Abstract
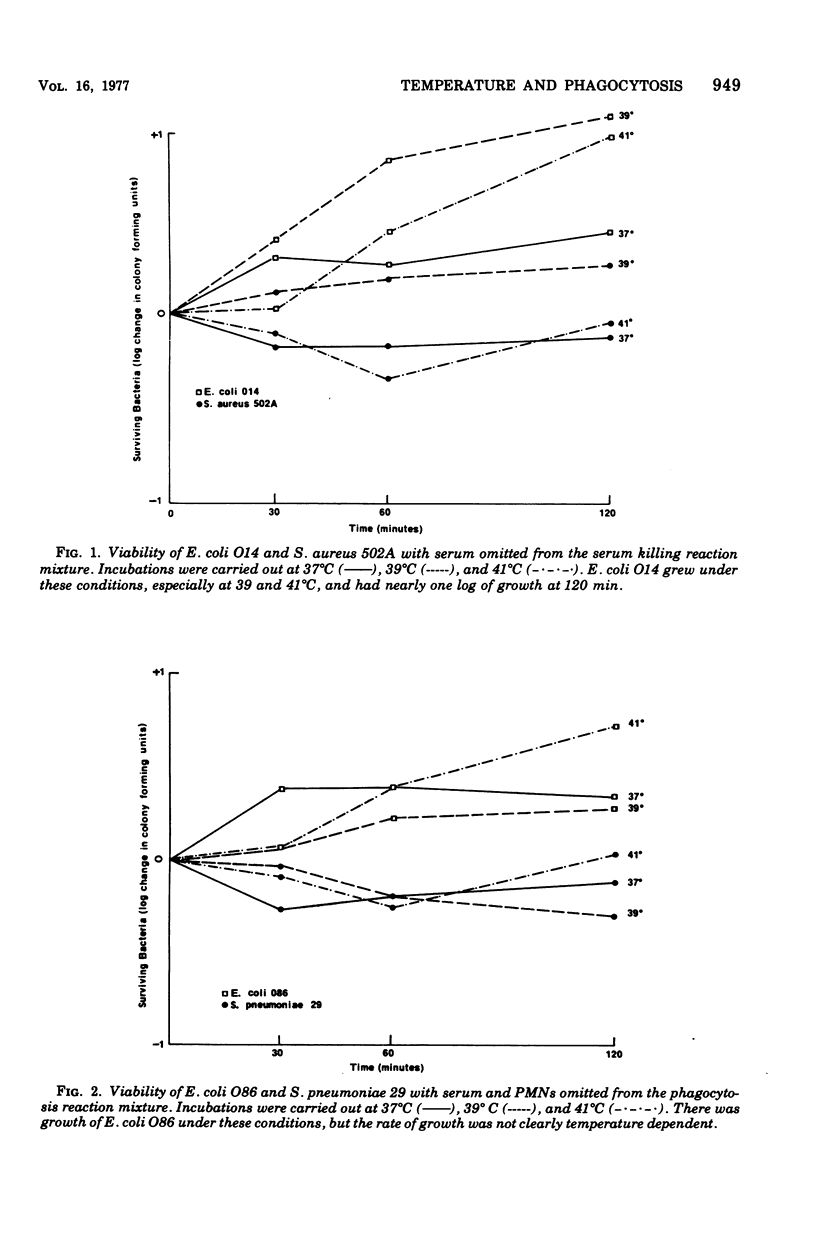
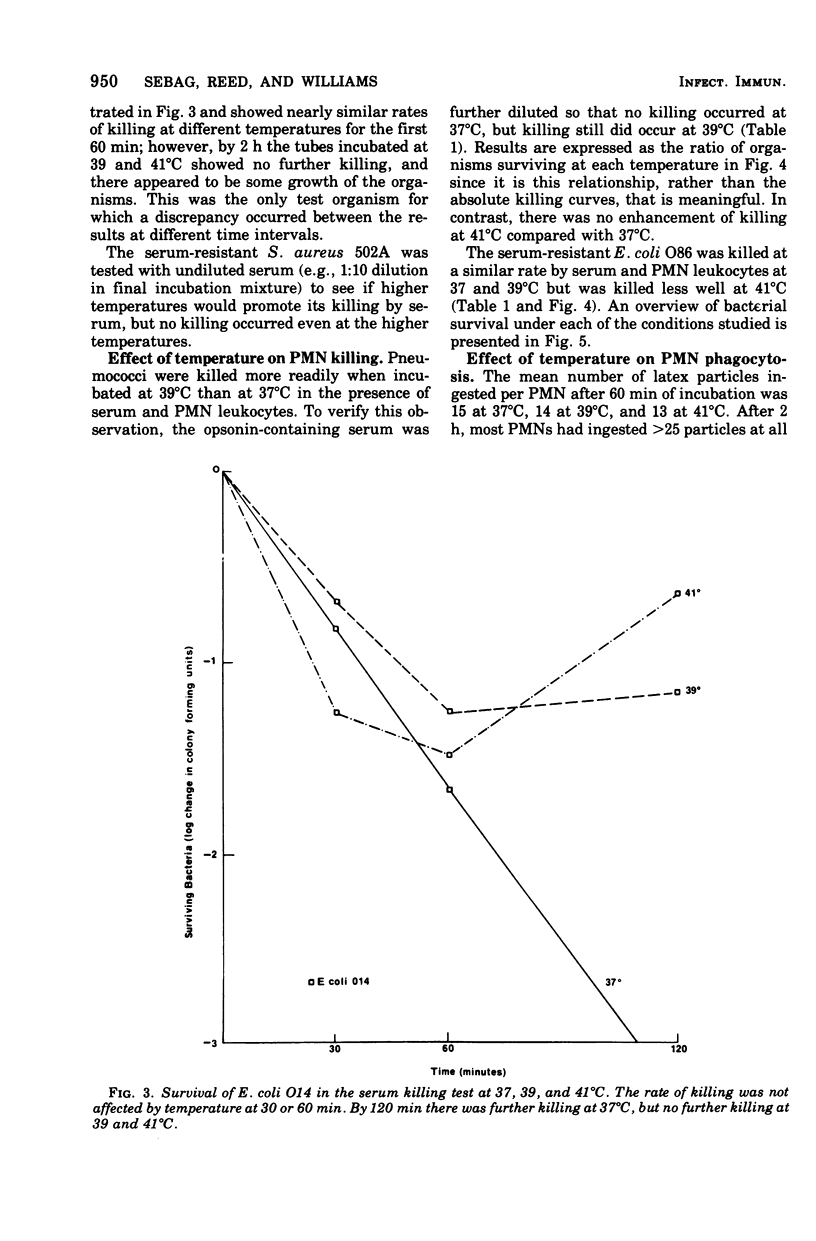
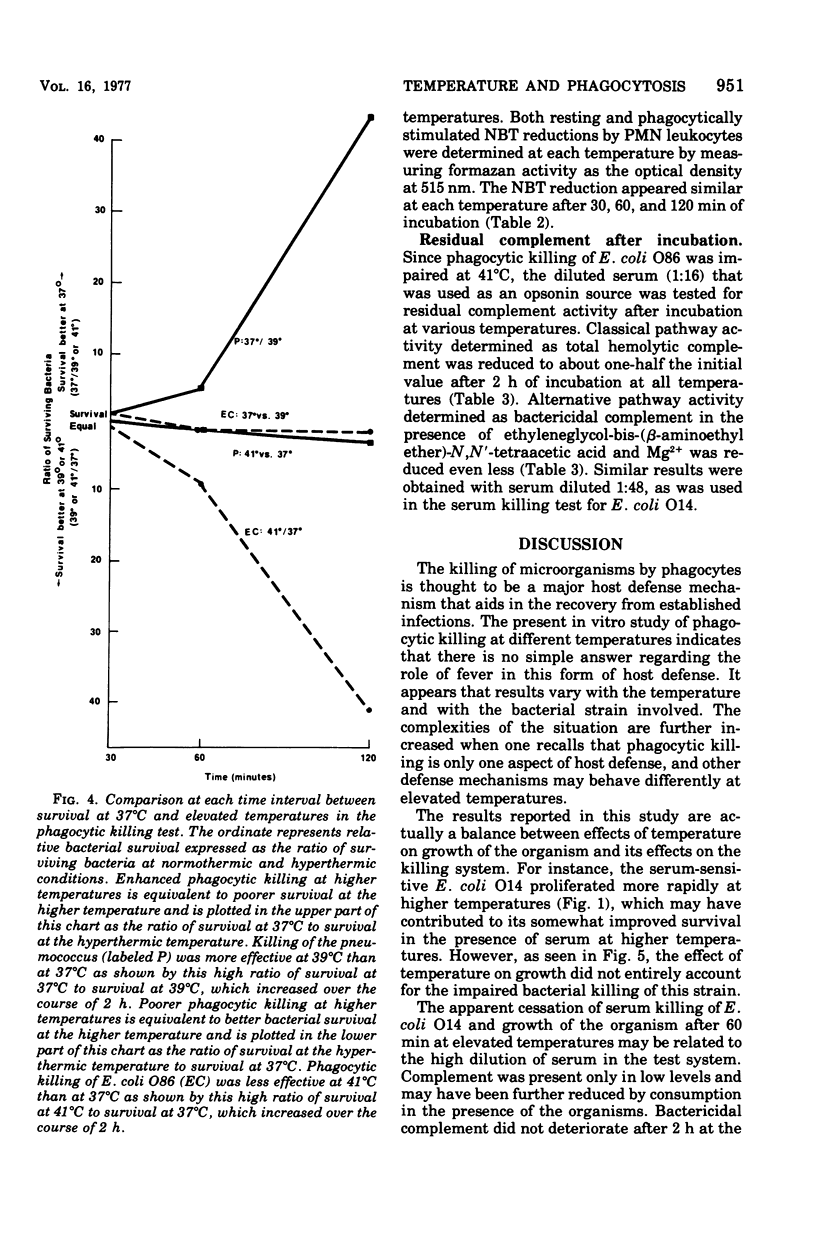
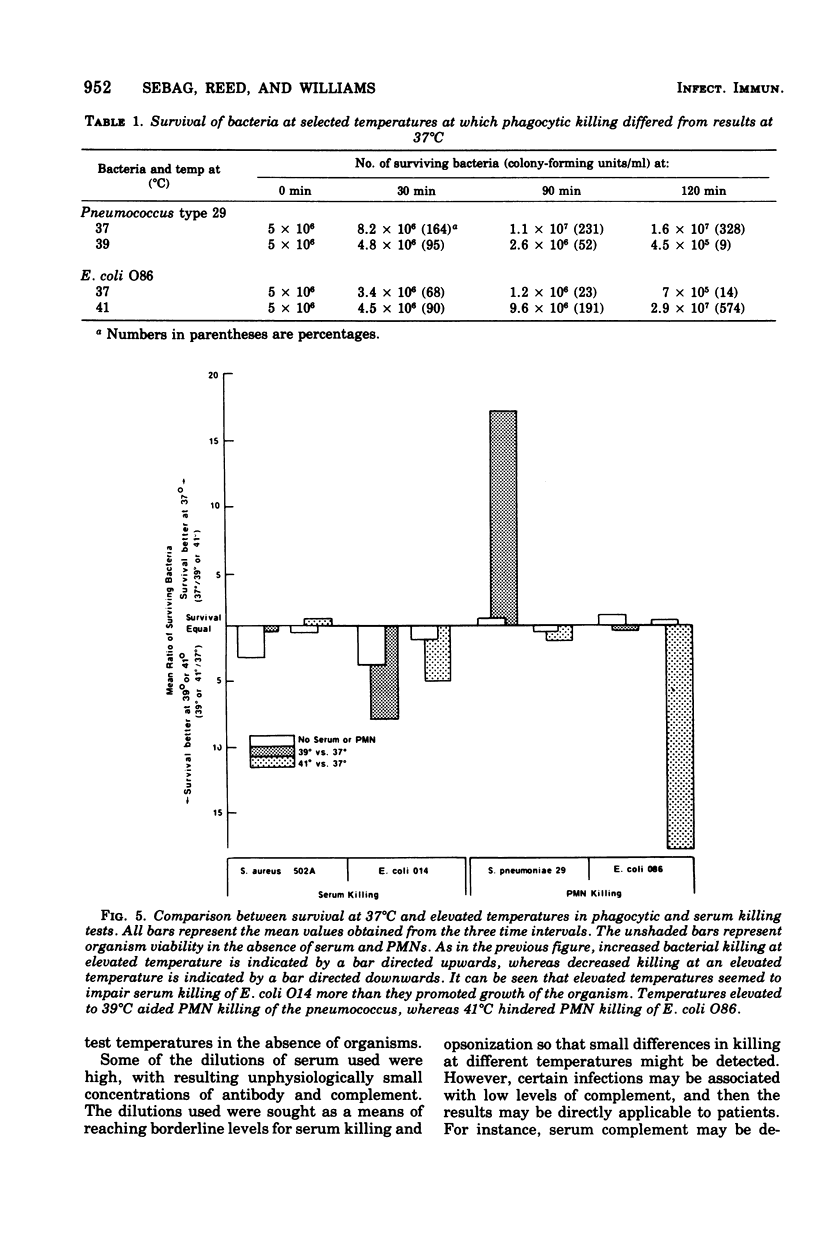
Bacterial killing by serum alone and by polymorphonuclear )PMN) leukocytes was studied at 37 degrees C and compared with killing at 39 and 41 degrees C. The test organisms for serum killing were Staphylococcus aureus 502A (serum resistant) and Escherichia coli O14 (serum sensitive). The organisms used in PMN killing tests were Streptococcus pneumoniae type 29 and E. coli O86.S aureus was not killed by serum alone at any temperature. Changes in temperature did not affect the rate of serum killing of E. coli O14 for the first 60 min, but by 90 and 120 min there was a discrepancy with continued killing at 37 degrees C, but no further killing at 39 and 41 degrees C. PMN phagocytic killing of the pneumococcus was enhanced at 39 degrees C compared with 37 degrees C, and phagocytic killing of E. coli O86 was decreased at 41 degrees C when compared with 37 degrees C. Therefore, it appears that under certain circumstances fever may aid the host PMNs in destroying organisms, whereas under other circumstances it may interfere with such destruction.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENNETT I. L., Jr, NICASTRI A. Fever as a mechanism of resistance. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Mar;24(1):16–34. doi: 10.1128/br.24.1.16-34.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 May 2;278(18):971–976. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196805022781801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig C. P., Suter E. Extracellular factors influencing staphylocidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1966 Aug;97(2):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., STRAUSS B. STUDIES ON HEAT-LABILE OPSONIN IN RABBIT SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IPSEN J., Jr The effect of environmental temperature on the immune response of mice to tetanus toxoid. J Immunol. 1952 Sep;69(3):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L. Effect of temperature on phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):221–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.221-223.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R. Serum complement levels in bacteremia due to gram-negative organisms. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jan 4;288(1):21–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301042880105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Extracellular and bacterial factors influencing staphylococcal phagocytosis and killing by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):496–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.496-501.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Davidson M. S., Williams R. C., Jr Complement system in pneumococcal infections. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1120–1125. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1120-1125.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERS F., CRAWFORD E. S., DE BAKEY M. E. Effects of hypothermia on experimental intracutaneous pneumococcal infection in rabbits. Surg Forum. 1957;8:92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer M. F., Enders J. F., Wilson J. THE EFFECT OF ARTIFICIAL FEVER AND SPECIFIC ANTISERUM ON THE ORGANISMS PRESENT IN CASES OF TYPE III PNEUMOCOCCUS MENINGITIS. J Clin Invest. 1938 Mar;17(2):133–145. doi: 10.1172/JCI100936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


