Abstract
Congenitally athymic nude (Nu/Nu) mice inoculated intraperitoneally with murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV), in doses as low as 1.3 X 10(1) plaque-forming units succumbed to the infection. In contrast, the mean lethal dose for heteroxygous euthymic (Nu/+) littermates was 4 X 10(3) plaque-forming units. Though histopathological changes consistent with MCMV infection were found in the spleen, lungs, and adrenals of nude mice, there were only small focal areas of involvement in the liver. In contrast, Nu/+ mice dying from infection had pathological evidence of severe hepatitis. Spleen cells from immune and control BALB/c mice were injected intravenously into syngeneic mice that had been inoculated previously with lethal doses of MCMV intraperitoneally. Mice receiving 1 X 10(7) or more immune spleen cells were protected against the infection, whereas mice receiving 1 X 10(8) control spleen cells or immune serum were not. Treatment of immune spleen cells with anti-theta serum and complement significantly reduced their protective effect. Immune mechanisms associated with T lymphocytes appear to be critical for recovery from MCMV infection.
Full text
PDF


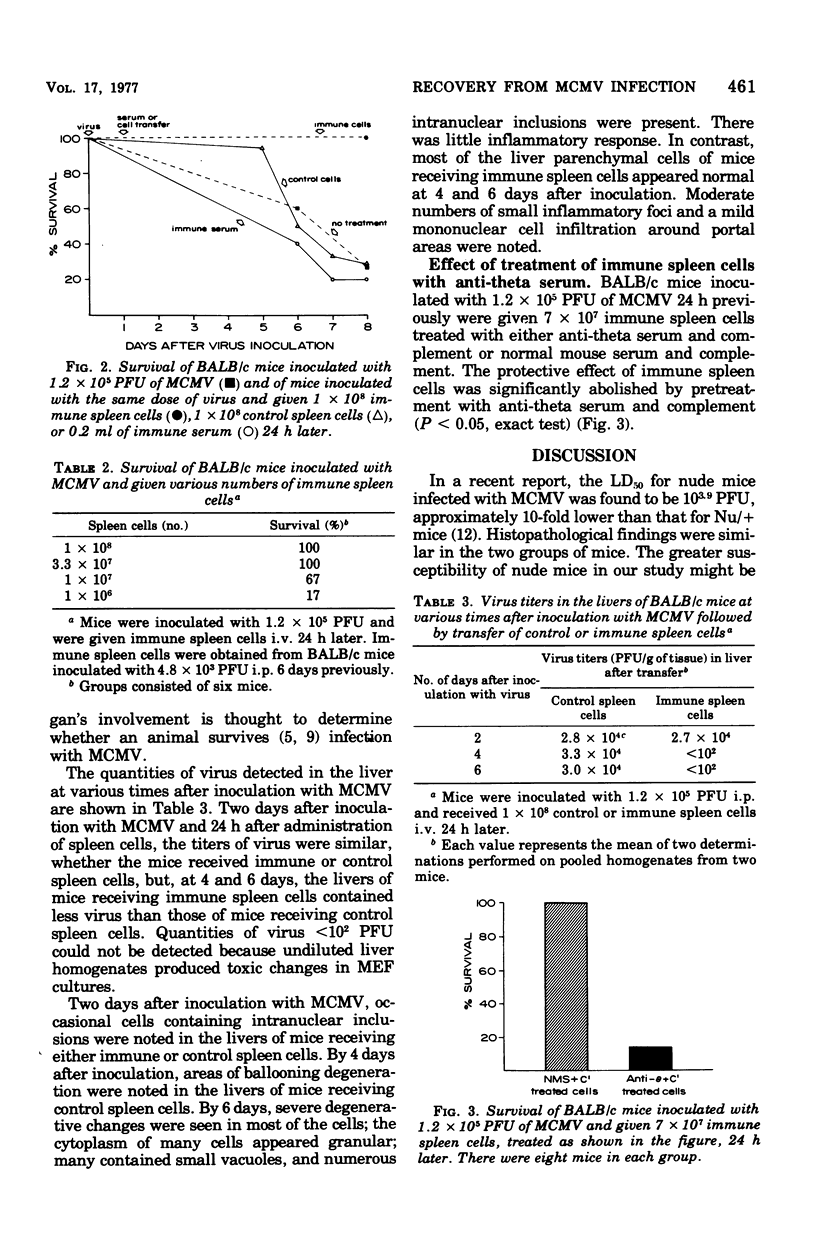

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Harington J. S., Birbeck M. An examination of the cytotoxic effects of silica on macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Aug 1;124(2):141–154. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison A. C. Interactions of antibodies, complement components and various cell types in immunity against viruses and pyogenic bacteria. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):3–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody A. R., Craighead J. E. Pathogenesis of pulmonary cytomegalovirus infection in immunosuppressed mice. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):677–689. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson D., Smith R. D., Gehrke J. Non-fatal mouse cytomegalovirus hepatitis. Combined morphologic, virologic and immunologic observations. Am J Pathol. 1966 Nov;49(5):871–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H. Influences of antilymphocyte serum on cell-mediated and antibody-mediated responses. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):156–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIMS C. A. ASPECTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF VIRUS DISEASES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Mar;28:30–71. doi: 10.1128/br.28.1.30-71.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn J. E., Medearis D. N., Jr Studies of relationship between mouse cytomegalovirus and interferon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Mar;121(3):819–824. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Kern E. R., Glasgow L. A. Effective antiviral chemotherapy in cytomegalovirus infection of mice. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133 (Suppl):A237–A244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.supplement_2.a237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantelouris E. M. Absence of thymus in a mouse mutant. Nature. 1968 Jan 27;217(5126):370–371. doi: 10.1038/217370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S. G. Host immune responses after administration of inactivated Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus vaccines. II. Kinetics of neutralizing antibody responses in donors and adoptively immunized recipients. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jul;134(1):39–47. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Ahmed A., Sell K. W., Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Effect of murine cytomegalovirus on the in vitro responses of T and B cells to mitogens. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1459–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selgrade M. K., Osborn J. E. Role of macrophages in resistance to murine cytomegalovirus. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1383–1390. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1383-1390.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]