Abstract
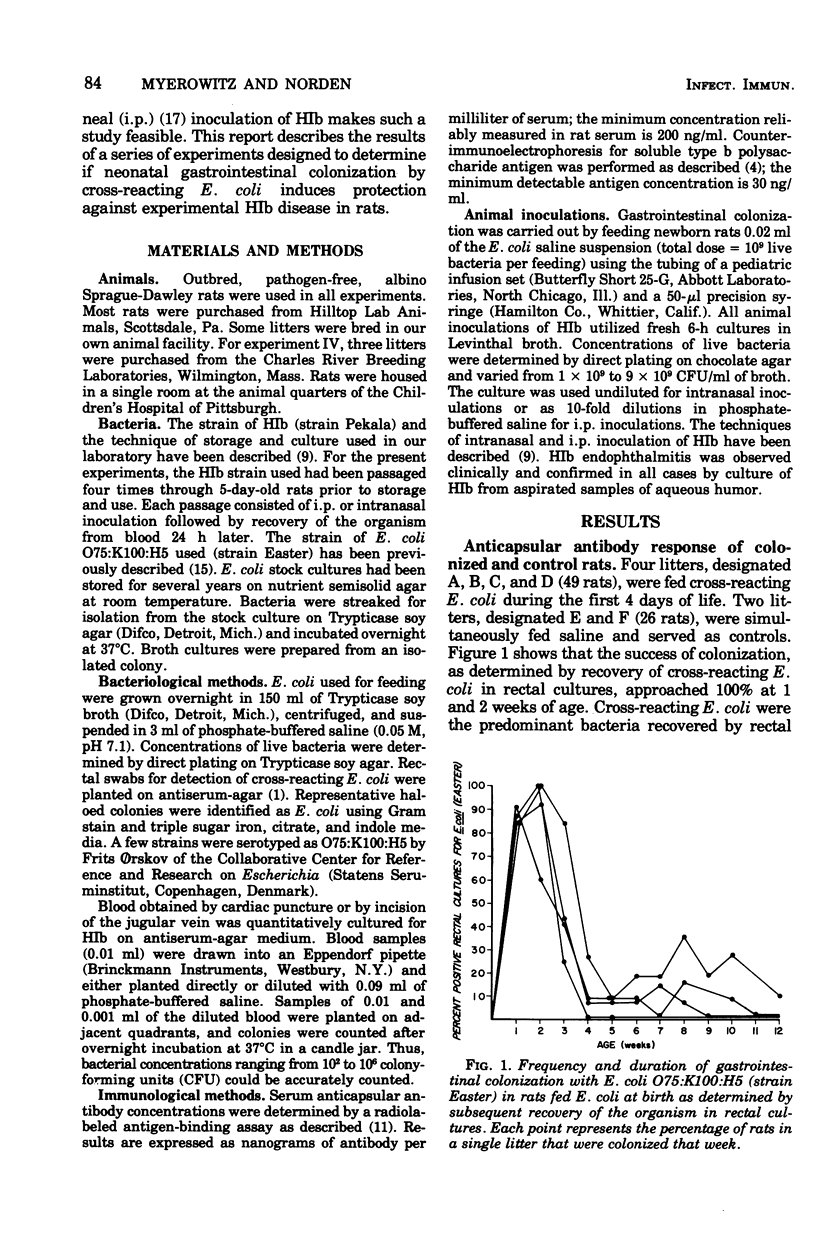
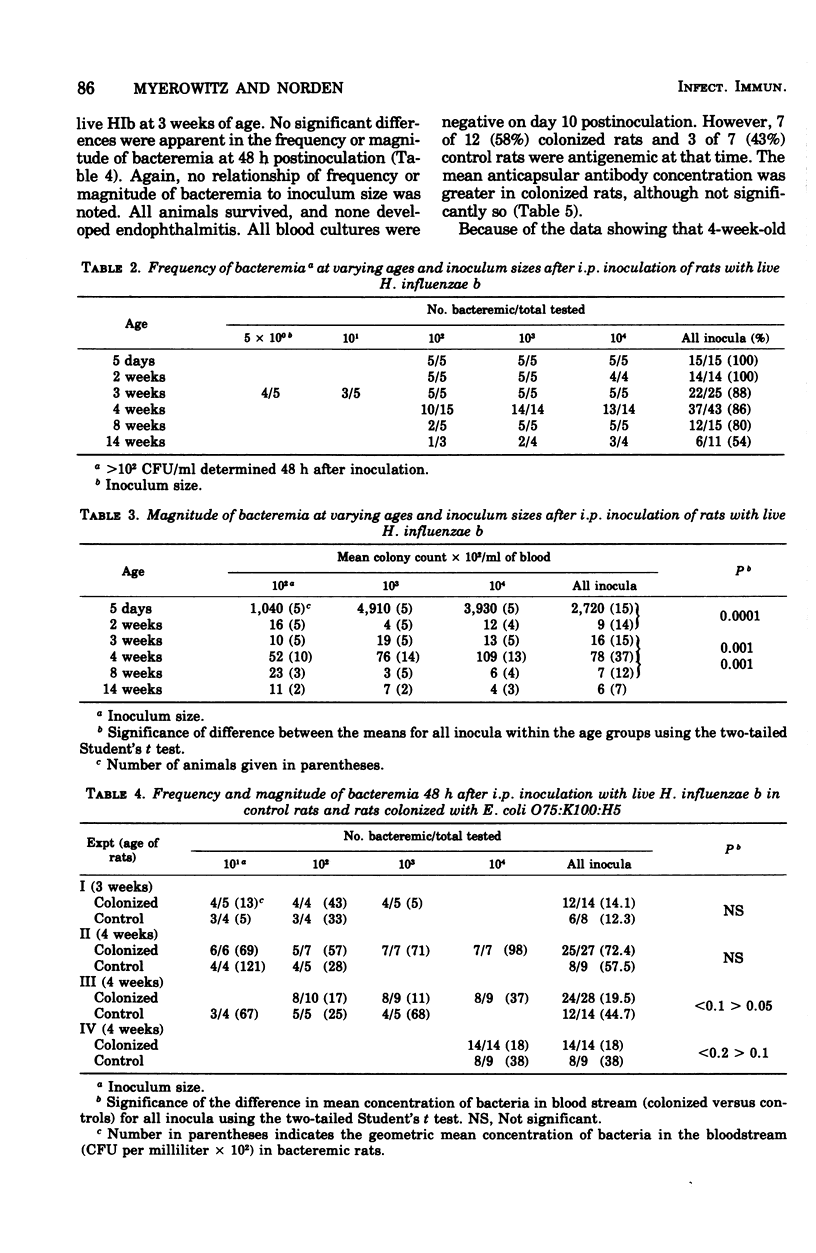
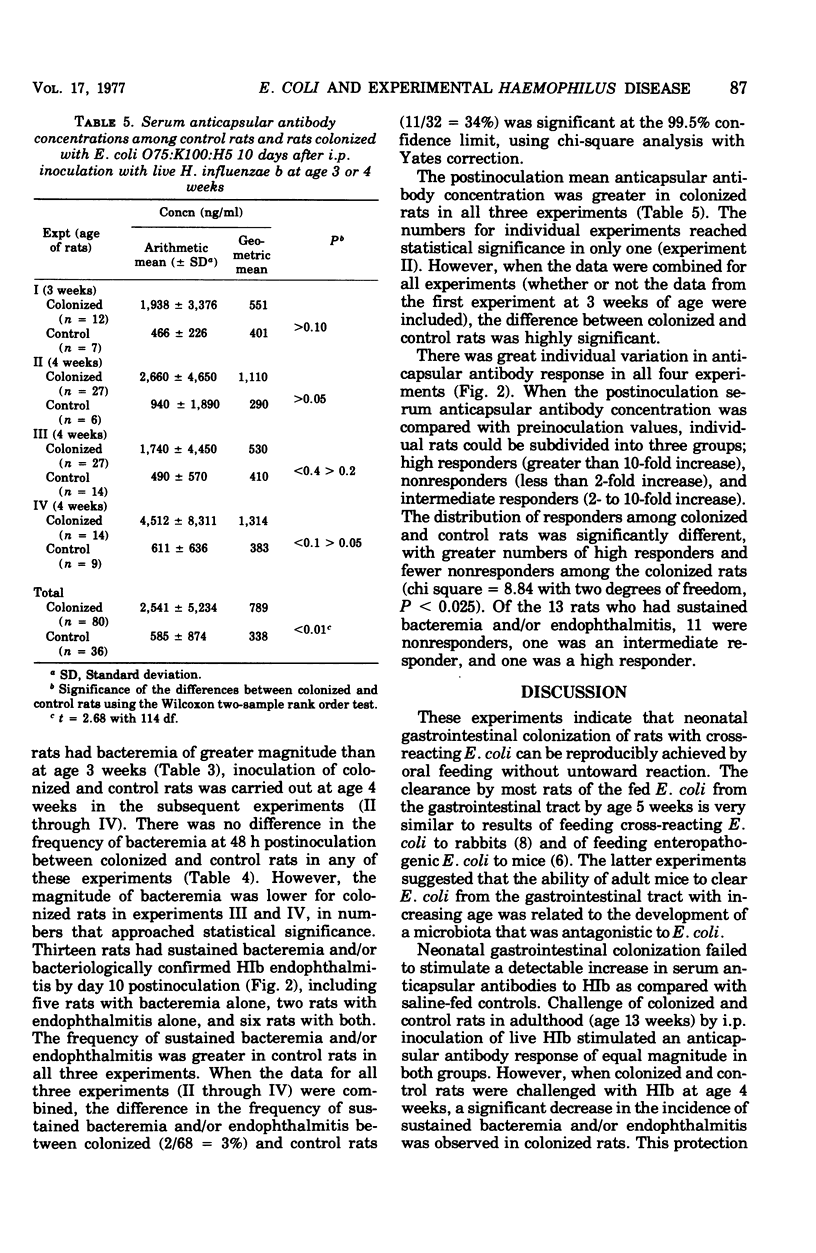
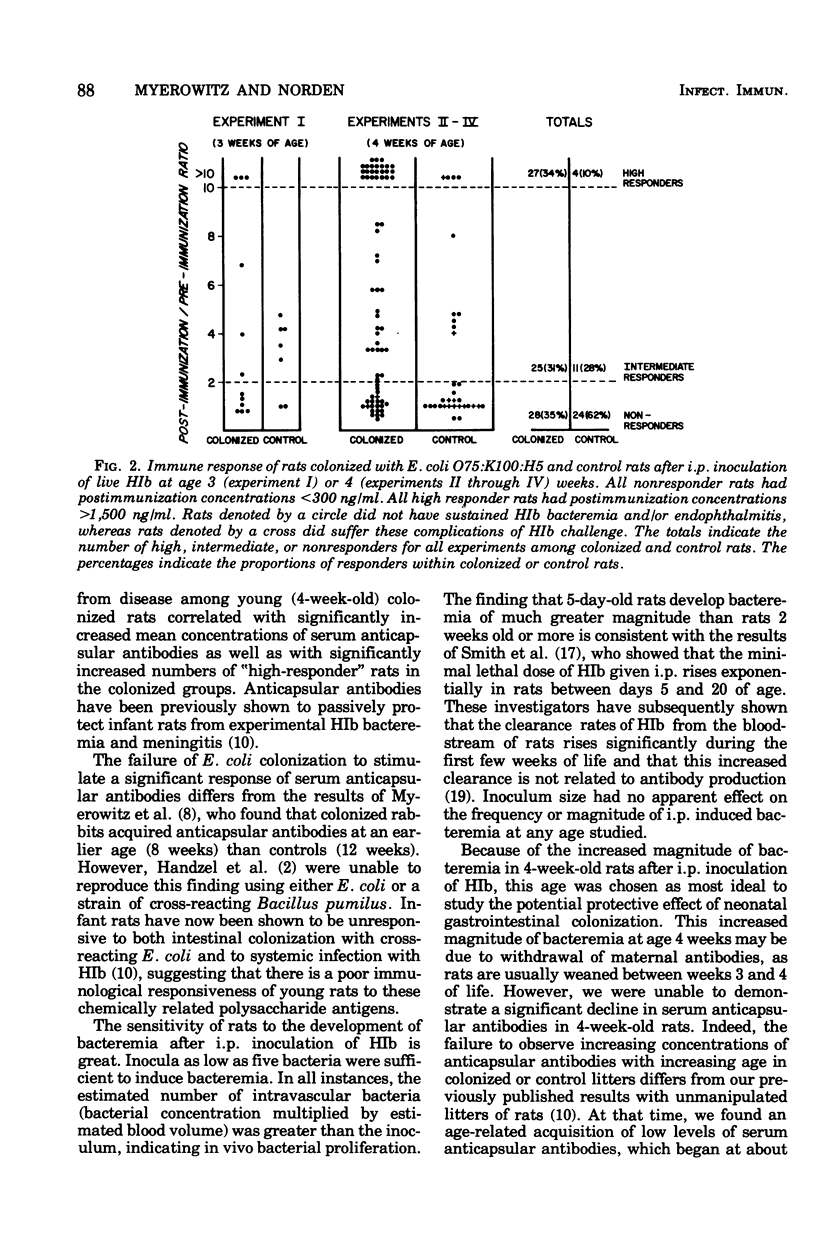
Neonatal gastrointestinal colonization of newborn rats with Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5, cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b, was harmless but failed to stimulated detectable ( greater than 200 ng/ml) serum anticapsular antibodies. Neonatally colonized rats, when challenged at age 13 weeks by intraperitoneal inoculation of H. influenzae b, showed no difference in the frequency, magnitude, or duration of bacteremia or in the postinfection anticapsular antibody response when compared with saline-fed controls. However, neonatally colonized rats challenged at age 4 weeks had a significantly decreased incidence of sustained bacteremia and/or endophthalmitis when compared with controls. This decreased frequency of disease correlated with a significant increase in postinfection serum anticapsular antibodies. Neonatal gastrointestinal colonization with cross-reacting E. coli appears to "prime" the young host to respond to infection with H. influenzae b with an anticapsular antibody response that protects against sustained H. influenzae b bacteremia and its complications.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradshaw M. W., Schneerson R., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Bacterial antigens cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Lancet. 1971 May 29;1(7709):1095–1096. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91837-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haemophilus influenzae type b: disease and immunity in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Feb;78(2):259–269. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-2-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handzel Z. T., Argaman M., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Heteroimmunization to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b induced by enteric cross-reacting bacteria. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1045–1052. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1045-1052.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H. Increase in influenzal meningitis. N Engl J Med. 1971 Sep 16;285(12):666–667. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197109162851207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels R. H., Poziviak C. S. Countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis for the diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia in children. J Pediatr. 1976 Jan;88(1):72–74. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)80730-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushin R., Dubos R. Colonization of the mouse intestine with Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1965 Oct 1;122(4):745–757. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Handzel Z. T., Scheerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular antibody in neonatal rabbits by gastrointestinal colonization with cross-reacting Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):137–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.137-140.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Klaw R., Johnson B. L. Experimental endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1043–1051. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1043-1051.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R. L., Norden C. W. Immunology of the infant rat experimental model of Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):218–225. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.218-225.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Michaels R. Immunologic response in patients with epiglottitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1973 Dec;128(6):777–780. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud P., Dickinson A. B., Sacquet E., Charlier H., Mocquot G. La microflore du tube digestif du rat. II. Dénombrement de différents genres microbiens dans l'estomac et l'intestin de rats conventionnels. Variation quantitiatives individuelles et en fonction de l'age. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jun;110(6):861–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K. Quantitative measurement of "natural" and immunization-induced Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Pediatr Res. 1973 Mar;7(3):103–110. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Bradshaw M., Whisnant J. K., Myerowitz R. L., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. An Escherichia coli antigen cross-reactive with the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b: occurrence among known serotypes, and immunochemical and biologic properties of E. coli antisera toward H. influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1551–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of serum Haemophilus influenzae type B capsular antibodies in adult volunteers fed cross-reacting Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 22;292(21):1093–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505222922103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Smith D. H., Averill D. R., Jr, Marino J., Moxon E. R. Production of Haemophilus influenzae b meningitis in infant rats by intraperitoneal inoculation. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):278–290. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.278-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Peter G., Ingram D. L., Harding A. L., Anderson P. Responses of children immunized with the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. Pediatrics. 1973 Nov;52(5):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


