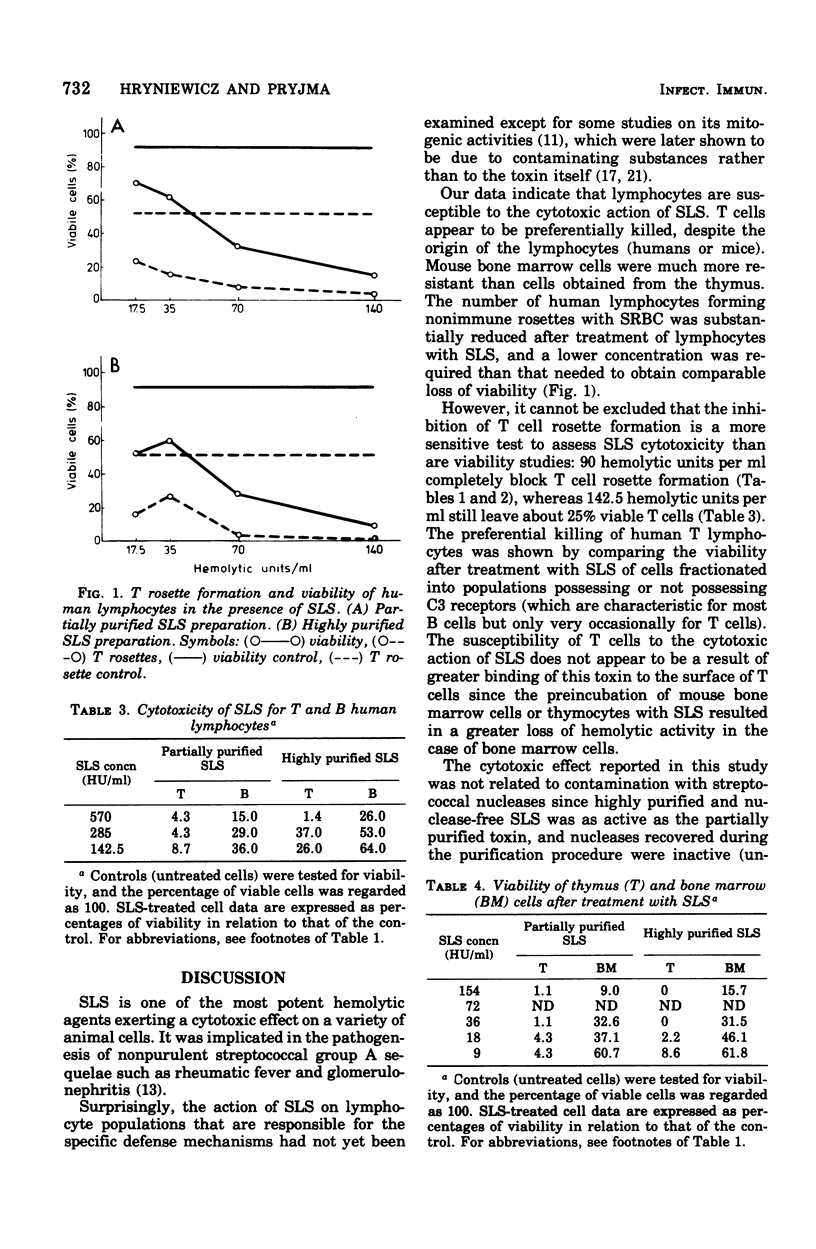
Abstract
The effect of streptolysin S on T and B human and mouse lymphocytes was studied. The dose-dependent inhibition of T cell rosette formation was observed, and this was accompanied by a dose-dependent cytotoxicity. The existence of a difference in the degree of susceptibility of T and B cells to the cytotoxic effect of streptolysin S is shown.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B. R., Cone R. Inhibition of human lymphocyte blast transformation by streptolysin O. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Aug;84(2):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourmashkin R. R., Rosse W. F. Morphologic changes in the membranes of red blood cells undergoing hemolysis. Am J Med. 1966 Nov;41(5):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. L., Mason L. Characteristics of streptolysin S hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):77–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.77-82.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I. Mechanisms of cell and tissue injury induced by group A streptococci: relation to poststreptococcal sequelae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Sep;126(3):294–340. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.3.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHHORN K., SCHREIBMAN R. R., VERBO S., GRUSKIN R. H. THE ACTION OF STREPTOLYSIN S ON PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES OF NORMAL SUBJECTS AND PATIENTS WITH ACUTE RHEUMATIC FEVER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1151–1157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., BERNHEIMER A. W., WEISSMANN G. MOTION PICTURE STUDY OF THE TOXIC ACTION OF STREPTOLYSINS ON LEUCOCYTES. J Exp Med. 1963 Aug 1;118:223–228. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.2.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker S. C., Gray E. D. Simple method for the preparation of streptococcal nucleases. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.368-371.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plate J. M., Amos B. Lymphocyte stimulation by a glycopeptide isolated from Streptococcus pyogenes C203S. I. Isolation and partial purification. Cell Immunol. 1970 Nov;1(5):476–487. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R., Kerman R., Ezdinli E., Stefani S. A modified assay for the detection of human adult active rosette forming lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1975;8(1-2):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90094-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington D. A., Arbuthnott J. P. The action of streptolysin S on mouse-liver mitochondria. J Med Microbiol. 1973 May;6(2):225–234. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-2-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranta A., Cuppari G., Quagliata F. Dissociation of hemolytic and lymphocyte-transforming activities of streptolysin S preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):605–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


