Abstract
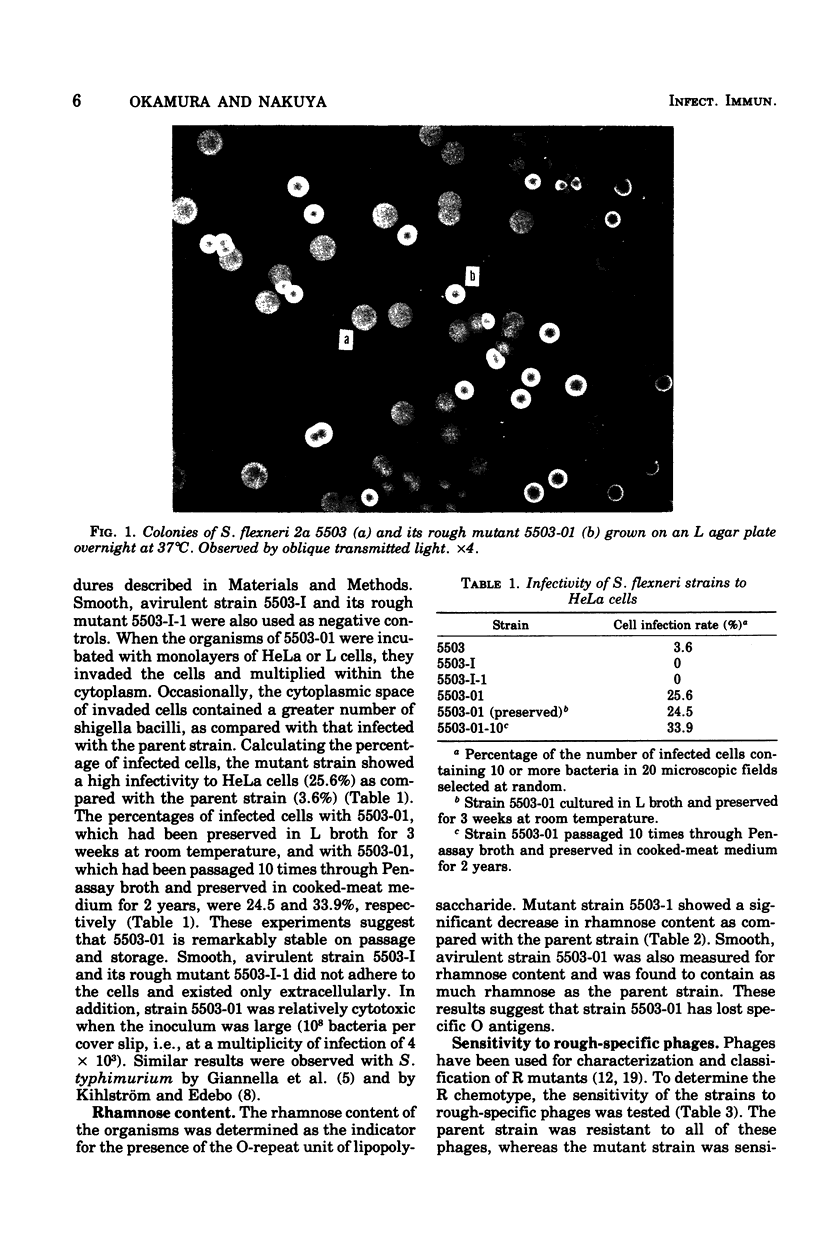
A rough mutant, designated 5503-01, has been isolated from a virulent strain of Shigella flexneri 2a 5503. Strain 5503-01 produced smooth opaque colonies, whereas its parent strain produced characteristic green-gold translucent ones. Characterization of 5503-01 by agglutination tests, rhamnose content, and sensitivity spectra to "rough-specific" phages revealed that it had lost the specific somatic antigens. When 5503-01 was used to infect HeLa or L cells, it penetrated the cells and multiplied within the cytoplasm. On the other hand, it could not evoke keratoconjunctivitis in guinea pigs. The properties of this strain were remarkably stable against serial passages and preservation for a long period. The presence of a rough mutant with the ability to penetrate tissue culture cells suggest that specific O antigen is not of significance in the early step of the invasive process of shigellosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Jr, Sheahan D. G., Washington O., Formal S. B. Virulence of Shigella flexneri hybrids expressing Escherichia coli somatic antigens. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):104–111. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.104-111.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Washington O., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Invasion of HeLa cells by Salmonella typhimurium: a model for study of invasiveness of Salmonella. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONJO S., TAKASAKA M., FUJIWARA T., NAKAGAWA M., ANDOO K., OGAWA H., TAKAHASHI R., IMAIZUMI K. SHIGELLOSIS IN CYNOMOLGUS MONKEYS (MACACA IRUS). II. EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH SHIGELLA FLEXNERI 2A WITH SPECIAL REFERENCES TO CLINICAL AND BACTERIOLOGICAL FINDINGS. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1964 Dec;17:307–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kihlström E., Edebo L. Association of viable and inactivated Salmonella typhimurium 395 MS and MR 10 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):851–857. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.851-857.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kétyi I. Role in virulence of Shigella flexneri antigens derived from lysogenic conversion. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):931–933. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.931-933.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABREC E. H., FORMAL S. B. Experimental Shigella infections. IV. Fluorescent antibody studies of an infection in guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1961 Nov;87:562–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüderitz O., Galanos C., Risse H. J., Ruschmann E., Schlecht S., Schmidt G., Schulte-Holthausen H., Wheat R., Westphal O., Schlosshardt J. Structural relationship of Salmonella O and R antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):349–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKEL D. C., LANGLEY L. F., VENICE L. A. The use of the guinea-pig conjunctivae as an experimental model for the study of virulence of Shigella organisms. Am J Hyg. 1961 Mar;73:219–223. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura A. Virulence of Shigella isolated from healthy carriers. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1967 Jun;20(3):213–223. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.20.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa H., Nakamura A., Nakaya R. Cinemicrographic study of tissue cell cultures infected with Shigella flexneri. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Aug;21(4):259–273. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed W. P., Cushing A. H. Role of immunoglobulins in protection against Shigella-induced keratoconjunctives. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1265–1268. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1265-1268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental keratoconjunctivitis shigellosa. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1957;4(4):367–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Wilkinson R. G., Mäkelä P. H. Genetic aspects of biosynthesis and structure of Salmonella somatic polysaccharide. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):334–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS H. M. Some attributes of virulence in Shigella. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1960 Nov 21;88:1167–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G., Gemski P., Jr, Stocker B. A. Non-smooth mutants of Salmonella typhimurium: differentiation by phage sensitivity and genetic mapping. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 May;70(3):527–554. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-3-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]