Abstract
Ribosomal vaccines prepared from Salmonella typhimurium SR-11 and 6707 an Re mutant bacterium of strain LT2, were effective immunogens in A/J and C3H/HeDub inbred mice. Only SR-11 ribosomes were able to induce significant protection in C3H/HeJ mice. C57BL/6J mice were not protected by either ribosomal preparation. A/J mice were protected against salmonella infection by purified SR-11 endotoxin preparations. Neither the C3H/HeDub, the C3H/HeJ, nor the C57BL/6J mice were protected by the endotoxin preparation. Passive hemagglutination studies showed that C3H/HeJ mice had no antibodies to O antigen but were significantly protected by SR-11 ribosomes. In contrast, C57BL/6J mice, which had the highest titers of O antibodies of the four inbred mouse strains, were not protected by SR-11 ribosomes. Endotoxin cannot totally account for the effectiveness fo ribosomal account for the effectiveness of ribosomal vaccines prepared from S. typhimurium.
Full text
PDF

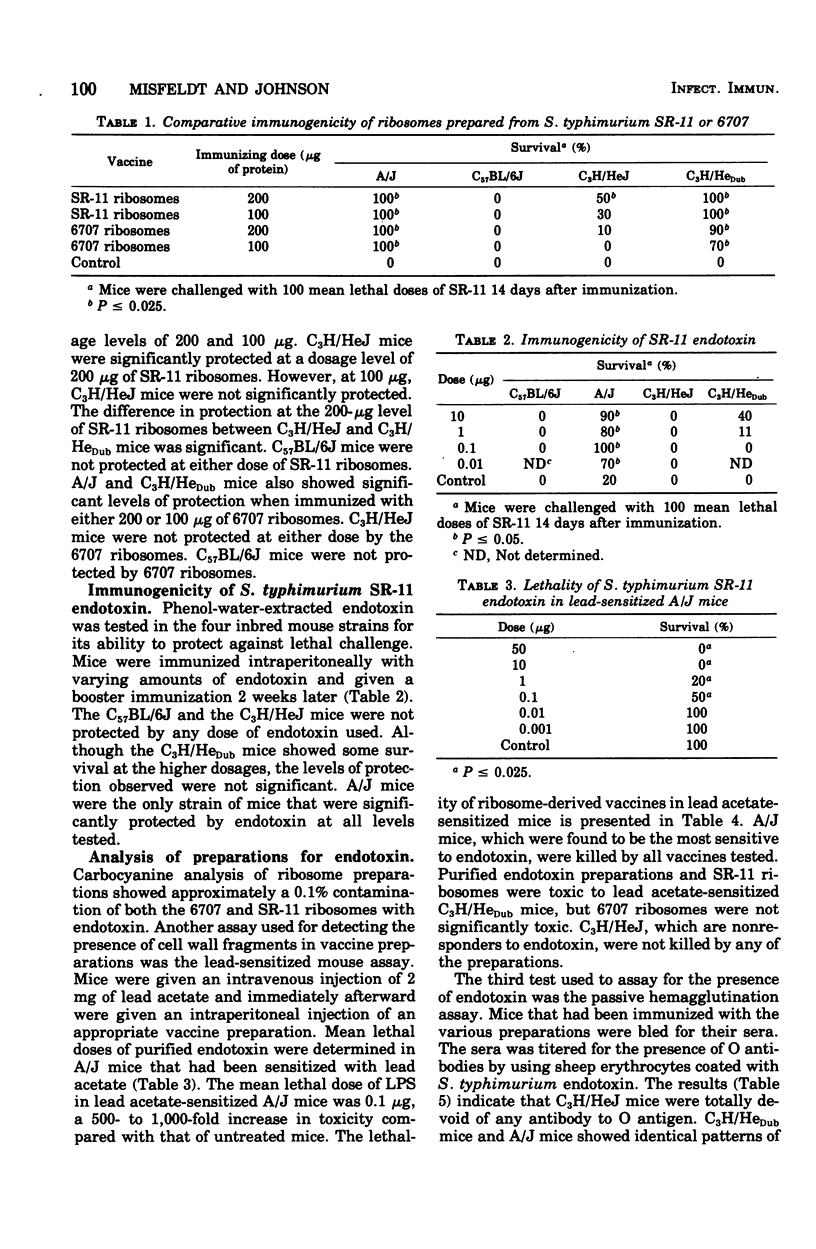
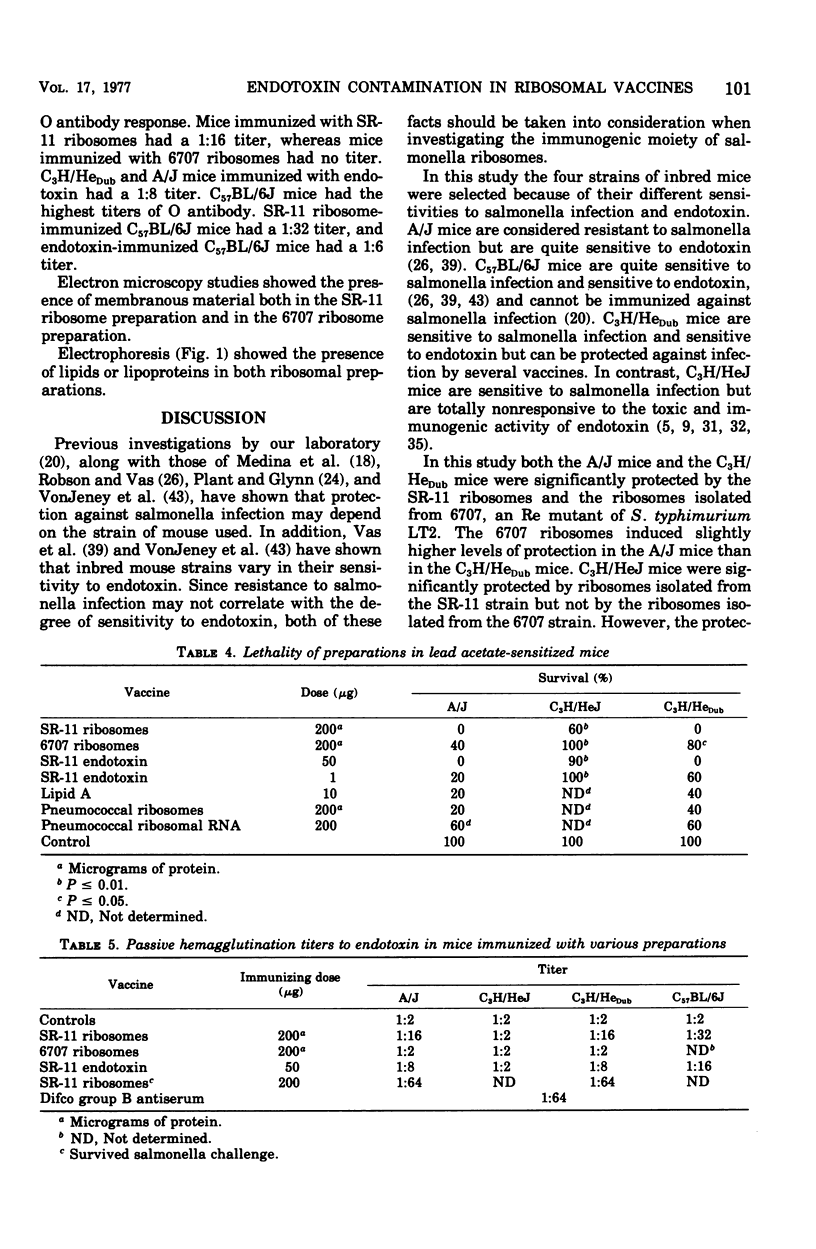



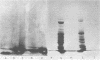
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Lee F. D., Durston W. E. An improved bacterial test system for the detection and classification of mutagens and carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F. Comparison of the immune response to sheep erythrocytes, tetanus toxoid and endotoxin in different strains of mice. Agents Actions. 1974 Oct;4(4):277–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01965231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedid L., Parant M., Damais C., Parant F., Juy D., Galelli A. Failure of endotoxin to increase nonspecific resistance to infection of lipopolysaccharide low-responder mice. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):722–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.722-727.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiller J. M., Skidmore B. J., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Relationship of the structure of bacterial lipopolysaccharides to its function in mitogenesis and adjuvanticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2129–2133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein T. K. Evidence for O antigens as the antigenic determinants in "ribosomal" vaccines prepared from Salmonella. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):364–377. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.364-377.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gürtler L. G., Rank W. R. Genetic differences between endotoxin-sensitive and resistant C3H mice. Intraperitoneal cell response to lipopolysaccharide and prostaglandins. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1976 Aug;151(1):420–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. W., Hibbitt K. G., Shears A. The stimulation by endotoxin of the nonspecific resistance of mice to bacterial infections. Br J Exp Pathol. 1974 Apr;55(2):194–202. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoops P., Prather N. E., Berry J., Ravel J. M. Evidence for an extrinsic immunogen in effective ribosomal vaccines from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1184–1192. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1184-1192.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houchens D. P., Wright G. L., Jr Immunity to Salmonella typhimurium infection: characterization of antigens in active protection by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):507–511. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.507-511.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. I. Immunogenicity of ribosomal fractions isolated from Salmonella typhimurium and Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):947–952. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.947-952.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. Ribosomal vaccines. II. Specificity of the immune response to ribosomal ribonucleic acid and protein isolated from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1973 Sep;8(3):395–400. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.3.395-400.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina S., Vas S. I., Robson H. G. Effect of nonspecific stimulation on the defense mechanisms of inbred mice. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1720–1725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Braun V., Galanos C. The lipoprotein of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli: a B-lymphocyte mitogen. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):473–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt M. L., Johnson W. Variability of protection in inbred mice induced by a ribosomal vaccine prepared from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):652–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.652-659.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinari J. L., Larralde C. Acquired immunity to murine typhoid induced in mice with fractions of Salmonella typhimurium. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1974 Oct-Dec;16(4):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Betz S. J., Jacobs D. M. Isolation of a lipid A bound polypeptide responsible for "LPS-initiated" mitogenesis of C3H/HeJ spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):840–846. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J., Glynn A. A. Genetics of resistance to infection with Salmonella typhimurium in mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jan;133(1):72–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson H. G., Vas S. I. Resistance of inbred mice to Salmonella typhimurium. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):378–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudbach J. A. Molecular immunogenicity of bacterial lipopolysaccharide antigens: establishing a quantitative system. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):993–1001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R., Johnson K. G. SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of lipopolysaccharides. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Dec;21(12):2013–2018. doi: 10.1139/m75-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selye H., Tuchweber B., Bertók L. Effect of lead acetate on the susceptibility of rats to bacterial endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):884–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.884-890.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Chiller J. M., Morrison D. C., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS): correlation between the mitogenic, adjuvant, and immunogenic activities. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):770–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skidmore B. J., Morrison D. C., Chiller J. M., Weigle W. O. Immunologic properties of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS). II. The unresponsiveness of C3H/HeJ Mouse spleen cells to LPS-induced mitogenesis is dependent on the method used to extract LPS. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1488–1508. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Detection of delayed hypersensitivity in mice injected with ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):384–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.384-389.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Bigley N. J. Ribonucleic acid-protein fractions of virulent Salmonella typhimurium as protective immunogens. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):377–383. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.377-383.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M. Genetic factors in leucocyte responses to endotoxin: further studies in mice. J Immunol. 1969 Jul;103(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultzer B. M., Goodman G. W. Endotoxin protein: a B-cell mitogen and polyclonal activator of C3H/HeJ lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):821–827. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vas S. I., Roy R. S., Robson H. G. Endotoxin sensitivity of inbred mouse strains. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jul;19(7):767–769. doi: 10.1139/m73-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J., Berry L. J. Immunogenicity of Ribonucleic Acid Preparations Obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):574–582. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.574-582.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R., Bigley N. J. Isolation and partial characterization of an immunogenic moiety obtained from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):140–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.140-148.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venneman M. R. Purification of immunogenically active ribonucleic acid preparations of Salmonella typhimurium: molecular-sieve and anion-exchange chromatography. Infect Immun. 1972 Mar;5(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.3.269-282.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAVDEKAR V. S., SASLAW L. D. A sensitive colorimetric method for the estimation of 2-deoxy sugars with the use of the malonaldehyde-thiobarbituric acid reaction. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1945–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Jeney N., Günther E., Jann K. Mitogenic stimulation of murine spleen cells: relation to susceptibility to Salmonella infection. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):26–33. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.26-33.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]