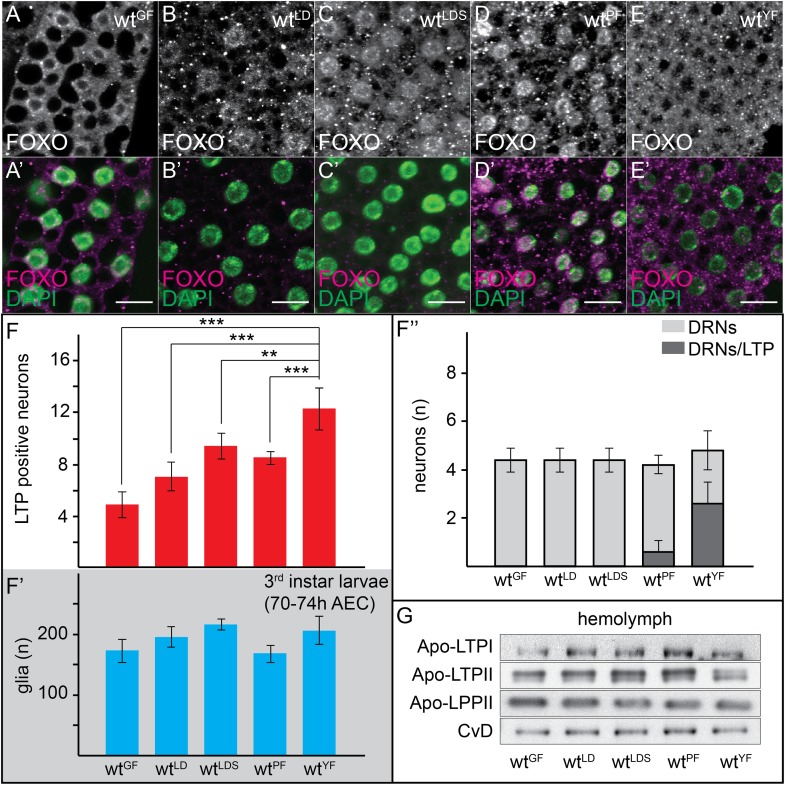
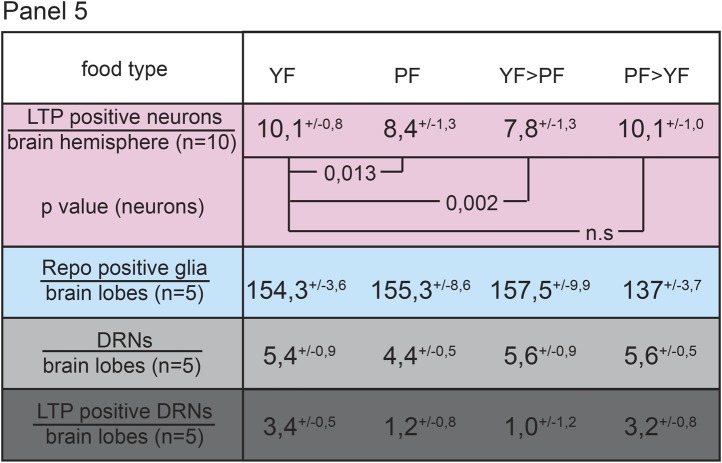
Figure 3. Neuronal LTP accumulation is diet-dependent.
(A–E′) Confocal stack projections of fat bodies from early third instar larvae raised on GF (A and A′), LDF (B and B′), LDSF (C and C′), PF (D and D′) and YF (E and E′) probed for FOXO (A–E and A–E′ magenta) and DAPI (A′–E′, green). Scale bars = 20 μm. (F–F′″) average number of LTP-positive neurons/brain lobe (F), glial cells/brain (F′) and LTP-positive DRNs (F″) in brains of larvae transferred from YF to indicated diets in the late second instar. Error bars indicate standard deviation. T-test significance: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (G) Equal hemolymph volumes from wt larvae raised on indicated food sources Western blotted and probed for the indicated Apolipoproteins.